Introduction
The research paper presents a strategic analysis of Tesla Motors, a globally recognized company that produces electric vehicles. It offers recommendations for possible improvements and strategies to overcome the problems it faces. With the introduction of the first high-powered electric automobile with cutting-edge technology, Tesla Motors stunned the automotive industry. It became the leader of the electric vehicles market with numerous clients and stable revenue.
However, the company faces some challenges today that may impact its future development and ability to generate income. Due to the financial crisis caused by the pandemic, rising prices, and the emergence of alternatives offered by its closest rivals, Tesla needs to make specific changes to maintain its leading position and move forward. Currently, the company struggles with new market conditions, which include rising commodity prices and gradually decreasing demand for its expensive products. This means that new measures must be accepted to address the problem. The proposed study will investigate the company’s annual reports, industry reports, and studies by other investigators to determine the scope of the problem and offer specific recommendations to address it.
Literature Review
The popularity of Tesla, along with its distinctive image, has garnered significant attention. The existing body of literature acknowledges the unique nature of the company and its significance to the electric vehicle market. Thus, the Silicon Valley-based firm Tesla Motors Inc. (Tesla) creates, produces, and sells battery electric cars (BEVs), lithium-ion battery packs, and electric vehicle engine products (Tesla Inc., 2021).
Teece (2018) acknowledges that introducing the first luxurious electric car produced by Tesla altered the market and the customers’ attitudes toward this type of vehicle. The corporation became one of the primary facilitators of change in the automotive industry, with the high potential for transforming it and holding leading positions (Dana, 2018). Thus, the company’s focus on using electric power to replace the remaining gasoline remains one of its most distinctive features (Bhasin, 2019). It helps create the brand’s recognizable image, attract clients aware of sustainability issues, and lay the groundwork for further change (Li, 2018). The company’s unique vision and mission were a powerful promotional tool, helping to attract public attention.
Moreover, Tesla is one of the companies that is vital to local and global economies. First, it is the pioneer of the electric vehicle revolution and promotes its further spread (Li, 2018). Statistics show that in 2021, the company and its subsidiaries employed approximately 99,000 employees globally (Wagner, 2020). It indicates Tesla’s influence and the scope of its activities.
Tiwari (2017) acknowledges that success is linked to the brand offering its clients green thinking and technology, which is vital in the modern world. As a result, it alters the automobile industry, benefiting the first-mover advantage, which helps preserve leading positions and generate high revenues (Teece, 2018). At the same time, Tesla faces the risks typical of first movers, such as the high likelihood of being copied by competitors and a gradual decline in client interest (Li, 2018). These factors may explain the emergence of specific issues that could impact the company’s future, despite its high sales.
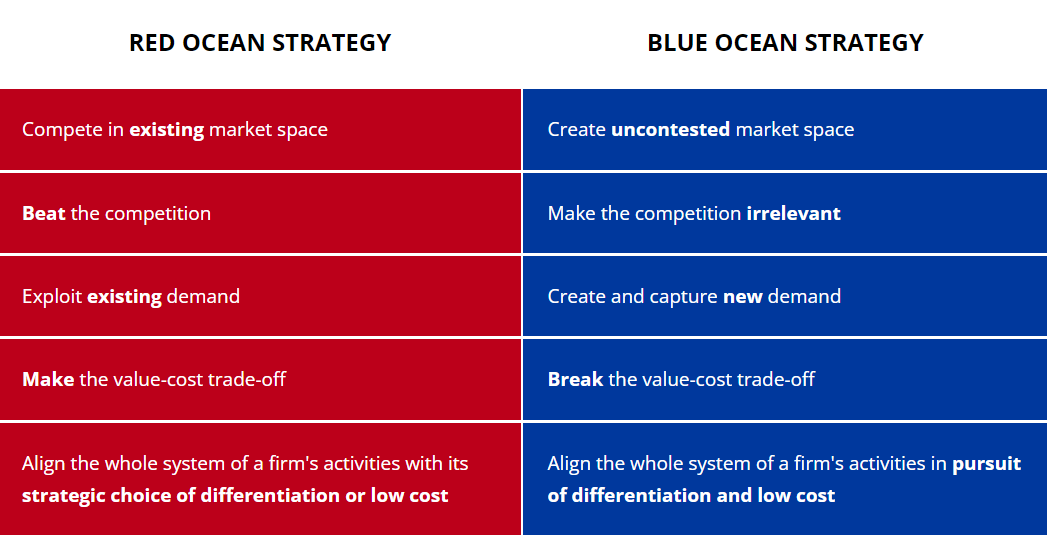
Tesla’s fast success and the emergence of specific challenges during its development can be linked to the strategy employed by the company. The corporation focused on creating and dominating the uncontested market space, making the competition insignificant (Li, 2018). This means that Tesla employed the blue ocean strategy, creating and capturing new demand and using differentiation to create an attractive image (Blue Ocean, n.d.).
Tesla decided to develop in a market with no rivals in 2003 (Teece, 2018). Other automakers at the time produced compliant and hybrid vehicles to demonstrate that they followed regulations requiring them to develop sustainable technology. Consequently, Tesla employed a scale-vertical integration strategy as a form of cooperative approach, pursuing deeper vertical integration; this strategy departs from that of conventional manufacturers (Wang et al., 2022). Tesla also controls the marketing, sales, and service processes, unlike automakers, who typically concentrate on producing and assembling engines and vehicles (Li, 2018). These factors were vital to the company’s growth and fast popularity.
However, this strategy helped the brand acquire leading positions in the first stages of its evolution. Nowadays, the situation is starting to change. The electric vehicle market has evolved, and new players are gaining significant influence. This suggests that Tesla may adopt a red ocean strategy, incorporating additional features (see Figure 3 in the Appendix). The company should either exploit a new demand by creating vehicles with features appreciated by clients or try returning to the blue ocean strategy by radically renovating its offerings and making the competition irrelevant. Choosing a new vector of development is one of the central dilemmas the brand faces nowadays.
The existing literature also emphasizes the role of marketing and client relations in creating the basis for Tesla’s success. Typically, the company offers its goods directly to customers through the website and physical storefronts (Bhasin, 2019). To accelerate the adoption of their products, they continued to develop customer-oriented infrastructure through a global network of mobile service specialists, vehicle service centers, power stations, body repair shops, and charging stations (Bhasin, 2019). Therefore, the company prioritized user and employee performance, appearance, and safety when designing and manufacturing its products, and it continually updated driving technology to enhance safety. Based on course concepts of competitive advantage, Tesla continually worked to lower manufacturing costs and offer modified financing options for its automobiles, thereby reducing the value of its customers’ possessions.
Ultimately, Tesla’s success is closely tied to its unconventional management and leadership models. In February 2004, PayPal creator and philanthropist Elon Musk joined Tesla as an investor in the monitoring and management of specific engineering processes. It became the turning point in the company’s evolution as he created a new vector of development and attracted public attention to the brand (“About Tesla,” n.d.).
The charismatic figure of Musk contributed to the formation of a specific Tesla image and its focus on innovation. However, the critical dependence on one person is also considered a weakness of the company, as his actions have caused reputational losses and damaged the company (Bhasin, 2019). The problem Tesla faces at the moment can be partially attributed to Musk’s actions and a lack of strategic thinking.
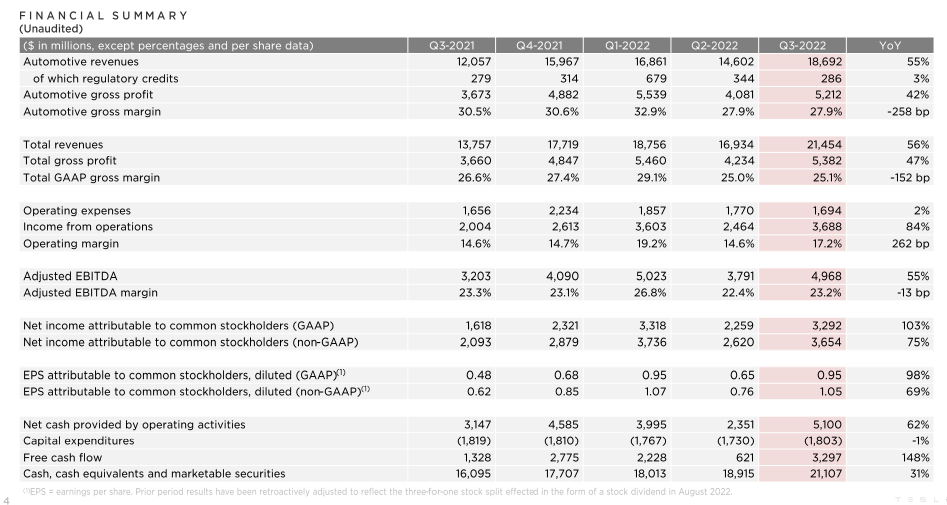
Altogether, the existing literature accepts the critical importance of Tesla and its success in the electric vehicle market. Using the blue ocean strategy, the company entered a segment characterized by the absence of rivalry and created a unique proposal that was attractive to clients. The company’s importance is evident in its financial statistics (see Figure 4 in the Appendix), the number of jobs it has created, and its role in transforming the automobile industry. However, at present, the firm faces significant challenges due to the global financial crisis, reduced demand for its premium offerings, and the emergence of numerous rivals offering similar vehicles at lower prices. It means it is critical to perform the company’s strategic analysis to outline the possible changes that might help the brand overcome the abovementioned problems and continue its evolution.
SWOT Analysis
Tesla’s strategic analysis can be performed by investigating the internal environment and aspects relevant to the brand’s functioning. Thus, using the SWOT analysis tool, the following results are acquired:
Strengths
- Tesla is the pioneer in the electric vehicle sector.
- Uses effective online sales methods to work directly with clients (Li, 2018).
- Tesla has numerous partners supporting its further development.
- Tesla is a highly innovative brand offering new solutions (Li, 2018).
- A solid brand reputation.
- Unique customer service and positive relations with clients.
Weaknesses
- Limited global presence (Li, 2018).
- Focus on the premium class, which limits vehicles’ affordability (Li, 2018).
- Ambiguous figure of the leader.
- Lack of support in other regions.
Opportunities
- Development of autopilot and autonomous vehicles (Li, 2018).
- Improvement of battery planning technology.
- Further development of environmentally friendly solutions.
- Government mandates and legislation supporting electric vehicles (Li, 2018).
- Public support.
- Broadening of the target audience.
Threats
- Rising competition.
- Problems of long-term sustainability (Li, 2018).
- The rise of new technologies might impact Tesla’s position.
- Economic instability.
The results of the SWOT analysis can be summarized and presented in the table:
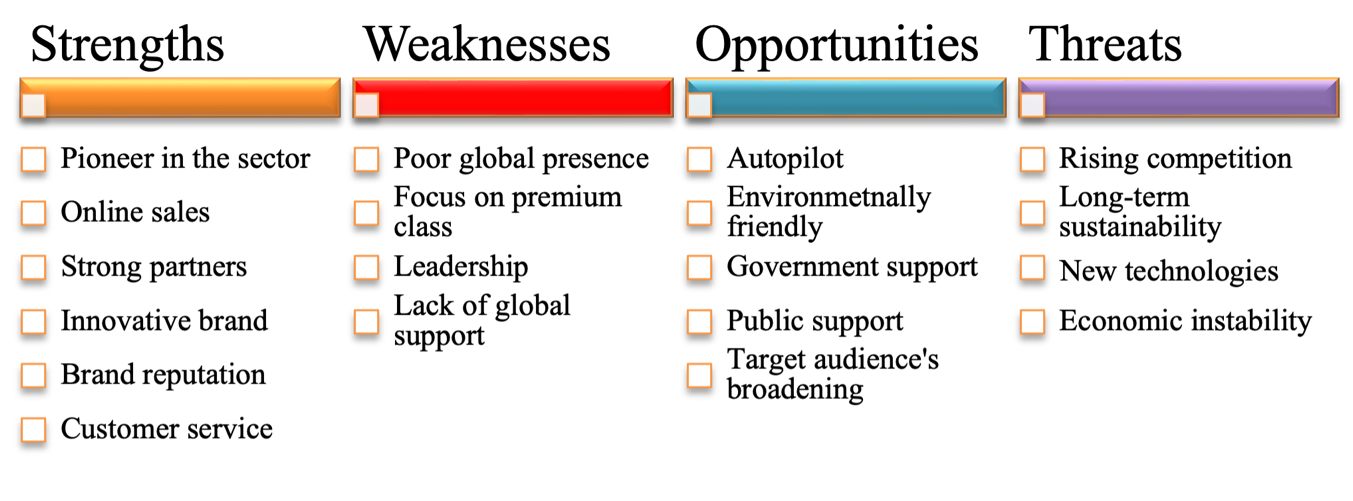
Altogether, the SWOT analysis shows that Tesla has a strong position. It remains the pioneer in the sector, with strong partners that might support its further evolution. It utilizes innovations as a significant factor to generate a competitive advantage, improve its brand reputation, and attract new clients.
The online distribution of cars also helps to create an unusual image of the company. However, the poor global presence can complicate its struggle against other companies. The limited access to other markets and lack of global support might create barriers to Tesla’s further evolution due to the lack of resources.
Moreover, leadership issues might impact the brand’s reputation. The focus on the premium segment is one of the brand’s crucial weaknesses that will impact its future. The lack of diversification and affordability prevents the company from entering other market segments.
Tesla also faces growing competition, a characteristic of the electric vehicle market today. Another threat is the issue of long-term sustainability, as the company’s batteries should be recycled, which also raises specific concerns. Finally, the emergence of new technologies that may impact Tesla’s global position and the economic instability influencing the corporation requires additional measures to address them.
The company’s significant opportunities include creating autonomous vehicles, which can help it return to a blue ocean strategy due to the lack of competition, and broadening its target audience. Utilizing existing public and governmental support, Tesla can focus on creating more affordable cars that will be accessible to the middle class. This will lead to a significant revenue increase and create the foundation for further growth and evolution.
Partnership
In contrast to many traditional automakers, Tesla also functions as the first product manufacturer. It creates electric drivetrain components that other automakers can purchase and sell under their own brand names (Tesla Inc., 2021). Tesla has production agreements with Lotus Cars, cooperation with electronics company Panasonic, and strategic alliances with two major manufacturers (Daimler and Toyota) (Tesla Inc., 2021).
In addition to the aforementioned alliances, Tesla strategically collaborates with hundreds of other automotive parts suppliers. One is Sotira, a French company producing carbon fiber body panels (Tesla Inc., 2021). The brand cooperates with Southeast APDA and Yes Energy to support renewable energy efforts and promote global change (Tesla Inc., 2021). In this way, numerous partners can help the brand engage in and support the change process.
Competitors
As stated previously, the market of electric vehicles is characterized by fierce and growing rivalry. Tesla’s major competitors are General Motors, Ford, NIO, and Volkswagen (Popli, 2022). The brand’s electric market share is forecasted to decrease from 70% in 2021 to around 50% or lower due to these brands’ activities (Kumar, 2018). Models offered by Ford, GM, and Volkswagen employ similar technologies, but are more affordable to the average user (Popli, 2022). As a result, they have started entering the market and attracting new clients who are also interested in electric cars.
Moreover, Tesla gradually loses its first-mover advantage due to the emergence of similar technologies in other brands and their ability to utilize them to create unique offerings (Bhasin, 2019). The high price of vehicles prevents the brand from entering other segments, meaning that the major competitors have numerous chances for further successful growth and acquisition of new market shares.
Current Strategy and Vision
Tesla’s success and market domination are closely tied to its effective strategy and approach to product distribution. At the same time, the company’s problems may also stem from its existing method. Thus, the brand’s vision is a significant factor influencing its strategy. Tesla states that the company’s primary marketing objectives are to build long-term brand awareness and manage corporate reputation; manage its current customer base to foster loyalty and customer referrals; stimulate demand for its automobiles and drive leads to its sales teams; and allow for consumer involvement during the product development process (“About Tesla,” n.d.). This means that the current strategy involves creating unique vehicles available to a select group of loyal clients.
Moreover, the brand justifies the high price of its products by their unique nature and cost. Tesla emphasizes that new technology is more expensive than old technology, meaning that the initial users are typically wealthy consumers who want access to innovations (Tesla Inc., 2021). Tesla’s strategy also implies using early adopters and returning to the drawing board if the quality of the product is inadequate. It guarantees the desired level of sales and helps the brand to ensure the high quality and innovativeness of the offered vehicles (Tiwari, 2017). This model is untypical for the market as the predominant business models encourage bulk manufacture and mass marketing of inexpensive vehicles (Benzidia et al., 2021). As a result, the combination of a unique vision, specific approaches to manufacturing and selling cars, and effective distribution helps the brand evolve and overcome rivalry.
However, the current strategy has some weaknesses, as evidenced by the company’s current struggles. Focusing on the expensive and luxurious segment requires economic stability and high client interest in the absence of rivals. Today, the financial crisis and the pandemic-induced income reduction have contributed to a decline in interest in Tesla’s products.
Moreover, the emergence of new electric cars and the gradual loss of exclusivity associated with the first models led to a deterioration in Tesla’s image as a unique proposition (Tesla Inc., 2021). The technologies have become cheaper due to their evolution, meaning that the price of vehicles manufactured by the company might be unreasonable. For this reason, Tesla needs to reconsider its pricing differentiation approach, enter new markets, and broaden its target audience.
Tesla’s Supply Chain
Tesla has numerous suppliers from around the globe, resulting in a complex and challenging supply chain that has some issues. Tesla’s supply chain is challenged due to its reliance on hundreds of suppliers across Europe, Asia, and the United States (Tesla Inc., 2021). Thus, there are some issues with industrial automation and the design of automotive batteries.
In addition to the possibility of price increases, purchasing cobalt increases the likelihood of supply and production constraints (Rachidi et al., 2021). AGC (windshield wipers), Brembo (brakes), Fisher Power (electric seats), Indiva Products (instrument panels), Modine Manufacturing (battery cooler), Sika (shock absorber), stabilizer (raising door), ZF Lenk system (power management mechanism), and others are other significant Tesla suppliers (Wang et al., 2022). Since Tesla relies on many suppliers and primarily produces to order (MTO), Tesla must establish lasting relationships with its dealers. Otherwise, there is a high risk of shortages.
For this reason, Tesla faces a critical need to improve its model to work effectively with suppliers and manage its supply chain. Like all modern businesses, the corporation must work to improve supply chain productivity and implement strategies to raise the standard (Rachidi et al., 2021). Tesla can stand out from the competition by implementing a successful and optimized chain management strategy, especially in the automobile sector. This is especially true for Tesla Inc. as it critically depends on its supply base and components manufactured by other companies (Tesla Inc., 2021). Implementing a new strategy requires enhanced cooperation with suppliers and improved resource management.
Third-party logistics organizations (3PL), distribution centers, cost, retail outlets, quality, location, and value are typically considered when choosing dealers. However, Tesla’s company is unique, though it has yet to succeed entirely (Bhasin, 2019). Rearranging the Fremont factory to incorporate high-level automation into diverse industrial processes is the primary emphasis of Tesla’s dedicated supply chain processes. Tesla’s primary source of value is the massive use of automated robots and linked supply chains (Valaskova et al., 2022). Tesla’s external logistics department handles warehousing and vehicle delivery after production and assembly.
Correctly realizing the need for change, Tesla aims to improve the efficiency of its supply chain network and generate a competitive advantage. The improvements focus on quick and flexible ways for suppliers to quickly deliver tools, raw materials, and parts, and technological collaboration with the business’s digital supply chain to upgrade existing customers (Valaskova et al., 2022). Additionally, while choosing dealers, Tesla considers information flow, product turnover, supply chain coordination tactics, and risk mitigation (Valaskova et al., 2022). A product’s timely and economical manufacture depends on managing supplier relationships, lessening the influence on the production process management.
Legal, Regulatory, and Contractual Obligations
Tesla aims to deliver their goods and services in a way that respects both the environment and human rights. The Tesla global team collaborates closely with suppliers, discussing our standards and helping them develop the ability to foster a human rights-aware workplace (Dana, 2018). As a condition of doing business with us, suppliers must abide by the supply chain standards, which outline the needs and prospects of suppliers and service providers throughout the supply chain (Dana, 2018). For their brand suppliers, Tesla offers instructions and information on how to adhere to their standards and expectations throughout the supply chain (Bhasin, 2019). These factors simplify the further alteration of the supply chain management and its improvement.
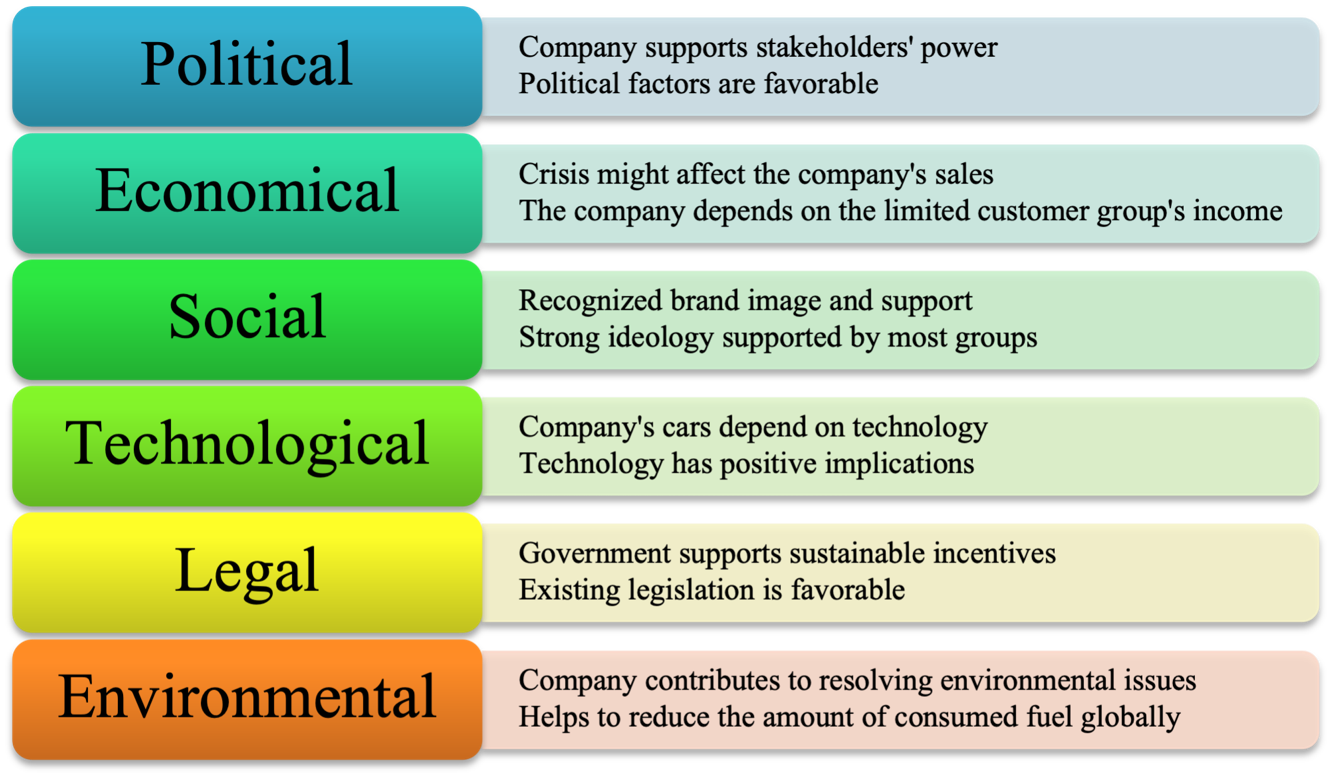
PESTEL Analysis
Using the PESTEL analysis tool, it is possible to investigate the external environment where Tesla operates:
Political Aspects
Political power can be defined as the ability to persuade lawmakers, society, or regulators to take steps that influence a firm’s actions or performance. Tesla Inc. is a leader in electric vehicles. The organization gives stakeholders more influence as it empowers its clients and helps them to cooperate to attract new members and broaden the target audience (Tiwari, 2017). Similarly, vendors frequently form trade associations to influence lawmakers for causes that support their sector. Unlike conventional cars, Tesla employs electricity and natural gas, which require more fuel.
Nevertheless, compared to conventional vehicles, these vehicles use less petrol (Biswas et al., 2020). The government decided to improve the development of hybrid and electric engines. Tesla is even eligible for some tax advantages when purchasing electric vehicles.
Economic Factors
Three significant economic issues that must be assessed are entry barriers, industry growth, and industry concentration. As the economy grows, Tesla sales will increase. The global budget is growing along with the sales of electric vehicles.
The cost of materials for Tesla is declining, which makes production easier (Tesla Inc., 2022). Remarkably, the low cost of batteries is excellent for the Tesla corporation. Even though their cars are well-liked by the public, the cost of the raw materials may decrease. This makes it a cheap means of transportation for people. This has a positive impact on material values as well. At the same time, the brand suffers from the decline in global income caused by the pandemic (Tesla Inc., 2022). The current strategy should consider it.
Social Factors
People generally support the idea of electric vehicles, especially those concerned about pollution or global warming. Fuel consumption disappears for electric and conventional vehicles, allowing the company to become a more potent player and generate high income over time (Dana, 2018). Few automobiles on the market have the power and style of Tesla. Additionally, Tesla did an essential job of upholding the ideological standing of individuals as electric vehicles. Technology aspects affected Tesla Inc.’s Simple entry into the automation and AI industries.
Technological Factors
Technology can help a business maintain an edge over the competition. It will help Tesla conserve more gasoline and open the road for stability and affordability in the future. These cars feature cutting-edge technologies compared to traditional automotive options (Dana, 2018). Due to upgrades, the most recent devices and apps might stop working after a year.
The fact that Tesla automobiles are entirely dependent on technology has positive and dire implications for the vehicle (Dana, 2018). Tesla is growing its customer base in new markets. The most recent international patents must be kept. If not, the expansion will require more time. It might also be illegal for specific reasons. Additionally, because cars are concerned with environmental protection, they can improve their energy efficiency and guarantee that they adhere to international environmental standards.
Environmental Factors
Tesla’s primary benefit is that it is advertised as ecologically friendly because it utilizes more electricity than fuel. Tesla vehicles abide by environmental regulations and do not significantly increase carbon emissions. Tesla has built a name for itself by focusing on the environment; almost no one can compare.
Legal Factors
The company benefits from the governmental incentives created to support electric vehicles and address environmental issues. As one of the pioneers of the electric vehicle industry, Tesla enjoys the state’s support and favorable laws promoting the sector’s further rise and becoming more critical in the future (Tesla Inc.,2021). Thus, it is possible to conclude that the existing legislation cannot be viewed as a barrier to Tesla’s evolution and rise.
Results of PESTEL analysis can be visualized by using the table:
Strategic Options
Altogether, the factors mentioned above show that Tesla has specific strategic options that might help it to overcome the current challenges and create the basis for further rise. First, the situation is not critical at the moment. The company can continue using the existing approach and introduce new models. Their popularity shows that Tesla remains one of the leaders and can enjoy its dominant position. For this reason, the company might continue creating luxurious products and sell them to a limited number of customers. The preservation of the exceptional image and the emphasis on innovativeness can help to support the further rise.
At the same time, as the market conditions become more complex, Tesla’s position might become weaker with time. The entry of numerous competitors with powerful resource bases and recognized brand names might reduce Tesla’s sales. Moreover, companies such as GM or Ford create more affordable vehicles oriented toward a broader target audience (Li, 2018). This means they can expect more clients and a better position than Tesla, especially when the global economy recovers after the pandemic. For this reason, Tesla’s strategic options should be diversified to ensure that the new requirements are met.
Recommendations
Making Affordable Cars
The problem of reducing demand for expensive products can be resolved in several ways. First, Tesla should focus on creating a new line of cars with higher affordability. Two factors justify the shift to this option. First, technology is becoming cheaper, meaning that Tesla can reduce the price of its cars while maintaining the same quality and innovativeness levels.
Second, the middle class continues to increase, transforming into the most attractive customer segment with potentially high revenues and sales (Li, 2018). Moreover, Tesla’s competitors focus on this segment, meaning the brand can lose its lead and powerful position. For this reason, it is vital to create a new line of affordable cars for the majority. It will help to address the problems associated with the recession and avoid a more profound crisis.
Simplifying Supply Chain Management
Second, Tesla can improve its supply chain management as it remains sophisticated. First, it can integrate the smaller components, generally outsourced, into its production process to achieve faster turnaround and shorter product development cycles thanks to the integrated vertical automation system (Li, 2018). It enables crucial flexibility in production, process, and supply chain management.
Second, the company might focus on reducing the number of actors involved in production to make its supply chain more efficient. These strategic options should be considered solutions to the company’s issues. These interventions might help to improve the company’s long-term performance and ensure it will remain a leader in the industry in the future.
Conclusion
Altogether, the information above shows that Tesla is the pioneer in the electric vehicle market. It enjoys the first-mover advantage as the corporation was the first to present a popular and luxurious car. The firm managed to conquer around 70% of the market segment and generate stable revenues. The existing literature admits the company’s innovativeness, focus on sustainable technologies, and unique distribution and promotion models, which have helped it remain popular.
At the same time, the company might experience difficulties in the future because of the growth in rivalry, the unstable economic situation, and the declining interest in costly cars. For this reason, it is vital to use new strategic options to ensure the company’s survival. These include focusing on the middle-class segment and building more affordable cars. It will help broaden the target audience and create the basis for the brand’s stable positions.
References
About Tesla (n.d.).
Benzidia, S., Luca, R. M., & Boiko, S. (2021). Disruptive innovation, business models, and encroachment strategies: Buyer’s perspective on electric and hybrid vehicle technology. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 165, 120520.
Bhasin, H. (2019) Marketing strategy of Tesla. Marketing91.
Biswas, T., Chatterjee, P., & Choudhuri, B. (2020). Selection of commercially available alternative passenger vehicles in the automotive environment. Operational research in engineering sciences: theory and applications, 3(1), 16-27.
Blue Ocean. (n.d.). What is blue ocean strategy?
Dana, C. (2018) A strategic audit of Tesla, Inc.: Electrifying our future or about to run out of energy? [Unpublished honor’s thesis]. University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Kumar, R. (2018) Electric vehicle market by type (battery electric vehicle, hybrid electric vehicle, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle), and vehicle type (passenger car, commercial vehicle, and two-wheeler) – Global opportunity analysis and industry forecast, 2018-2025. Allied Market Research.
Li, Z. (2018). Strategic audit on Tesla. [Unpublished honor’s thesis]. University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Popli, N. (2022). Tesla is no longer alone in the electric vehicle race. Time.
Rachidi, N. R., Nwaila, G. T., Zhang, S. E., Bourdeau, J. E., & Ghorbani, Y. (2021). Assessing cobalt supply sustainability through production forecasting and implications for green energy policies. Resources Policy, 74, 102423.
Teece, D. J. (2018). Tesla and the reshaping of the auto industry. Management and Organization Review, 14(3), 501-512.
Tesla Inc. (2021). Annual report on form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021. Sec.gov.
Tesla Inc. (2022). Q3 2022 Update.
Tiwari, J. (2017). Marketing research on Tesla Inc. – strategic analysis. Strategic Engineering Management.
Valaskova, K., Nagy, M., Zabojnik, S., & Lăzăroiu, G. (2022). Industry 4.0 wireless networks and cyber-physical innovative manufacturing systems as accelerators of value-added growth in Slovak exports. Mathematics, 10(14), 2452.
Wagner, I. (2020). Tesla – statistics & facts.
Wang, X., Zhao, W., & Ruet, J. (2022). Specialised vertical integration: the value-chain strategy of EV lithium-ion battery firms in China. International Journal of Automotive Technology and Management, 22(2), 178-201.
Appendices