Background and Significance
A dietary approach to stop hypertension, popularly known as the DASH diet, is often recommended by nutritionists and doctors as a good way of managing high blood pressure without the use of medication. The nutritional approach to managing hypertension has gained massive popularity not only in the United States but also in other parts of the world. According to Tyson et al. (2015), the DASH diet is often recommended for patients aged over 50 years, especially when they are in the early stages of hypertension. The goal of this diet is to reduce sodium in one’s diet as much as possible while increasing the intake of potassium, magnesium, and other nutrients known to fight high blood pressure. This diet is also known to help in managing other chronic illnesses such as diabetes, coronary conditions, stroke, and obesity (Challa et al., 2020). The significance of the study is to establish if indeed DASH dietary approach can help adults aged 45-65 to manage their blood pressure without being put on medication (Tyson et al., 2015). It will help address doubts that sometimes exist about the usefulness of this form of medication. The following PICOT question will guide the investigation in this study.
- In patients, aged 45-65 with hypertension, what is the effect/ benefit from DASH diet management on blood pressure compared with no diet modification ( western diet) over 3 months period?
Literature Review
The dietary approach to stop hypertension is a topic that has attracted scholars in the past as an alternative to the use of medication in addressing the problem of high blood pressure. According to Simmons (2018), hypertension has become one of the most common health problems in the United States and other parts of the world. The kind of lifestyle that many people lead is blamed for the rise of the problem. A study by Evans (2018) shows that many Americans are leading highly stressful lives. Pressure at work is one of the leading causes of stress. Many are struggling to get promotions while others are working hard to meet high targets set by their managers. The increasing cost of living has forced many people to take two or three jobs a day just to earn enough to support their families. The expectations of families are another source of stress to many Americans. Most parents feel that they have the responsibility to meet the financial needs of their families, which sometimes forces them to ignore social needs. Cracks soon emerge in marriages and in the end, some of them end up in divorce (Simmons, 2018). Children also need socio-emotional support from their parents, even in cases where one is a single mother. They have to find a delicate balance between work and family.
The growing popularity of fast foods is another major cause of hypertension among the majority of Americans. As they struggle to balance their limited time, it is easier for them to pick chicken wings or pizza at McDonald’s instead of cooking at home (Challa et al., 2020). The problem with fast food is that one cannot have an accurate understanding of the calories and sodium that they take. It is common to exceed the required limit of these nutrients. Reduced physical exercise is another common cause of hypertension even among children. According to Tyson et al. (2015), outdoor games which were popular in the past are becoming less common. Children and adults currently prefer indoor games and online forms of entertainment. Eating junk food coupled with limited physical exercise is a direct cause of blood pressure. The situation is worsened when one has to deal with constant stress caused by social and economic challenges.
The use of medication to manage hypertension has been the standard practice for decades. Some may be put on medication for a period while others may have to rely on it for the rest of their lives when the condition becomes chronic. Studies have shown that regular medication has negative consequences on one’s liver and kidneys. These organs have to constantly clean the blood from the toxics of the medicine (Simmons, 2018). It means that when one continues to use medication for a long period, they may develop other serious health problems. As such, there has been a need to find ways of managing high blood pressure without relying on medication. Medical research has often focused on the use of healthy foods as a way of managing this problem. The approach focuses on limiting the intake of salt and increasing intake of potassium and magnesium because of their benefits in lowering the pressure.
Scientific studies have revealed that when one maintains a regular healthy diet that limits the intake of salt and fat, they can fight hypertension. A study by Evans (2018) indicated that potassium has the capacity of lowering blood pressure if taken regularly and in recommended quantities. It has the opposite effect of sodium in terms of the management of blood pressure. One needs to understand the amount of sodium they take in their food for them to regulate their daily intake. They have to know how to limit taking excessive amounts of salt because of its dangers. In many cases, one can rely on a dietary plan provided by a nutritionist to limit their intake of salt. Studies have confirmed that one can significantly lower their pressure when they maintain a healthy diet.
The biggest challenge to the use of the DASH diet as a means of managing blood pressure is that it may not be easy to implement it. Those who have suffered from hypertension may use it for the first few days when they are going through pain and discomfort associated with the disease. However, as their condition improves, they tend to forget about the need to stick to the recommended diet (Challa et al., 2020). They find themselves tempted to go back to junk food. Others may claim that the affordability of some of the food items in the DASH diet is not affordable. This form of managing hypertension works well when one can maintain regular physical exercise and manage stress. Addressing these challenges can help in ensuring that the DASH diet is a success.
Supporting Evidence
Hypertension is currently one of the most common health problems among adult Americans. Studies have shown that the problem is caused by factors such as wrong diet, excessive intake of alcohol, obesity, lack of exercise, and stress (Simmons, 2018). High blood pressure can have serious health consequences which include stroke and heart attack. Evidence has shown that this serious medical problem can be managed by having the right diet, managing one’s stress levels and body weight, and maintaining regular exercise (Evans, 2018). In terms of maintaining a proper diet, the study suggests that one should limit intake of salt. Exercise amount of sodium in one’s food has been proven to be one of the main causes of hypertension. This mineral makes blood vessels narrower and more rigid. The condition can be worsened when one takes in excess amounts of cholesterol in their food. Identifying dangerous food items and eliminating them from one’s diet is essential. At the same time, it is important to identify food items that can enable the body to fight the disease effectively. One can then develop a dietary plan that is limited to the harmful nutrients while increasing the intake of healthy ones. According to Tyson et al. (2015), most of the health problems that people suffer from are caused by the kind of food they eat. Fast foods are believed to be a major cause of diseases such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and many other health problems. It means that when one embraces dietary discipline and maintains a healthy diet, they will not only be fighting the problem of high blood pressure, but also many other medical problems.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the study is to examine the effect or benefits of DASH management on blood among patients aged 45-65 with hypertension. The investigation will determine if this diet has positive effects on these patients when compared with no diet modification (western diet) over 3 months period. Simmons (2018) strongly suggests that the western diet significantly contributes to cases of high blood pressure among adult Americans. The excessive intake of this mineral (sodium) has proven to be a major factor that is often associated with high blood pressure (Tyson et al., 2015). Although sodium is an important mineral to the body, it should be taken in moderation to ensure that it does not have negative consequences. The aim of the study is to identify specific benefits of the DASH diet to the selected cohort. The investigation seeks to provide evidence-based advice to the group so that they can understand how to manage their diet as a way of combating various health problems, especially hypertension.
Theoretical Framework
Diet management is a topic that has attracted the attention of various scholars over the years. Evans (2018) explains that it has become increasingly evident that most of the health problems that people have are caused by the food they take. As such, theories have been developed to help guide people on how to lead a healthy lifestyle by taking into consideration the type of food they take. 90/10 theory is one of such concepts that have gained popularity over the recent past. It holds that one should strive to eat healthy foods 90% of the time and allow oneself to indulge in whatever one craves for 10% of the time (Tyson et al., 2015). It holds the argument that 90% of events that people go through are fully within their control, while the other 10% may happen because of uncontrollable forces. As such, during the time that one has full control of their actions, they should maintain a healthy diet. On a few occasions when they have to eat a certain meal because of a given reason, they should have the freedom to indulge in junk food as long as it is not a regular occurrence. One should take deliberate steps to limit their intake of salt as one of the ways of fighting hypertension.
Classical conditioning is a behavioral theory that can be used to define actions that one embraces when taking food (Challa et al., 2020). It emphasizes the need to associate a given naturally occurring phenomenon with a neutral stimulus (Challa et al., 2020). The goal is to ensure that one embraces positive behavior by associating it with what they consider desirable. In terms of diet, one can associate a diet with a low intake of salt, with a healthy lifestyle. At first, it may appear to be a punishment as the person may be forced to ignore many cravings. However, through practice, they get to like such foods, especially when they are able to witness the actual health benefits. Simmons (2018) argues that learning such habits may require continuous or patient reinforcement as one learns to appreciate the significance of their behavior. Knowing about the health consequences of taking junk food, especially those with exercise amounts of salt and fat, can be a significant reinforcement for these people to maintain a healthy diet. They get to learn about the significance of maintaining such practices.
Methods, Design, and Sampling
The study used data from both primary and secondary sources. Secondary data was obtained from books and journal articles. They formed the basis of the literature review section above. The researcher also considered it necessary to collect data from primary sources. The target was to collect data from nutritionists and physicians in the local healthcare institutions (Klugman & Lamb, 2019). Collecting data from these experts would help to understand the topic based on recent studies. Judgmental sampling was the most desirable method of identifying the sample because of the nature of experts needed. As Philippopoulos (2017) observes, this method gives a researcher the freedom to choose participants based on specific criteria. In this case, the desired participants had to be nutritionists or physicians in the local institutions of healthcare. A sample of 20 experts was appropriate for the study.
Once the sampling method had been defined, the researcher had to reach out to these participants to collect data from them. Using phone calls and social media platforms, the researcher reached out to these participants, explained the significance of the study to them, and informed them of their role in it. They were also informed why they were considered appropriate for the study. Given the current COVID-19 containment measures that discourage physical interactions, the researcher conducted an online survey. A questionnaire was developed and sent to the participants through their e-mail. They were requested to answer those questions and send the document back. Once primary data had been collected, they had to be processed in a way that makes sense. The quantitative research method was the most ideal design that could help in achieving the primary goal of the study (Trueman, 2016). It allowed the researcher to use a quantitative research study with randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to determine the significance of the DASH diet in the management of blood pressure. It means that participants will be classified into two groups, the experimental group, and the control or comparison group. The strategy helps to eliminate bias when collecting primary data. Microsoft Excel was used to facilitate the statistical analysis.
Proposed Interventions
Dietary approaches to stop hypertension have gained massive support over the recent past because of their relevance in addressing the problem. Traditionally, patients with hypertension are often put on medication to help manage their problems. However, the dietary approach is a new intervention that focuses on managing nutrients that a patient takes. Instead of medication, this intervention emphasizes the need to reduce sodium intake, which is one of the primary causes of high blood pressure, while increasing minerals such as potassium and magnesium known to reduce the pressure (Simmons, 2018). When one takes a DASH diet as per the recommendations of a nutritionist, it is likely that they will achieve the goal of lowering their blood pressure.
The proposed intervention is to have a properly calculated intake of specific nutrients and minerals needed by the body. Although it is responsible for increasing blood pressure, sodium is still an important mineral to the body (Evans, 2018). Taken in the right quantities, this mineral can play an important role in the body. Research has shown that adults should not take more than 2.4g of sodium in a day. The problem is that sometimes one may exceed this amount because of eating salted food items without knowing the quantity of salt they have. Challa et al. (2020) believe that increasing the intake of food items such as banana, which is rich in potassium, may help to counter the excess sodium in the body. One needs to understand specific foods that they should take frequently in specific quantities as a way of managing their blood pressure.
Expected Results/Outcomes
The researcher intends to conduct a comprehensive primary data collection and analysis soon after the pandemic is managed. It was desirable to collect data from a large population of experts and patients who have used the DASH diet to manage their blood pressure. However, that was not possible because of the pandemic. In fact, these patients with hypertension are considered high-risk groups, and as such, having a physical interaction with them was not possible. However, the preliminary data collection and analysis conducted with the 20 experts can help in determining the expected outcomes of the study when it is finally conducted. It is possible to know the actual benefits of dietary approaches to stop hypertension. The following are some of the questions that the researcher responded to when conducting this preliminary investigation.
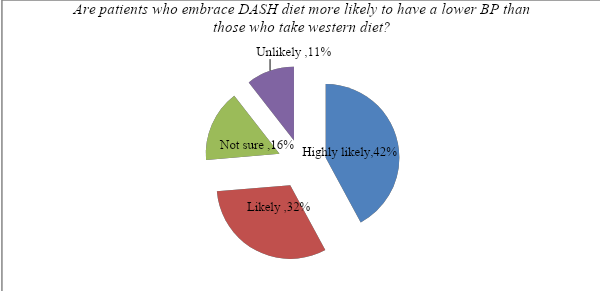
Do you believe patients who embrace the DASH diet are more likely to have a lower blood pressure than those who take the western diet (no modification)?
The first question directly focused on investigating the effectiveness of the DASH diet in managing high blood pressure. When the question was posed to the few experts who participated in the data collection, figure 1 below shows their response. It is evident that 42% felt that it is highly likely, while another 32% stated that it is likely. It means that an overwhelming majority (74%) of the participants feel that the DASH diet is likely to lower blood pressure than the western diet. 10% stated that they are not sure about the benefits of this diet. Another 16% felt that it is unlikely for this diet to have the desired effect if one does not maintain practices such as managing stress levels and maintaining physical exercise.
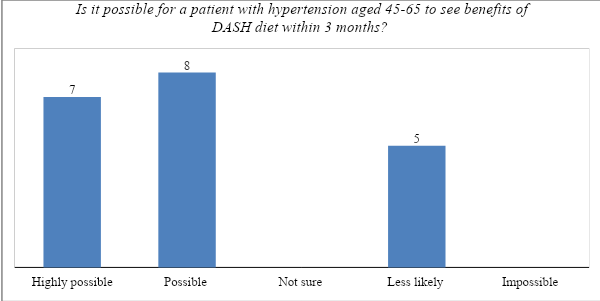
It is possible for a patient with hypertension aged 45-65 to see the benefit of the DASH diet within three months?
When managing a given health problem using a specific strategy, sometimes it may take a while to notice its benefits while in other cases it may take a short period. It depends on the intervention that one has taken and their level of commitment to it. In this case, the researcher was interested in determining if a patient who uses the DASH diet can see its benefits within 3 months. 7 participants stated that it is highly possible while another 8 of them stated that it may be possible. It means that the majority of the participants (75%) believe that for patients aged 45-65, it is possible for them to see the benefits of the DASH diet within 3 months. The other 25% stated that it is less likely to see the benefits of this intervention within that period. they explained that the DASH diet requires a lot of discipline, and for its benefits to be seen within such a short period, one also needs to embrace other measures such as managing stress and maintaining regular physical exercise. Figure 2 below shows their response.
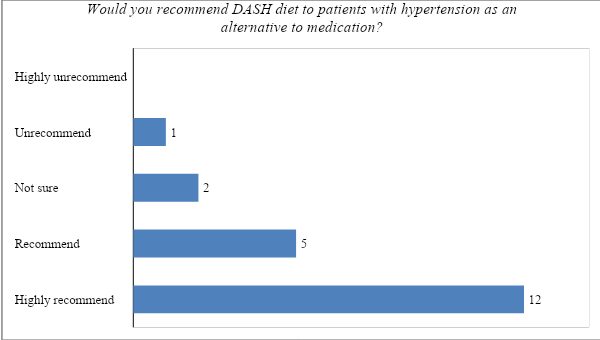
Would you recommend the DASH diet to patients with hypertension aged 45-65 as an alternative to medication?
As explained in the methodology section above, the researcher interviewed a small sample of experts (nutritionists and physicians) to get their views about the benefits of the DASH diet. It was necessary to determine if they would consider recommending the Dash diet to their patients as an alternative to medication. 12 out of the 20 participants stated that they highly recommend the diet as it can be used instead of medication if one remains disciplined and accompanies it with regular physical exercise and stress management. Another 5 participants stated that they recommend it as a way of addressing high blood pressure without the use of medication. It means that an overwhelming majority of the participants (85%) strongly believe that the DASH diet can be used to manage hypertension without the need to use medication. 10% of the participants stated that they are yet to have a statistical analysis of the capacity for DASH to manage blood pressure without using medication. 5% of the participants felt that they would not recommend the DASH diet to patients who should be on medication. They explained that they can only advise patients who have already managed their high blood pressure to use DASH as a preventive measure. Figure 3 below shows their response.
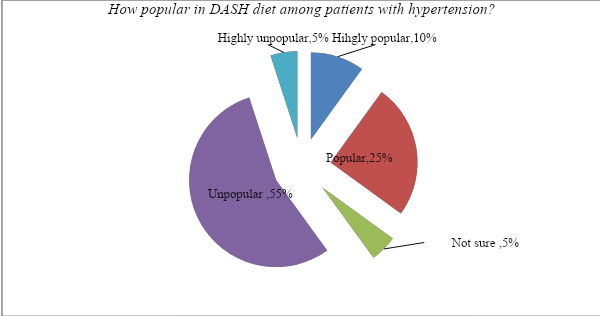
How popular is the DASH diet among patients with hypertension in the United States?
It is evident that the DASH diet may help manage hypertension among patients aged 45-65. It was necessary to determine if it has gained popularity among patients in the country. An intervention may be effective in addressing a given problem, but when its use depends on the discipline and preferences of a patient, it is important to popularise it. The specialists were asked to state whether this intervention is popular among patients based on their experience. The majority of the participants (60%) stated that the DASH diet is unpopular in the United States. They explained that the majority of Americans have tight work schedules and do not have time to maintain such diets. They prefer fast foods (junk food) that they consider delicious and easily accessible. Figure 4 below shows that although the majority feels that this form of managing hypertension is yet to gain popularity, there is hope. 35% of the participants feel that this form of intervention is gaining popularity in the country, especially among adults who understand the dangers of hypertension. The other 5% of the participants stated that they are not sure. It means that despite the obvious benefits of this form of managing hypertension, it is still important to find ways of promoting it among patients. They need to appreciate its ability to manage their condition without necessarily maintaining medications.
Anticipated Conclusion
The preliminary investigation has revealed that the DASH diet has a significant impact on the management of blood pressure among patients aged 45-65. When one maintains this diet, they will significantly reduce their intake of salt, which is a major factor responsible for exacerbating hypertension. They will learn to maintain a specific amount of salt in their foods within a day. They will also appreciate the significance of taking food rich in other healthy minerals such as potassium and magnesium. Taking this approach means that a patient may be less reliant on medication. The review of the literature revealed that if a patient maintains a proper diet, they are less likely to rely on drugs. The body will respond positively to the intervention and may never need to take such medications for a long period.
The study shows that despite the obvious benefits of the DASH diet, it also has some challenges that cannot be ignored. One of the main challenges is the level of discipline that is required when using this intervention plan. As shown in the 90/10 theory, one is required to maintain the right diet 90% of the time, while 10% may indulge in junk food. The problem is that many people tend to forget that they are on diet. They may start well, maintaining healthy foods for a given period. However, along the way, they find it difficult to stick to the plan. The study has indicated that patients find it challenging to overcome their love for fast foods. It is also important to note that when using this intervention plan, one must be committed to maintaining regular physical exercise and avoiding unnecessary stress.
Possible Limitations
It is important to appreciate the possible limitations to the DASH diet despite the numerous health benefits that it has. One of the main limitations is the ability to apply it among convicts serving jail terms. In the penitentiaries across the country, there is a standard diet that prisoners have to take. The government cannot afford to give prisoners a special diet. People who are not in prison may also find it difficult to maintain such a diet. Although it is possible to maintain the dietary approaches to stop hypertension without spending much, sometimes it may be necessary to include food items considered highly nutritious. Some people may not afford to purchase such food items on a regular basis. Discipline is another major limitation. Some patients may maintain the diet for a while, but they soon forget about it when they start craving junk food. It is also important to note that this approach to managing high blood pressure works well when one also embraces regular exercise. The problem is that many people find it challenging to maintain physical exercise.
Potential Implications to Practice
The outcome of this study may have major implications for practice. It is evident that one can manage their blood pressure by maintaining a DASH diet instead of using the medicine. As Tyson et al. (2015) explain, the DASH diet will not only help in managing hypertension but also in addressing various other health problems. A hypertensive patient will also be addressing diabetes, coronary complications, various types of cancer, and obesity among many other complications when they maintain a healthy diet. As such, practitioners are likely to shift from recommending the use of medicine and instead emphasize the use of the Dash diet. A patient’s condition may be managed medically to a certain level before they are put on a strict diet. Such practices may reduce overreliance on medication when it comes to the management of blood pressure.
References
Challa, H., Ameer, M., & Uppaluri, K. (2020). DASH diet: Dietary approaches to stop hypertension. Current Hypertension Reports, 3(1), 1-15.
Evans, M. (2018). DASH diet: The ultimate dash diet guide to lose weight, lower blood pressure and stop hypertension fast. Publish Drive.
Klugman, C., & Lamb, G. (2019). Research methods in health humanities. Oxford University Press.
Philippopoulos, A. (Ed.). (2017). Research methods in environmental law: A handbook. Edward Elgar Publishing Limited.
Simmons, J. (2018). DASH diet cookbook: Recipes and guide to lower blood pressure lose weight and maintain optimal health. Publish Drive.
Trueman, L. (2016) Research methods for the biosciences. Oxford University Press.
Tyson, C., Nwankwo, C., Lin, P., & Svetkey, L. (2015).The dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) eating pattern in special populations. Current Hypertension Reports, 14(5), 388-396.
West, H. (2018). The complete beginner’s guide to the DASH diet. Web.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Dash diet

Appendix 2: Impact of DASH Diet on Blood Pressure