This paper explores the evolution of number system from ancient to modern. Here, you’ll find information on the development of number system of the Egyptians/Babylonians, Romans, Hindu-Arabics, and Mayans.
History of Numbers: Essay Introduction
The evolution of numbers developed differently with disparate versions, which include the Egyptian, Babylonians, Hindu-Arabic, Mayans, Romans, and the modern American number systems. The developmental history of counting is based on mathematical evolution, which is believed to have existed before the counting systems of numbers started (Zavlatsky 124).
The history of mathematics in counting started with the ideas of the formulation of measurement methods, which the Babylonians and Egyptians used, the introduction of pattern recognition in number counting in pre-historical times, the organization concepts of different shapes, sizes, and numbers by the pre-historical people, and the natural phenomenon observance and universe behaviors. This paper will highlight the evolution history of counting by the Egyptians/Babylonians, Romans, Hindu-Arabic, and Mayans’ counting systems. Moreover, the paper will outline the reasons why Western counting systems are widely used contemporarily.
The Egyptians/Babylonians Number History
The need for counting arose from the fact that the ancient people recognized the measurements in terms of more or less. Even though the assumption of numbers based its arguments on archeological evidence about 50,000 years ago, the counting system developed its background from the ancient recognition of more and less during routine activities (Higgins 87). Moreover, ancient people’s need for simple counting in history developed odd or even, more or less, and other forms of number systems evolved into the current counting systems. The need for counting developed from the fact that people needed a way of counting groups of individuals through population increase by birth. In addition, Menninger asserts that the daily activities of the pre-historical people, like cattle keeping and barter trade led to the need for counting and value determination (105).
For instance, in order to count cows, prehistoric people used sticks. Collecting and allocating sticks to count the animals helped determine the total number of animals present. The mathematical history evolved from marking rows on bones, tallying, and pattern recognition, which led to the introduction of numbers. The bones and wood were marked, as shown below.

Moreover, the development of numbers evolved from spoken words by pre-historical people. However, the pattern of numbers from one to ten has been difficult to trace. Fortunately, any pattern of numbers past ten is recognizable and easily traceable. For instance, eleven evolved from ein lifon, which was used to mean ‘one left’ over by the prehistoric people. Twelve developed from the lif, which meant “two leftovers” (Higgins 143). In addition, thirteen was traced from three and four from fourteen, and the pattern continued to nineteen. One hundred is derived from the word “ten times” (Ifrah and Bello 147). Furthermore, the written words used by the ancient people, like notches on wood carvings, stone carvings, and knots for counting, gave a solid base for the evolution of counting.
The Incas widely used counting boards for record-keeping. The Incas used the “quip,” which helped the pre-historical people record the items in their daily lives. The counting boards were painted with three different color levels. These were the darkest parts, representing the highest numbers; the lighter parts, representing the second-highest levels; and the white parts, representing the stone compartments (Havil 127). In addition, the quip was used to do fast mathematical computations (Zavlatsky 154). Generally, the quip used knots on cords, which were arranged in a certain way to give certain numeral information. However, the quip systems of record keeping and information have been associated with several mysteries which have not yet been established. Examples of how the knots looked are shown below.
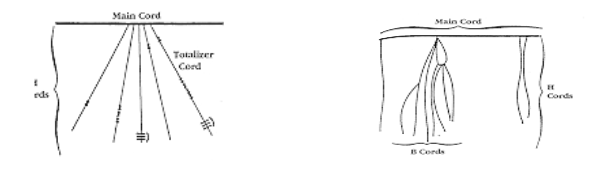
The Hindu-Arabic Number History
This form is the common system of counting and numbers used in the 21st Century. In India, Al-Brahmi introduced the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 (Menninger 175). The Brahmi numerals kept changing with time. For instance, in the 4th to 6th Century, the numerals were as shown below.
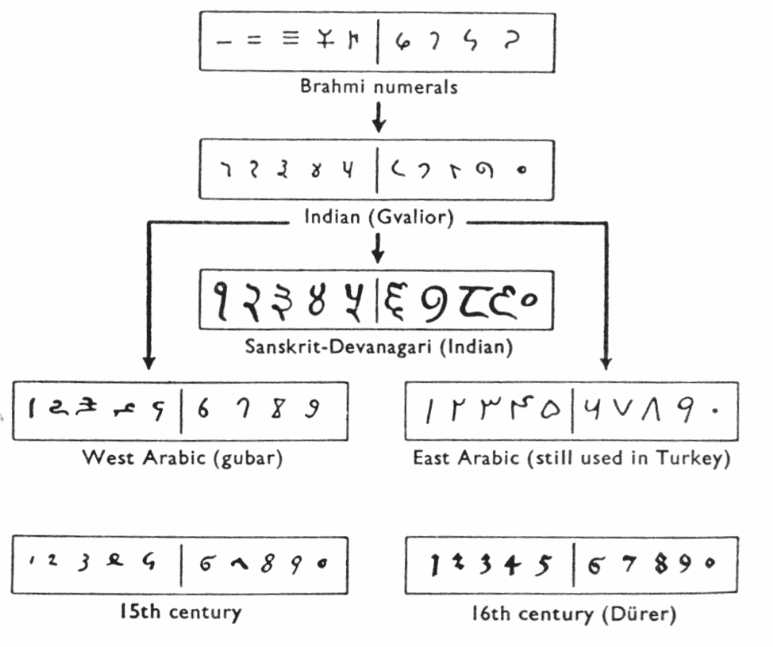
Finally, the numerals were later developed to 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 with time. The earliest system of using zero was developed in Cambodia. The evolution of the decimal points emerged during the Saka era, whereby three digits and a dot in between were introduced (Hays and Schmandt-Besserat 198). The Babylonians introduced the positional system, whereby the place value of the numerical systems was established. Moreover, the positional system by the Babylonians developed the base systems to the numerical, and the Indians later developed it further. The Brahmi numerals took different incarnations to develop, which resulted in the current number system (Higgins 204).
The Gupta numerals were one of the processes passed by the Hindu-Arabic number system to become the commonly used American number version. Currently, theories about the formation and development of the Gupta numerals remain debatable by researchers.
In addition, the Europeans adopted the Hindu-Arabic system through trading, whereby the travelers used the Mediterranean Sea for trade interactions (Havil 190). The use of the abacus and the Pythagorean dominated the European number evolution. The Pythagorean used “sacred numbers” even though the two systems diminished after a short while. With time, the Europeans borrowed the Hindu-Arabic number system to establish their mathematical number systems (Ifrah and Bello, 207). However, the process through which the Europeans adopted the Hindu-Arabic system has not been proven fully. It is believed that the Europeans adopted the Hindu-Arabic number system by relying heavily on it to build their current strong numerals (Higgins 210). For instance, the scope of the positional base system is quite large, which involves the conversion of different bases using the numerical number 10.
The Mayan Number History
The Mayan civilization of counting and number systems developed in Mexico through ritual systems. The rituals were calendar calculations involving two ritual systems, one for the priests and the other for the ordinary civilians (Higgins 217). For instance, priestly calendar counting used mixed base systems involving numerical number multiples. The Mayan number systems form the base of mathematical knowledge. Moreover, the Mayan system of numbers used the positioning of numbers to allocate the place value of the combined digits (Havil 223).
The Mayans used the place value of numerical numbers, which were tabled to add and multiply numbers. Ultimately, the Hindu-Arabic and the Mayan number systems contributed highly to the evolution of numbers as opposed to the Egyptian/Babylonian number systems (Menninger 199). Nevertheless, the Western number system of counting and mathematics incorporated the strong features of all the other evolutions to get a standard solid number system. For instance, the American system, commonly used in most countries, uses decimal points, place values, base values, and Roman numbers from 1 to 10 (Ifrah and Bello 225). The figure below represents a sketch of the tabled digits by the Mayans.
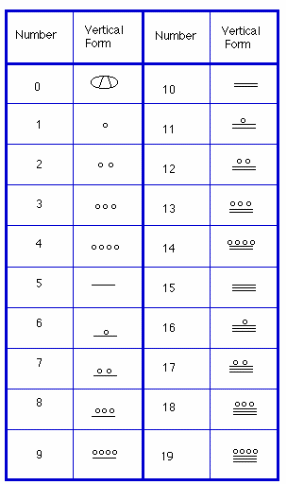
The American version of numbers and counting used all the development features of the Mayans, Babylonians, Incas, Egyptians, and Hindu-Arabic systems to develop a reliable and universally-accepted number system (Hays and Schmandt-Besserat 214). This aspect is outstanding as it makes the American system stand out of all the number systems and counting. Nevertheless, the commendable work of the Mayans, Babylonians, Egyptians, and Indians cannot be underrated, as the historical trace of counting and number systems would be impossible without them.
History of Numbers: Essay Conclusion
The historical trace of number systems and counting covers a wide scope of pre-historical archeological evidence. Tracing ancient times by researchers poses a significant challenge in establishing counting and number systems. The research on number systems and counting has not yet been settled on the actual source information for evidence. Ultimately, the most effective number systems that led to the current dominant Western number system are the Mayans, Hindu, and Babylonian systems relying on the Incas’ developments. The prehistoric remains left mathematical evidence as stones and wood carvings, which led to the evolution of counting. Hence mathematical methodologies evolved. The methodology of research and arguments varies on the evolution of numbers. Consequently, there are no universally-accepted research findings on the mathematical and number systems evolution.
Works Cited
Havil, Julian. The Irrationals: A Story of the Numbers You Cant Count on, Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2014. Print.
Hays, Michael, and Denise Schmandt-Besserat. The History of Counting, Broadway: HarperCollins, 1999. Print.
Higgins, Peter. Number Story: From Counting to Cryptography, Gottingen: Copernicus, 2008. Print.
Ifrah, Georges, and David Bello. The Universal History of Number: From Pre-history to the Invention of Computer, Hoboken: Wiley, 2000. Print.
Menninger, Karl. Number Words and Number Symbols; Cultural History of Numbers, Mineola: Dover Publications, 2011. Print.
Zavlatsky, Claudia. Africa Counts; Number and Pattern in Africa Cultures, Chicago: Chicago Review Press, 1999. Print.