Introduction
Culture is a unique way of organizing and developing human life, presented in the form of material and spiritual values. This concept distinguishes the way of life of a person from the way of life of any other living being. It is no secret that culture has a reasonably close, deep, and robust connection with communication and the processes of socialization, and the search for one’s own identity (Glassdoor Team, 2021). Furthermore, it is one of the primary sources and root causes that form and develop interpersonal aspects in society (Abdulla, 2018). Culture serves as an enrichment of human values and unique experiences, subsequently applied in discussions or communication between several people (Abdulla, 2018). Every act of transmission and passing of messages and information is accompanied and reinforced by cultural moments inherent in both an individual and a group of people. Hence, without any doubt, culture, in its innumerable forms and representations, intersects with elements of social and human communication (Croucher, 2020). On the one hand, the culture in which people are socialized forms a particular type of communication. On the other hand, communication processes create, support, and change certain cultural phenomena.
Therefore, the type of culture generates the form of communication and contact, as well as through the prism of interactions of people, particular inclinations inherent in a certain participant of communication are formed. Culture not only influences communication but is itself influenced by it. Most often, this happens in the process of inculturation when a person learns the norms, values, customs, and traditions of a certain people in one form of communication or another. Often, behavior, feelings, emotions, and spoken words are conditioned by the culture that exists in a continuum in a certain period and time (Stadler, 2019). From the point of view of these arguments, people use a fairly wide range of strategies aimed at practicing certain behavioral reactions and actions or at deliberately ignoring them (Stadler, 2019). In addition, by reading, listening, observing, exchanging opinions and news with acquaintances or strangers, one influences their and other cultures, which becomes possible through some form of communication. Consequently, culture has a relatively solid and predominant impact on communicative elements in the modern world.
Literature Reviews
There is a reasonable assumption and reasoning that culture has a direct, strong influence on communication types, forms, and styles. There is a close, deep, and inextricable connection between these concepts since they combine similar, interrelated, complementary determinants, quantities, and establishing factors. This correlation has been studied for quite a long time and continues to be reflected in some modern studies. For instance, Croucher et al. (2017) claim that culture and communication are essential elements of human existence, progress, development, and improvement. The key difference lies only in the interpretation and conceptualization of terms (Croucher et al., 2017). Nonetheless, the concepts themselves are an integral part of the world order and pattern and the organization of human consciousness, body, and soul. They have a causal relationship; together, these aspects complement each other, and in some way, even replace and substitute.
However, the currently existing case studies have their weak sides. Unfortunately, today there is a small number of research on the deep, thorough subject of analyzing the relationship between two critically important elements of a state, society, and an individual. Subject to this position, scientists do not lose enthusiasm, aspiration, and desire to clarify the details, essence, and features of correlations between culture and communication. Primarily, communication is a complex and multifaceted social process that has been systematically developing for a particular historical moment and continues to be improved, transformed, and modified to this day. Hence, Bâlc (2018), in his research, theorizes that culture and society are inseparable from each other, and all the concepts that are interconnected with them have to some extent an indirect or immediate connection. Everything that constitutes large communities functions from the processes of communication within and between group systems (Poepsel, 2018). In this case, culture acts as an auxiliary means, an intermediary in the expression of these relations, without which it is also impossible to implement and enforce adequate communication and interaction processes (Bâlc, 2018). There is a universal tendency, facts, and assumptions to confirm this statement.
In addition, several empirical investigations have also focused on studying this area. Communication implies the exchange of meanings and symbols between people, the definition of which will vary from the national heritage (Poepsel, 2018). Consequently, understanding and interpretation of the meaning of the worlds are reinforced precisely by cultural experience; respectively, the style and forms of communication directly follow from these phenomena (Creanza et al., 2017). The use of language, words, and phrases are used in entirely different ways, and verbal and non-verbal communication, in general, varies depending on cultural values (University of Houston-Victoria, 2020). For example, even such a seemingly “simple” word as “yes” can have completely different meanings and be perceived in a narrower sense and a broader definition (University of Houston-Victoria, 2020). Indeed, there is a rich abundance of means of expressing thoughts and feelings, developed during the evolution and development of humankind, which was subsequently distributed into certain communities, groups, and states (Lewens, 2017). Gao and VanderLaan (2020) say that expressing certain emotions, feelings, and the utterance of specific phrases and words imply certain elements. As mentioned before, they developed during long-term practice that reflects the country’s and certain people’s culture.
The following idea should also be noted and highlighted as evidence of these judgments. Language, knowledge, and information transfer have systematic and cumulative relationships at the level of intercultural communication (Szkudlarek et al., 2020). For example, special and unique trends manifest when people from different countries communicate. Furthermore, according to Xiaomeng et al. (2018), the design and formulation of the same problems, judgments, and opinions can differ significantly from completely different people from different states. In compliance with Bonvillain (2019), through the prism of transmitted messages and sent “signals” of communication, a person deliberately, or even sometimes in an unconscious form, informs the interlocutor about their identity, worldview, and ideology. Thus, culture also forms certain principles that manifest themselves in these conditions (Brown et al., 2020). Human behavior is conditioned by independent variables that can be predicted and forecasted, and as a rule, they include the values, customs, and traditions of a certain people (Hall et al., 2017). Undoubtedly, this causal, close relationship has its vital, independent significance (Hall et al., 2017). Despite this, it can lead to distorted ideas and hypotheses too.
In brief, there is much detailed data, information, and knowledge about both “culture” and “communication,” but only a small proportion of the studies the correlation of these concepts. There is still a problem in a more reliable, accurate, and objective explanation of the relationship between these two aspects and judgments about how and to what extent culture can influence communication. Thus, the relevance of the research topic is manifested, expressed in a detailed, comprehensive, and thorough analysis, accompanying the previously indicated points.
Research Design
The following key aspects were applied as the strategy and design of the empirical study. Primarily, this project combines mixed methods to determine the problem solution’s essence – quantitative and qualitative research methods. Each of the strategies involves using specific techniques of data collection and analysis. In this case, the quantitative method applies a deductive approach and the analysis and synthesis of the information obtained. This helps to test the hypothesis’s validity and confirm its objectivity.
Moreover, the principles and mechanisms of quantitative tactics and strategies were also involved in this work. The fundamental basis of the methods is an inductive approach to the development of theory, rejection of positivism, and focus on the interpretation of reality. Quantitative models have been applied in practice within the experimental, correlation, and descriptive types of design. In addition to this, the author of the project used such research elements as questionnaires and feedback analysis. The objects of the study were a group of people (Internet users) consisting of 30 people. The research was conducted on the Livejournal blog platform, which provided an opportunity to publish an entry about the topic of research and questionnaire development. The ideas and thoughts of each interested party were taken into account and carefully studied.
The results obtained were interpreted into quantitative data and percentages using methods of selecting common aspects. It took about a week to collect the data and describe the study. The work’s scientist, having the necessary arsenal of research skills, was able to fully obtain the essential, valuable data in the specific space and the conditions in which the questionnaire and feedback analysis were conducted. The outcomes obtained indicate the reliability and validity of the study. The information obtained can be produced a second time according to a sequential scheme; the knowledge also reflects the assumptions.
Results
Today, communication and culture are among the most important and significant elements and phenomena that advance society, science, and progress. Moreover, these moments are especially pronounced against the background of globalization and the main event that influenced these trends (Kamalipour, 2019). It is quite challenging to imagine the modern world without products of human activity and communication. These elements reflect the reality, the essence of people, and their existence and survival in general.
People are a product of socialization; they precisely become individuals through communication. Communication is of great importance both for the formation of a person and for their further life in society (McLeod, 2017). The “transmission” process covers the social relations of members of society – joint activities, interaction, and communication itself. Orderliness is achieved with the help of rules, norms, and cultural values that regulate the nature of contact with others, depending on purpose and means. When communicating, individuals must consider the collective social norms, customs, and traditions in the civilization. Moreover, the mood, the state of the nervous system, well-being, and peace in families and collectives depend on how people talk to each other. Finally, success in work largely depends on the manner of communication.
The whole system of a person’s attitude to others is realized in communication, and this concept is central in the system of psychological and social knowledge. Communicating, people can exchange opinions, experiences, interests, feelings; a person is formed and self-determined, revealing their characteristics (McLeod, 2018). The result of communication is the establishment of specific relationships with other people. Through this, people are integrated; norms of behavior and interaction are developed. The connection of people in the communication process is a condition for the existence of a group as an integral system. “Message path” coordinates people’s joint actions and satisfies the need for psychological contact.
Knowing specific cultural values, standards, and traditions, a person does not hesitate to show some features and unique ways of communication and gestures in practice. Each epoch of human development produces its norms, customs, and national communication identity between people (Mansouri, 2017). Culture is characterized by normativity, which determines how individuals should communicate in a particular society and a specific situation (The National Academy of Sciences, 2018). Today, the problem of the relationship between culture and communication is becoming quite important because, in the era of globalization, international and interpersonal relations with various countries of the world are intensively developing.
Culture acts as an organizer of social life and a prism through which a person looks at the world; societies and groups cannot exist without this social element. Therefore, each newly formed group develops its standards of behavior and communication. Depending on the type of culture in which people were raised, they perceive, interpret and evaluate rules, behavior, objects, and people differently (Mansouri, 2017). Hence, if individuals live in a society with people who were raised in the same culture, they feel that they live in a safe and friendly environment. On the contrary, if people are lived in other cultures, as a rule, they feel uncomfortable because they notice their otherness and cannot predict and understand their behavior.
Most of the rules of a culture that regulate people’s lives remain invisible and unconscious. The cultural regulations are located below the border of the consciousness and other things. It often includes ways of expressing emotions, raising children, decision-making processes, determining health and illness, and concepts of time and space. These factors influence how a person behaves, perceives, and understands the world. Since some of them remain unconscious, the individual takes them for granted and does not realize that a specific problem can be perceived completely differently in other cultures. This is especially noticeable in the case of contacts with representatives of different cultures, who people often evaluate through the prism of their own experience. However, primarily, it is necessary to avoid stereotypical thinking, which can become a massive barrier in intercultural communication.
In accordance with the above information, there is a need to confirm it using specific methods and means. Hence, in order to obtain a more objective, accurate, and reliable assessment of opinions from respondents, a survey was implemented on an online platform. In total, 30 people (Internet users) participated in this “experiment.” Each of them was able to fully answer three questions. The answers received were taken into account, carefully processed, and formed numerical values for a more reliable quantitative analysis. The questions and answers that were asked to the participants looked as follows.
- What influenced your style and manner of communication the most?
- Culture and Environment;
- Personal Characteristics;
- Heredity;
- Other Factors.
- In your opinion, due to what factors can a “bad” and “good” style of behavior and communication with the interlocutor be formed?
- Upbringing;
- Education;
- Culture;
- Heritage.
- What do you think is one of the most significant elements in forming a person’s identity and their type of relationship and contact with people?
- Nature, environment, and society;
- Heritage;
- Personal experience;
- Culture.
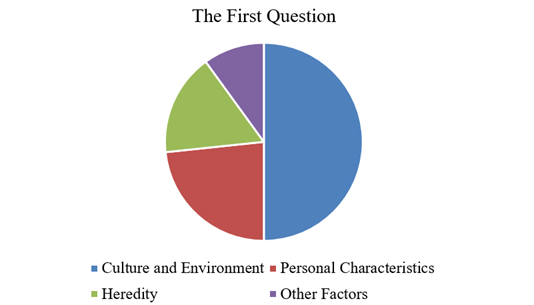
When interpreting the answers to the first question, the following picture of the situation is revealed. For example, 15 people showed great interest in the culture and the environment in which communication occurs. Seven people answered that personal characteristics, character, and temperament influence their communication style. Five people responded to the question in such a way that heredity and biological factors became dominant in the process of their formation as individuals and their type of interaction with people. Accordingly, three people noted that utterly different factors influence their style and manner of communication.
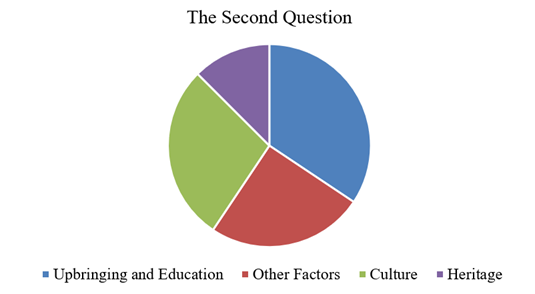
As for the second question, the following equally essential aspects should be noted. “Bad” and “good” behavior and communication manners, according to 26 users, are formed in a person due to educational, educational, and cultural elements and values. According to 11 users, upbringing and education are one of the critical areas of personal potential development and communication. Six respondents voted for “other factors” and nine for “culture.” In contrast, four respondents noted that hereditary factors contribute to the development of such phenomena.
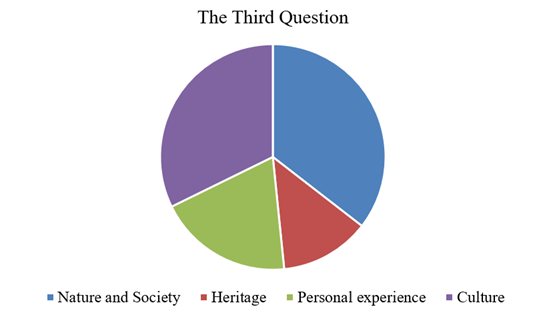
As for the results of the last question, the following conclusions can be drawn. Primarily, Undoubtedly, each of the answers can be “correct.” However, the purpose of this question was to find out people’s opinions about one of the essential criteria for forming particular inclinations, abilities, and characteristics. Thus, according to 11 users, society and nature come to the fore in this context. Accordingly, culture takes “second place” in this list and gains nine votes. The final plans include “personal experience” and “heredity,” which in total scored ten votes each.
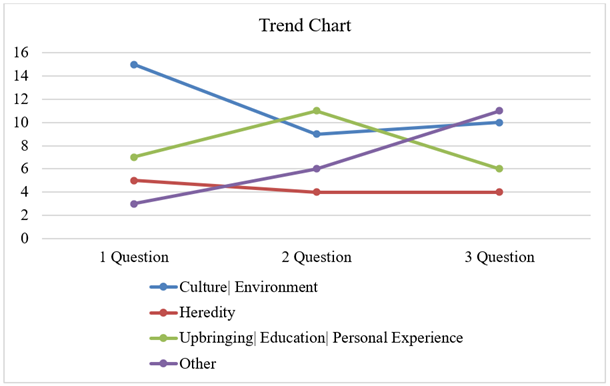
In short, the obtained results reveal the following patterns and principles. Consequently, the environment and culture occupy leading positions in the study results. However, it is worth noting that these elements are identical and similar in some way; they are in contact with each other and interact together in a certain path. Thus, culture is crucial for forming and developing types and forms of communication.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the outcomes demonstrate a close, deep and inextricable connection between cultural and communicative elements. It is proved that culture and its parts are directly related to the formation and development of speech skills, ways of expressing thoughts, and selecting words, phrases, emotions, and feelings. The correlation between the two concepts indicated in the study allows one to discuss various socio-cultural phenomena, universal values, and modern paradigms. Finding the relationship between these two components is relevant, of scientific interest, and if solved, the knowledge gained will be of great practical and theoretical importance. Furthermore, the data can be further interpreted and used in subsequent scientific research. The results obtained are of crucial importance for implementing social and psychological studies. Undoubtedly, this study has its positive and negative sides and strengths and weaknesses. For example, the author of the work managed to determine the essence of the issue, identifying the specifics and features of the topic. However, it should also be noted that the survey is not one of the best tools. In addition, it is also necessary to introduce other quantitative methods and ways to evaluate people’s responses.
Suggestions
In addition to the above concepts, the following points should be outlined. Practitioners should consider a more thorough and comprehensive study of specific aspects based on the findings. Since this study identifies a general and universal relationship between culture and communication, there is a need to analyze these connections within a certain society, state, period, and epoch. For instance, according to Hunley, Chakraborty, and MacDonald (2018), these concepts can be easily implemented within the work environment and business industry. Thus, Graca and Barry (2017) claim that communication in terms of cultural values, attitudes, traditions, and customs can impact the quality and productivity of the team, employees, and superiors.
Moreover, it is recommended to designate these determinants in a more narrowly defined sense and understanding. For instance, culture may be established not only in the broad meaning. In this vein, its elements and fundamental components will be an excellent help for future research projects. For the most part, these parts may include the results of people’s activities, values, rituals, norms, traditions, manners, etiquette, customs, language, and symbols (Brown et al., 2020). On the contrary, communication should be considered in terms of methods and means of connections within predetermined conditions.
References
Abdulla, M.R. (2018). Culture, religion, and freedom of religion or belief. The Review of Faith & International Affairs, 16(4), pp. 102-115. Web.
Bâlc, S. (2018). The relationship between culture and communication within the Ecclesia. Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, 211, pp. 258-264. Web.
Bonvillain, N. (2019). Language, culture, and communication: The meaning of messages. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Brown, N., McIlwraith, T., & de González, L.T. (2020). Perspectives: An open introduction to cultural anthropology (2nd ed.). The American Anthropological Association.
Croucher, S. M., Zeng, C., Rahmani, D., & Sommier, M. (2017). Religion, culture, and communication. In Oxford University Press (Ed.), Oxford research encyclopedia of communication. Oxford University Press. Web.
Croucher, S.M. (2020). The importance of culture and communication. Frontiers in Communication, 5, p. 61. Web.
Creanza, N., Kolodny, O., & Feldman, M. W. (2017). Cultural evolutionary theory: How culture evolves and why it matters. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(30), pp. 7782-7789. Web.
Gao, B., & VanderLaan, D. P. (2020). Cultural influences on perceptions of emotions depicted in emojis. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 23(8), pp. 567-570. Web.
Glassdoor Team. (2021). The effect of culture in communication. Glassdoor. Web.
Graca, S. S., & Barry, J. M. (2017). Culture impact on perceptions of communication effectiveness. International Business Research, 10(1), pp. 116-128. Web.
Hall, B.J., Covarrubias, P.O., & Kirschbaum, K.A. (2017). Among cultures: The challenge of communication (3rd ed.). Routledge.
University of Houston-Victoria. (2020). How does culture affect communication?. University of Houston-Victoria.
Hunley, B., Chakraborty, S., & MacDonald, S. (2018). The impact of cultural communication on team performance. Engineering and Technology Management Student Projects, pp. 1-12.
Kamalipour, Y.R. (2019). Global communication: A multicultural perspective. Rowman & Littlefield.
Lewens, T. (2017). Human nature, human culture: the case of cultural evolution. Interface focus, 7(5), pp. 1-7. Web.
Mansouri, F. (2017). Interculturalism at the crossroads: Comparative perspectives on concepts, policies and practices. UNESCO Publishing.
McLeod, S. (2017). Communication rights: Fundamental human rights for all. International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 20(1), pp. 3-11. Web.
Poepsel, M. (2018). Media, society, culture and you. Rebus Community. Web.
Stadler, S. (2019). Conflict, culture and communication (1st ed.). Routledge.
Szkudlarek, B., Osland, J. S., Nardon, L., & Zander, L. (2020). Communication and culture in international business–Moving the field forward. Journal of World Business, 55(6), pp. 1-9. Web.
The National Academy of Sciences. (2018). Addressing the social and cultural norms that underlie the acceptance of violence: proceedings of a workshop – in brief. The National Academies Press. Web.
Xiaomeng, H. U., Feng, Y. U., & Kaiping, P. E. N. G. (2018). How does culture affect morality? The perspectives of between-culture variations, within-culture variations, and multiculturalism. Advances in Psychological Science, 26(11), pp. 2081-2090. Web.