Introduction
The strategic asset of the allocation ranges, as well as the tactical assent of the investment fund is the generally accepted universal aspect of analyzing the investment environment. Originally, this type of analysis is considered to be the most effective tool for defining the realities of the investment environment, nevertheless, it requires multi angled and complex analysis of the background factors. Thus the analysis of the investment environment is closely associated with the regional premises of the investment fund location, and the attention, which is paid to infrastructure. Originally, decision-making depends on selecting several regions, and the comprehensive considerations on the matters of the critical factors, thus, the paper will be based on the analysis of the special problems. The main aim of the paper is to analyze the current issues in the investment environment, present alternatives for plausible strategic asset allocations, and deliver recommendations for the fund committee. The paper will be also focused on the extents of the fund, which should be used in the relation of the ‘active’ versus ‘passive’ investment approaches in the different asset classes.
Environmental Analysis
Originally, the analysis of the environment is closely associated with the financial and investment risks, which any investment fund may be subjected to. Thus, there is a strong necessity to consider the necessity to analyze the risk and the structure of the investment flow from the perspective of these risks. Thus, in accordance with Holland and Riddiough (2002), it should be emphasized that the risk of failure is one of the most serious risks, which may be observed from the perspective of the risky environment. Consequently, it should be emphasized that the required level of the technical performance of the investment fund fully depends on the defects in the investment flow structure. In the light of this consideration, it should be emphasized that the necessity to ensure the required quality of financial management is closely associated with the achieving of the necessary capacity level of the planned investment flow. As it is stated by Murphy (2000, p. 431): “This risk is usually a sequent of suppliers defaults and errors in projection. To reduce this type of risk in the conditions of the Russian economy it is recommended to make the examination of project execution in various stages.”
Marketing risks are often considered less dangerous than project failure risks, nevertheless, this type of risks is closely associated with the matters of marketing strategy and unachieved plan volumes of sales. As Reid (2001, p. 128) emphasized in the research:
Marketing risk is usually the most essential risk in the processing stage of the investment project and is a consequence of price and demand fluctuations, market competition, errors in product choice, errors in the market appraisal, errors in market choice, the erroneous strategy of marketing and price-formation policy, failure of the advertising campaign.
Therefore, the necessity to arrange a proper design for the cash flow operations is the requirement of the highest value, and the requirements and aims of the investment environment information system should be the following:
- Retrieval of the investment environmental information. It means that the users of the investment fund should have an opportunity to retrieve the required spatial and non-spatial information on the required factors and aspects of the investment environment.
- The investment fund structure should be subjected to investment environment evaluation. Thus, the stakeholders of the fund should have an opportunity to select the factors, which influence the investment environment, get the full reports on the selected aspects, and make the corresponding amendments (Munter, 2004)
- Decision making analysis is the most important feature, which should be attributed to the investment flow structure. The stakeholders should be capable to leave their preferences for discussion and select the required decision from the perspective of the realities of the investment environment. (Jiang, 2006)
The realities of the investment fund are the following:
The fund holds £13.5 million of assets. 35% are stored in UK equities, 20% are in overseas equities, 15% ‑ in UK corporate bonds, 20% ‑ in UK government bonds, 5% ‑ in commercial property, and 5% ‑ in cash and short-term instruments. Consequently, the structure is rather detailed, and is aimed at responding to almost any type of environment, nevertheless, the corporate bonds are regarded to be the least stable for storing the financial resources. (Chung, Scholtes and Turner, 2007) Thus, in international capital markets, bonds need to be assigned a credit rating to make the issue marketable, while, in general, longer maturity governmental bonds have a longer duration. (Holland and Riddiough, 2002)
Considering the necessity to review the structure from the perspective of the investment environment, it should be emphasized that originally, the structures of the investment funds where stakeholders have an opportunity to withdraw their funds within a short term are generally flexible enough, for filling the occurred financial gaps. Thus, the funding structure should be the following:
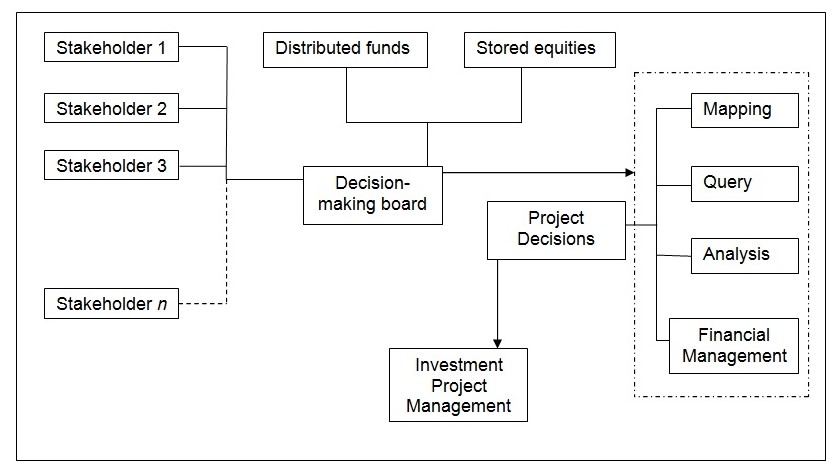
Nevertheless, in spite of the decision-making board and the set of decision-making tools, the main force and power are after the stakeholders. (Murphy, 2000) The parallel chain of investors provides the required level of financial flexibility, thus, making the stakeholders free to invest and withdraw their funds. Nevertheless, as it is stated by Scott and Conwell (2006, p. 87):
A specific Stakeholder may not always agree with the experts of the decision-making board. The differences in decisions and preferences may relate to the issues of templates, candidates, evaluations of the project. Thus, the opportunity for users to establish their own decisions should be offered. Firstly, stakeholders may upgrade the existing decisions, which are common for their needs. Therefore, those modifications will enable stakeholders to make use of experts’ knowledge to satisfy their own needs at the same time.
UK Equity
Originally, UK equity may be regarded as the most stable financial asset, which may be resorted to for the tools of investment and funding. The fact, that UK stakeholders and investors prefer this form of equity is emphasized by the statement that up to two-thirds of the returns of this equity were originated from income. Thus, as Saigol (2006) emphasized:
UK equity income tends to be steady and unspectacular, but over the long term often wins the races. In the UK stock market, income is an important component of the overall return. Equity income funds also meet what I believe is the main objective for people approaching retirement, namely to grow capital and give income growth too. They could also appeal to younger investors, who can reinvest the income and benefit from many years of compounding that will enhance their return.
Overseas Equity
The strategic asset of the investment funding generally presupposes the necessity of storing part of the reserves in the overseas funds. The rules of the overseas equity storage presuppose the allocation of the financial reserves, and the funding of the investment projects coincided with the requirements of the bonding factor. Thus, numerous stock markets of Latin America are regarded to be beneficial equities for fund storage. (Scott and Conwell, 2006) In accordance with Morarjee (2008), it should be stated that it is the widely accepted practice, to store funds overseas, through the UK banking system:
It has indeed from the larger company’s exposure and the emerging markets theme, with stocks such as Brazilian and Peru stock markets all performing well. As with all things, there is a downside too – in this case, the banking sector in the UK, which has continued to lag, and two other shares, which have recently been disappointing. However, the market has somewhat overreacted to the bad news on these latter two stocks, and they look good value.
In the light of this statement, it should be emphasized that the overseas equities may be regarded as the beneficial, but not stable enough tool for storing the reserves of the fund, consequently, the values of the overseas equities are covered only in the returns, which depend on the stability of the stock market. (Zarsky, 2003)
Corporate Bonds
As for the corporate bonds, the reliability of these aspects have been already defined, nevertheless, it should be emphasized that the terms of the total face value of the outstanding of the bond market values, the treasury of the UK and governmental agencies are regarded from the perspective of numerous options of bonding and choices. Thus, as Thomas (2008) emphasizes:
The bad situation of the economy recently regarding the credit crunch period, the corporate bond still highly recommended as good investment class compared with other classes. Europe corporate bond market had been reopened by National Grid Company (one of the UK companies) at the start of 2009.
Moreover, the corporate bonds are often regarded as the financial reserves, which are aimed at expanding the funding opportunities and performing the financial expansion operations. (Munter, 2004)
Government Bond
The governmental bond is the financially stable tool of funding and investment, nevertheless, it is closely linked with the governmental policy and the requirements of the governmental economic principles. On the other hand, these bonds are risky enough, as the government may change the taxes in order to redeem the bond at maturity. In accordance with Sharma (2006), these actions are associated with the “risk-free” tools, which are based on currency stabilization, subjecting it to devaluations and currency exchange rates changes for attracting or keeping the foreign investors. (Glasgow, 2008)
Commercial Property
As Thomas (2008) emphasizes, 25 percent of UK commercial properties fall in summer 2008. People believe that it is going to fall more. They presume that the market is going to fall more than 50 percent because of the struggling retail occupiers who are facing bankruptcy. Nevertheless, commercial property is one of the most reliable strategic assets, which are regarded by investment funds researchers. (Duyn, et.al. 2009)
Alternatives assets allocations
Allocation of the assets is the most important aspect of the investment funding, and, it should be emphasized that the correct allocation of the resources is generally defined by the necessity to save the funds, and get the income, simultaneously providing the opportunity of development for the invested project. Thus, considering the aspects of stability, benefits, and safety of the financial reserves, the best allocation variant is the following:
- 70 percent ‑ government bond:
- 15 percent ‑ corporate bond:
- 5 percent ‑ UK equities:
- 5 percent ‑ overseas equity:
- 5 percent ‑ commercial properties:
Thus, as the government bonds are considered to be risk-free, the main part of the assets should be in governmental bonds. Considering the marketing situation, it is rather risky to have a higher percentage of assets in a corporate bond, nevertheless, by the forecasts, the situation will change, thus, there is no necessity to reject these bonds. (Tarzi, 2005)
As for the equities and commercial property, it should be emphasized that the original marketing situation is not favorable for supporting these equities financially, consequently, the low percentage is the best solution. (Baker, 2004)
Conclusion
Finally, it should be stated that the strategic asset of the allocation ranges is the generally accepted universal aspect of analyzing the investment environment. Consequently, the assets and the values of the economic principles, regarded in this paper, should be closely associated with the investment funding processes. Moreover, the allocation of the assets will not be full without the analysis of the marketing premises of the equities and bonds of various origins.
References
Baker, J. C. (2004). Foreign Direct Investment in Less Developed Countries: The Role of ICSID and MIGA. Westport, CT: Quorum Books.
Chung, J., Scholtes, S.,Turner, D. (2007). UK bonds retreat after rate shock, Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Duyn, A., Mackenzie, M., & Bullock, N.,(2009). Corporate bonds find hope from new issues, Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Glasgow, F., (2008). Fund managers find favor with corporate bonds again, Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Holland, A. S., Ott, S. H., & Riddiough, T. J. (2002). The Role of Uncertainty in Investment: An Examination of Competing Investment Models Using Commercial Real Estate Data. Real Estate Economics, 28(1), 33
Jiang, F. (2006). The Determinants of the Effectiveness of Foreign Direct Investment in China: an Empirical Study of Joint and Sole Ventures. International Journal of Management, 23(4), 891
Morarjee, R., (2008). Stagflation fears drive investors from equities,Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Murphy, A. (2000). Scientific Investment Analysis (2nd ed.). Westport, CT: Quorum Books.
Munter, P., (2004). UK gilt prices fall on interest rate worries, Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Reid, C. R. (2001). Environment and Learning: The Prior Issues. Rutherford, NJ: Fairleigh Dickinson University Press.
Saigol, L., (2006). Equity issues raise $15bn in Middle East,.Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Scott, M. S., & Conwell, V. (2006). Secrets of Successful Investment Clubs: Following These Strategies Can Help Yours Enjoy Longevity. Black Enterprise, 36, 87
Sharma, D. C. (2006). A Risky Environment for Investment. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(8), 478
Tarzi, S. (2005). Foreign Direct Investment Flows into Developing Countries: Impact of Location and Government Policy. The Journal of Social, Political, and Economic Studies, 30(4), 497.
Thomas, D., (2008). Commercial property slump in the UK to last two years, Financial Times Online, [internet] Web.
Zarsky, L. (2003). International Investment Rules and the Environment: Stuck in the Mud?. Foreign Policy in Focus, 4, 1.