Introduction
Airport security is currently one of the most pressing concerns in the aviation sector. Numerous past incidents and accidents have been blamed on security lapses, some of which claimed hundreds of innocent lives. As technology advances, the piloting of planes and inspecting of people and cargo is becoming simple and more efficient processes than they were in the past. However, new challenges have emerged that many in the aviation sector did not anticipate. The cyber threat is now becoming a serious security issue in this industry. Criminals are also using sophisticated ways to smuggle weapons into airplanes to enable them to commit acts of terror or crime. Conyers and Kiyuna (2015) argue that a new problem is also emerging where pilots are deliberately crashing their planes because of psychological issues or religious commitments. The source of the problem (whether it is committed by external criminal gangs and terror groups or internal employees keen on committing suicide or working for some terror agencies) does not matter. The most important thing is that planes and airports must be protected from any criminal and terror activities. The management of airports must come up with ways of enhancing their security based on the ICAO policies and other local aviation guidelines. In this paper, the focus is to discuss security motivation as a practical measure that can be taken to engender an effective security culture.
Discussion
Understanding the Problem
The aviation industry is one of those that knows no geographic boundaries. A plane may take off at Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport in France with its destination being Los Angeles International Airport. If there is a security breach, the threat may easily affect any of the two airports and the passengers on board. It means that the management of Los Angeles International Airport should be interested in an enhanced security system at its facility and that of other airports around the world. A breach of security in airport A can easily affect other airports around the world. One of the biggest threats in modern society is a possible terror attack. September 11, 2001 terror attack on the United States’ soil was a major turning point about the approach taken in managing security. It became evident that a small terror group operating outside of the United States can have a potential for planning, and executing a serious attack. Many lives were lost, and properties worth millions of dollars were destroyed. Another major problem that is emerging in aviation security is constant cyber attacks. According to Maszka (2017), the aviation sector suffers over 1,000 attacks from hackers every month. The biggest fear is that one day a hacker may remotely take control of an airplane and crash it or make it disappear from the radar (Kazda & Caves 2015).
The International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), The International Air Transport Association (IATA), European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), and many other international air transport organizations have been working together to address this emerging threat (Maszka 2017). Criminal gangs interested in robbing travelers also pose a threat to the security of the aviation sector. It is also an emerging concern that some pilots are considering committing suicide while on duty, leading to the death of hundreds of innocent people. On March 24, 2015, a Germanwings Flight 9525’s co-pilot deliberately crashed the aircraft into the mountains after locking out the pilot from the cockpit (Maszka 2017). All the 150 people on board the plane perished. The incident was not an isolated case. Several similar cases have been witnessed before. On October 31, 1999, a flight officer crashed EgyptAir Flight 990 into the ocean when the pilot left the cockpit, causing the death of 217 people.
On November 29, 2013, a commercial flight pilot on LAM Mozambique Airlines Flight 470 intentionally crashed the plane after locking out the co-pilot from the cockpit, killing 33 people in the process (Maszka 2017). These cases are closely related and need a united front to manage them. Air travelers, airport facilities, and workers need to be assured of security. There is a need to ensure that these facilities are protected from a wide variety of threats. As Smith (2014) observes, managing airport security should be a multi-faceted process that brings together various stakeholders and systems to ensure that the weaknesses of one process can be addressed by other processes. This paper focuses on just one of the ways of enhancing airport security, and that is security motivation. The study will look at how security motivation can enhance the development of an effective security culture.
Airport Security System
The airport security system is a complex process that integrates human resources and advanced technologies to help ensure that airports and airlines are kept as safe as possible. The technology aspect of airport security has improved tremendously over the last two decades. In the past, most airports relied on a manual screening of people and cargo to ensure that safety was enhanced. That is no longer the case in modern society. Although human services are still indispensable in airports, technology has advanced and is currently doing the work of screening. State-of-the-art technologies are currently used throughout the world in major airports to enhance security. Rossi (2014) notes that one of the most common technologies currently used at major airports is Accurate Biometrics which helps in electronic fingerprinting and live scanning of equipment.
Face4 System is also becoming popular, and it is used in the facial recognition of passengers at the airport. The concept was popularised because of the need to identify individuals who are already on police records as a terror suspect, sympathizers of terror groups, and dangerous criminals who may pose a serious threat to passengers and airplanes. Garrett Electronics is used for metal detection. It is important in detecting possible handguns, knives, or any other metal weapon that a passenger may have. X-ray screening equipment, CCTV systems, fully-automated passenger flow management, and tracking solutions are all popularly used in modern airports. They have made the process of screening passengers and bags easier than it was before. They have significantly reduced the margin of error at airports. However, it is important to understand that these technologies cannot be successful in enhancing airport security without the support of skilled human resources.
Airports have employees responsible for maintaining security in various departments. At the screening points, private security agents trained in aviation security are often responsible for inspecting luggage and travelers to ensure that dangerous items are not allowed into the planes. The government also assigns the paramilitary the responsibility of enhancing security at the airport. They have a wide range of duties. They can make arrests whenever one is found with contraband goods or weapons as they try to board planes. They work closely with private guards to enforce laws and regulations within the airport. In case of an armed attack, they are responsible for engaging the criminals or terrorists to diffuse the threat within the shortest time possible.
Security officers may also be called upon to defuse bombs or other explosives identified within the airport. These security officers, when they work in close coordination and harmony with the currently existing technology, have a great potential of identifying and eliminating any form of threat that may be directed to airports, airplanes, passengers, or officials working within the airport. Smith (2014) observes that it is important to have a close working relationship among officers responsible for managing security. They should have a clear communication system where they can share information to improve the rate of response. The system should also have its intelligence that will enable it to collect critical information about an impending threat or a plan to breach the security system. Security motivation is at the center-stage of achieving these tasks within the airport security system.
Security Culture
Security culture in an airport setting is important in ensuring that travelers, airport employees, airport facilities, and aircraft are kept safe at all times. International Civil Aviation Organisation (2016, p. 4) defines security culture as “that assembly of characteristics and attitudes in organizations and individuals which establishes that, as an overriding priority, safety and security must be observed at all times.” A strong culture of security is manifested both in the mode of operation and in the mindset of the people involved. It is possible to have the best and latest security technology in airports, but if the mindset of the security officers and all other stakeholders involved does not emphasize the need to ensure that safety is upheld, critical mistakes can be committed that may have a devastating impact on lives and property. Developing a security culture is the only sure way of ensuring that airports achieve sustainable security. Rossi (2014) argues that a sustainable culture of security has four primary defining features. The first feature is that it is a deliberate process. Sustainable security cannot come as an accident. It must be a carefully planned process that focuses on ensuring that everything is done to secure the airport from any form of attack. The second feature is that it is a fun and engaging process. People involved in the process should find it fun and engaging. They should not be coerced into undertaking specific activities that would enhance safety.
The involved parties must understand that it requires a team spirit to achieve the desired success. The third feature is that it is a rewarding process. A threat to security endangers the lives of everyone, including the security officers. It often strikes unannounced, and anyone can be a casualty. When the security officers and the entire airport community work as a unit to enhance security, everyone gets to benefit from the safe environment created. Lastly, a sustainable security system provides an impressive return on investment. The management must understand that effective security culture can only be achieved if proper investment is made. Investment is needed in purchasing the latest technology in the security sector. The security officers and the entire community may also need some form of training to improve their efficiency. The investment needed may be substantial, but the benefits outweigh it. The aircraft and facilities cost millions of dollars. The reputation of an airport and airplanes about safety may also take years and huge resources to build. As such, airport managers should understand that an investment made in enhancing airport security shall yield impressive returns. The argument about return on investment makes it easy for the stakeholders to understand the need to invest in promoting security culture.
Using Security Motivation to Engender Security Culture
It is important to use security motivation to promote security culture within airports. Security motivation helps in ensuring that everyone remains security-conscious and that nothing is taken for granted or deliberate. As Smith (2014) explains, developing a security culture cannot be just focused on the security officers. Indeed it is the responsibility of security officers (private security officers, the paramilitary officers, and the military officers if necessary) to ensure that the airport remains safe. However, there are cases where a security breach can be detected by employees who are not in the security department. Critical information can be accessed by other employees, and if properly shared, it may help in managing potential threats. As such, security motivation will focus on all the employees, but with special interest on the security officers. According to Rossi (2014), it is primarily the role of the management unit to enhance security motivation. As explained above, the entire process must be deliberate, fun, and engaging. Figure 1 below identifies specific ways of ensuring that employees are motivated towards enhancing security within the workplace.
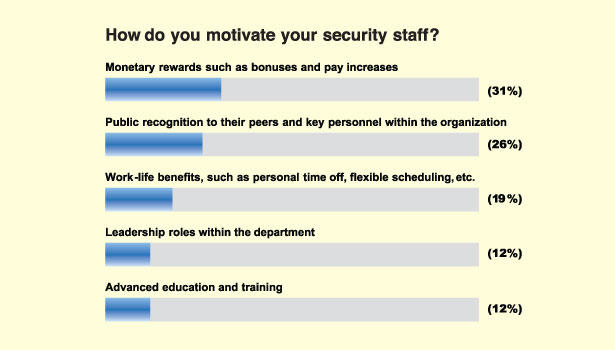
Monetary rewards
The monetary reward has always been one of the most important approaches to motivating employees. Many employees in some of the developed countries such as the United States often take two or three jobs to make ends meet (Executive Office of the President 2014). They do that because the income they get from their work is not enough to meet their expenses. Taking two or three jobs splits an employee’s loyalty. Such an employee would be more loyal to the employer paying the best salary. They may not be concentrated on their work as they wait for the end of their shifts to move to their next jobs. Such employees can easily make mistakes. They can ignore a simple security breach that may have a devastating impact on the airport or airplanes and their passengers. It is necessary to ensure that officers working in the security department do not work in other places because that reduces their efficiency.
The only way of doing that is to offer them attractive remunerations. They should feel contented working for the airport. They will always remain alert and focused on their job. McHoes and Flynn (2017) argue that cases, where security officers are paid to help in breaching security systems, are common among the underpaid. However, proper remuneration makes them satisfied and more committed to their work. They are less likely to be compromised. Rossi (2014) advises that other than offering standard salaries that would eliminate the desire to work at other companies, it is also important to reward people who have performed beyond the expectation. The strategy helps in motivating others to concentrate more on their work to get the financial reward. Although the emphasis will be on the security department, other departments should not be ignored.
Public recognition
Monetary rewards are not the only way of ensuring that employees remain motivated. A human being, by nature, likes recognition. Human resource experts have identified a direct relationship between public recognition and level of employee’s delivery (Kazda & Caves 2015). People often struggle to get recognition within the workplace or in other settings. When they are publicly recognized, they develop a sense of pride. They draw admiration from others who may wish to be in the same position. It is important to have a system where employees who deliver exceptional performance are publicly praised for their work. It can be done at the end of the financial year. Having a performance contract may be needed in such a system. Their output is measured and compared with that of other colleagues to determine the one who has recorded the most impressive score. Each department should have its champion, and an overall champion in the organization can also be identified. Smith (2014) recommends that sometimes it is necessary to make instant recognition, especially when an employee does something exceptional. The focus should be to ensure that all workers feel appreciated for their effort in the company. They should feel that every time they go the extra mile to deliver the best output to their employer, systems are in place to ensure that they are rewarded.
Work-life benefits
Occupational burnout is a real threat to the quality delivery of services among employees. In many cases, it is caused by unresolved job stress and poor work-life balance. The management of airports needs to ensure that their employees have a proper balance between the time spent at work and that spent with family away from work. Overtime may be common among security officers within the aviation sector. However, it should not be too frequent to deny employees their right to enjoy quality time with family members. Work-life benefits should also involve offering these employees fully-paid leave to allow them to have fun with their families. Burnout should be eliminated among the security officers as much as possible because it may easily lead to mistakes or lapses in the screening of passengers and cargo.
Leadership roles
The advancement in one’s career is always the desire of every employee. McHoes and Flynn (2017) note that employees should be promoted based on their performance. They should be aware that their ability to get to leadership position depends on their value to the organization. However, it does not mean that a leadership role cannot be assigned to those who are yet to climb the career ladder. In some cases, junior officers may be assigned roles that are often managed by senior employees. It may happen when the senior officer is away or overwhelmed with responsibilities. The goal of assigning their leadership roles is to make them responsible for their work. It will enable them to understand the challenges that their leaders face in ensuring that the goals and objectives of the organization are achieved. It also makes employees understand that they can be promoted at any time based on their performance at work.
Advanced training
One of the critical aspects of security motivation as an integral part of an airport security system is advanced training. The security landscape in the aviation sector is changing rapidly because of emerging technologies. About two decades ago, concepts such as cybercrime, cyber terrorism, and cyber-attack were non-existence (Maszka 2017). However, they are currently major security concerns in the aviation sector. Technology is getting to the center-stage of security management, and security officers need to be empowered. According to a report by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (2016, p. 6), “employee awareness programs are indispensable to the secure operation of the airport.” It is important to have programs that not only promote awareness but also empower these officers in their respective workplaces. In the past, the main instruments used by these officers were batons and guns. However, the landscape is changing rapidly, and security officers must understand their new position. They need to be taken through regular training to understand the cyber threat and how it can be managed in the best way possible. The need to understand the problem of terrorism, including homegrown terrorism and increasing cases of sympathizers of terror groups, and how it can be dealt with in an airport setting. Empowerment should be done through two main approaches.
The first approach should be on-job training where experts come to the airport and help these officers to understand how they can use modern technology to undertake their regular duties. The second approach may be to sponsor these officers to enhance their education in the local or international institutions of higher learning. The training should focus on making these security agents understand the new strategies and processes of managing security in modern society based on the recommendations made by international aviation bodies such as ICAO, IATA, and EASA among others. International Civil Aviation Organisation (2016, p. 3) says that “ICAO advocates a strategy for improving the pre-departure screening process which involves improving the process itself (making it less predictable and by using profiling or selection techniques to allow more resources to be focused on passengers that pose the greater risk.” These officers need to understand how to coordinate the screening process such that any lapse in one stage is addressed in the next stage of inspection. The training also improves their knowledge of how to share information within departments to enhance coordination and cooperation.
Benefits of Security Motivation
ICAO has been working with different regional and international organizations to ensure that security at airports around the work is enhanced. One of its current recommendations is security motivation as an integral part of an airport security system. The practical measures discussed above outlines how motivation can be realized within an airport setting. When security motivation is achieved, everyone will understand and appreciate the importance of taking relevant actions, however insignificant they may be, to protect their workplace. The culture created will mean that not only the security officers will be focused on enhancing safety at the airport, but also other employees who may have access to intelligence that may help thwart attempts at security breach. The culture will enhance security at airports, eliminating attempts by criminals and terror groups to harm innocent travelers. When the security is enhanced, it has numerous benefits to employees, travelers, airport, and airline companies. Employees, including security officers, will enjoy working in an environment where their safety and security are assured. The possible causes of terror or criminal attacks that may lead to death or injury of employees in the workplace will be eliminated if not significantly reduced. Travelers using these airports will be assured of enhanced security.
On June 28, 2016, three terrorists executed a well-choreographed attack on Ataturk Airport, killing 45 people and injuring 230 others in the process (Muḥammad 2017). The airport is yet to overcome the negative image that the attack earned it in the international aviation sector. Its failure to stop criminals or neutralize them within the shortest time possible was an indication that it was unable to deal with such threats effectively. Many still view it as an unsafe airport that cannot assure its customers and employees of their security. Improved security can help in eliminating such negative images. The airline companies also rely on the security offered by airports to ensure that their passengers and aircraft are safe from a terror attack or criminal activities. An Airbus A380-800 costs $428 million. When it is blown up by terrorists, it results in a massive loss to the airline company and the relevant insurance company. Such losses can be eliminated when security is enhanced.
Conclusion
Security motivation should be considered an integral part of an airport security system, as advised by ICAO. Security management of these airports should involve promoting security motivation as a way to engender an effective security culture. As discussed in the paper, the culture should not just focus on security personnel but also employees in other sectors within the airport. Everyone should feel responsible for enhancing security. Intelligence should be shared so that actions can be taken at an appropriate time. Coordination of departments is also necessary to help in thwarting security threats.
Reference List
Conyers, L & Kiyuna, A 2015, Cyber warfare sourcebook 2015, Lulu.Com, Raleigh, NC.
Executive Office of the President, 2014, Budget of the United States government, analytical perspective, U S Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
International Civil Aviation Organisation, 2016, Security at airports: ACI policy and recommended practices handbook, 8th edn, International Civil Aviation Organisation, Montreal.
Kazda, A & Caves, R 2015, Airport design and operation, Emerald, Bingley.
Maszka, J 2017, Al-shabaab and Boko Haram: guerrilla insurgency or strategic terrorism, World Scientific, London.
McHoes, M & Flynn, M 2017, Understanding operating systems, Cengage Learning, Boston, MA.
Muḥammad, J 2017, European intelligence services in the face of the “Islamic State” cells: flabbiness of the European intelligence services, AlMaktab AlAraby LilMaaref, Cairo.
Rossi, F 2014, EU legal framework for safeguarding air passenger rights, Springer, Cham.
Smith, M 2014, Europe’s common security and defence policy: capacity building, experimental learning, and institutional change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.