Introduction
Amazon Corporation is one of the leading competitors in the global e-commerce market segment. Founded in 1994, the corporation has grown very fast through the constant acquisition of businesses, introduction of superior products, and appreciation of emerging technologies to improve its operational model. The company has an effective research and development (R&D) department that examines the nature of modern technologies and their implications for online marketers. This R&D team is characterized by competent information technology (IT) specialists, programmers, marketers, application (app) developers, and engineers. The role of Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is a unique area that has captured the attention of this research team.
The ultimate goal is to develop a new retailing procedure that supports the changing needs of different stakeholders such as customers, online marketers, managers, logistical experts, wholesalers, and distributors. The managers at the company understand that technology is something capable of reducing operational costs and minimizing losses. Since technology makes it possible for corporations to collect information automatically, the company can acquire new insights and models that can be implemented to foster business performance. This paper begins by giving a detailed background of Amazon Corporation. The discussion highlights the major achievements and successes that have been recorded by the company within the past two decades. An evidence-based RFID technology implementation plan is suggested that can make a difference for the company and support its business goals.
Amazon Corporation
Organization Background
The 1990s presented numerous opportunities due to the increasing popularity of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the Internet. The decade was characterized by new innovations such as superior computers that transformed the manner in which people pursued their obligations (Salam, 2016). The Internet became a critical tool in different sectors and business operations. This development paved way for future innovations that are used today to promote business performance. During the same period, more companies emerged in every region across the world. A new process of marketing goods over the Internet became a reality. New companies emerged in the e-commerce sector. Amazon was one of the corporations that emerged during the decade.
Amazon is today one of the leading retailers that “sells a wide range of products over the Internet” (Salam, 2016, p. 2). This online retailer has an interesting background. The corporation was founded by a young entrepreneur named Jeff Bezos in the year 1994. As indicated earlier, the 1990s was a revolutionary period that presented numerous opportunities to upcoming entrepreneurs such as Bezos. The founder’s original idea focused on marketing specific products over the Internet such as compact discs, videos, books, and computer hardware. Together with his dedicated teammates, Bezos was able to create a website that became common among users within the first year.
Originally, the company had around 2,000 titles that were stored in a warehouse in Seattle. The business model was also designed in such a way that the company would collect books from different wholesalers and publishers and deliver them to its customers. Within a few months, the company was able to fill orders from many states and countries across the world (Salam, 2016). Although the company started as a bookstore selling its products online, it had managed to diversify its products by adding music, electronics, apparels, and DVDs within a period of 10 years. In 2005, the corporation acquired companies such as BookSurge, CreateSpace.com, and MobiPocket.com. Amazon Prime was introduced during the same year to ensure free shipping was done to support the needs of more students. By 2010, the company had acquired a number of small firms such as the Election 2008 store and AbeBooks.com. These achievements made it possible for the company to expand its operations and offer superior services to targeted customers.
The corporation is known for its unique culture that mostly focuses on the diverse needs of the customer. The workers are empowered and motivated using various incentives such as insurance covers, disability plans, medical support, and retirement benefits (Salam, 2016). Amazon’s mission is to become the most customer-centric organization whereby people can purchase their favorite products. In March 2017, the corporation had over 269,000 employees working in different regions and markets. The company has been focusing on the best strategies to maximize its goals and offer premium services to its global customers. Amazon attracts technical experts and professionals to support its innovative culture (Salam, 2016). The corporation’s engineers and programmers handle a wide range of duties in an attempt to build a successful e-commerce platform that can meet the diverse needs of its merchants, business partners, sellers, and customers.
Products, Services, and Markets
The company currently markets a wide range of services and products to its customers. Retail goods include software, baby products, groceries, kitchen items, apparel, hardware equipment, and healthcare products. In 2012, Amazon expanded its offerings to include gaming (Salam, 2016). Amazon Art is a platform that makes it possible for people to market their artworks. The company’s positive performance has led to the introduction of new services such as video content, online books, and wireless solutions. The organization segments and targets its markets using exemplary services and products. However, customers must be in a position to shop online. Sixty percent of the corporation’s sales are recorded in North America. Its international market is composed of the United Kingdom, Germany, and Japan (Salam, 2016).
RFID Technologies
Amazon has been embracing new technologies that have the potential to foster business performance. The use of RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology in the company’s supply chain has led to maximized inventory visibility (Salam, 2016). Products and shipments can be tracked successfully using this technology. In 2014, it was reported that Amazon was using RFID technology to detect products taken from a given shelf by a customer (Salam, 2016). The use of this kind of technology makes it possible for the company to detect and track items and products in every outlet store. Some experts have gone further to indicate this revolutionary technology is being tested and tried to support various processes at the company. For instance, technology has become a powerful solution to make sure online inventory is managed and completed seamlessly.
Within the past year, Amazon has identified new procedures to incorporate the use of this new technology in its grocery stores. This model is expected to support its ambitious endeavor given the name Amazon Go (Salam, 2016). This revolutionary store will be designed in such a way that the customer will not have to check out with an attendant. The technology will be implemented to ensure the customer does not have to queue. The customer will only need to download and install the Amazon Go app on his or her phone and use it for shopping. Although this new venture appears to be complex, the outstanding observation is that it might be founded on the power of RFID technology. The company has indicated that the know-how adopted for the Amazon Go store is given the name “Just Walk Out”. However, analysts in computer technology have indicated that the new model must be characterized by the unique features associated with RFID. This is the case because the proposed technology must be characterized by computer learning processes, sensor fusion, and algorithms to make the retailing process possible (Pradham, Chai, Sundaresan, Rangarajan, & Qui, 2017).
This discussion reveals that many retailers across the globe are working hard to identify new practices and procedures that can be adopted to ensure RFID technology is adopted to deal with the major challenges facing their retailing strategies. Pradham et al. (2017) believe strongly that the use of RFID technology can ensure inventories are managed in a faultless manner. Amazon is keen to consider the benefits of this technology and develop superior models that can maximize sales without compromising the quality of services available to its global customers. This discussion, therefore, shows that RFID is a technology that is in its infancy at Amazon Corporation. It is also notable that many companies have not managed to realize the full benefits of revolutionary innovation. The good news is that the future will be brighter as more corporations continue to undertake new research studies. Amazon remains one of the leading corporations that can implement and benefit from the use of this revolutionary technology. When the idea is studied and merged with various business operations, the corporation can maximize its sales, support the changing needs of its customers, and become a leading player in the e-commerce industry.
Outline of the Proposed Plan
Amazon can embrace the power of RFID technology in order to become more competitive in the global online marketing sector. The deployment of this technology can result in enhanced visibility throughout the supply chain process and efficiency whenever tracking various products (Haddud, Dugger, & Lee, 2015). The Amazon Go example can be studied as a prototype for the implementation of this new technology. According to experts, the innovation is capable of empowering more customers since they will not need an attendant. Gupta and Margam (2016) believe strongly that technology is capable of reducing operational costs and minimizing losses.
When technology is adopted to support different processes, the level of human intervention is reduced significantly. This move can be considered by a company that plans to minimize its expenses. It is worth noting that the use of modern innovations can increase the quantity and quality of information that is collected automatically (Menosky, 2017). As marketing management shifts to a new paradigm characterized by research, the proposed RFID technology will equip Amazon Corporation with new insights and concepts that can be studied carefully to foster business performance. The outline below proposes a framework that can be used to support the execution and use of RFID at the corporation.
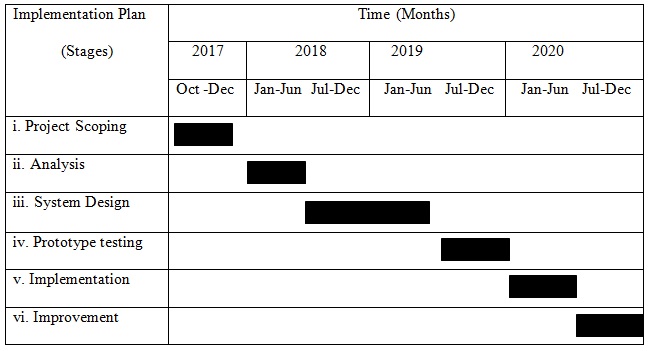
The first step that can be adapted to support the process is projected scoping. The leaders at Amazon should begin by outlining the benefits, disadvantages, and issues arising from the use of RFID technology. This knowledge will ensure the objectives of the project are clearly defined. It is during this phase when different experts and stakeholders should present their insights and considerations that can support the agenda (Haddud et al., 2015). The second stage should be to analyze the current nature of operations and the utilization of RFID at the company. This process should begin analyzing the existing system and how it supports the company’s business aims (Ting, Tsang, & Tse, 2013). The developers and leaders should consider how the use of RFID technology in different stores has influenced performance. They should use appropriate analytical tools to examine the company’s ability to implement technology and emerging benefits.
The third stage is designing the right system. This means that the right software and hardware will be selected. This phase is complex since it requires the expertise, know-how, and contributions of competent programmers and engineers (Menosky, 2017). When executed in a proper manner, this process is what dictates the success of the implemented technology. Companies that want to implement and use a given technology should recruit the right people, empower them, and provide adequate resources to support their goals.
The fourth step is testing the prototype (Coustasse, Cunningham, Deslich, Willson, & Meadows, 2015). Processes such as system debugging and adaptation should be executed during this stage. The main goal during this stage is to ensure the intended technology does not malfunction. With effective testing, the team identifies specific weaknesses that might affect its performance. Menosky (2017) goes further to acknowledge that testing should be an ongoing process since new improvements and design changes are usually common after a given technology has been adopted by a corporation.
The fifth stage should be in the implementation process. This process is done to deploy the intended RFID technology. Training or empowerment is critical to support this stage. The last (sixth) stage is known as continuous improvement. This stage is necessary because it will ensure there is constant monitoring of the system’s efficiency. Feedbacks should be collected periodically from different employees and users (Menosky, 2017). The acquired information will ensure the new technology becomes an integral part of Amazon’s business model.
Detailed Outline of the RFID Implementation Plan
Amazon Incorporation has remained a leader in online-based marketing. The company has succeeded in a number of areas such as the delivery of consumer goods in a timely manner, supply chain, and management. The use of RFID has mainly been associated with the corporation’s supply chain. However, the benefits of technology explain why it has the potential to transform Amazon’s business process. This means that the company can utilize the technology to track products, improve service delivery, and make better marketing decisions based on consumer behaviors (Ting et al., 2013). The discussion presented below gives a comprehensive plan that can guide Amazon to implement the use of RFID technology successfully within the next three years.
Project Scoping
This is the first stage for implementing RFID technology in any given business organization. During this phase, a competent team characterized by technological experts should be formed. That being the case, the leaders at Amazon Corporation can create a group characterized by competent professionals to study and present useful insights about the nature of RFID technology. The established team at the organization can begin by outlining the unique benefits and limitations associated with the proposed RFID system (Haddud et al., 2015).
This understanding will make it easier for the team to come up with the specific objectives that can act as guidelines throughout the implementation process. The group should go a step further to identify every unrealistic outcome that can affect the success or effectiveness of the technology (Menosky, 2017). The individuals in the scoping process should devise meaningful and evidence-based strategies to deal with the weaknesses associated with RFID. Such approaches should be analyzed and experimented in an attempt to ensure every outlined objective is realized in a timely manner (Owunwanne, 2016). The selected RFID system for each operation should be able to deliver desirable outcomes. Both long-term and short-term must be identified during this stage. The timeline for the stage is two months. This process is relevant because it will ensure the team comes up with a desirable timetable to be followed throughout the implementation process.
Analyzing the Current System
Amazon has been using RFID technology as part of its supply chain management strategy (Coustasse et al., 2015). The technology has supported a wide range of operations in different stores. It has also been experimented to support the Amazon Go stores. These developments can be used to explain why Amazon stands a chance to benefit from the power of modern technologies. However, the desire to expand the use of technology should be supported using evidence-based information. The leaders will have to analyze the unique issues associated with the organization’s current system. This goal will be achieved by collecting quality information and analyzing it adequately (Owunwanne, 2016). For instance, issues such as efficiency, improvements, and deficiencies within the existing system should be captured during this stage. The process should be undertaken within six months. This knowledge will ensure the leaders at Amazon focus on the right objectives and approaches to implement the intended RFID technology.
System Design
The third stage will be considered to inform the managers at Amazon about the major processes that can be embraced to deal with the existing gaps. During the stage, the team plans to implement the technology that can identify the right design for the proposed RFID technology. This knowledge will be informed by the corporation’s requirements and business needs. For instance, the company has to focus on new regions and markets across the globe. The right technology should, therefore, meet this critical business objective (Menosky, 2017). Similarly, the technology should be able to address most of the predicaments affecting the company.
With competition becoming a reality in the e-commerce industry, Amazon Corporation should identify the most appropriate technologies that alter the playing ground and eventually become successful. Areas for improvement should also be considered during this stage (Owunwanne, 2016). The most appropriate design will therefore dictate the hardware, software, and data that should be captured by the RFID technology. The technology’s ability to interpret data or information should be critical towards guiding the process (Pradham et al., 2017). The selected software and hardware must be tested during this stage. This approach will ensure the system is capable of handling data and presenting accurate information. The stage is expected to take 12 months.
Prototype Testing
The third stage is critical because it delivers a system that can produce the intended results. However, the team cannot go-ahead to use it without testing it (Lai & Cheng, 2014). Depending on the role of the targeted RFID system, the testing process will be used to capture signals from the selected devices. Issues such as duplications, tag collisions, and confusions should be monitored during the phase (Cheng & Prabhu, 2013). The technical staff at Amazon Corporation will be required to identify areas that should be improved. The simulation process will be characterized by debugging and adaptation of the system. The adaptation procedure is necessary because it will ensure the implemented RFID system is capable of delivering desirable goals or outcomes. Six months will be adequate for this process.
Implementation
After the RFID technology has been tested successfully, the team will go further to install the necessary software and hardware systems (Lai & Cheng, 2014). During this stage, training and change can be critical in order to deliver tangible results. The existing RFID system in the company’s supply chain can be improved during this stage. The tested system should then be configured in such a way that it supports the intended operations in the organization. The managers and leaders at the company should be willing to be involved throughout this phase (Cheng & Prabhu, 2013). This move will be essential since the company has many employees whose contributions might be needed during the stage. Issues such as change management and organizational culture must be considered during the phase (Menosky, 2017). This understanding is informed by the fact that many individuals will tend to resist new changes especially when they affect their comfort zones (Coustasse et al., 2015). This is the stage whereby appropriate concepts and organizational theories must be taken seriously. This process should take six months. The use of this approach will ensure different workers are empowered, guided, and trained to support the implementation process. This evidence-based strategy will reduce conflicts, omissions, errors, and inefficiencies.
Continuous Improvement
This is the last stage of the RFID technology implementation process. The implemented system should be monitored and analyzed continuously in order to identify various gaps that can affect its effectiveness. Feedbacks from different stakeholders can be helpful in improving the functionality of the system. The success of the implanted RFID system should be tracked during this phase (Cheng & Prabhu, 2013). Areas that can be improved will be identified during this stage. These steps can therefore make it possible for Amazon to implement RFID technology and remain relevant in the online retailing sector.
Supporting the Implementation Process Using Theories and Change Models
Different theories have the potential to support and sustain the proposed RFID technology implementation process at Amazon Corporation. For instance, the Theory of Diffusion has been embraced by scholars in the world of innovation. According to the theory, new technological developments can result in better performance and make it possible for companies to achieve their goals much faster. The theory asserts that leaders or change agents must be willing to be part of every implementation stage or process. They should bring on board competent persons, support their needs, and create the best environment to ensure the targeted stage is implemented successfully (Cheng & Prabhu, 2013). When this idea or theory is considered during the implementation period, it will be possible for the involved players to focus on every stage or phase. The practice will ensure the targeted change is sustainable and capable of supporting the corporation’s e-commerce business agenda.
Kurt Lewin’s model of change is another powerful framework that is widely used by companies that want to implement or adopt the use of new technologies. This model is applied in different situations because it creates room for new processes by encouraging every follower to support the change (Coustasse et al., 2015). The model is simple, manageable, and capable of delivering desired results within the shortest time possible. The first stage is known as refreezing. At Amazon, the workers, engineers, logistical operators, and RFID technology developers will be informed about the major changes experienced in different parts of the world. The concept of RFID technology and its potential will then be discussed by the stakeholders. The actors will be aware of the benefits and be ready to learn more about technology.
The second phase of the model is implementing the intended change. This step will guide the major implementation phases described below. This means that the major players will acquire the right resources, prepare different workers to adopt the technology, and address emerging challenges. The employees can be trained to understand how technology can be utilized to add value to the company. Kurt Lewin’s change theory can ensure the right activities and procedures are undertaken throughout the implementation process. This analysis shows conclusively that the second stage of Lewin’s model will form the backbone of the RFID implementation plan. The major actions such as system designing, prototype testing, and implementation will be guided by the second phase of the theory. The role of the change process is to ensure the level of resistance is reduced (Cheng & Prabhu, 2013). The workers at the corporation will also be updated about the unique benefits of the change and how it will transform the corporation’s performance.
The proposed RFID technology will be implemented successfully at the company and become part of its business model. This means that the third stage of freezing will be considered to ensure the implemented technology is supported by every stakeholder. The employees will be willing to utilize the technology to deliver the intended services and products to customers. It is during this final stage when emerging issues can be identified, analyzed, and resolved (Coustasse et al., 2015). From the above implementation plan, it should be observed that the final stage (continuous improvement) should be an ongoing process. The team must address gaps and weaknesses that might affect the effectiveness of RFID technology (Menosky, 2017). Every stakeholder should be included during the phase to ensure emerging concerns are identified. These practices will present appositive improvements to ensure various organizational functions and operations are supported using the new technology.
The collaboration of different experts and professionals can make sure the technology is supported and redesigned depending on the changes experienced in the market. The ultimate goal should be to use various models or theories to deliver a meaningful change characterized by the use of RFID technology (Coustasse et al., 2015). When this is done in a professional manner, the company will be in a position to improve its business model and deliver its products to more customers in a convenient manner.
The organizational theory explains how project managers must be willing to lead their followers, make timely decisions, solve emerging concerns, and create the best culture to deliver meaningful results. Amazon Corporation has always been associated with one of the best organizational cultures whereby employees are trained and empowered to support various business processes. This theory will be utilized by the leaders of the project to ensure every person is ready to achieve positive outcomes (Menosky, 2017). When the implementers of the RFID technology are guided and empowered, they will be willing to work hard and focus on the best results. These practices will make it possible for Amazon Corporation to utilize RFID technology in most of its operations.
Conclusion
Amazon Corporation utilizes a powerful business model that makes it competitive in the e-commerce industry. The company has identified new markets and products that can be delivered to more customers using online marketing. The organization has numerous stores and outlets that support its business aims. The presented plan can ensure the company implements RFID technology successfully in its departments, logistical processes, stores, and operations. Amazon’s market research can be supported by using this development. The technology can be used to collect data and information that can predict the purchasing behaviors of its customers. These gains can then be tapped to develop superior business models that resonate with the emerging needs of its customers. Consequently, the company will become competitive and remain relevant in the global e-commerce industry.
References
Cheng, C., & Prabhu, V. (2013). An approach for research and training in enterprise information system with RFID technology. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(3), 527-540. Web.
Coustasse, A., Cunningham, B., Deslich, S., Willson, E., & Meadows, P. (2015). Benefits and barriers of implementation and utilization of radio-frequency identifcation (RFID) systems in transfusion medicine. Perspectives in Health Management Information, 12(1), 1-13. Web.
Gupta, P., & Margam, M. (2016). RFID technology in libraries: A review of literature of Indian perspective. Journal of Library and Information Technology, 37(1), 1-12. Web.
Haddud, A., Dugger, J., & Lee, H. (2015). Lee manufacturing control, asset tracking, and asset maintenance: Assessing the impact of RFID technology adoption. Journal of International Technology and Information Management, 24(2), 35-54. Web.
Lai, Y., & Cheng, J. (2014). A cloud-storage RFID location tracking system. IEEE Transactions on Magentics, 50(1), 1-16. Web.
Menosky, A. (2017). Walk out technology: The need to amend section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act to protect and promote corporate transparency. Journal of Technology Law & Policy, 17, 35-52. Web.
Owunwanne, D. (2016). Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology: Gaining a competitive value through cloud computing. International Journal of Management & Information Systems, 20(2), 1-17. Web.
Pradham, S., Chai, E., Sundaresan, K., Rangarajan, S., & Qui, L. (2017). Konark: A RFID based system for enhancing in-store shopping experience. Web.
Salam, M. (2016). Devising a business model of Amazon’s 1995-2004 journey. Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 6(3), 1-4. Web.
Ting, S., Tsang, A., & Tse, Y. (2013). A framework for the implementation of RFID systems. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 5(9), 1-16. Web.