Introduction
Amazon is a global corporation headquartered in Seattle, United States. It is principally an online retailer and technology company based on cloud computing, artificial intelligence, digital streaming, and e-commerce. Amazon is, therefore, renowned for its technological prowess including the revolutionary development of the Amazon Go shopping experience. Amazon Go embodies a novel variety of stores requiring no queues while checking out. Shoppers do not have to wait in line as the store functions using the Amazon Go app for iOS or Android. A shopper simply enters the store and picks the products and using technology the items are billed for and amount charged on the Amazon account (Wadhwa et al. 2020). From an 1800 Square feet store in Seattle, Amazon Go has expanded to include 25 stores in the United States and 17 across Europe.
Amazon Go is relatively new in Europe and is referred to by the name Amazon Fresh. The European market is very promising and the company seeks to expand its footing in the continent (Sperber, 2020). Hence, this paper covers the analysis of the European market. The first part entails the external market environment in the region based on the PESTLE analysis and Porter’s five forces framework. The second part covers the internal analysis using the SWOT analysis and stakeholder analysis. The report also covers the company’s SMART strategic objectives, market segmentation, and marketing mix.
PESTLE Analysis of Amazon
The PESTLE framework is widely used in strategic planning to enable organizations understand the impact external factors may have on particular markets. It is an acronym of some main factors, including Political (P), Economic (E), Social (E), Technological(T), Legal (L), and Environmental (E) factors (Feys and Probert, 2019). Figure 1 below shows the PESTLE framework;
Political Factors
Politics plays a crucial role in enabling the conduct of efficient business operations. The government helps to strike a balance between systems of public control and free market operations. Amazon is expected to benefit from the political stability in the European region. The presence of the European Union helps to manage political affairs of independent states that reduces political instability. The tax region in the area is favorable even as independent governments define their tax regulations (Sperber, 2020). The EU ensures there is no business discrimination and that businesses are sufficiently protected from bad practices. Additionally, the EU single market policy facilitates seamless flow of goods and services across borders. This makes it easy for businesses to manage competition and introduce diversified products.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are based on the economic wellbeing of a region. In modern times, there have been major shifts in the economy as a result of the global financial crisis and the coronavirus. Governments in Europe has enacted stronger regulatory measures to safeguard a safe economic environment such that crises may not cause major business downturn. The region has a positive economic outlook up from a favorable performance in previous years. In particular, the service sector that is the mainstay of Amazon is expected to post positive growth. The region has one of the lowest interest rates in the world. Even though Europe has had low inflation, there have been indications of rising inflation that may cause an upsurge in prices of essential commodities to be stocked in Amazon Go stores (Rossman, 2017). However, people have favorable purchasing power backed by increasing disposable incomes as businesses boom back to provide employment. This will enable the company to improve on sales and boost it’s financial performance.
Social Factors
Social factors go a long way to support sustainable development of businesses. The European region supports free movement of labor particularly after the 2008 global financial crisis and the coronavirus pandemic to allow people seek new opportunities and employment (Rosenbaum-Elliott, 2018). This has resulted in a higher number of immigrants, especially young people. The shifts in demographic trends will cause a rise in consumerism in the region. Bolstered consumerism gives Amazon Go an incentive to extend the scope of their services and e-commerce. However, challenges such as pay wealth inequality may limit opening of many branches in the region.
Technological Factors
Amazon is basically a technology company, hence, it needs to keenly evaluate the technological environment of the destination market. Technological advancements can help to optimize internal efficiencies and support a product or service from becoming technologically outdated. Technology keeps evolving and there should be adequate support for research and development activities to move with the emerging technologies (Fahmi, 2018). The European region is technologically advanced and presents a good region for investment. It has adequate technologies to support information and communications technology (ICT) development and enhance business cost efficiencies. The region has developed protections to enable Amazon battle against the increased rate of cybercrime attacks (Pride et al. 2018). The impressive improvement in the IT resources provides the company with the capacity to boost its results. Besides, the current EU Cohesion Policy greatly supports research and innovation in the ICT sector as a preferred way for provoking investment and growth.
Legal Factors
The European market is characterized by diverse regulations touching on Amazon’s operations. Legal considerations such as greater product enforcement and escalating legislation on environmental matters pertaining to corporations will impact on the business (Mandal, 2017). However, controls in goods and services will help the company to boost its attempts to curtail stocking of counterfeits. Heightened environmental legislation helps the organization to enhance its brand value through corporate social responsibility (CSR).
Environmental Factors
The passing of the Paris Agreement require countries and companies to limit carbon emissions. Europe faces a key challenge of ensuring they meet their targets amid increasing energy prices, climate change mitigation, and depletion of natural resources. These challenges may affect business operations as the governmental impose increased emphasis on market sustainability, and increased involvement in environmental projects (Kotler and Armstrong, 2018). Amazon Go faces a key requirement to play its part in ensuring it supports sustainability that will help to improve its corporate reputation.
Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s five forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive position of a company and spot where power lies in a business. It was developed by Michael E. Porter 1979, a Harvard scholar who identified five forces that define the competitive vigor and attractiveness of a market. The tool is incredible in strategic planning since it can enable Amazon Go to understand whether its products or services will generate a return from the European market (Rossman, 2017). This is by discerning where market power lies, identifying areas of strength, improving on weak areas, and avoiding errors. Figure 2 below depicts the five forces:
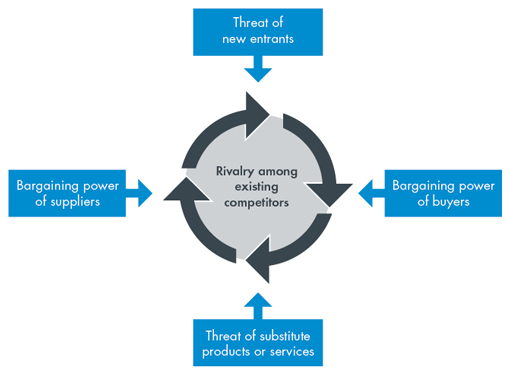
The threat of new entrants is based on the ease of entry into the market. Amazon operates in the e-commerce market segment that is characterized by a threat of new entrants desiring to gain from its high growth. Different organizations are rushing to embrace e-retail as customer now prefer to shop online for their commodities. However, the threat may not be so high for Amazon given that is has been in the market for a long time. The sector also requires high investments in storage warehouses, shipping, product promotion, and supply logistics (Rosenbaum-Elliott, 2018). Amazon already has also built a strong brand image in the sector making it a dominant player that may instill fear in potential entrants. In general, the threat for entrants facing Amazon is not of major concern.
Bargaining power of buyers refers to the potential for the customers to exert pressure on companies to lower their prices. In the retail sector buyers have a high bargaining power thanks to the many choices presented to them. The buyers have minimal switching costs in shifting from one retailer to another (Pride et al. 2018). Therefore, Amazon has to ensure its merchandiser are fairly prized to attract new shoppers and satisfy the existing clientele. It also has to keep up timely shipping and delivery of items, including refunds and replacements handling.
Bargaining power of suppliers refers to the capacity suppliers have to drive prices upwards. Amazon derives its products from diverse suppliers and each of the suppliers provide different products. The company has an established reputation and has built a reputation that gives it dominance over the suppliers (Mandal, 2017). Therefore, the bargaining power of suppliers is relatively low and they may face high switching costs from shifting their partnership from Amazon to a different retailer.
The threat of substitutes reduces the attractiveness of a market if filled with alternative products or services. The retail sector is Europe is filled with many alternatives, which increases the threat of substitution. Outlets such as Schwarz, Sainsbury, Carrefour, Tesco, and Aldi are a danger to Amazon Go. Apart from having physical stores, the retailers have an established online presence. Competitive rivalry is mainly characterized by product differentiation among the existing players (Kotler and Armstrong, 2018). The online retail market has a high number of players offering undifferentiated merchandise. This raises the competitive rivalry as Amazon Go competes with eBay, Alibaba, and Flipkart. Traditional brick and mortar stores are also reinvigorating their online presence adding to the competitive rivalry. The stores also have an expanded product portfolio covering electronics and clothing.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is an anthology of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is a strategic management tool that enables a company to be fully aware of all the factors confounded in making business decisions (Seth, 2018). Strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) pertain to internal forces that are within the control of the company. Opportunities (O) and Threats (T) are external forces the company has to plan on how to manage for successful business operation (Dibb et al. 2017). SWOT analysis is commonly represented in a matrix as depicted in table 1 below;
Table 1: Amazon Go SWOT matrix
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis is a strategic planning process of identifying parties that will be affected by the company operations. It involves identifying their interests and influence on the company. The main stakeholders of Amazon Go include customers, employees, the government, suppliers, and communities in which the company operates (Pride et al. 2018). The company appreciates the place of customers in supporting their expansion plans. Amazon accord clients the first priority making them the most important stakeholder group. It aims to ensure they are attended to in the best way through excellent customer service. The company provides a wide range of products with the intention of ensuring customers visiting the store do not lack essential commodities and leave the premises satisfied. Customers have the highest impact on the business because it is through them that the company will generate revenues and make a return on investment.
Employees are the second most important stakeholder group who can define the success of the company. They are the image of the company in guaranteeing quality services. They link the customer to the company and create a culture that will enable the company to succeed in the market. Through high quality human resource management, their interest can be managed to engender more productivity and efficiency in servings the customers (Mandal, 2017). In the current digital age bad actions by employees can be broadcast widely, hence, cause a major negative impact on the company’s operations.
The government plays a major role in guaranteeing the success of Amazon in the European market. Governments define business policy from business registration, employee engagement, business sustainability, and many more laws that govern the company’s operations (Chen et al. 2017). Governments also make laws on taxation that can be attractive to business or hinder entry into the market. They also create a positive political environment by ensuring there is stability and peace that is needed for business to thrive in their jurisdiction.
Suppliers are a key stakeholder group whose role majorly involves the supply of merchandise to the company for retailing to the final consumer. They have a keen interest in Amazon in ensuring they are paid in time and supported to grow their businesses along with the success of the company (Giannino, 2019). Suppliers also define the quality of products delivered to the company based on the product manufacturing processes.
Lastly, Amazon Go premises are based across different locations in Europe. The locations are inhabited by diverse communities who have different expectations from the company. The communities interest mainly involve corporate social responsibility (CSR). CSR encompasses different aspects that ensure the company in accountable in its business activities (Pride et al. 2018). This involves environmental preservation, observing human rights, and animal rights. It also involves supporting the local communities in developments, such as building schools, and hospitals.
SMART Strategic Objectives
SMART refers to Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Timely objectives. The strategic objectives specify the company’s direction in realizing the goals, vision, and mission. They enable the company to focus resources on specific areas that will drive the success of the company in the long term (Ives et al. 2019). Amazon Go’s SMART strategic objectives include to expand its reach by opening 1,500 new branches in the next three years, and to gain over 10 percent of the market share in the next three years.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing the company’s target market into manageable factions. This is to create subdivisions based on the market needs, interest, demographics, and behavior to enable better understanding of the target audience (Banerjee, 2017). Amazon can divide the European market based on the factors to enable it satisfy the different consumer groups by delivering the correct products and providing custom-made services. The company can also easily attend to concerns of definite consumers as opposed to attending to a larger market that is not correctly defined.
One consumer segment the market can focus on is defined by demographics. Amazon can choose to focus on the youthful age group aged between 20 to 35 (Baines et al. 2017). The consumer category is the most suitable in terms of using the company’s shopping technology. It covers the working population who have limited time for shopping and do not wish to spend time in queues. The technology also fits into their lifestyle as they are exposed to different technologies that they wish to interact with continually.
Amazon can position its brand by focusing on the psychological appeal of the target market. The company should continue to enhance the service using the app solution to eliminate queues in the retail store (Giannino, 2019). The technology can be able to attract users seeing to save time in shopping by simply picking items and leaving as the app takes the responsibility of detecting the items, calculating the total bill and charging the amount form the shopper’s Amazon account.
Marketing Mix
Marketing mix refers to the actions and strategies for producing and promoting its goods and services. It helps a company in strategic planning through proper organization of marketing operations to enable the company grow its revenue and profitability (Aaker and Moorman, 2018). The company is able to identify different options that are adaptable and improve its competitive standing in the market. Amazon Go can adopt a marketing mix through which it can identify areas of consumer concern and how to improve on arising challenges.
The discussion on pricing, promotion, and distribution is based on the company’s electronics category. This cover a electronic products, such as cameras, laptops, mobile phones, gaming equipment, and tablets. In pricing, Amazon can use a value-based strategy, the market-oriented strategy, and price discrimination. Value-based pricing is charging a price based on the perceived value shoppers attach to a product. The market-oriented strategy can enable the company to provide attractive and competitive electronic products at an affordable price (Dean, 2019). In price discrimination, the company can charge different products on the same item in different market segments.
Amazon Go can promote the electronics product using technology drives means, particularly through ads. The company can integrate discounts in ads and other incentives to appeal to a wider customer base. Finally on distribution, Amazon Go can take advantage of the company’s diverse distribution network comprising over 175 fulfillment centers (Acimovic et al. 2020). These distribution centers are mainly centered in Europe and North America. The company can also avail the products in the physical Amazon Go stores from where they can be picked by shoppers.
Conclusion
Amazon Go is an idea that appeals to the European market that is incredibly attractive. The region is characterized by political stability and impressive economic standing. The European Union has created a huge single market by reducing barriers of trade across different countries in the region. However, the region is characterized by huge competition from other established players. Amazon Go should leverage on its strong brand name to penetrate the market. The use of the app to eliminate queues in shopping premises will attract the youthful population seeing to save time and reduce the stress of standing in queues to be served by tellers.
The technological growth in the regions with a high penetration of mobile telephony provides an opportunity. The company can leverage on its online experience to provide a distinctive shopping experience. However, Amazon should invest in cyber security systems to reduce the threat of cube attacks. This will enable the company to open more shopping centers and gain more market share in the next three years. The use of market segmentation and brand positioning will enable the company to attend to different needs in the market. The company can further use a marketing mix based on pricing, distribution, and promotion to better serve the customers.
Reference List
Acimovic, S., Mijuskovic, V. and Milosevic, N. (2020). Logistics aspects of goods home delivery: The case of Amazon company. Marketing, 51(1), pp.3–11.
Aaker, D.A. and Moorman, C. (2018). Strategic market management. 11th ed. Hoboken, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Baines, P., Fill, C. and Rosengren, S. (2017). Marketing. Oxford City: University Press.
Banerjee, S. (2017). ‘Strategic Brand-Culture Fit: A conceptual framework for brand management’, Journal of Brand Management, 15(5), pp.312–321.
Chen, P.-L., Kor, Y., Mahoney, J.T. and Tan, D. (2017). Pre-Market Entry Experience and Post-Market Entry Learning of the Board of Directors: Implications for Post-Entry Performance. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 11(4), pp.441–463.
Dean, N. (2019). Product promotion promotes uptake. Nature Energy, 4(7), pp.531–531.
Dibb, S., Simkin, L., Pride, W.M. and Ferrell, O.C. (2019). Marketing Concepts and Strategies. 8th ed. Andover, Hampshire, United Kingdom: Cengage Learning.
Etzel, M.J., Walker, B.J. and Stanton, W.J. (2017). Marketing. Maidenhead: Mcgraw-Hill Education.
Fahmi, A.M. (2018). ‘Social media marketing, functional branding strategy and intentional branding’, Problems and Perspectives in Management, 16(3), pp.102–116.
Feys, B. and Probert, C. (2019). PESTLE analysis. 50Minutes.
Giannino, M. (2019). Selective Distribution Networks for the Marketing of Luxury Branded Products Versus the Amazon Marketplace: The Sisley v Amazon Case before the Court of Milan. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Ives, B., Cossick, K. and Adams, D. (2019). Amazon Go: Disrupting retail? Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases, [online] 9(1), pp.2–12. Web.
Kotler, P. and Armstrong, G. (2018). Principles of marketing. 17th ed. Hoboken: Pearson Higher Education.
Mandal, P. (2017). ‘Understanding Digital Marketing Strategy’, International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 5(6).
Pride, W.M., Ferrell, O.C., Lukas, B.A., Schembri, S., Outi Niininen and Riza Casidy (2018). Marketing principles. South Melbourne, Vic. Cengage.
Rosenbaum-Elliott, R. (2018). Strategic Brand Management. 4th ed. Oxford University Press.
Rossman, J.E. (2017). The Amazon Way: 14 Leadership Principles behind the World’s Most Disruptive Company. SDMIMD Journal of Management, 8(1), p.95.
Seth, C. (2018). SWOT analysis. S.L.: 50Minutes.com.
Sperber, E. (2020). The Amazon or Amazon. Capitalism Nature Socialism, pp.1–1.
Tomar, D. (2020). Porter’s Competitive Forces Model and SWOT Analysis To Payments. International Journal of Computer Trends & Technology, 68(10), pp.56–59.
Wadhwa, B., Vashisht, A. and Phutela, N. (2020). Business model of amazon India-A case study. South Asian Journal of Marketing & Management Research, 10(1), p.32.