The report aims to study the impact of IT governance application in organizational operations using COBIT 5. The framework reduces the risk inherent in cloud computing, such as data protection, identity and access management, and virtual operating risks. Research conducted on COBIT 5 gathered quantitatively analyzed qualitative data. Questionnaires were used to achieve the study’s purpose among populations from various fields. The study’s outcome was that all COBIT 5 decisions regarding planning and organization, guidance and control, monitoring, and evaluation affect risk reduction in cloud computing. Based on the study’s findings, the report recommends organizations should activate security control roles to increase application levels against environmental hazards that companies face from cloud computing. Developing and updating information technologies help to keep organizations updated with emerging IT trends.
Introduction
Organizations are increasingly dependent on the information available to create better products and services to gain a competitive edge over their rivals. COBIT 5 fills the gap of information necessity required by companies to provide IT expertise for governance and management. COBIT 5 achieves this purpose by creating optimal value from their IT services to help organizations strike a balance between risk optimization and resource allocation and realizing benefits. The COBIT 5 framework has process referencing models, several governance practices, and enabler tools for supporting organizational governance.
Communication and information revolution enables organizations to interact with all data categories to increase their Information and communications technology (ICT) management affairs.
Technology contributes to building progressive societies and pushes them to establish fostered customer relations to positively impact market share (Okour, 2019, p. 2). Output quality also influences users’ ability to make informed decisions after identifying, planned, and organized corporate IT strategies. Information revolution also helps organizations determine accessibility, use their resources, and deliver them to several management stages (Putra et al., 2017, p. 4). The evolution of information pushes organizations to develop and modernize their methods and tools to continue providing top-notch services.
Technological advancements and IT systems evolution created cloud computing. The originative system refines organizational operations as they endeavor to benefit from IT in reducing business costs. Information technology helps organizations maximize their capabilities by exploring external parties’ supply benefits (Okour, 2019, p. 3). Although IT plays an essential role in cloud computing, aspects and risks related to security get the most attention. Most organizations strive to control information system tools because of the increased need to adopt IT-governing control frameworks. The report aims to determine the influence of IT management on minimizing computing hazards under COBIT 5.
Objectives of the Report
The report’s primary objective is to demonstrate IT applications using COBIT 5 outline to mitigate cloud computing hazards in various institutions. COBIT 5 operates on five principles that strengthen organizations to construct effective management and governance framework. The method helps optimize the information and technological investments for all organizations (Okour, 2019, p. 3). The report’s objective is motivated by the prominence of cloud computing in offering services to organizations across all fields. However, physical, human, and legislative hazards that stem from the usage of cloud computing are among the leading obstacles to implementing technology in organizations (Astuti et al., 2017, p. 570). COBIT 5 framework provides the most prominent solution to the governance of organizational technology. The study’s problems revolve around elaborating COBIT 5’s effectiveness in reducing cloud computing risks.
The Importance of the Report
The essence of this report emanates from its subjects that emphasize information protection to achieve security of prominent contemporary issues and modernity of the residents. It is also anticipated that the report will constitute logical innovation to its users and add to the best practices that guarantee data safety (Okour, 2019, p. 3). Another advantage of the report originates from its application of COBIT 5 to assess risk associated with cloud computing (Puri et al., 2017, p. 44). The report also ensured quality improvement to ease the use of IT services in speeding up operations. COBIT 5 helps organizations to plan, build, and run their activities to improve governance on an ongoing basis.
The Research’s Hypothesis
The report’s objectives contribute to the formulation of the hypothesis. The null hypothesis of the study is that the level (α≤0.05) has no significant statistical effect for COBIT 5 decisions in mitigating cloud computing risks. Furthermore, the report simplified the hypothesis into smaller subsections to evaluate them based on the principles (Putra et al., 2017, p. 5). The subsets include planning and organizing, guidance and control, monitoring and evaluation, support and delivery, and progression and implementation.
Theoretical Framework of the Report
IT Governance
The phrase “IT governance,” as used in most sections of the report, originates from corporate governance. IT governance developed from scandals and economic crises that plagued significant global companies (Puri et al., 2017, p. 45). IT governance forms an elementary part of company management consisting of business structure, leadership, and processes, emphasizing technological support in companies (Okour, 2019, p. 2). Achieving organizational efficiency requires the integration of IT processes into its strategies and objectives. Likewise, IT governance also refers to inspiring desired actions relating to the use of information technology accountability frameworks and decision making (Astuti et al., 2017, p. 574). For instance, IT helps organizations to realize their strategies through their operational actions and leadership structures.
IT governance refers to applications and set principles implemented by the senior management to control and information technology design and implementation. The primary goal of IT governance is to enhance an organization’s activities by verifying available innovation to serve the company’s constrained needs (Okour, 2019, p. 3). Other authors, such as Solomon et al., postulated that IT management is similar to information control, and they refer to establishing successful relations between information users and technology service providers (Okour, 2019, p. 3). Moreover, the topic of IT governance is hailed by Freeland, who believes that it shapes an organization’s technology strategy by users’ interests in using the technology (Putra et al., 2017, p. 6). Hence, organizations use IT strategies to enact rules, policies, and procedures in their departments.
Significance of IT Governance
IT governance is essential for organizations because it helps in pushing them towards accomplishing their objectives. Organizations achieve IT flexibility in structuring the operations of information systems. Plasticity helps organizations activate information technology management and control roles (Astuti et al., 2017, p. 576). Companies can leverage the growing awareness of the utility of information technology in organizational operations to gain a competitive edge over their rivals and reduce operating costs.
Additionally, companies can invest in information technology to exchange information (Okour, 2019, p. 3). COBIT 5 offers an enabling environment for firms to achieve their objectives on IT governance and maintenance. IT governance is vital for organizations since it contributes to giving organizations a competitive edge by heightening the management’s understanding of the COBIT 5 operations (Okour, 2019, p. 4). Governance and control frameworks support the IT government to comply with regulatory requirements in their endeavors to increase shareholders’ value (Puri et al., 2017, p. 46). Successful organizations utilize IT to assess the risks and exploit derived benefits such as aligning business and information system strategies.
COBIT 5 and IT Management
The critical development in the field of technological governance is COBIT 5 framework. Essentially, the framework was developed to reduce challenges present in automated systems. Also, the framework focuses on creating operational guidelines for professionals such as accountants in the IT field. It also enables companies to maximize the benefits from gathered data. Organizations with access to information have an in-depth understanding of risks in their industries and plan to mitigate their effects.
Benefits of COBIT 5 Implementation
Implementing the COBIT 5 framework has significant benefits to organizations, such as obtaining more excellent value from IT investments. For instance, organizations can increase compliance with policies, regulations, and relevant laws. Overall, the benefits help organizations to establish relationships between their IT goals and the business needs to increase their revenues (Okour, 2019, p.7). COBIT 5 also improves how empowering factors lead to better risk management for any company seeking an IT operation mechanism (Putra et al., 2017, p. 6). Besides, the guidelines involve creating efficient and effective hazard mitigation strategies that increase stakeholders’ value.
IT Control under COBIT 5
COBIT 5 framework facilitates IT control through efficient scheduling and management. The cornerstone of creating an IT and company management is a carefully-crafted plan that will shape an organization’s activities. Successful planning and organization require that a company incorporate several objectives to coordinate its technology and activities (Astuti et al., 2017, p. 577). Organizations can achieve this success by implementing practical short and long-term planning goals. The management functions of planning and organization ensure that a company translates its governance frameworks and IT features into actual procedures and practices (Okour, 2019, p. 7). Additionally, firms can improve their strategic alignment processes by giving their management a general description of shareholders’ needs. Communicating the company’s management structure enables it to identify the capacities it needs to achieve goals.
The second control is progressiveness and implementation, necessitating that organizations identify and acquire information technology requirements to execute operations successfully. Parameters under progressiveness and implementation include change, provision, knowledge, and project management (Okour, 2019, p. 8). Organizations need to acquire an in-depth understanding of the information needs and what they have and strive to bridge the gap through IT. Establishing an awareness of information technology enables organizations to counter competition from rivals since they will anticipate changes in the environment and adequately prepare to manage them within their business.
COBIT 5 framework also helps organizations control support and delivery systems by adding value to their IT systems. Enterprises are better placed to sustain their business activities by providing data support and processing. Similarly, they can maintain information flow continuity and make it permanently available for users such as the business community and operations management (Okour, 2019, p. 9). Controlling support and delivery systems enable companies to create value by effectively innovating and using IT in their enterprises. Generally, COBIT 5 ensures a closer alignment of IT objectives and business needs.
System monitoring is another control area by COBIT 5 frameworks. Guidance and control help companies collect and analyze information relating to activities during a project’s implementation. Guidance and control framework includes risk improvement, value creation, delivery of services, and stakeholders’ transparency (Puri et al., 2017, p. 48). Firms can evaluate their business processes to identify risks and apply strategies to mitigate their effects (Okour, 2019, p. 9). Likewise, stakeholders’ transparency implies enhanced information flow within an organization to ensure that stakeholders communicate accurate financial information about the company.
Cloud Computing
Individuals and organizations are giving cloud computing considerable attention. Cloud computing refers to a technical means of data processing and storage outside an organization’s site. The process involves the service provider giving companies external access to their data via the internet. Despite the convenience and progression in cloud computing, it still has controversial electronic cloud computing issues (Okour, 2019, p. 8). According to some researchers, information integrity can be achieved by electronically managing cloud information from an internal network security system. Most cloud-related security problems are related to the service providers and customers (Astuti et al., 2017, p. 579). Cloud computing plays a crucial role in maintaining secure electronic cloud information. More often than not, this process requires firms to focus on various elements such as verification of user identity. Cloud computing service providers can also ensure that users have accounts that will help keep customer information secure.
Managing Corporate Risk based on IT governance Guidelines
Businesses face risks in their activities depending on the nature of their operations. Risk management entails the identification of vulnerabilities and threats existing in an organization’s structure. After identifying the hazards, managers proceed to design appropriate measures of minimizing their effects on IT resources. The process of managing risk is endless and commences from assessing an organization’s exposure to hazards, identifying critical perils, and minimizing them using tools and control (Nugroho, 2017, p. 52). Managing risks using IT governance practices involves analyzing and evaluating exposures from information technology applications, monitoring and controlling internal control efficiency, and ensuring good IT services.
Using IT under COBIT 5 framework will minimize operation time based on its governance practices. Thus, IT governance helps manage corporate risks by improving a company’s auditing practices and reducing costs. Computer information security risks require the provision of appropriate levels of electronic protection to guide monitoring operations. COBIT 5 primarily focuses on developing clear policies and acceptable security control practices. The framework distinguishes itself as a well-structured IT governance outline for auditing accounting systems by giving precedence to control over execution.
Materials and Methodology
The report is designed to assess IT governance’s impact on reducing cloud computing risk using COBIT 5 framework. The report follows sequential procedures to analyze the mixed methods of its results. The study quantitatively analyzed qualitative data to determine the impact of using COBIT 5 in IT governance to reduce cloud computing risk (Trianto, 2018, p. 4). Furthermore, the report also analyzed hypotheses tests to determine drawn conclusions and recommendations. Theoretical studies were also reviewed by the report to crystallize their foundations. Questionnaires were also issued to achieve the study’s purpose and develop the research questions.
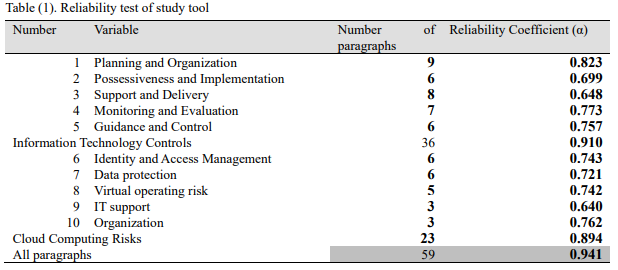
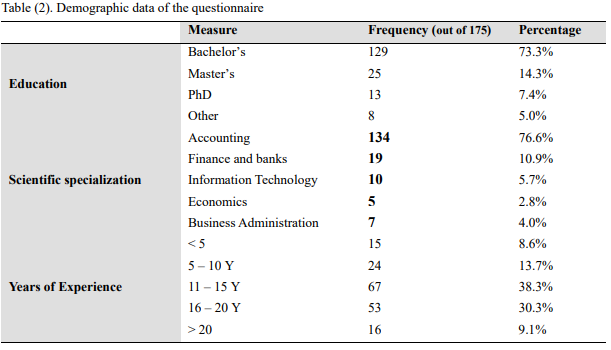
Qualitative data was appropriate for the study because it provides trends in cloud computing that determine IT governance’s possible effects in mitigating inherent risks using COBIT 5. The issued questionnaire was significant in collecting qualitative data and providing a guideline for expressing the results using statistical figures. The study classified data used in the research as primary or secondary sources. The questionnaires provided preliminary data, while secondary sources were from journals, books, and previous studies (Trianto, 2018, p. 5). The study’s population was drawn from accountants using IT governance. The actual sample of the population comprised 192 accountants who received the questionnaires through the mail (Wulandari et al., 2019, p. 169). Recovered questionnaires totaled 184. 9 were incomplete, while 175 qualified for statistical analysis. The research also used Cronbach’s Alpha Coefficient of 0.941 while its range was from 0.640 to 0894, justifying the questionnaire’s reliability.
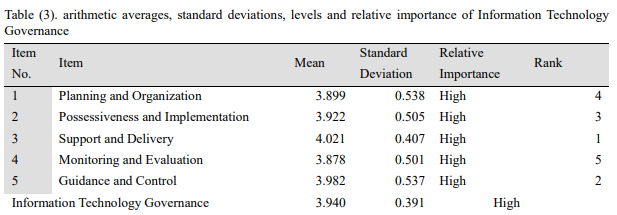
Standard deviation is used in measuring and determining the risk ratios in the business world. According to the study’s results, IT governance’s standard deviation is 0.391, while the average mean is 3.940 (Nugroho, 2017, p. 56). Likewise, the study had a high combined relative importance of IT management. The results also highlighted that the fits events as support and delivery while the last rank was monitoring and evaluation. The results indicate that there is improved compliance with policies, regulations, and strategies due to increased monitoring of the company’s operations (Nugroho, 2017, p. 56). Also, the results show that most companies align their strategic objectives with their IT decisions. It shows that managers are increasingly interested in maximizing the value added by IT in the company’s activities.
Appendix 4 shows that the average cloud computing risk means 3.962 while the standard deviation averages 0.472. Hence, the cloud computing risk has a high combined relative importance. The study ranked priorities as identity and access management, data protection, and support in that order. According to the results, cloud computing risks emerge with high relative importance (Wulandari et al., 2019, p. 172). According to the study’s results, the sample’s sook reduces risks generated from technology and their procedure’s efficiency (Okour, 2019, p. 8). Integrity, data validation, and maintenance can reduce the negative impacts of risks on companies and their customers.
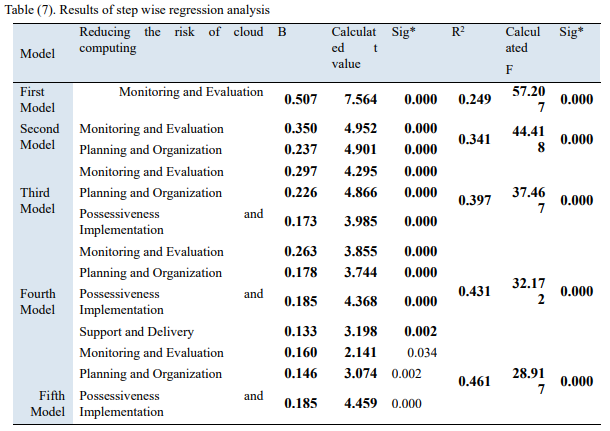
Moreover, the study used bivariate Pearson correlation to make data multicollinearity free. Calculations in Appendix 5 show that the highest correlation and coefficient value of 0.517 originated between independent variables. There was a lower correlation coefficient between other study variables, which indicated the absence of a perfect relationship. Likewise, the study tested the hypothesis using multiple regression analysis. Appendix 6 indicated the correlation coefficient as 0.679 as the association between variables. The study found a statistical significance between the effect of independent variables on dependent variables statistically significant.
Consequently, the table of coefficients depicted that management (B) reached 0.146, while T is 3.074 with a 0,002 significance. Since the considerable level is less than 0.5, it shows that the impact the risk has on IT governance is significant. Accordingly, this study rejected the null hypothesis because there is an effect on the level planning and organizing coefficient reducing cloud computing risk and accept the alternative hypothesis. Also. Appendix 6 showed that support and delivery clocked 0.128 while T’s value was 0.3155 with a 0.002 significant level. Hence, the study rejected the null hypothesis and accepted the alternative that supports and contribute to reducing cloud computing risk.
The study rejected the null hypothesis and accepted the alternative based on the above findings that there is a significant statistical impact at (α≤0.05) level for COBIT 5 in reducing cloud computing risk. Furthermore, the central hypothesis illustrates the IT governance’s essential role in enhancing information security and protecting private data (Nugroho, 2017, p. 53). Companies can protect themselves from falling prey to cybercrimes by using COBIT 5 framework to minimize the risks.
Results and Discussion
COBIT 5 framework has relative significance to organizations as it helps them to leverage the value of technology, save costs, and minimize cloud computing risks. The first principle of COBIT 5 is to meet stakeholders’ demands through the sustainable development and implementation of IT governance guidelines (Nugroho, 2017, p. 57). The second principle is conveying the business end-to-end by enhancing system design and capabilities. COBIT 5 also applies a single integrated framework to ensure that all functions are controlled by a central management chain (Okour, 2019, p. 9). Structures to promote IT governance in organizations should also focus on establishing a holistic approach (Putri et al., 2017, p. 44). Another crucial finding from the study is the need to separate management from management to align information needs with the organization’s goals effectively.
Recommendations
Based on the study’s results, the recommendations which can be made include implementing more IT governance. Organizations should create a specialized department to assess exposure to risks and how they mitigate them before occurrence (Trianto, 2018, p. 6). Likewise, companies need to activate security control to shield themselves from possible environmental hazards (Okour, 2019, p. 9). Also. There is also a need to develop and update information technologies to enhance the organization’s plan to obtain a vivid picture of smooth operations without data disruption.
Conclusion
COBIT 5 fills the gap of information necessity required by businesses to provide IT expertise for governance and management by creating optimal value from their IT services to help organizations strike a balance between risk optimization and resource allocation and realizing benefits. The COBIT 5 framework has process referencing models, several governance practices, and enabler tools for supporting organizational governance. The report’s primary objective is to demonstrate IT applications using COBIT 5 framework to mitigate hazards in various institutions. Managing menaces using IT governance practices involves analyzing and evaluating exposures from information technology usage, monitoring and controlling internal control efficiency, and ensuring sound IT services. Companies need to activate security control to protect themselves from possible threats in the business environment.
References List
Astuti, H. M., Muqtadiroh, F. A., Tyas Darmaningrat, E. W., & Putri, C. U. (2017) ‘Risks assessment of information technology processes based on COBIT 5 framework: a case study of ITS service desk’, Procedia Computer Science, 124, 569–576.
Nugroho, H. (2017) ‘Proposed IT Governance at Hospital Based on COBIT 5 Framework’, IJAIT (International Journal of Applied Information Technology), 1(01), pp.52-58. Web.
Okour, S. (2019) ‘The Impact of the Application of IT Governance According to (COBIT 5) Framework in Reduce Cloud Computing Risks’, Mod. Appl. Sci, 13(7), p.25. Web.
Putra, I.N., Hakim, A., Pramono, S.H. and Tolle, H. (2017) ‘Adopted COBIT-5 framework for system design of Indonesia navy IS/IT: An evaluation’, International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 12(17), pp.6420-6427. Web.
Putri, M.A., Aknuranda, I. and Mahmudy, W.F. (2017) ‘Development of a Conceptual Framework to Determine Improvement of IT Governance using COBIT 5 and AHP-GA’, Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering (JTEC), 9(2-8), pp.43-49. Web.
Trianto, W. (2018) ‘August. Evaluation of patient information system in public health service using the COBIT 5 framework’, In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing, (Vol. 407, No. 1, p. 012166). Web.
Wulandari, S.A., Dewi, A.P., Pohan, M.R., Sensuse, D.I. and Mishbah, M. (2019) ‘Risk assessment and recommendation strategy based on COBIT 5 for risk: Case study sikn Jikn helpdesk service’, Procedia Computer Science, 161, pp.168-177. Web.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Reliability test
Appendix 2: Demographic data
Appendix 3: Averages
Appendix 4: Cloud computing risk
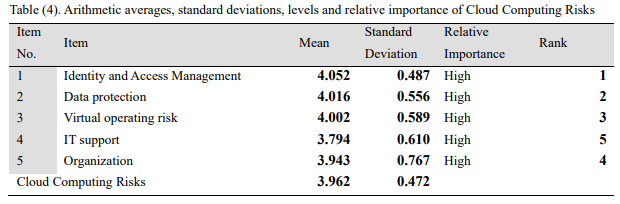
Appendix 5: Cloud computing risk
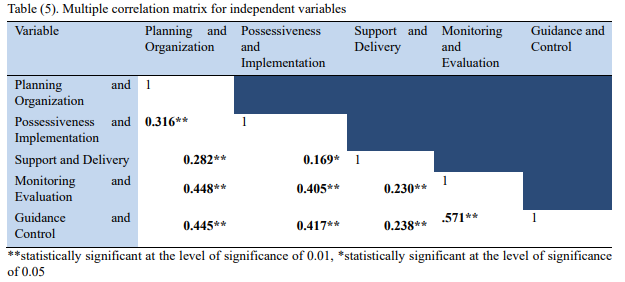
Appendix 6: Hypothesis test
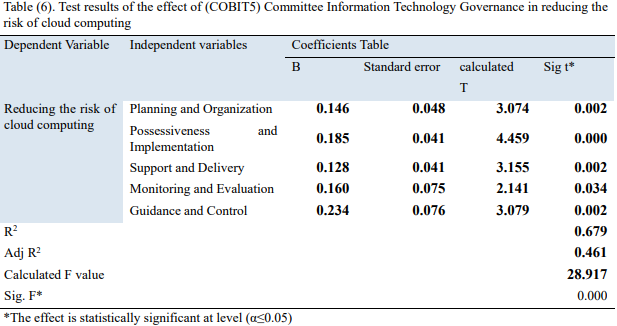
Appendix 7: Regression analysis