Introduction
Over the recent past, several companies have been devising strategies that facilitate penetration of international and domestic markets. The need to penetrate international and domestic markets emanates from the advancement in technologies that have led to the globalisation of markets and change in consumer behaviour. To succeed in international and domestic markets, companies need a useful model that helps them identify markets, consumers, achieve their goals, and determine the prevailing levels of competition. One such model is the Porter’s Diamond Model, which has components such as level of rivalry, factor conditions, firm strategy, and demand conditions. Practically, by employing these components, companies can effectively penetrate and succeed in international and host markets. Hence, it is within this backdrop that the essay discusses the usefulness of Porter’s Diamond Model in explaining home and host location strategies of international business using Coca-Cola and Samsung companies.
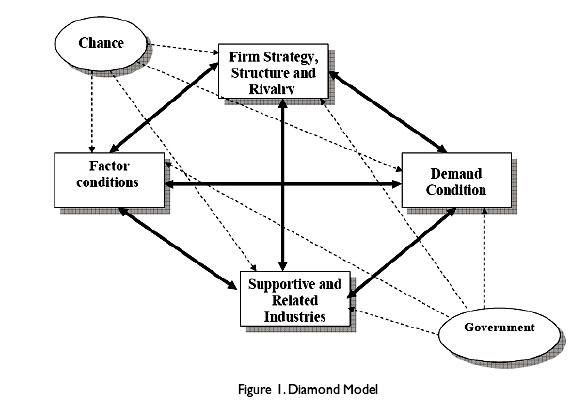
Porter’s Diamond Model
Home and host markets require different strategies depending on the nature of consumers present in the respective markets. As such, companies need to devise strategies that enable them to meet the demands prevailing in the respective markets. Porter’s Diamond Model is one of the models that are very useful for companies that intend to match the needs of domestic and international markets. The focus of the model, which revolves around consumer demands, competition and rivalry, resources and firm’s strategies, is very instrumental in company’s intend to achieve the required success in the domestic and international markets. Barbe and Triay (2011) in figure 1, explain that Porters Model is a compass used by companies that need international growth. While the model has benefits that facilitate company success, it also has drawbacks that limit its usefulness. Therefore, the essay intends to undertake an in-depth analysis of the essence of the model in the development of strategies for international business.
Case studies
To actualise the study, the essay uses Coca-Cola and Samsung companies as case studies. The study examines how Coca-Cola and Samsung have used the model to undertake marketing strategies in home and host markets. Moreover, the study scrutinises factors that the companies can employ to progress and effectively use the model in their favour. By examining the companies and using them as case studies, the essay presents an actual argument that explains the usefulness of the model in strategy development and business growth. The essay also wishes to assess the extent to which the two companies, Coca-Cola and Samsung, have employed the components of the model to win the market share and increase the number of their consumers in the competitive domestic and global markets. Benefits and drawbacks presented by the model help in developing an argument that substantiates the relevance of the model in international marketing.
Benefits
Market Identification
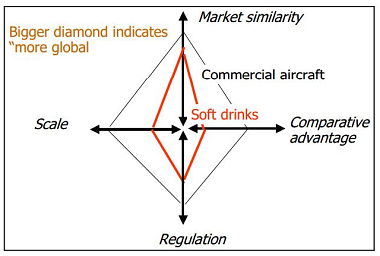
One of the factors that compound the usefulness of the model is market identification. Since the model focuses on demand conditions, the model is elementary in company’s quest to understand the potential consumers and the prevailing conditions in the market. By providing an in-depth analysis of competition and rivalry of companies, the model plays an integral role in helping them understand the factors that determine international markets. As a result, companies devise strategies that align them with market conditions. In figure 2, it is evident that Coca-Cola Company uses the model to penetrate international markets (Lessard 2003). By understanding what consumers need in these markets, as well as the level of competition, the company developed strategies that led to its growth in the respective regions. For instance, in regions such as Europe, Asia, and Africa, the prices of Coca-Cola products are lower as opposed to competing products. Strategic organisation of prices is one of the factors that explain the essence of the model and its role in facilitating the development of international companies in the home and host destinations.
Components presented by the model are very useful in enabling companies understand the various markets in international and domestic destinations. The model helps companies to understand the level of competition and consumer demands. In addition, the model augments the understanding that companies have on the conditions of the home and host locations concerning marketing. The model also helps companies check and establish whether their strategies are in line with the marketing requirements presented by the home and host markets. As a result, companies devise strategies that align them with the requirements in the home and host destinations. According to Bell (2008), Samsung introduced products that blend well with the needs advanced in the marketing environment in the United States. For instance, Samsung developed smartphones that matched the demands of trendy, dynamic, and liberal consumers of the United States.
Readiness for Home markets
The relevance of the model is also evident in its ability to educate international companies on the prevailing requirements in the home markets. Since home markets form the basis of marketing for companies that intend to engage in international marketing, the model helps them understand the conditions and the extent to which their products match consumer demands. In effect, the company can use the home market to ascertain the performance of its products before entering the international destinations. For instance, Samsung engaged in extensive marketing in its home destination, before finally entering the international market (White 2004). As such, companies can use the model to understand the home based market requirements and eventually introduce products that meet consumer demands, a factor that helps them develop and progress in the home and international markets. It is imperative to highlight that readiness for the home market and influence helps companies use the market as a microenvironment, within which they use to establish the prospects in the international market.
Identification of Consumer Needs
Fundamentally, consumers have diverse demands based on the different locations, lifestyles, and religious orientations. As such, an assessment of the model helps companies to ascertain the divergent needs of consumers in the targeted locations. In effect, companies, which fail to ascertain the needs of consumers in the domestic and international markets, release unwanted products consumers to the markets. Therefore, the model is very important as it makes companies see the relevance of consumer needs and the existing variance. A good example is the case of Samsung, which uses the concept to develop smartphones that meet the trendy, dynamic, and technologically oriented consumers (Bell 2008). The implication of the focus on consumer needs, as advocated by the components in the Porter’s Diamond Model, is an amplified market share and consumer base in domestic and international markets.
Drawbacks
Culture compromise
Compromise in culture is a drawback that limits the usefulness of the Porter’s Diamond Model in explaining home and host strategies for international businesses. While the model encompasses several components, such as level of competition, firm strategy, demand, and factor conditions, it fails to recognise the influence of culture on revenues and overall performance of a firm. Imperatively, for a company to succeed in the market, whether domestic or international, it has to align itself with the conditions and cultures of its potential consumers. In the elucidation of Barrow (2011), Coca-Cola has over time engaged in marketing campaigns that integrate the cultures of host communities while maintaining its product brands. As a result, products from Coca-Cola continue thriving in continents such as Africa and Europe. In essence, culture is one of the determinants that dictate what consumers buy from a respective company. Moreover, culture is a basic ingredient in the development of perceived product quality. By aligning themselves with the culture of consumers in the home and international destinations, companies grow and eventually amplify their market share.
Bias
Fundamentally, a scrutiny of the components of the model reveals some level of bias. The bias emanates from the overemphasis on elements of competition that the model demonstrates. Components such as rivalry, factor condition, firm strategy, and demand condition are very important for enhancing the performance of a company in aspects that relate to competition and outsmarting rivals in a given market. However, the model fails to advance various elements that are evident in the external and internal environments of the market. Ma (2014) states that for Samsung to progress, its managers integrated the model with a range of other models like PESTEL, 4Ps, and the marketing mix, which cover aspects of the external and internal marketing environments. Overemphasis on components that advance its level of competition renders a company incapable of handling other aspects that affect the external and internal environments of marketing.
Disregards Government Influence
Another limitation associated with the model is its disregard of government influence. The components in the model do not cover issues that relate to the influence that the government has in the marketing environment and internationalisation of companies. Practically, the government presents companies with a range of uncertainties that they should understand in their attempt to market their products in domestic and international markets. By failing to address the issue of government influence, the components advanced by the model, makes managers incapable of devising plans and policies that minimise the negative effects that uncertainties can present before them.
To counter the challenge, Coca-Cola penetrated an international market such as China market after developing a liaison with companies based in China. The liaison occasioned after the company engaged in due diligence and established the presence of a regulation in China, which compels international companies to liaise with a home based company so that they enter its market (Chang& Moser 2006; Huang 2003). Since the model fails to educate companies on elements of government influence and does not scrutinise the probable uncertainties, marketing managers cannot underscore the essence of due diligence in preparedness for uncertainties.
The Model is not Self-Sufficient
Apparently, the Diamond Model advanced by Porter is not self-sufficient. Just like other models, the Diamond Model is not self-sufficient, and thus, managers need to incorporate other models so that they can successfully enter a new market and win the market share. According to Cho and Moon (2000) while Porter’s Diamond Model covers several aspects that advocate for competition and rivalry in the domestic and international markets, it does not address other aspects in the wider field of marketing. Issues regarding SWOT analysis, external and internal marketing environment, and the marketing mix comprise the factors that the model fails to address.
Figure 3 shows the components covered by the model and clearly demonstrate the absence of self-sufficiency (Lessard 2003). Failure to address these factors compels smart managers in international companies to execute other models and research extensively on issues that influence internationalisation of companies so that they can succeed in developing market entry strategies. Notably, effective application of the model alongside other models leads to an enhanced understanding of the marketing environment, prevailing conditions, and amplified market share in domestic and international markets.
Conclusion
Porter’s Diamond Model is a useful model that helps smart managers in international companies to devise strategies that propel the companies to grow at domestic and international levels. The components that the model advances, which are demand and factor conditions, firm strategy, and competition, are useful in elevating the understanding of companies in matters of international marketing. An elevated understanding of the importance of marketing and consumer demands leads to an increase in market share and revenues. Therefore, the model is one of the useful models that explain home and host location strategies of international businesses. Remarkably, while application of the model leads to a range of benefits, the model also has limitations that affect its usefulness. The model has benefits comprising market identification, readiness for home influence, and identification of consumer needs. On the other hand, the limitations or drawbacks include culture compromise, bias, disregard of government influence, and absence of self-sufficiency. Practically, the model is useful, but it requires integration with other models so that it facilitates the development of strategies that help international companies to win the market share in domestic and international markets.
References
Barbe, F & Triay, M 2011, ‘Is Porter’s diamond applicable to developing countries? A case study of the broiler industry in Uruguay’, International Journal of Business and Social Science, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 17-28.
Barrow, C 2011, The 30 Day Mba in International Business: Your Fast Track Guide to Business Success, Kogan Page, Philadelphia.
Bell, S 2008, International brand management of Chinese companies: Case studies on the Chinese household appliances and consumer electronics industry entering US and Western European markets, Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Chang, J & Moser, M 2006, Foreign trade investment and the law in the People’s Republic of China, Oxford University Press, Hong Kong.
Cho, D-S & Moon, H-C 2000, From Adam Smith to Michael Porter: Evolution of competitiveness theory, World Scientific, Singapore.
Huang, Y2003, Selling China: Foreign direct investment during the reform era, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Lessard, D 2003, ‘Framworks for Global Strategic Analysis’, Journal for Strategic Mnagement Education, vol.1, no.1 , pp. 1-12.
Ma, T 2014, Professional Marketing and Advertising Essays and Assignments, Tony Ma, London.
White, C 2004, Strategic management, Palgrave Macmillan, Hampshire.