Introduction
Identifying the objective algorithms for optimizing individual operational processes and the entire mode of operation of the organization as a whole requires a preliminary assessment and careful analysis of available solutions designed to improve specific aspects. Based on the evaluation of the Telstra Corporation, an Australian telecommunications service provider, the relevant implications of specific theoretical and practical changes will be assessed from a range of perspectives. The change management method will be considered in terms of its impact on business outcomes and interaction with the company’s personnel, as well as in relation to the effectiveness of planning the benefits of intervention. Through critical analysis, conclusions about the change project will be given, and appropriate recommendations for future potential interventions will be highlighted. The purpose of this work implies evaluating the proposed objectives for making changes to the operating activities of the Telstra Corporation to determine the appropriateness and value of specific interventions for solving the set optimization tasks.
Organizational Context
Since the goal of the proposed project is the need to transform the individual aspects of the business of the corporation in question, the appropriate steps described as relevant solutions and interventions should be evaluated. Based on the literature review, Lewin’s 3-stage model of change is judged to be an alternative theoretical framework for this project. This concept involves following three main steps, which is a convenient methodology and involves addressing clear objectives in the context of the stated goals to implement (Dijesh and Mary, 2017, p. 1354). In Figure 1, a scheme of this model is presented.

In addition to Lewin’s model, some other theoretical frameworks are proposed to be considered, one of which is the nudge theory. This model describes incentives for pushing change within the organization and involves different stakeholders as participants in the decision-making process (Ebert and Freibichler, 2017, p. 2). Along with this framework, this is crucial to evaluate the practical measures to support changes to have an idea of all the steps taken to meet the set operational objectives for the transformation of the Telstra Corporation’s business.
Change Management Method
Based on the assessment of the potential implications on the workflow and related business objectives, the nudge theory is considered the most convenient and, most importantly, effective change method. In Figure 2, the basic structure of this model is presented, and by analyzing it, one can find that, unlike, for instance, Lewin’s model, this framework includes more steps. Both identified theoretical concepts are similar in their intervention strategy, but the nudge theory is a more robust methodology. Moreover, in accordance with the provisions of this concept, one of the prerequisites for its application in the context of the change project in question is the idea of “libertarian paternalism”, which involves influencing behavior through stimulation but not coercion (Jalili. 2019, p. 206). By addressing the goals and objectives of the project under consideration, company leaders can create a favorable environment for influencing the work intentions of subordinates, which is one of the ultimate goals of intervention. Therefore, this model is a credible theoretical framework that contributes to consolidating the proposed changes in the operational process of the organization and creating a positive background for accomplishing targeted HRM activities.
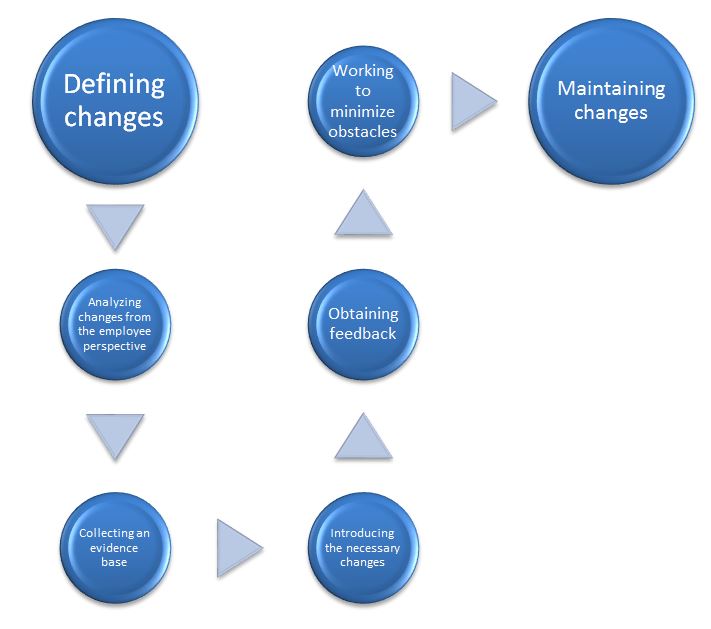
The ethical aspect of the change methodology is an essential criterion to take into account. In accordance with the structure of the considered nudge theory, interaction with employees is a mandatory step. From an ethical perspective, this factor is a significant advantage of the model since, in the absence of interaction with subordinates, there is a risk of autocracy within the organization, which, in turn, is fraught with a decrease in work engagement and job dissatisfaction on the part of the team. Compared to traditional tools for influencing job behaviors and attitudes, the nudge theory acts rather as an enabling than a mandatory framework to follow (Lin, Osman, and Ashcroft, 2017, p. 301). This perspective is consistent with the ethical standards of governance and does not violate the democratic principles of control. Moreover, even in the case of ethical debates, the theory includes the feedback stage when stakeholders can express their views on upcoming changes before they are directly implemented in the workflow, which creates an empirical background (Lin, Osman, and Ashcroft, 2017, p. 30). As a result, this concept cannot be characterized as violating the ethical standards of management.
Given the goal of the change project, particularly increasing the competitiveness of the Telstra Corporation in the target market, the chosen method corresponds to the task set. One of the important features of the nudge theory is that the framework creates cognitive stimuli based on a real picture of the current situation, thereby identifying the most relevant steps for intervention (Viale, 2019, p. 146). In other words, competencies are preserved, and only the range of upcoming operations is changing. Engaged participants are not forced to urgently learn or develop new skills but are encouraged to change traditional working patterns with an emphasis on updated objectives. Thus, by building an understanding among the organization’s employees of the need to adapt to a specific struggle, Telstra’s management sets the staff on the right course without resorting to drastic shifts in responsibilities, thereby making the change process easier.
While taking into account the features of the change management method, the respective strengths of the chosen framework can be summarized in Table 1. Based on the stepwise nature of the nudge theory, the role of each of the stages of this model can be assessed from the perspective of the impact on the work of personnel and the overall performance of the organization as a whole. The above arguments confirm the value of this method in relation to the tasks set for change and can help the corporation to strengthen its market position.
Table 1. Advantages of the Change Management Method
Identification and Management of Business Impact
The business impact of the proposed change project and its effective management can be assessed in terms of several key factors, particularly justification, communication, documentation, and evaluation. By conducting a literature review and identifying relevant findings on the given topic, an appropriate evidence base has been collected to determine which modalities and tools for the planned intervention are optimal. As criteria for justification, this is critical for corporate management to consider not only the benefits for operations but also positive implications on customer experience because this parameter is a significant aspect in building brand trust and maintaining the interest of the target audience in the services sold (Yue, Men, and Ferguson, 2019, p. 3). The rationale contributes to emphasizing convenient ways to optimize the business and, at the same time, correlates with risk minimization, including savings in labor and material resources.
Another factor related to the business impact is the communication of the planned change project to all stakeholders, including senior management and subordinates. This factor is essential for controlling the necessary intervention since relevant ideas on the ways to improve the outcomes of work can come from both team leaders and ordinary employees who can identify potential threats of failure and methods for their timely mitigation. Staff incentives directly affect the degree of engagement, and in the project under consideration, involvement in the decision-making process is an important factor in building staff confidence. In Figure 3, additional ways to increase job engagement are presented, which can be applied with changes, but in the analyzed project, no rewards and training are not promoted (Presbitero, 2017, p. 64). In the presented case, the main emphasis is on building a strong team in which each member has the right to express personal views on the upcoming changes.
As a relevant approach to identifying and managing the business impacts, the practice of documenting all the changes has been applied. This method of control is adequate because even in the absence of significant shifts in the workflow and operational outcomes, real changes can be monitored and conclusions drawn regarding the effectiveness of the steps taken. Moreover, the documentation method is actively used in research practice to interpret relevant findings and identify the optimal materials to use in the planned practice (Bathmanathan, Rajadurai, and Sohail, 2018, p. 961). The documenting method is closely related to the communication phase since all the actual tasks to implement within the change project are combined and notified in accordance with the established plan. In addition, displaying all the necessary measures allows for identifying the cost items and determining the time frame, which is a valuable prospect for effective project management.
The evaluation stage is another important step in determining business impacts and managing all processes during the intervention. This practice allows for critically assessing all possible uncertainties and comparing subtotals with planned objectives. Different stakeholders can be involved in this process, and increased participation enhances the validity of the findings through the contribution of different team members to the analysis and interpretation of current work (von Thiele Schwarz et al., 2020, p. 417). In addition, the evaluation can help identify possible barriers to the effective implementation of the tasks set, which, in turn, saves human and material resources if the causes are timely identified and eliminated. From the perspective of business impact, this management practice is an important factor in consolidating the results achieved because, without a qualified assessment, the threat of falling productivity and discrepancies between planned and real results persist. All the aforementioned aspects of intervention management are relevant methods that positively affect the change project in question.
Identification and Management of People Impact
In the considered change project, much attention is paid not only to operational interventions associated with the transformation of individual stages of the work process but also to targeted work with personnel. The role of employees in achieving the goals is extremely important, particularly in light of the aforementioned business impacts. The analysis of the impact of changes in the Telstra Corporation on the workforce and the management of these interventions can help determine the objectivity and relevance of the measures taken.
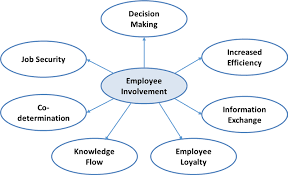
The unity of the staff within the framework of the change project is largely achieved through involvement in the decision-making process. The overwhelming majority of employees are convinced that honest and open communication between managers and subordinates regarding any changes in the operational process is a crucial factor in building mutual trust (Appelbaum et al., 2018, p. 46). Moreover, engagement in the decision-making process is not the only positive impact that can be achieved through close supervisor-subordinate communication. In Figure 4, a range of employee involvement outcomes are presented, and these implications confirm the relevance of the team member’s interaction in the context of accomplishing the desired intervention outcomes more effectively and quickly (Bashir Memon, Syed, and Arain, 2017, p. 55). The personnel of the Telstra Corporation can expect to receive comprehensive information about the anticipated results to be achieved and the necessary steps to take. These perspectives help maintain a favorable microclimate in the team, which, in turn, directly correlates with the performance and loyalty of the organization’s employees.
Due to the mechanisms of interaction with the personnel, the impact on the performance of the corporation’s employees has become a valuable implication, reflecting a positive effect on the business. Participation in the decision-making process stimulates productive activities and successful collaboration in the team. Teamwork at the Telstra Corporation has intensified as employees who are united by a common goal have become more motivated and engaged, thus confirming the aforementioned argument for involvement. Moreover, from the perspective of labor efficiency, the activities of the team members can be evaluated in the context of financial gains. According to current findings, cost analysis is one of the convenient practices used to analyze performance by comparing the results of the work performed before and after interventions (Fedotova, Tikhonov, and Novikov, 2018, p. 466). The productivity of the workforce is a criterion that determines the effectiveness of targeted work with subordinates. Due to management activities to create conditions for the involvement of personnel and successful collaboration, the impacts on the company’s employees can be assessed as positive.
To prepare the staff for participation in the change project, along with management interventions, appropriate software has been applied, particularly the Whatfix application. This program is a tool designed to train employees and act as an auxiliary platform that simplifies the decision-making process in the context of ongoing transformations (Ninan, Roy, and Thomas, 2019, p. 788). The use of such software is a convenient and common practice since this is challenging to control the performance of each individual employee. Whatfix has a number of valuable advantages, and in Table 2, a comparison between this platform and its competitors is made from the perspective of important parameters that influence usability and efficiency (Whatfix alternatives and competitors, 2021). Thus, when summing up people impacts, one can note that high personnel involvement, the necessary monitoring, including cost analysis, and the use of the effective digital tool to help employees have made a significant contribution to the performance of the Telstra Corporation team and strengthening the role of each worker in the change project.
Table 2. Whatfix Alternatives and Competitors (2021)

Benefits Management
One of the successful approaches that have made it possible to evaluate and plan the benefits of implementing the presented change project is the analysis of relevant academic literature. Through the exploration of suitable theoretical concepts and methodologies, optimal models have been selected, thereby allowing specific interventions to be based on a justified background. In general, literature analysis is a common practice for evaluating governance mechanisms in organizations and is utilized to identify the strengths or weaknesses of planned practices (Ul Musawir et al., 2017, p. 1659). By comparing the findings from academic sources, relevant trends have been identified, and subsequent change management can be carried out based on the established course of work in accordance with the evidence base. For instance, the analysis of the nudge theory and Lewin’s model has made it possible to determine the convenience of operating activities in the right direction and to argue the value of the former methodology for achieving positive outcomes. Therefore, literature analysis has become an essential factor in evaluating and monitoring planned benefits.
Another practice that has played a significant role in the benefits management and effective implementation of the planned steps of the change project is the involvement of the Telstra Corporation personnel. By working together to solve potential barriers and participating in problem-solving tasks, the team has brought together and, in addition, achieved the maximum productivity necessary to accomplish the desired results. Any change process should be accompanied by employee engagement because without the support of subordinates, leaders cannot rely on sustainable quality management and continuous improvement of the essential aspects of the work process (Bakotić and Rogošić, 2017, p. 1209). Trusting employees to suggest appropriate steps can help save money on outsourcing. This, in turn, is in line with one of the goals of the proposed design change; controlling the budget and keeping corporate assets safe has become a valuable factor in supporting employee engagement, and this measure helps maintain continuous team communication, thereby strengthening the collective spirit and increasing the likelihood of successful interventions.
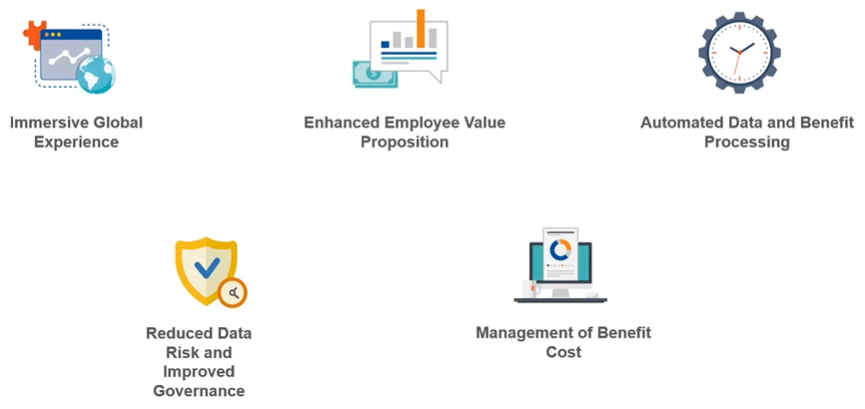
Finally, as a factor that has positively influenced benefits management and contributed to accomplishing the planned tasks in accordance with a clear plan, one can note the use of an appropriate technological base. In Figure 5, the objective reasons for utilizing innovative digital software are indicated, and among them, cost management and improved governance are relevant criteria that confirm the relevance of attracting specific tools within the considered change project (Why are companies using global technology? 2020). The aforementioned Whatfix application has become one of the instruments to control the progress of work and monitor productivity in real time, thereby making appropriate adjustments to the operational process as needed. Moreover, the digital base is an important addition not only to corporate work but also to user experience (Hamidi, 2017, p. 51). While striving to increase competitiveness in the target market, the Telstra Corporation utilizes a strong innovation base. Thus, while benefiting from this practice, the organization addresses several tasks at the same time, which indicates the effectiveness of the chosen method of work.
Findings and Recommendations
The analysis of the Telstra Corporation’s change project shows that the approach to optimizing the operating mode and achieving the set goals, particularly strengthening competitiveness and reducing costs, is adequate and justified due to the theoretical background engaged and benefits management initiatives. The nudge concept is a corresponding methodology for step-by-step addressing the stated steps, and Lewin’s model can be viewed as a supportive framework for evaluating the outcomes. The role of the interventions in the context of the impact on subordinates’ productivity and the business of the corporation as a whole is high. The use of the digital application for real-time performance monitoring is a valuable factor in enhancing benefits management and stimulating employee involvement in the decision-making process.
Future projects implying changes in the operating mode and involving the employees of the organization may include steps to promote the organization through relevant marketing steps. As the Telstra Corporation provides telecommunications services, media analysis can be performed, and actions may be taken to expand the company’s reach on specific platforms, including collaborations with other target market participants. As a mechanism for enhancing benefits management, in addition to the digital methods of monitoring and employee engagement, more attention could be given to the ways of measuring planned outcomes, for instance, by comparing performance metrics.
Reference List
Appelbaum, S. H. et al. (2018) ‘Impact of business model change on organizational success’, Industrial and Commercial Training, 50(2), 41-54.
Bakotić, D. and Rogošić, A. (2017) ‘Employee involvement as a key determinant of core quality management practices’, Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 28(11-12), pp. 1209-1226.
Bashir Memon, S., Syed, S. and Arain, G. A. (2017) ‘Employee involvement and the knowledge creation process: an empirical study of Pakistani banks’, Global Business and Organizational Excellence, 36(3), pp. 53-63.
Bathmanathan, V., Rajadurai, J. and Sohail, M. S. (2018) ‘Generational consumer patterns: a document analysis method’, Global Business and Management Research, 10(4), pp. 958-970.
Dijesh, K. J. and Mary, R. R. (2017) ‘Analysis of change models and evolving business strategies for proposed change in dynamic environment’, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(3), pp. 1351-1357.
Ebert, P. and Freibichler, W. (2017) ‘Nudge management: applying behavioural science to increase knowledge worker productivity’, Journal of Organization Design, 6(1), pp. 1-6.
Fedotova, M. A., Tikhonov, A. I. and Novikov, S. V. (2018) ‘Estimating the effectiveness of personnel management at aviation enterprises’, Russian Engineering Research, 38(6), pp. 466-468.
Hamidi, H. (2017) ‘A model for impact of organizational project benefits management and its impact on end user’, Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 29(1), pp. 51-65.
Jalili, Y. A. (2019) ‘I rather share my knowledge: applying gamification approach and nudge theory to develop an incentive system’, VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, 50(2), pp. 203-217.
Lin, Y., Osman, M. and Ashcroft, R. (2017) ‘Nudge: concept, effectiveness, and ethics’, Basic and Applied Social Psychology, 39(6), pp. 293-306.
Ninan, N., Roy, J. C. and Thomas, M. R. (2019) ‘Training the workforce for industry 4.0’, International Journal of Research in Social Sciences, 9(4), pp. 782-790.
Presbitero, A. (2017) ‘How do changes in human resource management practices influence employee engagement? A longitudinal study in a hotel chain in the Philippines’, Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality & Tourism, 16(1), pp. 56-70.
Ul Musawir, A. et al. (2017) ‘Project governance, benefit management, and project success: towards a framework for supporting organizational strategy implementation’, International Journal of Project Management, 35(8), pp. 1658-1672.
Viale, R. (2019) ‘Architecture of the mind and libertarian paternalism: is the reversibility of system 1 nudges likely to happen?’, Mind & Society, 18(2), pp. 143-166.
von Thiele Schwarz, U. et al. (2020) ‘How to design, implement and evaluate organizational interventions for maximum impact: the Sigtuna principles’, European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 30(3), pp. 415-427.
Whatfix alternatives and competitors (2021) Web.
Why are companies using global technology? (2020) Web.
Yue, C. A., Men, L. R. and Ferguson, M. A. (2019) ‘Bridging transformational leadership, transparent communication, and employee openness to change: the mediating role of trust’, Public Relations Review, 45(3), p. 1-13.