Tourism is an essential pillar of the economic growth and development of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It is crucial to enhance the apt promotion of socio-cultural and entertainment activities. On the one hand, engagement fosters a prominent boost in the diversification of the tourism experience among the customers. On the other hand, the advocacy for the Saudi Arabian cultural and entertainment engagements renders the participants recognition of social identity. Primarily, the researcher collected information from respondents within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to comprehend the foundational augmenting of culture and entertainment gaieties in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. There is an interdependent relationship between customer service satisfaction, cultural diversity, and tourism business, mainly moderated by the advancement stages in a region.
Findings
Age Distribution among Respondents
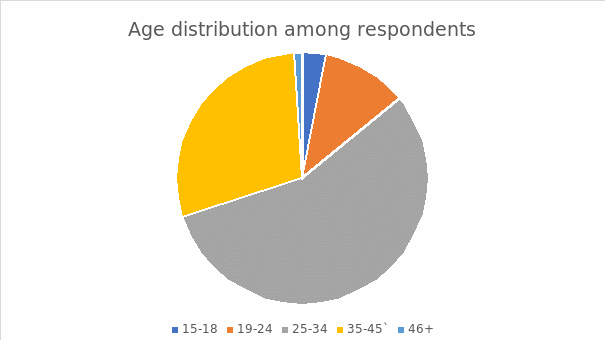
The above figure illustrates the apt distribution of ages among the respondents. The majority of the interviewees engulfed the age bracket of 25-34 years old at 56%. The second leading age group entailed 35-45 years old indicating 29% representation, while the 19-24 age group showed an 11% mark. Individuals with 46+ years old encapsulated 3% as 15-18 years old personnel represented 1%. The optimal distribution of age differences contributes to understanding comparative history and modern practices promoting culture and entertainment activities.
Gender Allotment among Respondents
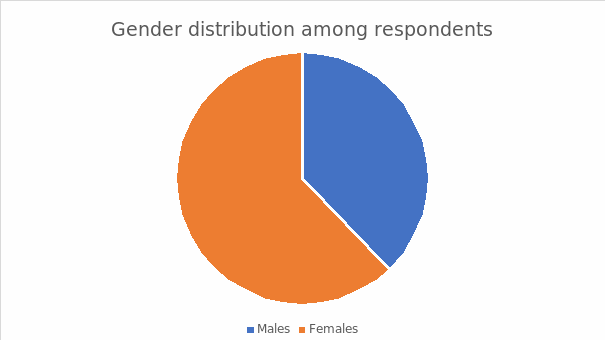
The above figure demonstrates the significant distribution of male and female respondents during the data collection. While the males represented 42%, the females enshrined 69%. Despite the dispensation among males and females, none of the respondents protested under the others category. Gender equality is an essential factor mainly because of its contribution to eliminating bias during the research process. Therefore, the researcher attributed the apportioning as a delimitation factor to justifying the scholarly exercise’s relevance and reliability.
Marital Status among Respondents
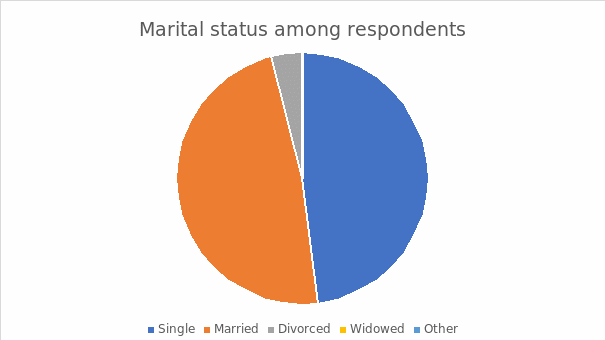
The above figure illustrates the dynamic marital statuses among the interviewees to ensure an optimal balance within the demographic spectrum. Transcendentally, individuals representing single marital status included 48%, equivalent to their married counterparts. The divorced respondents enshrined 4% while none of the personnel marked as widowed or other categories. The quotient fosters an elevated comprehension and analysis regarding the effectiveness of the development of culture and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, mainly on human behavioral response.
Occupation Status among Respondents
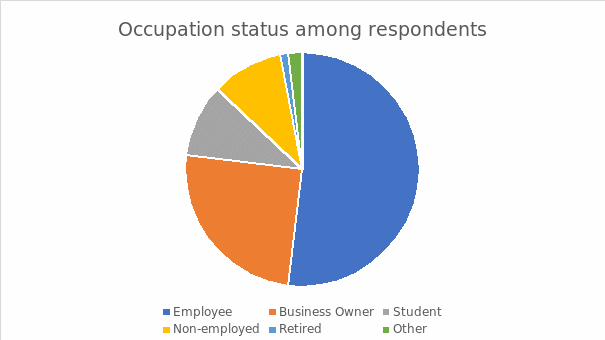
The diagram above demonstrates the dynamic occupational status among the interviewees. 52% of the counterparts were employees, 25% represented business owners, and 10% entailed students equivalent to non-employed personnel. The retired individuals exhibited 1% while 2% engulfed other interviewees in different professional and casual practices, such as house girls and freelancing. Primarily, the distribution fostered an in-depth evaluation of opinions and attitudes among people in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia concerning the development of culture and entertainment activities.
Nationality Status among Respondents
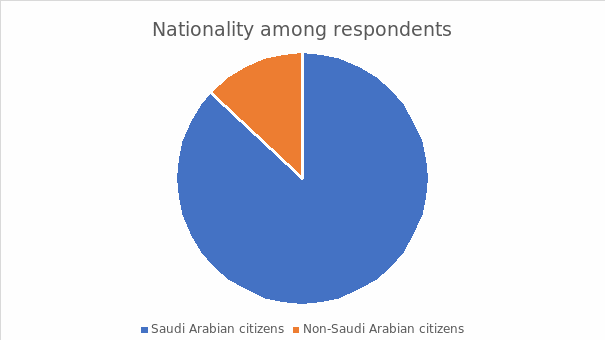
The above figure engraves the significant distribution of citizenship among the interviewees during data collection. Ideally, at least 87% of the respondents included Saudi Arabian citizens, while 13% represented non-Saudi Arabian citizens. Transcendentally, the researcher collects objective insights based on comparative analysis concerning the progress in the development of culture and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Despite the focus on diversifying the overviews, a proficient concentration on Saudi Arabian citizenship reflects reliability and relevance mainly because of the imminent engagement and association with the initiative.
Residential Status among Respondents
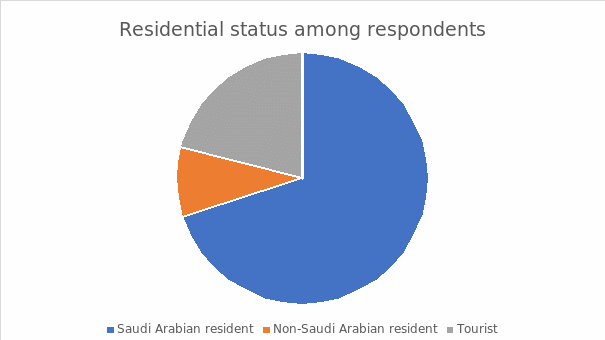
The above figure features the interviewees’ distributive sequence of residential status in three categories. The Saudi Arabian residents constituted 70%, non-Saudi Arabian residents included 9%, and the tourists enshrined 21%. Advocacy for the balanced sequence rendered the attribution and justification of the reliability quotient mainly because of the involvement of three dynamic groups. The tourist’s opinion focuses on a comparative compound regarding Saudi Arabia’s progress in culture and entertainment activities’ development and the global tourism practice. The involvement of the Saudi Arabian and non-Saudi Arabian residents plays a significant role in objectively justifying the impact on social growth and development within the region.
Initial Source of Information regarding Seasons and Festivals in Saudi Arabia among Respondents
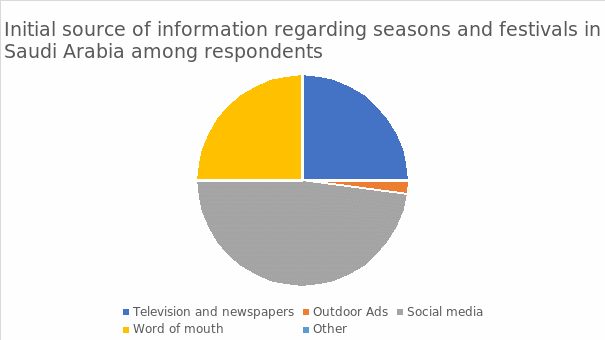
The above figure demonstrates the response frequency among the interviewees based on the first time they heard about the seasons and festivals in Saudi Arabia. The different channel media encompassed television and newspapers, outdoor advertisements, social media platforms, word of mouth, and others. Transcendentally, the percentages enshrined social media (48%), word of mouth (25%), television and newspapers (25%), and outdoor advertisements (2%). Fundamentally, different individuals attested distinctive modes of accessibility to the developmental culture and entertainment activities.
The Respondents’ Preferential Events or Location
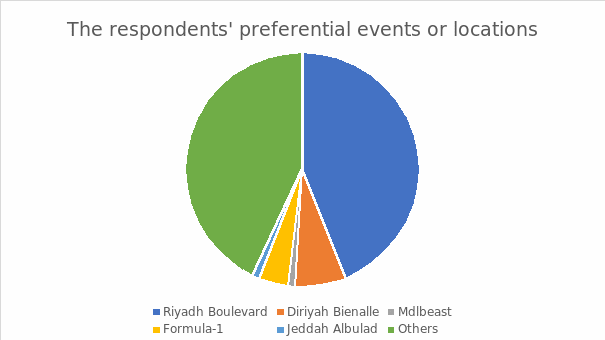
The above figure focuses on the superior locations and events reported by the respondents in Saudi Arabia. The data indicates a profound distributional balance, that is, Riyadh Boulevard (44%), Diriyah Bienalle (7%), Mdlbeast (1%), Formula-1 (4%), Jeddah Albulad (1%), and others (43%). In the case of others, the majority of the respondents argued based on events than locations as provided in the questionnaire hence the higher mark than the rest of the categories. Essentially, the response system indicated proficiency in desires based on events than locations among the interviewees.
Impact of Festivals and Events on Respondents’ Saudi Arabian Cultural Knowledge
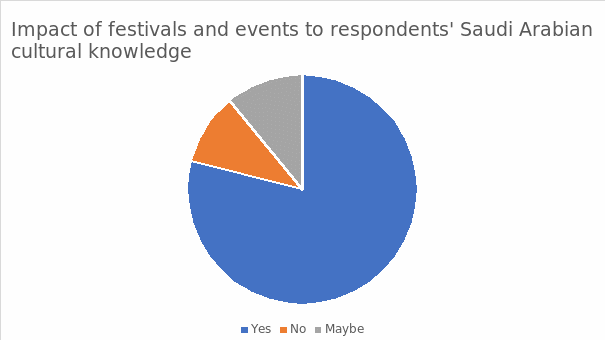
The figure above illustrates the distribution of opinions among the interviewees regarding the effect of festivals and events on individuals’ cultural knowledge of Saudi Arabian communities. Transcendentally, 79% agree that there is a profound impact, 10% disagree, and 11% show a lack of clarity. Primarily, the results affirm an effect based on the development of culture and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Comparability Quotient of Saudi Arabian Festival or Season to Other Attended Events among Respondents
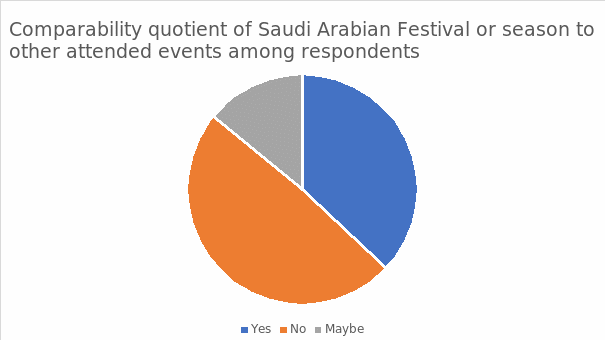
The figure above demonstrates the frequency of responses among the interviewees regarding the comparative essence of Saudi Arabian events to other attended occasions. There is a slight margin among the counterparts concerning their opinions and relativity to the consumer service experience. Ideally, 37% agree that there is a profound comparison, 49% disagree, and 14% show uncertainty regarding the differentiation and similarity indexes. The prominence fostered through the data justifies that apart from rendering an effective development structure on cultural experiences, the Saudi Arabian project attributes a unique service experience among the clients.
Positive Relationship between Customer Service Experience and Value Quotient for The Money
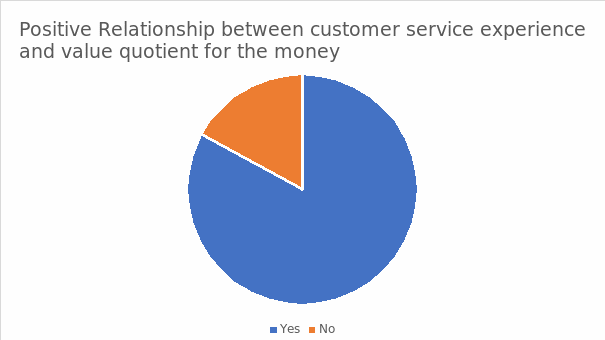
The figure above illustrates the distinctive opinions among the interviewees concerning the positive relationship between value for money and the customer service experience in cultural and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 83% of the counterparts agree that the cultural and entertainment experience is worth the money value, while 17% disagree. The response system fosters an in-depth insight regarding the interdependent relationship between customer service experience and the pricing strategy for the products and services.
Analysis
There is a significant interdependent relationship between customer service experience, satisfaction, and loyalty under the spectrum of developed cultural and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. According to the findings, one of the coherent factors that indicate success in the implementation process of the endeavors entails an average ranking of 7 on customer service experience among the respondents. Apart from the average rating, the respondents further show a proficient attachment indicating the lack of association between the product and service and different global tourism quotients. Ideally, the findings establish an apt outcome of the necessity of promoting cultural heritage and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Cultural Diversity in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is one of the best countries to visit and explore, mainly because of its dynamic features and cultural practices. The geographic location of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is Southwest Asia and within the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. It is the largest country in Arabia, and a king rules it, with a significant part of the year experiencing an extremely hot climate (Alofan et al., 2020). The kingship is hereditary, and it is the responsibility of the royal family to determine the critical governance ideologies within the country. Apart from the governance system, it is crucial for the teams visiting the country to note that the nation upholds profound policies regarding behavior and morals, especially in the public domain.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia utilizes the Sharia law and court system to enforce order within the society. Therefore, rulings in the court reflect Islamic beliefs and traditional practices. Transcendentally, it is vital for visitors to learn dynamic etiquette and social interaction codes. One of the nation’s nominal rules is that the Saudi government forbids any public display of affection, including handshakes. It is an initiative that regulates immorality hence the justification for the prohibition of alcohol consumption mainly in the public domain. Although polygamy is allowed in the country, a significant percentage of the residents formally marry through the Sharia court, and any other religious marriage ceremony is not recognized. Primarily, all policies reflect the appreciation of the Muslims’ practices. Therefore, it is vital to note the Islamic ceremonies and events to avoid the violation of the virtues. The conditional behavioral context is further affirmed through the developed etiquette among all dwellers and visitors during the Ramadhan period. It is essential to avoid eating in the public domain to circumvent discipline measures from the government.
In a different aspect, the dress code for women involves ensuring the covering of all body parts. An Islamic law construct ensures morality, and a female visitor is not allowed into the country while traveling alone. Primarily, a woman in Saudi Arabia is inferior to a man hence the lower representation in the senior position. Transcendentally, women mainly engage in house chores and soft-core labor engagements. While traveling alone, the female visitor is mandated to present an invitation from a resident or husband in the country. The Sharia government system articulates instructions regarding the interaction between a man and a woman (Alofan et al., 2020). The law offers an allowance for secret dating, and the legal age for marriage encapsulates 18 years and above. Homosexuality, rape, and infidelity are forbidden, and disciplining measures bind the accused. There is a distinct moral code of behavior and interaction in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Cultural diversity in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia focuses on Islamic practices and belief systems. Therefore, the government structure is in the Sharia spectrum and the courts. It is crucial for a visitor with a family to note that a misdemeanor is punishable in the public domain. Further, marriage and coupling is justified within the constraints of the Islamic religion. Apart from marriage, individuals are forbidden from alcohol consumption, and the country appreciates support and respect for the Islamic system. In the case of violating the legal framework, the person faces prominent disciplinary measures that include the death penalty. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the visitors to adhere to the moral code and appreciate Islamic beliefs.
One of the prominent issues during the Hajj celebration is overcrowding around the worship areas. In the case that a public health problem arises during the Hajj celebrations, it is essential to regulate the mass gatherings and the interactions. A significant percentage of the global population visits the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for the Hajj (Alroqi, 2017). Therefore, the emergence of a health problem threatens global population health. It is crucial that researchers focus on the significance of the Islamic celebrations and the government efforts to conduct law enforcement. As a result, the research begins with evaluating the health problem and its level of impact on human health. The realization of the nature of the disease gears the development of cautionary measures to boost performance. Providing information regarding the health problem is an objective initiative that cultivates the derivation of effective measures to protect the public during the Hajj.
The establishment of objectivity in research spearheads the interdependence between the dynamic variables. The dynamic variables encompass the significance of Hajj to the Muslim population and the risks associated with the health problem. The assessment of the interdependent relationship ensures the derivation of information about the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders (Alroqi, 2017). As a result, the researcher conducts an in-depth content analysis based on the essence of integrating the interests of the stakeholders and the prevailing health problem. The ideal objective that a researcher seeks to establish entails an inductive or deductive conclusion based on the analysis and insights from different sources, both primary and secondary.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia hosts a significant Islamic population annually for events such as the Hajj. Therefore, the emergence of a health problem during the Hajj poses a profound risk to the global population mainly because the attendants travel from different nations. It is paramount to establish the effect of the health problem and involve all stakeholders in developing strategies that protect human lives and promote essential religious practice.
The Significance of Sustainable Growth and Development
There is a proficient interdependent relationship between technological advancement, intensified human activities, and the alteration of the natural environment. According to Burns et al. (2018), the emergence of technology intensified interaction between the natural environment and individuals. However, the negative implication contributed to altering nature’s aesthetic value. Ideally, it is the responsibility of key stakeholders to establish policies that regulate the exploitation of natural resources while ensuring the production of sufficient products for human consumption and satisfaction. Technology advancement is a necessary tool that improves the quotient of resource exploitation and satisfaction of the human population under the gradient of sustainability.
Over the decades, the human population increased mainly because of the optimal consumption and availability of adequate resources. In Akpoviroro and Owotutu’s (2018) research, the researchers argue that the interaction between people and nature is a system akin to a business environment. According to the researchers, proficient interaction between internal and external environmental variables renders an apt outcome concerning competence (Akpovirovo & Owotutu, 2018). Transcendentally, the relationship between nature and human beings relies on distinctive variables. One of the vital issues fostered by the relationship is deforestation, which diminishes the value. On the one hand, the increase in human population rendered deforestation to create space for settlement. On the other hand, the practice is attributed to the limitation of natural habitat for wildlife hence intensifying human-wildlife conflict among the entities. Primarily, technological advancement empowered personnel to destroy the natural environment by compromising its aesthetic value.
A different negative outcome of the interaction between technological advancement and nature is the overexploitation of non-renewable sources of energy. Gao et al. (2018) argue that the green initiative that emerged through the establishment of sustainable development goals was a necessity for promoting the protection of non-renewable natural resources. According to the researchers, the overutilization of water and fuel as sources of energy led to one consequential natural event (Gao et al., 2018). On the one hand, the overexploitation of water for hydroelectric power production negatively affected aquatic life mainly because of pollution. On the other hand, the source of fuel enshrines the trees hence the promptness in clearing trees for the sustenance of manufacturing industries. However, companies incurred lesser costs, and the process rendered reducing tree cover globally while reducing biodiversity. Notably, technological advancement formed the baseline consequence of the degradation of the pristine and aesthetic value of the natural environment.
The reduction in the tree cover and the intensified expansion of manufacturing industries played a profound role in the climatic change. Goudie (2018) depicts that the human population significantly contributed to the degradation of natural environmental value by exploiting technological tools. The research further establishes that one of the outcomes is climate change (Goudie, 2018). The concept refers to the weather patterns’ alteration causing an optimal impact on the living entities on earth. The reduction of tree cover led to the significant emission of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Trees aptly use carbon dioxide for growth; however, the reduction renders the accumulation in the atmosphere. As a result, CO2 forms a layer that, apart from shielding the earth from escaping hot air, reacts with the ozone layer. The ozone layer contributes to the protection from the penetration of dangerous sun rays on the earth’s atmosphere. Therefore, the concentration of CO2 fosters global warming mainly because of the increased temperature and hot air in the atmosphere.
The increased presence of hot air profoundly impacts climate change due to the contribution to the melting of ice in mountains and Arctic regions. The ice melts into water, which leads to an increase in the volume of oceans and a rise in oceanic tides. Ideally, the relationship of technological advancement significantly contributes to the intensification of the domino effect towards the adept concept of climate change. Despite the adverse effects posed by technological advancement on the relationship with the natural environment, Kattumuri (2018) establishes that the solution and mediating factor to interdependence is sustainability.
Sustainability is the optimal exploitation of natural resources for the long term without compromising the aesthetic value. Kattumuri (2018) articulates that it is crucial to identify distinctive, sustainable solutions in the changing environment. The main reason engulfs the ability to incorporate mediating features complementing the vital use of the resources. An excellent example is the replacement of non-renewable natural resources with renewable natural resources. A significant paradigm shift in the manufacturing industries involved intensifying solar and nuclear energy use for machinery and household processes.
A different sustainable initiative elaborated through the sustainable development goals is the regulation of fishing and the disposal of plastics. Despite the technology providing tools for intensifying fishing activities, institutions incorporate policies that enhance the monitoring of economic activity as a formative aspect of enhancing the protection of aquatic diversity.
One of the significant issues that technology fosters in the natural environment is the intensification of the production of plastics. According to Kattumuri (2018), the use of non-biodegradables is a threat to the environment mainly because of the prevalent pollution of the aquatic environment. The research indicates that the core responsibility among counterparts encompasses incorporating measures regulating the significant use of plastics. One of the natural environments profoundly polluted by plastics is aquatic. The main reason enshrines the disposal of plastic bags and bottles in the water bodies that drain into the ocean. Transcendentally, the technology establishes the solution to the problem by introducing biodegradable packaging materials. It is the responsibility of the relevant stakeholders to incorporate regulations attributing to the limited use of plastics to limit environmental pollution.
Technological advancement significantly contributes to the intensified improvement of the living quotient among people. One of the approaches that technology steered the amplification of peoples’ livelihood encompasses agricultural activities. According to Kumar et al. (2019), technology fostered the production of chemical fertilizers, impacting the effective growth of crops used to feed the increasing human population. The researchers indicate that chemical fertilizers intensify the agricultural production of food while improving quality. However, the environmental consequence enshrines the leakage of the chemicals into the aquatic life and the soil. Despite the benefits of chemical fertilizers, they alter the salinity and acidity levels of the soil, which significantly affects the survival of the microorganism responsible for the decomposition of biodegradable components. The solution to the pollution issue involves using fertilizers with lesser chemical composites and percentages while ensuring the regulation of their use in the agricultural sector.
A proficient advantage of technological advancement to human society is contributing to the development of a global village. Coccia and Bellito (2018) argue that technology fostered the intensification of the evolution process of human society. On the one hand, technology steered the development of empowerment tools for distinctive processes. On the other hand, computerization is attributed to the emergence of the internet and social media networks. Internet fostered the optimal sharing of information among people from different geographical regions. Transcendentally, a significant percentage of the communities attained insights concerning the technological tools and the accessibility to boost the quality of living.
Individuals exploit technological systems for particular processes with apt accuracy in modern society. Von Grunebaum and Caillois (2021) stipulate that computerization and automation of processes is a dream for distinctive human societies. The key benefit of the machinery enshrines promoting the efficacy level in the production process. Ideally, the concept further affirms Bai’s et al. (2020) insight regarding blockchain technology. Bai et al. (2020) depict that in modern society, the efficiency in accomplishing technology activities is attributed to the intersection of crucial variables to enhance competence. The entities encapsulate sustainability, business, environment, and strategy. Technology harmonizes the operability of business activities across different environmental conditions to foster sustainability as an emblem of management strategy.
The Relationship between Product and Service Diversification and Customer Service Experience in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
The introduction of festivals and seasons within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia significantly contributes to the diversification of tourism products and services. Research by Ibrahim et al. (2021) establishes the incorporation of cultural and dynamic entertainment mainframe attributes to the apt improvement in the tourism business within the region. An excellent example is the demonstrated interests and relations among respondents from the findings. One of the interviewees attests that the service experience reflects a surprise element akin to the London winter wonderland. Additionally, the findings further illustrate a variation in opinions concerning the uniqueness of the practice. Essentially, the implementation of the program in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a boost to the socioeconomic growth and competence across the Middle East and internationally on tourist customer satisfaction quotient.
Customer service experience is vital in amplifying a profound framework on the importance of coordination among the stakeholders. During data collection, the researcher identifies inherent variants anent to the value worthiness of money among the respondents. The majority of the counterparts indicate that the core reason for increased expenditure despite high prices enshrines the uniqueness and product diversity. It is a perspective that Ibrahim et al. (20210 further approve based on the necessity of integrating distinctive tourist attractions. The researchers articulate that the clientele baseline gauges the product and service worthiness through advertising strategies (Ibrahim et al., 2021). Transcendentally, it is crucial to introduce factors enhancing the use of dynamic media channels, mainly social media, television, and radio to promote tourism products. The research findings during data collection indicate that majority of the respondents accessed the promotions through social media platforms, television, newspapers, and word of mouth. As a result, the outcomes establish the importance of intersecting the promotional media with highly competent approaches to product and service development.
Customer service experience is a multidimensional phenomenon significantly influenced by the essence of product and service diversification. One of the distinctive features to explore entails the development of a structure improving stakeholders’ participation and coordination in tourism development. Ibrahim et al. (2021) argue that the promptness in amplifying tourism activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia emanates from decreasing economic growth from oil refining and exportation. Transcendentally, the researchers indicate that product diversification plays a profound role in the mediation of sustainable economic development. The research findings demonstrate a relative association and success indicator regarding the implementation process. Ideally, the incorporation of cultural and entertainment activities within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia contributed to the identification of variant preferential locations. During the analysis, the researcher identifies that the majority of the respondents prioritize events that locations thus justifying a customized and highly competent service experience quotient. Despite the respondents showing interest in such locations as Riyadh Boulevard, Dirriyah Bienalle, Mdlbeast, Formula-1, and Jeddah Albulad, a significant percentage recall distinctive attachments and personal appeals to events.
Understanding customer service experience as a variable during culture and entertainment activities development promotes sustainability. Abuhjeeleh (2019) investigates the dynamic initiatives utilized by Saudi Arabian government to achieve the vision 2030 goals. Within the tourism sector, the researcher notices that the main aim involves diversifying tourist activities. The approach fosters sustainability based on the optimal utilization of the available resources at a scalable rate. Research findings establish that in addition to intensifying the money worthiness, the intimacy with the Saudi Arabian cultural construct fosters an influx of tourists, evident from the statistical analysis. The research results indicate that the prominent factor attributing to sustainability encompass demographic diversity and natural resource exploitation. Although Ibrahim et al. (2021) advocate for establishing additional tourist destinations and attraction elements, the scholars agree that promoting cultural practices fosters prominent and positive effects. The core paradigm shift entails amplifying the customer service experience within the spectrum of product and service diversity on short- and long-term outlines.
The Relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Sustainable Socio-Economic Development in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
The Saudi Arabian government proficiently upholds the sustainability initiative within the growth and developmental frameworks. Transcendentally, Habibi (2019) focuses on the vision 2030 as a balance sheet, especially about tourism activities. The researcher appreciates the incorporation of cultural and entertainment activities mainly because of the imminent diversity (Habibi, 2019). Over the decades, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia optimized pilgrimage as the core tourist activity involving the visitation of Muslims globally visiting Mecca. Despite the religious significance, the endeavor fostered optimal consequences to the socio-ecological environment due to the congestion. However, incorporating cultural and entertainment practices within the tourism mainframe contributes to the distribution of entities and tourists across dynamic regions. An excellent example is cultural event planning in Riyadh and Diriyah Bienalle on different dates. The approach renders the product and service diversity among the tourists based on the variety of consumptive baselines.
The implementation of a tourism program on cultural and entertainment facets in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia plays a crucial role in the decongestion of the tourist population across the region. Habibi (2019) depicts that the interim balance sheet in the scope of tourism development entails the incorporation of methodologies reducing the populace percentage on visitations while enhancing an optimal trickle-down effect of accrued benefits. An excellent illustration is a comparative quotient on the ideological regions the respondents in the research affirm as the next destinations. During data collection, the researcher notices that at least 93% of the interviewees plan to visit other Saudi Arabian cultural tourist destinations to intensify the service experience. On the one hand, the respondents argue the pricing of tourism commodities is high compared to other global destinations. In a different spectrum, the interviewees establish that the worthiness of money is prominent in other international regions. Transcendentally, the introduction of cultural and entertainment events and festivals emerges as a sustainable solution for boosting the tourism business in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Customer satisfaction is a mediatory factor in the paradigm shift concerning the development of cultural and entertainment activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In the study by Alotaibi (2021), the scholar identifies inbound tourism as a prominent factor in elevating the business and return on investment to major entities. The main argument lies in understanding the essence of distributing the accrued benefits. The intersection of cultural and entertainment activities within the routine practices among the Saudi Arabian residents and non-residents attributes to the interest build-up in inbound tourism. Understanding an individual’s socio-cultural background plays a vital role in the development of social identity. As a result, the participation of the Saudi Arabians in the tourism program proficiently impacts self-realization and appreciation of traditional and conceptual origins. In the research findings, there is an apt relation between the frequency of Saudi Arabian citizenship, residency, and indebtedness to attaining cultural knowledge. The respondents agree that apart from amusement, the personalities seek further insights regarding the Saudi Arabian heritage.
The customization of service experience yields intensified satisfaction and loyalty mainly under the overview of comparative inbound and outbound tourism. Alshammari et al. (2019) postulate that there is a profound gender disparity in the distribution of inbound tourism frequency among Saudi Arabian. Akin to the research findings, the majority of the female respondents actively affirmed the association between the cultural experience with childhood memories of visiting different regions. Customer satisfaction attributes to the alignment of loyalties concerning participation in the local tourism activity. The advocacy for inbound tourism on cultural and entertainment activities enhances the interaction and exchange of knowledge among the Saudi Arabian, enriching the heritage. Ibrahim et al. (2021) further acclaim that it is the responsibility of the Saudi Arabian government to ensure the proficient proclamation of dynamic heritage sites. The initiative plays a crucial role in promoting diversity and prestige among the residents and nationalities on demographic diversity.
The Relationship between Customer Loyalty and the Development of Cultural and Entertainment Activities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
The core mandate of promoting customer loyalty encapsulates customizing the service experience quotient within the multidimensional phenomenon of cultural and entertainment activities. Alotaibi (2021) postulates that the preferential baselines among youths in the tourism business in Saudi Arabia involve the promotion of inbound activities. Apart from enhancing unity among the citizens and residents, the program attributes to the prevention of acculturation incidences. A significant percentage of local cultures encounter a major threat under the paradigm of commercialization and commodification hence eventually losing their meaning and relevance. Therefore, Alotaibi (2021) depicts that the core mandate among the stakeholders encompasses implementing policies ensuring the boost in the heritage against the capitalistic consequence upon the traditional cultures. One of the crucial entities of culture and entertainment activities enshrines the retention of a prominent aesthetic value. Ideally, intersectionality focuses on an apt necessity of amplifying youths’ participation and the elderly towards promoting the intergenerational transfer of cultural knowledge.
The primary customer loyalty attribute involves the promotion of an aesthetic value quotient leading to a unique customer service experience. Transcendentally, Alotaibi (2021) and Abuhjeeleh (2019) concentrate on a profound essence of integrating initiatives on interdependence to advocate for product and service diversity. Tourism is an emblem of Saudi Arabia’s economy mainly because of the diminishing returns. Transcendentally, it is crucial to establish the core foundational element of customer loyalty features. On one spectrum, the research findings articulate that the respondents encounter distinctive surprise features during the cultural and entertainment activities’ experienced in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. An alternate perspective enshrines an articulation of client feedback and relativity to the advertising media channels. The core mandate among the relevant stakeholders engulfs a determinant concept upon improving the customization features of cultural practices.
Different tourist destination sites feature distinctive service experiences among tourists. During data collection, a significant percentage of respondents’ feedback enshrines complaints on the high pricing of commodities and services. The analysis justifies the prominent impact on the essence of involving the government and the public in the implementation process of the tourism program. The lack of coherence leads to the unsustainable exploitation of resources and opportunities, negatively affecting consumers’ loyalty index. Habibi’s (2019) interim balance sheet focuses on the establishment of features, such as promotional heritage sites, formalizing cultural events and festivals, and integrating the norms within the governance system and structure. Intensifying inbound against outbound tourism fosters the profound exchange of value and financial benefits within the Saudi Arabian community. As a result, the international society identifies the coherent value quotient of Saudi Arabian cultural and entertainment activities based on authenticity and aestheticism.
Reference List
Abuhjeeleh, M. (2019) ‘Rethinking tourism in Saudi Arabia: Royal vision 2030 perspective’. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure, 8(5), pp.1-16.
Akpoviroro, K. S. and Owotutu, S. O. (2018) ‘Impact of external business environment on organizational performance’. International Journal of Advance Research and Innovative Ideas in Education, 4(3), pp. 498-505.
Alofan, F., Chen, S. and Tan, H. (2020) ‘National cultural distance, organizational culture, and adaptation of management innovations in foreign subsidiaries: a fuzzy set analysis of TQM implementation in Saudi Arabia’. Journal of Business Research, 109, pp. 184-199.
Alotaibi, N.B. (2021) ‘Youth attitudes towards the economic and social impacts of inbound tourism in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(7), pp. 451-458.
Alroqi, H. M. (2017) Perceptions of the community toward the nursing profession and its impact on the local nursing workforce shortage in Riyadh. Doctoral dissertation. Anglia Ruskin University. Web.
Alshammari, F., Whaley, J., Hur, S. and Kim, Y.K. (2019) ‘Gender differences in motivations to attend festivals in Saudi Arabia’. International Hospitality Review, 33(4), pp. 126-141.
Bai, C. A., Cordeiro, J. and Sarkis, J. (2020) ‘Blockchain technology: business, strategy, the environment, and sustainability’. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(1), pp. 321-322.
Burns, T. J., Hekmatpour, P. and Speer, K. C. (2018) ‘Human Interaction with the Natural Environment: the POETICAS Model as a Framework for Understanding and Praxis in Late Modernity’. International Journal of environment and Climate Change, 8(3), pp. 234-68.
Coccia, M. and Bellitto, M. (2018) ‘Human progress and its socioeconomic effects in society’. Journal of Economic and Social Thought, 5(2), pp. 160-178.
Gao, Y., Tsai, S. B., Xue, X., Ren, T., Du, X., Chen, Q. and Wang, J. (2018) ‘An empirical study on green innovation efficiency in the green institutional environment’. Sustainability, 10(3), p. 724.
Goudie, A. S. (2018) Human impact on the natural environment. John Wiley & Sons.
Habibi, N. (2019) ‘Implementing Saudi Arabia’s vision 2030: an interim balance sheet’. Middle East Brief, 127, pp. 1-9.
Ibrahim, A.O., Baqawy, G.A. and Mohamed, M.A.S. (2021) ‘Tourism attraction sites: boasting the booming tourism of Saudi Arabia’. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 8(4), pp. 1-11.
Kattumuri, R. (2018) ‘Sustaining natural resources in a changing environment: evidence, policy and impact’. Contemporary Social Science, 13(1), pp. 1-16.
Kumar, R., Kumar, R. and Prakash, O. (2019) Chapter-5 The impact of chemical fertilizers on our environment and ecosystem. Chief Editor, 35, p. 69.
Von Grunebaum, G. E. and Caillois, R. (Eds.). (2021) The dream and human societies. University of California Press.