The FIFA world cup is a significant mega-event that prominently engages people from diverse backgrounds for sporting competitions. The concept fosters a profound impact on the host country, mainly the economic growth and development (Mair et al., 2021). Qatar is hosting the FIFA sporting activity in 2022, rendering optimal opportunities for improving brand image and business operations. In this case, the government expects an influx of visitors, thus the focus on incorporating measures to enhance branding. Mair et al. (2021) postulate that the accommodation of the tournaments contributes to the proficiency in socially-based positive and negative effects. The researchers further articulate that the critical approaches profoundly influenced include sports development, environmental sustainability, social cohesion, and Qatar branding. The hosting of FIFA by Qatar is a prospect to market the region based on strategic branding.
Hosting a mega-event is a quotient that prominently contributes to the boost of the socio-cultural and economic performance of a country (Mair et al., 2021). Research indicates that the preparation process fosters the improvement of infrastructure and the international status as a long-term investment concerning high standard sporting venues (Knott et al., 2012). The Brazilian government focused on the essence of branding the cities as tourist destinations based on the highly developed infrastructure (Ritchie et al., 2009). Therefore, hosting mega-event poses imminent demand on investment to advance the facilities’ standards but renders an opportunity to intensify international branding practice.
Qatar is a city within the Asian continent that poses prominent infrastructure to support distinct mega-events. According to records, the region hosted 2006 Asian-based games, the 2015 handball championship, and the 48th Artistic Gymnastics world championships (Meza Talavera et al., 2019). The occasions attributed to the economic growth and development boost to enhance the trickle-down effect of the accrued benefits. The government optimized on improving environmental sustainability and Qatar’s branding. It is vital to develop measures and guidelines that intensify the interrelation overview concerning the optimization of the gains from the increased influx of visitors across Qatar.
The hosting of FIFA World Cup 2022 in Qatar intensifies the credibility of the destination for corporate and tourist activities. On the one hand, the international community attains an insight concerning the capacity of the region’s administration to render competent hospitality services (ElGahani & Furlan, 2018). On the other hand, the Qatar society attains the chance to advance labeling of the city in Asia and globally. This study aims at investigating the dynamic effect of hosting FIFA to Qatar as a brand.
Literature Review
Since the focus is on assessing the sports mega-event on Qatar brand image, it is reasonable to identify the literature that focused on how such events already affected other host nations and cities. Evidence from reputable, credible, and timely scholarly articles will demonstrate how various mega-events impacted Brazil, South Korea, London, Russia, and others. The section can figuratively be divided into two parts because some authors highlight the positive effects of hosting such events, while others emphasize adverse outcomes.
To begin with, one should explain that many scholars comment on the positive influence of the World Cup, Olympic Games, and others on host countries and cities. According to Amponsah et al. (2018), image promotion and positive attitudes arise because such events result in infrastructure development and the influx of tourists. This statement denotes that tourists get acquainted with the country or city and distribute its good reputation globally. Lu and Lin (2020) also admit that successful hosting of a mega-event helped a country or a city raise the image with the help of having a developed infrastructure and displaying national identity. Many researchers support this claim and stipulate that the World Cup, the Olympic Games, and similar competitions offer numerous advantages to hosting sides, and they include economic development, infrastructure improvement, tourism increase, and cultural exchange (Kim et al., 2021; Perić, 2018). These findings explain how the FIFA 2022 World Cup can improve Qatar brand image.
Other factors can also contribute to improving the country’s reputation. According to Kim et al. (2019), mega-events can lead to a positive change in safety and urban images. Simultaneously, Rojas-Méndez et al. (2019) state that positive media coverage of the hosting country can lead to a better reputation that, in turn, will result in an increased tourism level. However, it is necessary to admit that not every event implies such benefits, meaning that proper organization can only lead to advantages (Kobierecki & Strożek, 2021). This information demonstrates that it is rational to invest costs in organizing such events and benefiting from them.
However, one should admit that positive effects are not obligatory, and it is reasonable to consider articles presenting adverse impacts. Ren and Li (2019) clarify that outcomes depend on what specific events are considered, meaning that the Summer Olympics typically lead to positive effects, while the World Cup’s impact is uncertain. Mega-events can lead to “security risks, traffic problems, environmental concerns,” and others (Perić, 2018, p. 176). A study of the 2016 Summer Olympics in Brazil also demonstrates that the country did not receive benefits and improved brand image because the event was highly criticized by the media (Tasci et al., 2019). This information indicates that prestigious tournaments and competitions can provide hosting countries with significant disadvantages.
In addition to that, a brand image can suffer even when an event was organized according to high standards. For example, Hahm et al. (2019) state that mega-events cannot lead to positive outcomes when they cannot change common expectations and visitors’ negative beliefs. This statement refers to the fact that Americans did not report an improved brand image of South Korea following the 2018 Winter Olympic Games (Hahm et al., 2019). Furthermore, the 2012 Olympic Games in London did not result in improved city branding, irrespective of the fact that the event was successful and did not witness much criticism (Kenyon & Bodet, 2018). This information demonstrates that it is challenging to predict how a mega-event will affect the country’s brand image. However, a hosting party should organize the event as per the best standards to maximize the chances of meeting positive impacts.
Significance of the Study
The key stakeholders in a country hosting a mega-event encompass the citizens, organizers, and decision-makers (Davies, 2021). Optimal coordination among the counterparts intensifies the trickle-down effect of accrued benefits when hosting FIFA. In this case, the participation of the dynamic groups contributes to the branding of the city at a local and international level. Therefore, the contextual exploration renders an addition to the existing literature mainly under the spectrum of the Arabian region. Notably, the proposed model theoretically and practically examines economic, cultural, and social benefits as composites to Qatar and the country’s brand image.
Theoretical contribution
The hosting of mega-events is an initiative that fosters a prominent effect on a country. Different research studies explored distinct perspectives concerning the impact of FIFA activity in a nation. According to Davies (2021), mega-events render apt benefits to a country based on the participation of the stakeholders. Ritchie et al. (2009) indicated that the sporting mega-event marketed London in 2012 as a luxurious tourist site with dynamic highly-graded facilities. The theoretical contribution of this study encompasses deriving insights regarding the impact of FIFA on Qatar’s branding. In this case, the study attributes to an assessment of the trickle-down effect across the Asian region hence a pool of information within the international spectrum effect of mega-events.
Practical contribution
The practical contribution of this study refers to the fact that every mega-event is an opportunity for a host country to grow economically and socially. In particular, Azzali (2019) admits that the FIFA World Cup can be considered an excellent opportunity for urban transformation. Lu and Lin (2020) also support this statement and claim that drawing sufficient attention to organizing such an event can provide the hosting party with many advantages. That is why it is possible to state that the study is practically significant because it reveals that Qatar should do its best while organizing the FIFA 2022 World Cup to receive numerous positive effects.
Research Model
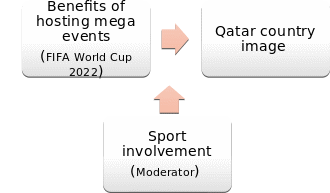
Methodology
The study will utilize exploratory research design and quantitative analysis of the data collected as an approach to measure the proposed model. The main purpose of exploiting the quantitative aspect entails determining the effectiveness of the relationships between the dynamic variables. The researcher will use a stratified random sampling technique during the gathering of data under the spectrum of different nationalities. The core mainframe encompasses assessing responses from individuals in Qatar with various citizenship. In this case, the researcher will objectively employ the constructs of the measuring scales from previous studies to alleviate bias.
Research Objectives
- To investigate the impact of hosting FIFA on a country.
- To measure the relationship between hosting FIFA 2022 and Qatar’s brand image.
- To assess the impact of respondents’ involvement in the relationship between hosting FIFA 2022 and Qatar’s brand image.
References
Amponsah, C. T., Ahmed, G., Kumar, M., & Adams, S. (2018). The business effects of mega-sporting events on host cities: An empirical view. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 16(3), 324-336. Web.
Azzali, S. (2019). Challenges and key factors in planning legacies of mega sporting events: Lessons learned from London, Sochi, and Rio de Janeiro. International Journal of Architectural Research, 14(2), 203-218. Web.
Davies, R. (2021). Defining legacy: A critical comparison of legacy literature definitions and the legacy objectives of the 2022 Qatar FIFA World Cup. Generations, 7, 8. Web.
ElGahani, H., & Furlan, R. (2018). Post-2022 FIFA World Cup in the State of Qatar: Urban regeneration strategies for Doha. Journal of Urban Regeneration & Renewal, 11(4), 355-370. Web.
Hahm, J. J., Tasci, A. D., & Terry, D. B. (2019). The Olympic games’ impact on South Korea’s image. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 14, 100373. Web.
Kenyon, J. A., & Bodet, G. (2018). Exploring the domestic relationship between mega-events and destination image: The image impact of hosting the 2012 Olympic Games for the city of London. Sport Management Review, 21(3), 232-249. Web.
Kim, Y., Kim, J., Cho, S., & Yim, K. (2019). The impact of mega sporting events on host country’s destination images: The cases of the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics and 2015 Beijing IAAF World Championships. Sport Marketing Quarterly, 28(3), 148-164. Web.
Kim, M., Park, S., & Kim, S. (2021). The perceived impact of hosting mega-sports events in a developing region: The case of the PyeongChang 2018 Winter Olympic Games. Current Issues in Tourism, 24(20), 2843-2848.
Knott, B., Allen, D., & Swart, K. (2012). Stakeholder reflections of the tourism and nation-branding legacy of the 2010 FIFA World Cup for South Africa. African Journal for Physical Health Education, Recreation and Dance, 18(sup-2), 112-122. Web.
Kobierecki, M. M., & Strożek, P. (2021). Sports mega-events and shaping the international image of states: How hosting the Olympic Games and FIFA World Cups affects interest in host nations. International Politics, 58(1), 49-70. Web.
Lu, H. F., & Lin, H. W. (2020). Does the legacy governance of major sporting events affect urban development? The stakeholder’s perspectives on the Taipei 2017 Universiade. International Journal of Sports Marketing and Sponsorship, 22(1), 87-106. Web.
Mair, J., Chien, P. M., Kelly, S. J., & Derrington, S. (2021). Social impacts of mega-events: A systematic narrative review and research agenda. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 1-22. Web.
Meza Talavera, A., Al-Ghamdi, S. G., & Koç, M. (2019). Sustainability in mega-events: Beyond Qatar 2022. Sustainability, 11(22), 6407. Web.
Perić, M. (2018). Estimating the perceived socio-economic impacts of hosting large-scale sport tourism events. Social Sciences, 7(10), 176. Web.
Ren, K. Y., & Li, Y. J. (2019). Economic impact of mega sporting events on host country. 2019 International Conference on Education Reform, Management Innovation and Social Science. DESTech Transactions. Web.
Ritchie, B. W., Shipway, R., & Cleeve, B. (2009). Resident perceptions of mega-sporting events: A non-host city perspective of the 2012 London Olympic Games. Journal of Sport & Tourism, 14(2-3), 143-167. Web.
Rojas-Méndez, J. I., Davies, G., Jamsawang, J., Duque, J. L. S., & Pipoli, G. M. (2019). Explaining the mixed outcomes from hosting major sporting events in promoting tourism. Tourism Management, 74, 300-309. Web.
Tasci, A. D., Hahm, J., & Terry, D. B. (2019). A longitudinal study of Olympic Games’ impact on the image of a host country. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 36(4), 443-457. Web.