The overall aim of this report is to explain the use of chromatography procedure in separating the components of lycopene. Conjugated polyenes with multiple single or double bonds alternating give fruits and flowers the different colorations feature. According to Answers.com (2010) lycopene is a red carotenoid pigment and a polyene results the red color in tomatoes. Lycopene with eight isoprene units has a C40-caretonoid. It is also an important caretoniod component in blood plasma as well as in prostrate tissue. It gives the flamingoes their coloration. Extraction of natural product has been there since time immemorial, by either infusion or distillation so as to obtain a concentrated extract. According to the George Mateljan Foundation (2010), he classifies tomatoes as fruits rich in lycopene. In order to extract a bigger portion of lycopene from tomatoes it is advisable to use tomato paste instead of using fresh tomato fruit. This is because the fresh tomato fruit is made up of 96% water and only a small amount (about 20mg) of lycopene can be extracted whereas in tomato paste a bigger amount (150 mg) can be extracted because water and skin are removed.
Column chromatography has been used to isolate lycopene. Initially, chromatography involved separation of pigments but currently through modifications it is applied in chemical separation. According to Answers.com, column chromatography in chemistry purifies through separation of chemical compounds that initially are mixed (2010). According to the column chromatography theory, the mobile and stationary phases feature in the main chemical chromatography techniques. The mobile phase involve either liquid or gas while, stationary phase is either a solid or a liquid. In this case, chromatography can be liquid-liquid, solid-liquid or liquid-gas with the reference to the first phase (stationary) and second phase (mobile), respectively. When separation process is being executed, the mixture in question is applied from to the top of the column. Mixture components are ferried along in the mobile phase to different extents such that they are separated. Consequently, the separated components can be collected downstream as they drip from the column. The size of the particles of the adsorbent influence column of the solvent in question (Nijihawan, 1999). In the case of flash chromatography, reduced particles are favored while in normal column chromatography, the size of particles will increase relative to those in the former case. Thus, the choice of stationary phase for application is an imperative matter. The extent that a solvent will flow through the column is subject to its polarity. In the centrifugal separation of chromatographic separation of lycopene pet spirit flow after adding drop wise on a chromatotron saturated with petroleum spirit leads to color band separation. First color which yellow is mainly of phytofluene followed by orange of lycopene. During the column separation for lycopene isolation using tomato extracts color changes observed when of the slurry extract is added in portions into toluene and petroleum mixture of concentration 5%, 10% 15% and 20%, respectively, a yellow band precedes an orange one.
From the UV spectrum the Lycopene investigated was found to have absorption peaks of 470.0, 502.0 and 446.0 nm with an average value of 473 nm to one decimal place. Pure lycopene has absorption peak values of 444, 470 and 501 nm with an average value of 472 nm to one decimal place. Making a comparison between this set of values you notice that there are slightly different – the average values differ by +1 nm. This is an indication that the lycopene under investigation is impure but the level of impurity is very low. An impurity according to Answers.com (2010) is a substance that if added to another substance thereby making it impure. Figure one below shows cause of the color of lycopene in the ultraviolet Spectrum.
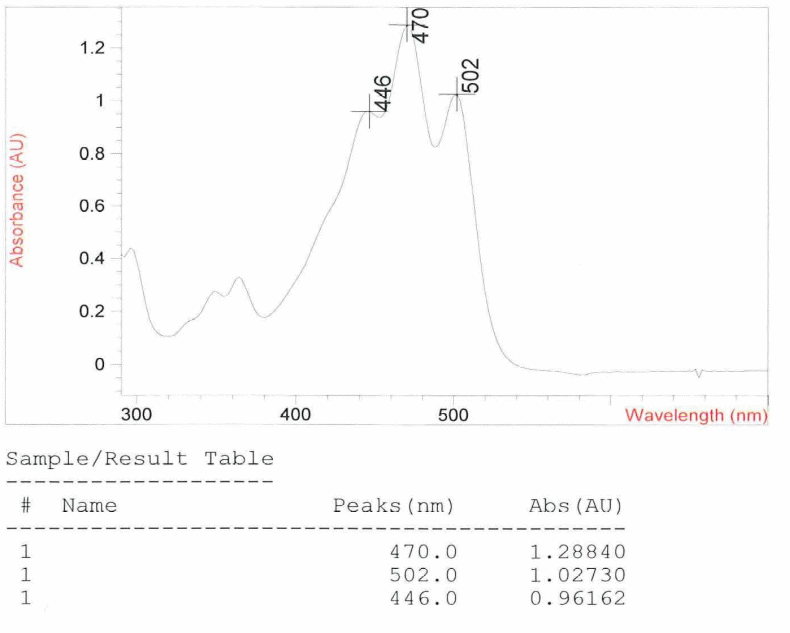
In addition, there is certainty that on the basis of the UV spectrum analysis, impurity is not Phytofluene or zeta-carotene. This is because both impurities have absorption peak values that are way below those of pure Lycopene. Pure phytofluene has absorption peak values of 331, 348 and 368 nm with an average absorption peak value of 349 nm whereas zeta-carotene has absorption peak values of 378, 398 and 424 nm with an average absorption peak value of 400 nm. Thus it is theoretically impossible for one of these impurities to have caused the +1 deviation in the lycopene being investigated.
During the calculation of the Ami Homo Lumo gap, it is zero when the pair of electron and a proton is separated. This is so because of the gain in energy for an electron by forming a MO. When contrasting the calculated HOMO and LUMO energy levels for the protonated and free-base forms of t, some electrons and protons indicate electron deficiency of the C60 cage and the HOMO−LUMO energy gap as result of N-protonation increasing (D’Souza et al. 2000).
In conclusion, through application of column chromatography the red carotenoid pigment of lycopene are isolated.
References
Answers.com, 2010. Column Chromatography. Web.
Answers.com, 2010. Impurity. Web.
Answers.com, 2010. Lycopene. Web.
D’Souza, F., Zandler, E.M., Deviprasad, R.G. & Kutne, W., 2000. Acid−Base Properties of Fulleropyrrolidines: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. Web.
George Mateljan Foundation, 2010. Lycopene. Web.
Nijihawan, k. & Holt, P., 1999. Isolation of Lycopene and b-Carotene1-3. Web.