The primary intention of engaging in any commercial venture is to make a profit. Therefore, it is no surprise that profitability is among the core elements considered in evaluating business performance. Profitability shows the proportion of profit made relative to equity, asset investment, or sales, and is a critical determinant of a firm’s perpetual existence (Fareed et al., 2016; Nguyen et al., 2020). The following three profitability ratios shall primarily be employed for this analysis: net profit margin (NPM), operating expense margin, and return on capital employed (ROCE).
Net Profit margin = Net Profit ⁄ Total revenue x 100
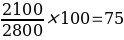 %
%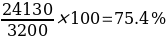
Operating Expense Ratio = Operating Expense ÷ Total Revenue
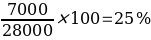
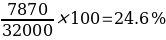
ROCE = EBIT/Capital Employed.
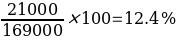
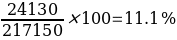
The NPM for Jim’s Auto Body is very high, with 75% for the 2014 accounting period and 75.4% for 2015. Overall these NPM figures illustrate that the management generates enough profit from sales by maintaining low operating costs. Maintenance of low operation costs can be exemplified by the relatively lower operating expense ratio of 25% and 24.6% for 2014 and 2015, respectively. Despite earning more revenue for the 2015 duration, the management succeeds in keeping the operating expense margin lower than 2014, indicative of efficient managerial techniques in generating higher revenue while keeping the corresponding costs low. Overall, these lower operating expense ratios contribute to higher profitability (Boateng, 2019).
To determine the real extent of managerial efficiency in the firm, the ROCE was calculated. Asness et al. (2019) assert that the ROCE provides a more comprehensive measurement of profitability as it expresses such gains relative to the capital used to achieve this profitability. The ROCE for the company is 12.4% and 11.1% for 2014 and 2015, respectively, which are lower than the 15% advanced as reflective of a good quality business more likely to generate a return well above its weighted average cost of capital (Tom Sieber, 2021). The ROCE dropped in 2015 by a 1.3% margin due to higher, lower current liabilities despite the management having a higher capital employed at its disposal.
Financial Report On Profitability
Investors
The firm registered revenue growth for the 2015 financial period. The revenues increased from $28000 in 2014 to $32000 in 2015 accounting for 12.5% margin growth. On the other hand, the net profit increased from 21000 in 2014 to 24130 in 2015, registering a 13% margin growth. However, the ROCE dropped from 2014’s 12.4% to 11.1% in 2015; this implies that for every $1 in capital invested, the investor gets back an additional 11.1 cents, a drop from 2014’s 12.4 cents.
Management
The firm’s ROCE for 2015 is 11.1%, down from 12.4% in 2014. The drop in ROCE comes at a backdrop of a higher capital employed of $217150 in 2015 from $169 000 in 2014 and higher amounts for current liabilities. The current ROCE is lower than the 15% advanced as likely to generate a return well above its weighted average cost of capital. There was an improvement in the operating expense ratio from 25% registered in 2014, to 24.6% in 2015, accounting for 0.4% drop margin.
References
Boateng, K. (2019). The relationship between efficiency, productivity and profitability of Ghanaian banks. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM), 21(6), 52-60.
Fareed, Z., Ali, Z., Shahzad, F., Nazir, M. I., & Ullah, A. (2016). Determinants of profitability: Evidence from power and energy sector. Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai, 61(3), 59.
Nguyen, T. N. L., & Nguyen, V. C. (2020). The determinants of profitability in listed enterprises: a study from Vietnamese stock exchange. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(1), 47-58. Web.
Asness, C. S., Frazzini, A., & Pedersen, L. H. (2019). Quality minus junk. Review of Accounting Studies, 24(1), 34-112. Web.
Tom Sieber, U. (2021). Using return on capital employed to identify quality stocks | Shares Magazine. Web.