Company overview
According to the annual report 2010 of Kellogg, this Company started its journey in 1906 and was incorporated in Delaware in 1922 and it is now one of the major players in the ready-to-eat cereals and convenience foods industry in the US market. However, human resources are the key assets of Kellogg and it has more than 31,000 dynamic employees around the world to operate the business in 180 countries (Kellogg 4). However, it has many opportunities to develop the customer base, brand awareness, financial strength, acquisition with other companies, increasing demand for health consciousness of the people, and new product development. On the other hand, the external threats are intense market competition, exchange rate, interest rate risk, and agreement between competitors, price of raw materials, global economic downturn, and compensation of the employees, high advertising costs, and several legal claims and many other issues.
The opportunities and threats of Kellogg

Opportunities
- Largest customer base: According to the annual report 2010 of Kellogg, Wal-Mart is the largest customer base of this company as this store contributes to sales more than 21% of net sales of Kellogg products and generates 27% of its US. Receivables balance. Also, Kellogg generated 46.0% of its net sales profits from the US market among them Wal-Mart helps to generate 34.0% of total revenue from this area; as a result, Kellogg has the opportunity to increase its sales in the global market by developing a close relationship with the similar stores like Tesco Corporation, Sainsbury and so on;
- Brand Awareness: Kellogg has the opportunity to widen its market by using its reputation as it has a business operation in about 180 countries in American, Asian, and European market;
- Financial strength: Kellogg Company is one of the major players in the ready-to-eat cereals and food industry, which has the economic strength to compete with other multinationals and other local companies by expanding its business operation in the existing market with the new and old product line. However, the annual reports 2009 and 2010 forecasted that –
Table 1: – Financial information of Kellogg. Source: self-generated from Kellogg (4).
- Health consciousness: The demand of the market has already increased by 39% as most of the target customers are trying to change their food habit and would like to take healthy nutritious food;
- Acquisition: this company has acquired many companies to expand its business, increase global market shares, and strengthen the company’s resources and capabilities;
- New product development: it has the opportunity to develop new products as it has a strong brand image;
- Strategy: Kellogg is the market leader in the US market, thus, it has the opportunity to capture the largest market share from the European market, and the marketers can adopt similar strategies to increase the customer base of U countries.
Threats
- Exchange rate: Fluctuation of US Dollars hurts the cash flow statement of Kellogg while instability in the translation of foreign exchange denominated income to US dollars;
- Competition: Intense competition is the main threat of Kellogg as it has both direct competitors that offer almost similar products and indirect competitors that offer segmented products. However, the major competitors of Kellogg are PepsiCo’s Quaker Oats and Frito-Lay, Kraft’s Nabisco, and General Mill’s ready-to-eat cereals and other similar companies;
- Interest rate risk: Kellogg sometimes apply interest rate swaps and forward interest rate contracts to decrease interest rate instability and subsidy costs associated with certain debt concerns;
- Agreement: merger and acquisition between similar companies, franchises, and joint venture agreement can create a threat for the business;
- Advertising costs: This company had spent a huge fund for advertising while competitors use new adverting policy taking advantages of new technologies to increase sales;
- Compensation: Kellogg has to spend comparatively large amounts to provide remuneration to the employees as the company is committed to giving all facilities to the employees. The company aims to reduce staff turnover as the recruitment and training process needs time and efforts
- Legal claims: Kellogg has to consider the threat of litigation because an increasing number of legal claims can destroy the reputation of the company and boost the operating expenses.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis for Kellogg
This report concentrates on Porter’s five forces model of competition to analyze the present competitive scenario of Kellogg at home and abroad; however, the following figure shows more specifically the external competitive environment of Kellogg.
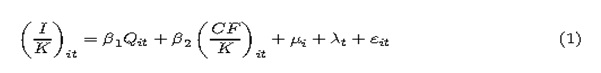
- Threats from new entrants: Large stores like Wal-Mart, Tesco, and Sainsbury always eager to offer new products for the customers, so they purchase products from new companies to increase sales, such as Tesco introduced five hundred new products to save the company from the global financial crisis. On the other hand, entering into the market is a matter of huge investment but banks and other investors can show less interest in these sectors because of intense competition in the food industry and the post-recessionary economic environment. However, small investors are trying to capture new market share of different segment, which also create hindrance for the different products of Kellogg Company. As a result, the threat of new entrants comparatively high for Kellogg;
- Bargaining power of the suppliers: The key suppliers of Kellogg are raw material suppliers including packing materials, corn, wheat, soybean oil, sugar and nuts, meat, and many other products related to the production. However, the rising price of the commodities is one of the main causes of such threats though according to the annual report 2010 of Kellogg, the bargaining power of the suppliers based on the issues like production area, adverse weather, and the actions of certain organizations, political situation, and financial circumstances;
- Bargaining power of the buyers: This threat is comparatively high in the case of Kellogg because the buyers can change the food brand any time without spending extra funds as the minimal switching off costs incurs in this industry; therefore, the bargaining power of purchasers is high. On the other hand, this risk would escalate if the Kellogg company increased the price of existing products and competitors offer similar items with competitive price;
- Rivalry among existing competitors: The competition of ready-to-eat cereals of Kellogg company is extremely high, and this company has to face competition from another segment particularly cookies, crackers, breakfast shakes, toaster pastries, cereal bars, Coffee brands, frozen waffles, meat alternatives, and so on.
- Threats of substitute products: the threats of substitute products are interrelated with many other factors such as the price of substitute products, production costs, cost-benefit ratio analysis, and so on. However, this risk of such substitute products is comparatively low for Kellogg because the product range of Kellogg is widest, so only organic food can be its substitute but the production costs of organic food is too high, which reduces the threat.
Kellogg acquires Quaker Oats or not
Nevo (4) mentioned that in 1992 and 1993 presented the UC-FMC (University of Connecticut, Food Marketing Center) surveyed with about thousand of supermarkets, drug stores, and food outlets and the outcomes of the market share of different RTE (Ready-To-Eat) companies including Kellogg in the diagram as bellow-
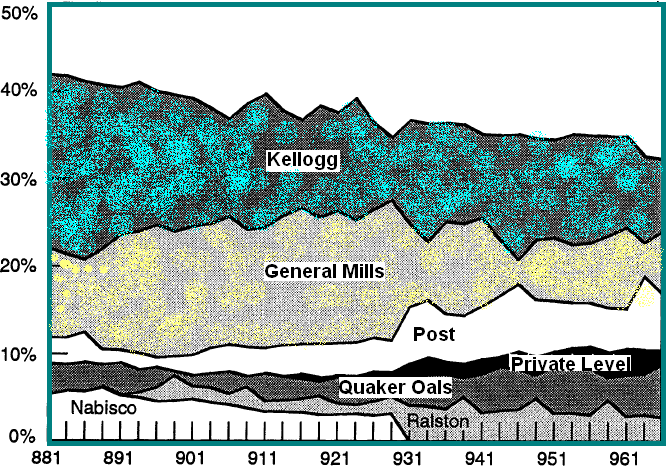
The above diagram demonstrates that Kellogg has a far better position than the Quaker Oats; moreover, Kellogg has the experience to be companied by the US- FTC (U.S. Federal Trade Commission) anticompetitive charge that hampered Kellogg’s brand image. Thus, for Kellogg, there is no emergence to acquire Quaker Oats and it is unlikely to be a good strategy, the RTE market has evidenced huge merger and acquisition proclamation, the regulatory observation may shift the strategic alignment. On the other hand in January 2006, shares of breakfast cereal maker Kellogg Co. climbed to over $50 as earnings climbed while has been gaining market share from competitors with gradual progress and kept its position at the top of RTE companies.
The key issues that Kellogg should focus on to make the acquisition a success
To assess whether the acquisition would be successful, Kellogg’s should undertake several different measures, such as strategic analysis based on internal and external factors, cost and benefit analysis, evaluation and consideration of any other potential opportunity costs involved, and most importantly, carrying out a proper investment appraisal. Inputting the entire assessment into context, a projected estimation of the cash flows and annual rate of return together with a brief idea of the net present values of the merged business is quite essential as well.
The pitfalls in strategic planning
The management of Kellogg should concentrate on the main objectives and the mission statement of the business to avoid any crisis at the time of the strategic implementation process. Also, the management of this company may fail to communicate properly with the staff who are responsible to perform under the guidance of the top management, which will create a severe problem for the company. However, the management of Kellogg should observe the pitfalls to avoid any crisis in strategic implementation, such as they must keep concerned for its vulnerable financial conditions, develop communication with the employees, and follow the regulation to implement the plan.
Five pitfalls
- Unrealistic goals: As Kellogg is one of the major players in the ready-to-eat food industry, it has enough financial strength to take a new strategic decision but it should not set such an objective, which is not realistic to implement for the management team;
- Lack of motivation: Kellogg has more than 31000 motivated employees who can serve the company on the right track but some plan may irritate the employees to execute due to lack of motivation;
- Ignore grassroots support: The top management has the ultimate power to take decisions by ignoring the minority shareholders’ and employees’ view. If the management ignore their opinion, the business may fall into serious crisis as they are the key resources for the company;
- Ignore alternatives: The management should consider several alternatives to attain ultimate success and if they ignore alternatives and drive to implement a single plan they may fail to get the highest success;
- Ignore the need for change: Also, the management may need to change their way to implement the strategy due to avoid any risk factor but sometimes they ignore this issue as their confidence level is too high.
Benefits of contingency planning
Kellogg will prepare contingency planning because effective planning allows coping with the crisis such as corporate problems, acquisition-related problems, the crisis of human resources for particular tasks, liquidity risk measurement, product development risks, and so on. Also, this process helps Kellogg to capture a better position by managing unexpected situations and avoiding the shock of absolute surprise. On the other hand, this process also minimizes indecision, vagueness, and unnecessary delays when something unusual occurs, for instance, a natural disaster can affect the entire operation management system. As a result, the management of Kellogg should consider this plan to assess the unusual events to protect the company from those risks by responding rationally.
The seven-step process of effective contingency planning
- Starting point – Realize importance: The management of Kellogg must recognize both favorable and unfavorable events because liability may extend severe range due to lack of previous preparation (Mitome and Karen 1);
- Assess Impact: It is important to note that Kellogg has already identified key risks and taken many initiatives to avoid any risks or natural disaster, for instance, the death of CEO, Hurricanes, Serious Earthquakes or Tsunami, credit-risk-related contingent features;
- Develop Plan: Kellogg should keep a large amount in a contingency fund, such as, may reduce the funds that the business has available for further growth or investment. However, this plan will include human resources management plan, effective communication system at the time of crisis, leadership development program, manufacturing process after a disaster, recognize the duties of key people, recruit suitable people for risk management;
- Test: In this stage, the management team of Kellogg must test the tools of the plans, and make sure proper people involved to minimize the unusual events. To do so, they will check the entire system and arrange a backup plan considering the pre-test report, such as fire extinguishing audition allows testing the system at the time of the unusual fire;
- Training: The firms should train the employees to provide knowledge about the risks and implement the contingency plan;
- Maintaining: The management should always up to date their plan to identify problems in the system and recommend changes;
- Changed-Plan: – The management team will test all the changed plans to measure the effectiveness of the entire process ensuring the system would function properly at the time of crisis.
Works Cited
Kellogg. Annual Report 2010 of Kellogg. 2010. Web.
Mitome, Yuko, and Karen Speer. Embracing disaster with contingency planning. 2001. Web.
Nevo, Aviv. “Mergers with differentiated products: the case of the ready-to-eat cereal industry”. RAND Journal of Economics. 2000.