Introduction
Modern HR managers believe that their work was successful if competitors began to poach employees from their company. It means that they managed to develop the skills of their employees to the extent that it is noticeable to others, including competitors. Strategic HR management is based on market knowledge since the HR responsibilities include creating strategies for the future. A company under the strict guidance of a professional can be flexible, changing the composition of departments every few years, increasing some and reducing others. It is vital to maintain a trusting relationship between departments. In addition, HR managers advise their bosses and managers of other departments, helping them make decisions. The London ClubHouse example provides insight into how strategic HR management can fundamentally impact its operations and help it cope with challenges such as personnel leaks.
Different Management and Leadership Theories
The theory of Behavioural assumptions recognizes behavioural aspects as the centre of any economic activity. The biological approach considers ambitions as instincts and the accumulation and increase in profits as the only possible and rational option for human actions. The classic idea is that people working in a business try to make the most of their talents to accumulate profits. Sometimes, “SHRM shared the same objective to maximise the profit through human resources” (Iqbal, 2019, p. 189). However, it is difficult to evaluate it as an applied example of a strategy since people usually face problems of demotivation, lack of guarantees from the employer, and others at work (Wilkinson, 2019). Other results and values now guide human economic behaviour; however, if the structure of the company were based on this theory, people would be easily manageable.
The bureaucratic management theory is based on documents, written statements, and a strict hierarchy. The described problem at the London Clubhouse can be attributed to this management theory, and, as readers can see, this management model led to a general turnover of personnel. It is difficult for people to gain a foothold in such a system that does not show proper flexibility, so they are forced to leave it quickly.
The systems approach in management theory puts complex information technologies and artificial intelligence at the forefront. It can complicate the work of an HR manager since the use of such technologies sometimes leads to a high turnover of staff and the inability of laid-off people to find another job (Wright and Ulrich, 2017). The inclusion of information technology in management should be very reasonable and gradual; otherwise, unemployment is inevitable.
Leadership theories go deep into the psychological aspects of personality, and one such theory is the reinforcement theory. According to this theory, leadership and training (which plays a significant role in the work of HR managers) should be based on encouragement. Then employees will be easier to retain in the company. Fahim (2018, p. 33) states, “Organizations that invest in their people need to guarantee that these investments are not lost, through developing strategies to retain staff long enough to obtain an acceptable return on their investments in employees’ skills and knowledge.” Techniques for rewarding and punishing disciplinary offenses are understandable and logical for everyone. It is difficult to argue with this theory for employees.
On the other hand, situational leadership theory can cause controversy, making the company structure too flexible and the strategy too incomprehensible. Often this theory is used by supporters of improvisation and charismatic leadership. They think that in a stalemate situation (loss of profit sharply, change of management), managers of different levels and ordinary workers will easily take control of the problem without fear of responsibility and possible mistakes.
Transactional leadership is known for its short-term strategic planning, as it is easier for bosses to control employees’ work from this perspective. Bosses use a reward and punishment system that motivates employees to work on a specific project (West, 2021). The company’s structure is highly organised, and bosses do not prefer sudden initiatives and spontaneity. The duties of employees are spelled out and clearly defined so that no one takes on the work for others.
Impact of Organisational Strategies, Structures and Culture on the Management of HR
Organisational strategies affect HR management primarily in employee performance evaluation and remuneration procedures. According to Al-Ayed (2019, p. 184), “SHRM has a significant impact on cognitive, behavioural and contextual aspects of organisational resilience.” In some companies, certain rewards are not available, while in others, managers can use them consistently. Some organisational systems promote the importance of efficiency; therefore, HR managers consider compensation and rewards for employees who become effective in a given period. The design will also indicate to the HR manager what types of rewards (external or internal) are acceptable for the company. External include housing allowance or the provision of apartment, exceptional benefits, commissions. Internal include authority among colleagues and superiors, as well as opportunities to improve qualifications.
Organisational structures have a severe impact on the work of an HR and attitude towards him in a particular company. There are companies in which an HR manager’s role is reduced to that of a consultant. The HR manager and the company work together, and the company does not subordinate this specialist to itself. There are structures where work is done in teams, and HR should consider this when calculating awards and calculating results. The approach to recruiting new people for positions also depends on the structure and can be either rigid or smooth and harmonious (Equality and Human Rights Commission, n.d.). The strict policy is based on searching for a specific person, down to the psyche characteristics and work habits. In addition, the interviews can be conducted either in several stages (complex structures) or in one step, and then the potential employee goes on to an internship, where he shows his skills.
The culture of an organisation culture keeps employees in the company and allows them to improve their skills and develop there consistently. For example, “Risk-tolerant cultures appear to create the room for the company to develop a capability for breakthrough innovation by attracting those who are self-motivated” (Choi, Ravichandran, and O’Connor,2019, p. 240). With the developed culture and corporate values, the company’s priorities are clear; following it, the internship, training, and integration of new employees into the team is built.
One of the most critical problems of the London ClubHouse was the lack of an adequate corporate culture based on hierarchy and rigid relations between superiors and subordinates. This example demonstrates how a lack of culture can affect employees and their turnover. However, “Strategic HRM research has treated employee departures as something that is costly in terms of lost productivity and increased bureaucratic activities involved with replacement hires and training” (Boon, 2017, p. 46). HR managers generally recommend placing trust, mutual assistance, and honesty at the centre of the corporate culture. One should not spare resources to improve the corporate atmosphere, as this will result in the presence of a strong team, where the employee is committed to the values of the company.
Current ClubHouse HRM
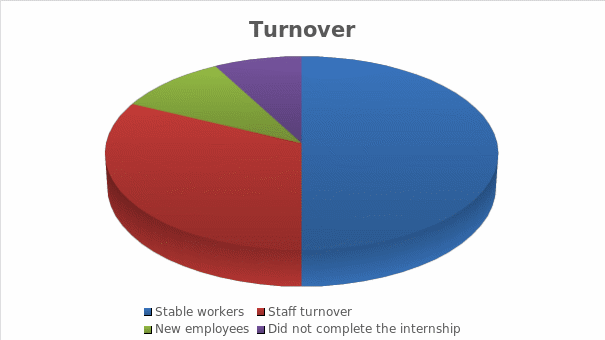
The HR manager should describe the London ClubHouse team’s environment. Judging by the data, it was a team without motivation, dedication, and organisation. Many workers experienced apathy and frustration with their skills and management. Strict hierarchical structures in the London ClubHouse put severe pressure on the on the workers; but this pressure is invisible to managers. As part of the new program on strategic HR management, it was proposed to transform this structure, paying attention to the lower regions. Leadership in the London ClubHouse was devoid of charisma, and bosses were not respected but feared. Many employees complained about the lack of integrating new employees, that is, the lack of adequate transfer of knowledge and training; all this led to staff turnover.
The HR management is characterized by rigidity and the complete disinterest of bosses in motivating subordinates. A method of rewards and punishments has not been developed, but the latter is much easier for bosses to commit. As a result, employees feel that they do not deserve their treatment. The new HR management is distinguished by high trust and attention to employees. The existing system’s efficiency is extremely low, as it forces the company to develop in a constant change of employees (ACAS, n.d.). In such a team, conflicts are constantly brewing, and over time, employees stop taking their duties seriously because they do not pursue the same goals that the bosses pursue.
The relationship between leadership and management and the HR management is close. In addition, “firms need to carefully manage the trade‐offs between employees, customers, and shareholders” (Collings et al., 2021, p. 3). With proper management, bosses can cooperate with an HR specialist and take on a symbolic burden. It was said above that with some structures (matrix, in particular), an HR specialist plays the role of a consultant and not a full-fledged worker manufacturing a product. An HR specialist will not be able to keep the team in the company if the management is not developed and the bosses do not meet the needs of the employees. A work in tandem is necessarily, taking into account the interests of all parties and their skills.
Culture and Structure of the ClubHouse
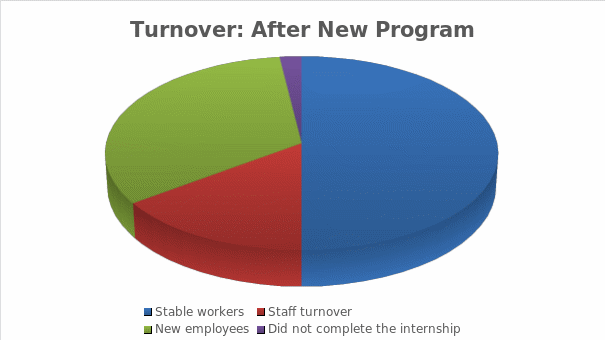
It is expected that staff motivation will rise to a very high level, as employees of all departments and qualifications will receive the oversight and care they so lacked. At the beginning of the implementation, personal communication between the HR manager and some employees, particularly those who planned to leave the company shortly, is acceptable. The company culture will be based on trust and guarantees to employees (Government Digital Service, 2020). Although “Most companies are facing a stressful situation in the market page,” employees will be protected as much as possible from possible impacts of the global market (Al-Khaled and Fenn, 2020, p. 56). It is considered to change the hierarchical structure, which will transform the psychological state of many employees.
Development, Monitoring, and Evaluation
Developing a leadership strategy will be based on a non-hierarchical but horizontal order. In general, London ClubHouse “ought to employ more HR that entirely relates to job satisfaction for a happy work environment” (Sareen, 2018, p. 1232). The help and “role of line managers who are directly responsible for implementing HRM systems” (Jiang and Messersmith, 2018, p. 23) are also critical. They will help to avoid hierarchy and at the same time make the structure not blurry. Monitoring the development of the strategy and compliance with the original plan can be achieved by receiving feedback from employees in various forms. Forms must be open, and some feedback can even be left anonymously. This feedback can also help in evaluating the implementation of the strategy. However, it would be comfortable for the authorities to see diagrams that show a decrease in employee turnover and the number of new hires; worker can use surveys, which also be made anonymous.
Conclusion
The proposed strategy will improve HR management and corporate culture, allowing employees to develop their skills. Combining leadership and organisational theories, the HR manager has created a comprehensive program that is unique to the London clubhouse and focused on the well-being of employees. The HR program was influenced by the structure of the company, its culture, and its strategy. The initial performance of the company is assessed as very low, with poor prospects in the form of the departure of key employees and the inability to hire new ones. The proposed program will be based on trust in employees and the devaluation of the hierarchical structure, which was psychological pressure on employees.
Reference List
ACAS (n.d.) Checking your pregnancy and maternity rights: Your maternity leave, pay and other rights. Web.
Al-Ayed, S.I. (2019) ‘The impact of strategic human resource management on organizational resilience: an empirical study on hospitals’, Verslas: Teorija ir Praktika, 20(1), pp. 179-186.
Al-Khaled, A.A.S. and Fenn, C.J. (2020) ‘The impact of strategic human resource management practices on organizational performance’, Berjaya Journal of Services & Management, 14, pp. 53-60.
Boon, C. et al. (2017) ‘Integrating strategic human capital and strategic human resource management’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(1), pp. 34–67.
Choi, B., Ravichandran, T. and O’Connor, G.C. (2019) ‘Organizational conservatism, strategic human resource management, and breakthrough innovation’, IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 66(4), pp. 529–541.
Collings, D.G. et al. (2021) ‘Strategic human resource management and COVID‐19: Emerging challenges and research opportunities’, Journal of Management Studies, 58(5), pp. 1-5.
Equality and Human Rights Commission (n.d.) Your rights under the equality act 2010 | equality and human rights commission. Web.
Fahim, M.G.A. (2018) ‘Strategic human resource management and public employee retention’, Review of Economics and Political Science, 3(2), pp. 20–39.
Government Digital Service (2020) Dismissal: Your rights. Web.
Iqbal, A. (2019) ‘The strategic human resource management approaches and organisational performance’, Journal of Advances in Management Research, 16(2), pp. 181–193.
Jiang, K. and Messersmith, J. (2018) ‘On the shoulders of giants: A meta-review of strategic human resource management’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(1), pp. 6-33.
Sareen, D. (2018) ‘Relationship between strategic human resource management and job satisfaction’, International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences, 7(03), pp. 1229-1233.
West, T. (2021, February 25) National living wage, real living wage, national minimum wage – what’s the difference? Web.
Wilkinson, A. (2019) The SAGE handbook of human resource management. London: Sage.
Wright, P.M. and Ulrich, M.D. (2017) ‘A road well traveled: The past, present, and future journey of strategic human resource management’, Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 4(1), pp. 45–65.