Why is McDonald’s revenue decreasing? Is it because of service quality? Is McDonald’s losing customers? What is wrong with their strategy? Find answers to these questions here!
Reasons behind McDonald’s Decline in Sales
McDonald’s used to be a popular place for families and children to enjoy a meal at a low price. McDonald’s has managed to sustain a consumer base focused on children successfully. The founder, Ray Kroc, believed that children are an important target due to their influence on their parents. Children not only have their purchasing power, but they strongly influence their parents’ buying decisions (Somesfalean, 2012).
In addition, children become adult consumers of the future, and it is essential to forge brand loyalties at an early age. McDonald’s Corporation, therefore, went as far as creating the Ronald McDonald image, Playlands, and Happy Meals, all targeted at young kids. While McDonald’s enhanced its market share in the fast-food industry by marketing products and services tailored to children, that has recently become one of its weaknesses. The parents of these children are mostly Millennials, and this has a significant impact on McDonald’s marketing. Most Millennials are health conscious and likely to insist on healthier food options for their children.
Out of the 11.6 million Millennial families with children, 76% of the parents adopt a decision-making style that enables them to make input on purchasing decisions for their children, including food choices (Fromm, 2015).
Nowadays, parents and governments have placed a heavy emphasis on health and food quality, which has created a disadvantage for the fast-food giant. The Millennials, who are not only parents but also major consumers of fast foods, have decreased the number of visits they pay to the restaurant due to the unhealthy menu offerings (Bowman, 2015). Survey reports indicate that the rate at which Millennials eat at fast-food restaurants has reduced by 5 percent while eating at fast-casual restaurants has increased by 7% (Glass & Bartlett, 2015). In this survey, 51% of Millennials who indicated they were eating less often at McDonald’s were doing so since they were switching to a healthier diet.
Consumer Health Preferences
In recent years, Asia has become a significant food supplier to the United States. Following the recent news about Asia’s artificial produce and toxic foods, US consumers have begun to look for products with USDA-approved labels that indicate the food is organic and natural, free of hormones and antibiotics. US organic food sales have increased by $17 billion from 2004 to 2014. It indicates a 60% increase in the purchase of more natural foods (Greene, 2014). Consumers are willing to pay more for food of a higher quality.
It is not the first time health concerns have affected McDonald’s operations. In the late 1990s, public worries about cholesterol and calories forced McDonald’s to change its high-fat and calorie menu (Berg, 1991). McDonald stopped using saturated fats that increase cholesterol levels and instead started using unsaturated fats (Sachdev, 2002). The company made a 100% switch to vegetable oils which are healthier than animal fats. Healthier selections such as salads and fruits were included in the McDonald’s menu to give people a choice of healthy foods.
Consumers’ preferences keep changing over the years due to diet trends, economic situations, and other factors. Restaurants that fail to meet customers’ tastes will soon be replaced by more adaptable ones. A survey conducted by Reuters/IPSOS shows that 60% of Americans would like restaurants to incorporate antibiotic-free meat (Baertlein, 2015). Another survey by Morgan Stanley indicates that while most consumer groups were not very concerned about attributes such as all-natural and locally-produced foods, these attributes were more important to Millennials (Glass & Bartlett, 2015).
These Millennials impact McDonald’s market since they are the parents to kids who contribute to McDonald’s high sales. This segment of the population also contributes to the restaurant industry’s growth since they eat out at least once a week. The health preferences of the Millennials might be a reason why companies such as Chick-fil-A and Chipotle Mexican Grill Inc., which provide antibiotic-free meats, have been taking shares from McDonald’s (Baertlein, 2015). In this case, consumers’ changing preferences have impacted McDonald’s revenue.
McDonald’s Marketing Issues: Outdated Menu
Fast-food restaurant chains need to come up with new products or seasonal products now and then to excite their customers. Consumers will likely become bored if they are only presented with the same old menus that never incorporate something new. It might cause the fast-food chains to lose customers. However, the new introduction to the menu should be fairly priced and something that is interesting and appealing to the public.
Such a new item can create a public discussion topic and raise curiosity. It can increase the company’s public exposure and attract customers to their restaurants. Some recent examples of restaurants that have tried introducing new menu options include Taco Bell with its Doritos Locos Tacos, Wendy’s with its Pretzel Bacon Cheeseburger, and Chipotle’s vegetarian “Sofritas.” Such on-trend new items help the company to gain attention and boost revenue.
Over the years, McDonald’s has continually expanded its menu. Today the fast-food chain offers over one hundred different selections on its menu. Although the fast-food giant continues to add new items to its menu, those items do not significantly impact sales. This can be blamed on the lack of novelty in the new items placed on the menu. When McDonald’s started serving more healthy items like salads, sales only increased by two to three percent in the United States. In 2013, McDonald’s launched a new product Mighty Wings, but it was an unsuccessful addition to its menu.
At the price of $1 a wing, the new product suffered from poor sales as many consumers consider this price too high (Horovitz, 2014). The fast-food chain was forced to admit that consumers were unwilling to pay this amount for their wings.
McDonald’s had not had a blockbuster menu item since 2003 when the McGriddle pancake sandwich was introduced (Jargon, 2013). Consumers are becoming pickier about their food choices because of the variety of choices available to them. Introducing a new product that is not interesting to the consumer or is well-priced will not positively impact sales. This is another reason McDonald’s has noticed a decreased sales revenue.
McDonald’s Marketing Issues: Dining Environment
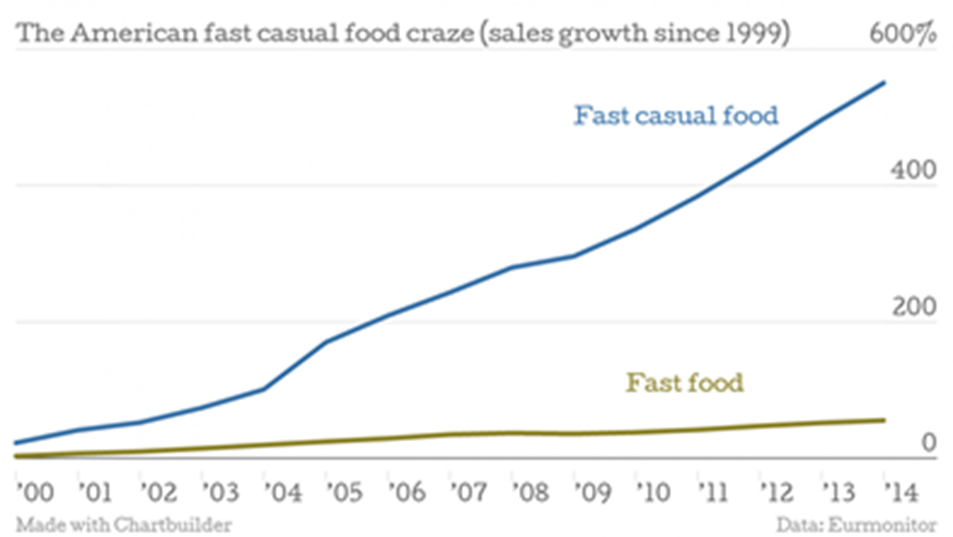
Following the financial crash of 2008 and the subsequent recession, Americans began to change their dining habits. Over the past five years, full-service and fast-food restaurants have witnessed stagnation in their earnings. In contrast, fast-casual restaurants have been growing their market share in the restaurant business from 1% in 2000 to 5% in 2015 (Ferdman, 2015). Fast-food restaurants like McDonald’s are characterized by their very cheaply priced meals. However, present-day consumers have a great interest in healthy diets and are, therefore, less willing to eat at restaurants that do not show a high commitment to offering healthy foods.
Millennials, who serve as an essential group for McDonald’s since they consume fast foods and dictate where their children will eat, are less willing to eat at the traditional fast-food chains that primarily offer unhealthy foods (Ferdman, 2015). Full-service casual restaurants are traditional sit-down restaurants, which are slower, more expensive, and waiter-dependent, like Olive Garden. These establishments tend to be too expensive for them to afford.
Fast-casual restaurants, therefore, have become the best option. This class of restaurants falls somewhere between the two extremes. The restaurants provide fair pricing, fast service, better ingredients, first-rate decor, flexible offerings, and wholesome fresh food, which appeal to Millennials and other health-conscious individuals (Ferdman, 2015). An excellent example of a fast-casual restaurant is Chipotle Mexican Grill, which offers meal prices around $10 per receipt.
It is more than the price of a fast-food restaurant meal, which is $5 on average, but less than a casual restaurant meal, which costs $20 on average (McEvoy, 2014). Consumers are not just looking for the cheapest-priced meal but a healthier and faster meal offered at a considerable price (Ferdman, 2015). Figures provided by Ferdman (2015) reveal that while the growth of fast food consumption has been modest over the last 15 years, fast-casual food consumption has increased by over 500%.
Impact Of McDonald’s Conversion to Antibiotic-Free Meat
In 2003, McDonald’s stopped using human-related antibiotics to stimulate chicken growth. However, the company continued to allow antibiotics to prevent and treat illnesses in poultry. McDonald’s recently announced plans to eliminate more antibiotics used in its chicken. It is going to stop selling chicken products obtained from chickens raised with any antibiotics that are important to humans.
However, it will still allow its suppliers to use antibiotics not used to treat many human diseases. McDonald’s announces that it will provide antibiotics-free chicken in all its US locations by 2017 (Galbraith, 2015). With the realization that customers have developed a taste for what they consider healthier food, McDonald’s plans to move its antibiotic-free meat plans beyond chicken. The fast-food restaurant chain plans to provide antibiotic-free beef and pork shortly (Huffstutter & Baertlein, 2015).
McDonald’s is a very cost-sensitive fast-food business. It has about 14,350 restaurants in the US, and even a slight increase in operating costs can considerably impact the business’s profitability. Whenever it plans to launch a new product, McDonald’s goes through steps of testing in its innovation center. Some of the major contributing factors in approving new products are supplier, speed, and cost. McDonald’s has to ensure enough suppliers with the ingredients for the new product to support its 14,000 restaurants in the US. It then has to ensure its employees can assemble the product in seconds (Berman, 2010).
The final important contributing factor to approving a new product is its cost. For this fast-food restaurant giant, every penny spent on ingredients counts. For example, McDonald’s planned to add double cheeseburgers to its dollar menu, but with one less slice of cheese because each slice costs around 6 cents (Hughlett, 2008). It illustrates that McDonald’s cares about every second and penny it can save to generate again. Although changing to antibiotic-free meats does affect the time needed to assemble products, it affects the other two major factors: supplier and cost.
Suppliers
According to Marion Gross, senior vice president of McDonald’s North America supply chain, changing to antibiotic-free meat is much easier with chicken meat than with other meat types. McDonald’s has already contracted with chicken suppliers to begin its conversion (Kesmodel et al., 2015). The biggest and most important supplier to McDonald’s is Tyson Foods (Huffstutter & Baertlein, 2015).
This company is the most prominent US poultry producer and has a long-term relationship with more than 4,000 chicken farmers. Tyson Foods ensures that all its farmers meet the company’s rising standards. This important supplier started working towards reducing the use of antibiotics in chicken as far back as 2011, and it has promised to switch to total human antibiotic-free chicken by 2017. While complete disuse of antibiotics would be desirable, Tyson Foods acknowledges that sometimes chickens require antibiotics, and denying them these drugs will cause them to suffer (Charles, 2015). The company is therefore committed to phasing out the use of antibiotics used to treat humans and only providing chickens with the non-human use class of antibiotics only when they need it.
While switching to antibiotic-free chicken is achievable quickly, changing to antibiotics-free beef will be more challenging for McDonald’s. Unlike chickens, which take about six weeks to mature, beef cattle take about two years, which makes it hard to effect quick changes in production methods (Kelsey, 2015). The current cattle rearing practice involves the heavy use of antibiotics to keep the animals healthy throughout their lifecycle and ensure they safely reach maturity.
Without antibiotics, most large-scale cattle farmers would suffer from animal loss, as their cattle would succumb to diseases due to the severe overcrowding and unsanitary conditions in which most industrial beef producers raise cattle (Kotkin, 2012). For this reason, most producers have continued extensively using growth hormones and antibiotics in cattle production. The current market share of antibiotic-free beef is minimal, with these products accounting for just 5% of beef sales in the US (Kelsey, 2015). Therefore, McDonald’s attempt to switch to antibiotic-free beef will be challenged by the difficulty in sourcing antibiotics-free beef in the supply chain (Kelsey, 2015).
In addition, McDonald’s beef supplier does not have the solid influence over cattle farmers that Tyson Foods has over chicken farmers. Lopez Foods, a primary beef processor for McDonald’s, does not have a strong relationship with beef farmers. Lopez Foods does not operate feedlots, so it buys cattle from a wide range of producers and middlemen, meaning that meat will likely pass through 4 or 5 middlemen between the farm and the McDonald’s restaurant. (Makower, 2014). Therefore, it is hard for McDonald’s to provide antibiotic-free beef since its supplier, Lopez Foods, has no strong relationship or control over the beef farmers who supply its meat.
Cost
The cost of raising livestock without antibiotics is significantly higher than when farmers use antibiotics since the chickens grow slower and are more prone to diseases. McDonald’s decision to switch to antibiotic-free meat chicken can cause an increase in the price of their menu options, which means converting to all antibiotic-free meats will create a greater chance of price increase. Currently, McDonald’s major competitive advantage in the restaurant business is its low-priced menu items.
Since people go to McDonald’s for its quick and cheap offerings, a price increase might result in a decline in customers visiting the fast-food chain. A Chicago-based research group 8Sages survey sought to determine how consumers feel about McDonald’s (Frost, 2015). One of the questions asked by the survey was for respondents to select which single change at McDonald’s would increase their likelihood of visiting. Almost half of the respondents indicated no change would incline them to visit the fast-food chain more. Eight percent of the respondents indicated that making breakfast available all day could increase their visiting chances.
The survey then indicated that if McDonald’s menu consisted of meat selections free of antibiotics and hormones, just over 14 percent of the respondents would be more likely to visit (Frost, 2015). However, 36.5% of the respondents indicated that they would consider visiting McDonald’s more if new value menus were introduced in its outlets. In addition, 34.3% of the respondents revealed that they would go to McDonald’s more often if the fast-food chain started offering antibiotics-free meat (Frost, 2015). From this, it is evident that switching to antibiotic-free meat can increase a consumer’s likelihood of visiting the chain. However, the cost of implementing this change might lead to a decrease in customers since low-cost meals are a significant incentive for many people to visit McDonald’s.
Loss of Sale During the Transition to Antibiotic-Free Meat
Transitioning to antibiotics-free meat will affect McDonald’s business operations, especially during the transition. Farmers have grown used to antibiotics, and adjusting to a new system will take time and effort. Feeding livestock antibiotics in their food and water supply to prevent disease and promote growth has been standard practice in most mass-producing facilities in the US for decades (Kotkin, 2012).
Changing to antibiotic-free meat will disrupt standard practice, and it can be expected that some farmers will have some trouble adjusting. Without antibiotics, farmers will need to put in more effort to produce the meat (Charles, 2015). Farmers might have to adopt new practices, such as regularly cleaning up the facilities where animals are kept instead of giving the animals low doses of antibiotics to prevent diseases. Farmers must make extra efforts to keep animals healthy without giving them drugs (Kotkin, 2012).
McDonald’s will therefore suffer from a loss of sales due to the lack of adequate supplies to meet its demand. At the moment, there is simply not enough antibiotic-free meat to replace all the meat from animals raised using antibiotics that are currently used to supply McDonald’s fast-food outlets (Huffstutter & Baertlein, 2015). Efforts by Mcdonald’s to transition to antibiotic-free meat are already leading to sales losses.
Some McDonald’s restaurants have been forced by the lack of adequate suppliers to issue signs telling customers that antibiotic-free meat is unavailable at the outlet since it could not be obtained from the market (Huffstutter & Baertlein, 2015). It translates to a loss of sales, as the fast-food chain cannot sell products to its customers. While McDonald’s will eventually benefit from moving to antibiotic-free meat, the company will first suffer from a loss of sales.
References
Baertlein, L. (2015). Parents are embarrassed to take their kids to McDonald’s — and that’s a huge problem for the brand.
Berg, E. N. (1991). McDonald’s struggles to tackle market problems. Web.
Bowman, J. How McDonald’s Lost Its Most Important Customer.
Ferdman, R.A. (2015). The Chipotle effect: Why America is obsessed with fast casual food. Web.
Fromm, J. (2015). Snacking Habits Of Millennial Parents Are Shaping The Category For Future Generations.
Glass, J., & Bartlett, J. (2015). AlphaWise Survey: What Millennials Want. Web.
Greene, C. (2013). Growth Patterns in the U.S. Organic Industry. Web.
Horovitz, B. (2014). Mighty wings get mighty big price reduction.
Jargon, J. (2013). At McDonald’s, salads just don’t sell. Web.
McEvoy, C. (2014). Fast-casual restaurants make traditional eateries old. Web.
Sachdev, A. (2002). McDonald’s to trim harmful fats in its french fries. Web.
Somesfalean, M.V. (2012). Children as target market. Studies in Business & Economics, 7(2), 172-183.
Charles, D. (2015). Tyson Foods to stop giving chickens Antibiotics used by humans.
Frost, P. (2015). Love on the Rocks: Survey Reveals Problems, Opportunities for McD’s.
Galbraith, R. (2015). McDonald’s promises hormone, antibiotic-free chicken in US.
Huffstutter, P.J., & Baertlein, L. (2015). McDonald’s antibiotic-free move could prompt U.S. chicken squeeze. Web.
Hughlett, M. (2008). McDouble–a double cheeseburger with one less slice of cheese–likely to join McDonald’s dollar menu. Web.
Kelsey, G. (2015). Antibiotic-Free Beef Is a Taller Order.
Kesmodel, D., Bunge, J., & Gasparro, A. (2015). McDonald’s to curb antibiotics in chicken; suppliers asked to halt certain drugs; ripple effect expected. Web.
Kotkin, M. (2012). Meat on drugs. NY: Consumer Reports.
Makower, J. (2014). Inside McDonald’s quest for sustainable beef. Web.