In order to predict the company’s financial performance and profitability during the next several years, it is important to focus on financial forecasting and develop pro-forma statements (Hillier, Clacher, Ross, Westerfield, & Jordan, 2014; Piper, 2010). The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate how pro-forma financial statements are used to forecast changes in businesses’ profitability, competitive advantage, and funding. Therefore, the paper presents pro-forma financial statements for Nintendo and Sony, the discussion of current strategies and future investments, and the ratio analysis.
Pro-Forma Financial Statements
The data provided in the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) 10-K reports for Nintendo and Sony are used to develop pro-forma financial statements for these companies. Appendix A presents the pro-forma statements (2016-2020) that are prepared for both companies with the focus on the certain assumptions. For Nintendo, it is possible to predict the tax rate in 25%. The interest rate will not change because the company does not depend on borrowings, but it is possible to increase the sales rate by 5% each following year due to the success of Mario Kart 8 and other games for Wii U (Nintendo, 2015). In addition, the launch of three new products is planned in 2017 to improve the company’s position in the market. For Sony, the interest rate is 30% because of the dependence on borrowings, and the sales rate will increase by 5% each following year (Sony, 2015).
Current Strategies and Future Investments
Nintendo actively develops the strategy oriented to the further global market expansion. The reason is that Nintendo has released successful products, and the company plans to enter new markets around the world. However, negative changes in the global market and the purchasing power of buyers can influence Nintendo’s liquidity and profitability. As a result, it is important to refer to investments while increasing the numbers related to global sales (Brigham & Houston, 2012; Moore, 2012). Overseas investors are planned to be attracted in order to reduce the impact of negative external factors and realize strategic plans regarding sales. Therefore, it is possible to expect the stable growth in the sales rate. The similar strategy is typical of Sony, but investors from the Asian region and North America are planned to be attracted in order to support the company’s production.
Ratio Analysis
While forecasting the future profitability of the company, managers also need to conclude regarding its potential liquidity and competitive advantage during the next five years. For this purpose, it is important to conduct the ratio analysis and calculate profitability, activity, leverage, and liquidity ratios for Nintendo and Sony as its competitor. The focus is on the data for 2016.
Profitability Ratio
To conclude regarding Nintendo’s future profitability, it is necessary to apply the formula for calculating Gross Margin Ratio (millions of yen): Gross Margin Ratio = Gross Margin/Net Sales.
Gross Margin Ratio for Nintendo = ¥202,044/¥577,269 = 0.35.
Gross Margin Ratio for Sony = ¥3,163,114/¥9,037,468 = 0.35.
The companies have equal gross margins projected for the end of 2016, and they are high enough in the context of the electronics (entertainment) industry. The next step is to calculate Return on Equity (ROE) following this formula: Profit after Taxes/Shareholders’ Equity.
For Nintendo, ROE = ¥81,633/¥13,029 = 6.2%, and for Sony, ROE = ¥169,728/¥37,510 = 4.52%. For 2016, it is possible to forecast the higher ratio for Nintendo because of increases in sales.
Activity Ratio
Activity ratios demonstrate how the company can use the available assets. Total Asset Turnover Ratio is calculated using the following formula: Total Asset Turnover Ratio = Net Sales/Total Assets.
For Nintendo, Total Asset Turnover Ratio = ¥577,269/¥1,362,958 = 0.4, and for Sony, Total Asset Turnover Ratio = ¥9,037,468/¥4,945,963 = 1.8. By the end of 2016, Sony will improve its approach to utilizing the assets, but more attention should be paid to managing assets in Nintendo in order to affect the ratio.
Leverage Ratio
The financial state of the company is determined with the focus on Total Debt Ratio that is calculated using the following formula: Total Debt Ratio = Total Liabilities/Total Liabilities + Market Value of Equity.
For Nintendo, Total Debt Ratio = ¥59,980/¥83,569 = 0.7, and for Sony, Total Debt Ratio = ¥12,178,180/¥12,122,787 = 1. By the end of 2016, Nintendo will be less dependent on loans than Sony because of the ratio.
Liquidity Ratio
Liquidity is measured with reference to Current Ratio that is calculated using the following formula: Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities.
For Nintendo, Current Ratio = ¥1,276,958/¥47,980 = 26, and for Sony, Current Ratio = ¥2 345 751/¥661 708 = 3.54. According to the ratio, Nintendo will be able to meet the short-term obligations easily. The ratio for Sony will also increase in comparison to the previous years.
For both companies, Nintendo and Sony, it is possible to project positive changes in liquidity. As a result, the companies will become more competitive, and it is important to note that the position of Nintendo can improve in the market. Still, changes in profitability are predicted to be slow because of the specifics of strategies followed by Nintendo and Sony.
Conclusion
The pro-forma financial statements (2016-2020) were developed for Nintendo and Sony as the main competitors in the electronics industry. The perspectives for the future investments were analyzed for both companies. The ratio analysis demonstrates that Nintendo and Sony preserve the stable leading positions in the market with the focus on high liquidity ratios.
References
Brigham, E. F., & Houston, J. F. (2012). Fundamentals of financial management. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Hillier, D., Clacher, I., Ross, S., Westerfield, R., & Jordan, B. (2014). Fundamentals of corporate finance. New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Moore, C. W. (2012). Managing small business: An entrepreneurial emphasis. New York, NY: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Nintendo. (2015). Annual Report 2015. Web.
Piper, T. (2010). Assessing a company’s future financial health. Harvard Business School Review, 91(11), 1-17.
Sony. (2015). SEC Report 2015.
Appendix A
Table 1. Assumptions for Nintendo.
Table 2. Nintendo Balance Sheet Data.
Table 3. Nintendo Income Statement.
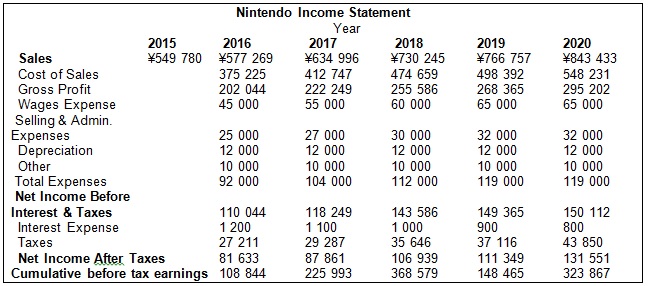
Table 4. Nintendo Cash Flow Statement.
Table 5. Assumptions for Sony.
Assumptions for Sony
Table 6. Sony Balance Sheet Data.
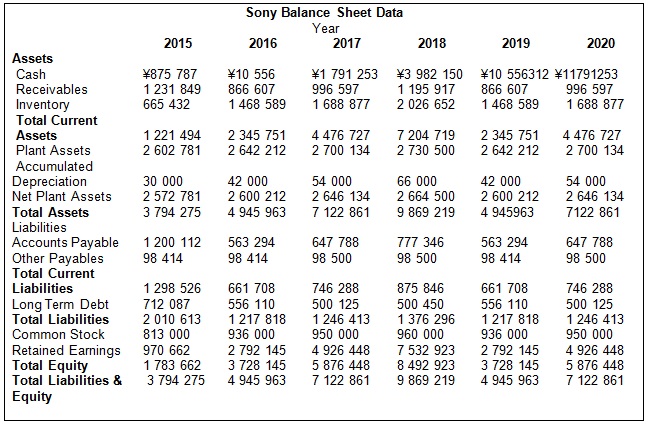
Table 7. Sony Income Statement.
Table 8. Sony Cash Flow Statement.