Introduction
Ensuring organizational effectiveness is one of the central tasks that companies face in the realm of the global economy. Due to the tight competition observed in the global market, as well as the presence of large corporations that pose an immeasurable challenge to new entrants, it is crucial to reach high levels of performance to build a functioning system of performance, communication, and R&D. For this reason, companies must embrace the concept of organizational change as the notion that drives their development forward and promote innovation-driven culture in their setting as the means of keeping the production process running. The importance of organizational effectiveness has gained even more significance over the past year as the development of the pandemic has curtailed the revenues of most organizations, making them develop innovative, sustainable tools for increasing organizational performance (Malik et al., 2017). Despite the increase in the levels of strain and the rise in the crisis rates, organizational effectiveness in contemporary companies can be enhanced once the focus on innovation and learning is incorporated into the organizational philosophy in a friendly and employee-oriented, culturally diverse environment with a strong organizational philosophy.
The goals of this paper include the analysis of challenges that the promotion of innovation and learning, in general, and the enhancement of innovative thinking and the extent of participation in decision-making within a company will entail. Specifically, the problem of resistance to change as one of the cornerstone impediments to the promotion of organizational effectiveness will be analyzed. Similarly, the issues associated with the improvement of communication, the need to increase the accuracy of forecasts and the efficacy of resource allocation, and embracing the role of a community in the workplace.
Managing Change: Reinventing the Corporate Environment
Promoting Innovation-Based Culture
The first and most important step in boosting organizational effectiveness rates would be the transition toward an innovation-driven environment. When pitched as the basis for the corporate philosophy, innovation might seem a rather nebulous concept, yet it has real-lie positive implications when applied correctly and combined with effective leadership. In other words, the organization will need to make changes in the corporate setting incremental, convincing staff members that regular introduction of new ideas, tools, and technologies is not merely necessary but, in fact, natural for successful companies.
At this point, the concept of shared identity as the experience of being a part of a team in the workplace environment will have to be brought up. To restructure the corporate philosophy toward innovation-based thinking, the organization will need to alter the attitudes of staff members toward decision-making in the organizational setting and the management of communication within a team. Applying the framework of organizational change offered by Kotter, one will realize that the second stage will require the development of what van Dick et al. (2018) referred to as shared identity. According to their research,
whenever such a shared identity is salient, individuals should provide more support to each other (as fellow ingroup members) and perceive a higher sense of collective self-efficacy, which both should reduce stress and strain. (van Dick et al., 2018, p. 21)
The creation of a shared identity aligns with the second step of Kotter’s Change Model, which suggests that the redesign of the corporate philosophy should be followed by the development of a team that would, later on, constitute the core for the promotion of organizational change (see Fig. 1). Specifically, Kotter insists that the process of organizational change should begin with creating urgency and establishing a guiding team that will support the further promotion of an innovative vision (Al-Kaabi et al., 2019). Therefore, by revisiting the current corporate values, shaping the company’s expectations toward innovativeness, and establishing a sense of shared identity that will empower company members to be more proactive and innovative, the company will build much more impressive organizational performance.
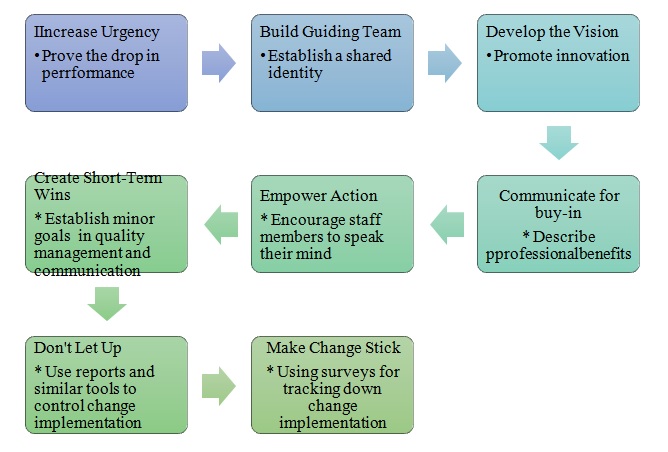
As Figure 1 above shows, the introduction of change should be conducted with the development of a guiding team in mind. The specified team, headed by a leader who uses a combination of the Transformational, Charismatic, and Innovation Leadership styles will allow implementing the change at a natural yet expeditious pace. As a result, the outcomes of implementing change will remain in place even with further permutations of the organizational management strategy.
Increasing Motivation in Employees
Although the creation of a team that will provide the bulk for the further improvement of the organizational effectiveness is vital, it is highly unlikely to produce the desired effect unless staff members are motivated and perceptive of change. In turn, the issue of motivation can be addressed by considering the factors that drive them to perform more effectively, as well as reducing the ones that make staff members feel discouraged. The specified approach aligns with what Herzberg’s Theory suggests, namely, the need to find the perfect balance between the motivational and hygiene factors (Lee et al., 2018). In the target setting, the presence of fear of being criticized, as well s the fear of failure, need to be seen as those that influence employees’ motivation to the greatest extent.
Therefore, to introduce the philosophy of innovation, it will be necessary to set a range of achievements, reaching which will lead staff members to corporate recognition, while simultaneously increasing their responsibility. Aligning with Herzberg’s theory as the crucial component of internal motivation, the specified factors will raise the levels of excitement in staff members. In turn, increasing workplace benefits and job security, as well as addressing issues in interpersonal relationships by building a dialogue- and compromise-driven conflict management strategy will reduce the impact of the hygiene factors.
In addition, the motivation issue observed in the target workplace setting can be addressed by introducing Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as the crucial model for understanding people’s motivations. As shown in Figure 2 below, the framework offered by Maslow suggests that basic needs should be covered first, whereas, to attain a high level of employee motivation, a company leader must introduce opportunities for self-actualization.
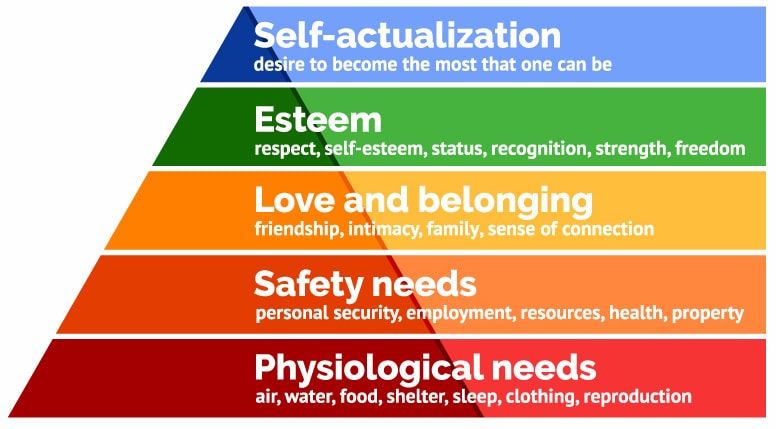
In turn, self-actualization opportunities in the target setting may involve giving employees responsibilities associated with decision-making on the corporate level, as well as encouraging them to produce the solutions that will affect a company on a larger scale. Specifically, the role of employees’ individual opinions during scheduled meetings will have to increase, with every suggestion being given detailed feedback. In addition, staff members will need to be provided with the responsibilities that will affect the end product, such as the decision to introduce improvements at a certain stage of product development.
Finally, the process of self-actualization will inevitably involve expanding the staff members’ level of expertise. For this purpose, the employees will be given an option to participate in courses and training sessions aimed at increasing the level of their competence.
Building Employee Engagement
In turn, to encourage faster acceptance of innovation as the basis of the corporate philosophy, as well as encouraging staff members to show greater rates of participation in the discussions of essential workplace issues, increasing the extent of their engagement in the organization’s performance is needed. Once employees are concerned with how the company performs in the target market, their level of performance and the rate of organizational effectiveness will increase as well. The outlined change will entail a shift toward building Corporate Social Responsibility in the target workplace.
Thus, the organizational culture in the target setting will be used to increase employee engagement by centering the needs of staff members and boosting their professional development, as well as upholding the standards for corporate integrity. Namely, the organization will follow Hewitt’s Model for increasing engagement in employees by identifying the factors that drive organizational effectiveness forward and those that reduce it.
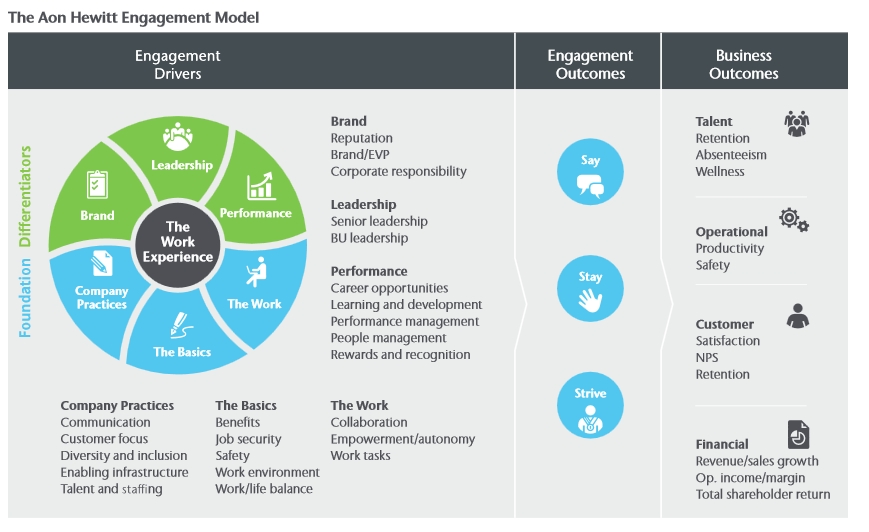
As Hewitt’s model shows, the increase in employee voice is one of the main factors in building the levels of employee engagement in the workplace. Indeed, Figure 3 above depicts the connection between the extent of expression and agency in the workplace and the levels of engagement in staff members. Namely, Jha et al. (2019, p. 5) state that “the employees who believe, they have enough opportunities to communicate their concerns to the management, carry more positive attitude which is reflected in higher performance by them.” Therefore, in the context of the target environment, it will be critical to reinforce the idea of employee participation.
Specifically, staff members will be invited to voice their opinions concerning possible improvements in the production process, the communication channel, and other relevant workplace issues. Thus, employees will gain the opportunity to accept the roles of leaders and connect themselves to the company and its brand. The following realization of their role in the company will make staff members develop increased levels of engagement, increasing their productivity and experiencing greater satisfaction (Manoharan & Singal, 2019). As a result, changes in their performance and, therefore, the overall organizational effectiveness will occur, whereas retention rates will rise.
Increasing Employee Satisfaction
The significance of employee satisfaction mentioned previously is tremendous for promoting innovation-driven thinking in the workplace. Therefore, ensuring that staff members are not only engaged but also satisfied is an essential step in addressing issues in organizational effectiveness. In turn, the levels of employee satisfaction will be boosted by changing the current leadership model toward a combination of Charismatic, Transformational, and Innovation Leadership styles. The proposed framework, namely, its charismatic aspect, will provide staff members with a model of organizational behavior and performance that they can use as a reference. In turn, the Transformational component of the leadership strategy in question will encourage employees to change and show them the direction in which they can improve, while simultaneously ensuring that the described change stays. Specifically, as stated in one of the recent studies on the issue,
Work engagement of employee would increase through transformational leadership attributes as transformational leader might drive desired outcome and specific belief by idealize influence and simply transmit inspirational motivation in employees in order to obtain clear visionary goal and performance up to standard. (Malik et al., 2017, p. 148)
Finally, the Innovation component of the suggested leadership approach will allow staff members to embrace the potential that innovative thinking and innovation-driven corporate philosophy hold. As a result, the staff members will be incentivized to change. Moreover, the proposed change will lead to a greater and more profound sense of satisfaction that employees experience as they complete work-related tasks and participate in decision-making processes. Indeed, studies show that once employees can place the effects of their performance in a context and understand their true contribution to the company’s performance, they can experience deep satisfaction with the value of the work that they complete (Malik et al., 2017). For this reason, promoting the involvement of staff members in decision-making is necessary so that they could develop a sense of responsibility and care for the organization.
Focusing on Teamwork
However, apart from the development of the factors that contribute to the improvement in staff members’ performance, the increase in organizational effectiveness will also require changes in how employees work as a team. Specifically, the principles of teamwork must be included in the current organizational setting due to the need to coordinate the actions of participants and ensure that projects are managed and implemented properly. In the management of projects, teamwork plays the leading role as the major factor determining the outcome. Therefore, creating an environment for teamwork will eventually lead to an improved level of organizational effectiveness.
To boost the extent of teamwork within the company, its leaders should set transparent goals with clearly defined roles being assigned to each participant accordingly. Moreover, the quality of communication must be outstanding, with each team member being fully aware of his or her responsibilities and tasks, as well as other details such as the deadline set and the goals associated with the respective assignment. Thus, the levels of effectiveness will increase immediately.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Teamwork
Promoting interdisciplinary cooperation in the target workplace is another crucial step toward excellence in organizational performance. By creating the framework for interdisciplinary cooperation, the company will be able to connect key processes within the workplace into a single framework, thus, placing every item in order and creating a perfectly structured organizational framework. Remarkably, the described change should not imply building a rigid power structure since it may lead to some of the members of the corporate hierarchy being tempted to misuse their power. Instead, the principles of equity must be introduced into the target setting.
Moreover, studies show that the presence of an implicit hierarchy and, therefore, the element of competition and enmity within the workplace will inevitably reduce the probability of high organizational effectiveness. For instance, the scenarios in which the opinion of some staff members may be dismissed by others due to the implied inequality within the workplace (Moe & Brataas, 2016). Therefore, it is the responsibility of a leader to break the cycle and introduce a new model of building relationships in the workplace becomes particularly important and challenging at the same time.
In the selected setting and industry, the threat of workplace confrontations and the presence of prejudices about people of certain job positions are not as likely as it is in other areas, such as nursing. However, the threat of the described relationships dynamics to occur remains rather high, which is why introducing the principles of interdisciplinary collaboration into the specified setting is imperative. Namely, the described change will cause staff members to reach agreements quicker and solve issues in the workplace faster.
Another important issue in favor of adopting interdisciplinary collaboration in the target setting, the presence of large amounts of data that each team member must embrace and utilize to make an informed decision needs to be mentioned. Since the information mentioned above is often quite big and rich in details, the probability of some of its elements being accidentally omitted remains high (Moe & Brataas, 2016). Thus, staff members need to learn to collaborate on an interdisciplinary level to ensure that every bit of information is transferred to the target recipient within the corporate setting properly and promptly.
Conflict Management: When Opinions Collide
The introduction of interdisciplinary cooperation will allow resolving one of the major problems that organizations face, including the company in question. Specifically, the collision of opinions and the resulting arguments affect the quality of performance. With the increase in the number of conflicts and their intensity, staff members are likely to overlook some of the faults in manufactured products, thus reducing the quality of the result and, consequently, the organizational effectiveness rates. In addition, with the rise in the number of confrontations, building and sustaining a shared identity within the selected workplace environment will become excessively difficult (Mukhtar et al., 2020). Therefore, the implementation of strategies that encourage interdisciplinary cooperation will be required.
Creating Communication Channels
Moreover, apart from improving communication between staff members by encouraging them to resolve conflicts more productively and suggesting that they rethink their perceptions of specific roles and responsibilities in the workplace context, communication between staff members and company leaders must be amended. The improved dialogue between employees and leaders will allow the former to have their requests heard and implemented accordingly, which, in turn, will lead to a rise in organizational effectiveness. Apart from having a massively positive emotional impact, the development of improved communication between employees and company leaders will cause an improvement in kay workplace processes. Indeed, due to the lack of connection to the basic production-related issues that staff members of lower rank must face regularly in the workplace setting, company leaders may ignore these challenges and create the leadership and change management frameworks that will ultimately fail.
However, as long as an insider look at the workplace processes occurring in the organizational context is provided, tools for improving the performance and removing the impediments toward successful management of workplace responsibilities will be designed. For instance, in the context of the target company, a significant number of leaders appear to be blissfully ignorant about the necessity to spend a significant amount of time on waiting for specific processes, such as quality assurance, to end before proceeding to an often unrelated phase. Therefore, the introduction of tools that would allow staff members to run several processes simultaneously would increase their organizational effectiveness to a significant extent.
Building a Strong Leader: Personality as an Inspiration
Speaking of leadership, the development of a strong leadership persona will be instrumental in addressing some of the current issues that prevent staff members from reaching new highs in their organizational effectiveness. For example, a strong leader could help to resolve the issue of reluctance to accept the change and the resulting resistance toward it in staff members. Moreover, as a leader, one will be able to promote the concept of innovativeness to staff members as the guiding notion that they would implement during crucial stages of decision-making, thus locating uniquely harmonic solutions to complex problems.
Therefore, as a leader, one must both provide staff members with an example and inspire them as a role models, at the same time promoting the concept of innovation to them. For this reason, a combination of Charismatic, Transformational, and Innovation Leadership styles will have to be applied to the specified environment. As a leader, one will have to be both appealing enough and encouraging enough to build the need to change in employees, which is why a combination of Charismatic and Transformational Leadership styles will be required. In turn, Innovation Leadership will introduce employees to the idea of applying innovative thinking into decision-making and project management, thus helping them to produce original solutions.
Accepting Employee Culture vs. Promoting Corporate Values
As a leader, one will have to make a range of difficult decisions in the workplace. Locating the solution between promoting corporate philosophy and being appreciative and supportive of employees’ cultures is one of those dilemmas. Since the setting of the target organization is very diverse, the specified dilemma is likely to emerge as one of the key concerns. Given the fact that innovation as the foundational principle of change described above, which will have to be implemented in the target setting, may conflict with some of staff members’ culture, searching for a compromise is critical.
Thus, as a leader, one could alleviate the transition toward an innovation-driven philosophy of decision–making and innovation-based corporate culture by acknowledging the culture-specific needs of staff members and meeting those needs accordingly. At the same time, in the scenarios that involve incongruences between the cultural values of employees and those of an organization, it is the role of a leader to help staff members to transfer to a new way of thinking. For instance, in the target setting, a significant portion of staff members has been adopting a very relaxed approach to time management. As a result, due to very loose adherence to set deadlines, the organizational effectiveness of the employees has been moderate to low. Thus, the company may choose to acknowledge the specified culture characteristic of staff members by setting more flexible deadlines, while also gradually introducing staff members to the need to meet organizational schedule more accurately. The described goal can be achieved by splitting the tasks into smaller portions and ensuring that the employees have enough time to complete them but not enough to procrastinate.
Enhancing Support as the Response to Resistance to Change
The issue of resistance to change also deserves a separate discussion as one of the major problems to be expected when promoting the system of innovation-driven decision-making. Since the specified change will entail challenges for staff members, including the necessity to adjust to every innovative solution produced by the organization, the creation of new roles and responsibilities, and similar alterations, the levels of resistance to change are expected to be quite high. To address the described issue, the company leaders will have to deploy the counseling framework mentioned above and encourage employees to accept change as an integral and even exciting aspect of their professional experience. Moreover, staff members must be aware that the company is not going to judge them harshly if they find it difficult to apply newly designed rules and standards to their work immediately. On the contrary, a gradual transfer to a new workplace environment will be facilitated.
Addressing Increased Stress Rates and Larger Workload
To introduce an innovation-based approach as the means of increasing organizational effectiveness, the company will also have to consider the future implications of the increased workload that the specified change will entail. With the creation of new roles and responsibilities for staff members, as well as the introduction of innovative frameworks to which the employees will have to adjust and get used, the organization will require a different approach for managing stress in the workplace. Specifically, the company will need to use innovation-driven philosophy to introduce a support system for staff members that have been experiencing an emotional crisis due to the rise in workload rates. Specifically, the organization will need to hire several experts in counseling and psychology to provide guidance and support to staff members. In addition, opportunities for building an improved skill set that will allow employees to complete workplace tasks within a shorter range of time and with lesser effort will have to be provided. Thus, the company will ensure that the employees will not experience workplace burnout. Since the latte is known as the mental health phenomenon that reduces the efficacy of employees’ performance, it is crucial to introduce every possible measure to avoid it.
Promoting Learning and Development of Professional Skills
In its attempts at building an innovation-driven workplace environment and decision-making as the means of improving organizational effectiveness, one must incorporate tools for educating staff members and encouraging them to gain new professional skills. Since the environment of the global economy has been particularly convoluted recently due to the emergence of a global crisis, the focus on building a competitive advantage rooted in professionalism and innovation as the extension of professional learning is required. For this reason, professional training should be mandated in the target organizational setting.
The significance of promoting learning as a crucial source of competitive advantage is critical for the company and its employees since it enables the employee sot embrace, internalize, and, ultimately, personalize the idea of innovation. However, the described change is likely to cost the organization a sizeable amount of money and other resources. As Manley et al. (2018, p. 135) explain, the “effectiveness of training activities requires a comprehensive organizational strategy to enable measurement of outcomes, performance and the overall return on investing in training.” Therefore, the company should prioritize providing its staff members with the tools for expanding their professional skillset, which will have a direct impact on the employees’ performance and organizational efficacy of the company.
Providing Continuous and Objective Feedback
As emphasized above, communication is the key to successful management of organizational performance and the improvement in the quality of the output delivered by staff members. However, the described effect is only possible once employees receive feedback about their performance. Thus, to increase the organizational performance of the target company, a framework for producing feedback will be required. Remarkably, a large number of staff members prefer not to voice their opinions at work, particularly, when discussing a certain choice and participating in the decision-making process initiated by the company. Cooper (2018) explains that the reasons for the observed lack of initiative may be explained in several ways, yet all of them boil down to two main factors, namely, indifference and fear of being judged.
Therefore, the focus on continuous dialogue and the provision of positive feedback is central to encouraging employees to speak their minds. As long as staff members recognize that they are valued and that their opinions are worthy of being considered, positive change can be implemented. The specified change will also allow staff members to feel more confident as they partake in the act of rebelliousness that is typically seen as a crucial part of building what is deemed as courage in the corporate setting (Hurt, 2020). Indeed, according to Hurt (2020), in the modern business environment, small acts of resistance are typically counted as the most satisfyingly courageous choices. Therefore, by promoting the culture of bold expressivity and the ability to go against popular opinion, challenging the existing standards, the company will be able to open communication.
Moreover, to fight indifference, the strategies for increasing motivation and engagement mentioned above must be deployed. Specifically, the company will have to show its staff members that it counts their opinions as important by offering feedback on every suggestion. Simultaneously, the organization will have to demonstrate carefully that even negative feedback can be constructive and should not be feared. As a result, the company will gain an opportunity to create a team of employees who voice their ideas freely, accept feedback, and use it to improve and produce even better solutions that will be incorporated into the company’s design.
Conclusion
The present-day business setting has been turning increasingly more complicated and strenuous due to the rise in the extent of the economic crisis and the resulting increase of pent-up anxiety among employees and managers. However, improvements to organizational effectiveness can be made with the introduction of innovation-geared leadership and the focus on the role of employee motivation and engagement in the organizational context. By creating an environment in which staff members will feel motivated and challenged professionally, thus developing the propensity toward continuous learning, one will be able to improve organizational effectiveness significantly and promote the introduction of change into the organizational design as its inalienable component.
Although the proposed change will imply the necessity to address the issues associated with employees’ fear of failure and the resulting opposition to the idea of accepting change and innovation-driven corporate values, the proposed solution will eventually help to raise organizational effectiveness. Once a strong leadership model is designed and the organizational setting is changed to create a workplace environment that is more inclusive and comfortable, while also being challenging and engaging, employees are expected to build stronger motivation. Moreover, once the company’s intention to invest in its employees, assisting them in the development of professional skills, becomes apparent to staff members, they are likely to perform more effectively, ultimately contributing to the rise in organizational performance. Finally, with a change in the organizational values and the notion of innovation, a company will be set for continuous progress, which will suggest that the quality assurance and the performance standard are increased accordingly. Thus, the needs of the modern audiences will be reflected, while company members will remain content and loyal, which will ultimately lead to an improvement of organizational performance rates.
References
Al-Kaabi, S. K., Selim, N., Al-Dahshan, A., & Chehab, M. (2019). Improving the birth registration service using Kotter’s Change Model: A quality improvement study from Qatar. Global Journal on Quality and Safety in Healthcare, 2(4), 98-104. Web.
Cooper, C. A. (2018). Encouraging civil servants to be frank and fearless: Merit recruitment and employee voice. Public Administration, 96(4), 721-735. Web.
Jha, N., Potnuru, R. K. G., Sareen, P., & Shaju, S. (2019). Employee voice, engagement and organizational effectiveness: a mediated model. European Journal of Training and Development, 43(7/8), pp. 699-718. Web.
Lee, Y., Mazzei, A., & Kim, J. N. (2018). Looking for motivational routes for employee-generated innovation: Employees’ scouting behavior. Journal of Business Research, 91, 286-294. Web.
Malik, W. U., Javed, M., & Hassan, S. T. (2017). Influence of transformational leadership components on job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences (PJCSS), 11(1), pp. 147-166.
Manley, K., Martin, A., Jackson, C., & Wright, T. (2018). A realist synthesis of effective continuing professional development (CPD): A case study of healthcare practitioners’ CPD. Nurse Education Today, 69, pp. 134-141.
Manoharan, A., & Singal, M. (2019). Organizational effectiveness in hospitality: Managers perspectives. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 80, 123-125. Web.
Mukhtar, M., Risnita, R., & Prasetyo, M. A. M. (2020). The influence of transformational leadership, interpersonal communication, and organizational conflict on organizational effectiveness. International Journal of Educational Review, 2(1), 1-17. Web.
Moe, A., & Brataas, H. V. (2016). Interdisciplinary collaboration experiences in creating an everyday rehabilitation model: A pilot study. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 9, 173.
Van Dick, R., Ciampa, V., & Liang, S. (2018). Shared identity in organizational stress and change. Current Opinion in Psychology, 23, pp. 20-25. Web.