Introduction
The presence of the internet has enabled continuous development and usage of social media networks. Other than personal use, social media has facilitated the storage of a large amount of content and a rapid diffusion of information. Most businesses have realized the benefits of social media and have exploited it to increase their competitive advantage. Consequently, the usage and popularity of social media have led to the development of social media analytics which refers to gathering data from social sites and analyzing it to help make the best business decisions. This paper describes social media analytics while focusing on five tools; Google, Hootsuite, Brandwatch, Audiense, and Falcon.io. In addition, the report presents an overview of social media analytics and a review of past studies on the same.
Overview of Social Media Analytics
The increased social media application calls for firms and managers to understand social media analytics better. Social media analytics (SMA) can be defined as collecting and analyzing social media data to help decision-making (Thelwall, 2018; Lee, 2018). The technique has been used by many firms and individuals, including business managers, social scientists, and other professionals. Stieglitz et al. (2018, p.157) defined SMA as “an emerging interdisciplinary research field that aims at combining, extending, and adapting methods for the analysis of social media data.” SMA focuses on the perspectives of the system and the users that create the content.
Literature Review
Research on social media analytics has attracted numerous scholars who study its different aspects. For instance, Wang and Ye (2018) looked at the main dimensions of social media data; time, space, content, and network, where they stated the significance of the information from each aspect. Furthermore, the data from the dimensions constitutes which impacts business sustainability as studied by Sivarajah et al. (2020). On the other hand, Holsapple, Hsiao, and Pakath (2018) focused on the nature and characterization of SMA. On the description of SMA, Misirlis and Vlachopoulou (2018, Table 1, p.272) analyzed various studies and presented several definitions in a table as shown below;

Social media analytics has been applied in numerous situations, with various researchers utilizing it in studying different domains. For instance, Park, Kim, and Choi (2019) used a social media analytic framework to analyze the information exchanges between various groups to identify the influential actors and content within the specific social networks in a tourism organization. Furthermore, Mirbabaie and Zapatka (2017) also illustrated using SMA to identify top influencers or opinion leaders. Finally, Granell and Ostermann (2016); Klonner et al. (2016); and Wang and Ye (2018) have studied the application of social media in the field of disaster management to get the necessary information for the development of situational awareness and improved disaster response.
Tools Used in Social Media Analytics
Google analytics
Google Analytics is offered by Google as part of the marketing platform brand and helps businesses track and report the traffic on their websites. It is a free analytical tool launched in 2005 (Brandon, 2019). Google Analytics installs a tracking code into a business’ website, which records the users’ activities when they visit the website and other information about the users, such as their age, interests, and gender (Google Analytics, 2022). The code then sends the recorded data to the server after the user’s exit from the website. Its main functions are shown in its interface as shown below (Google Analytics, 2022);
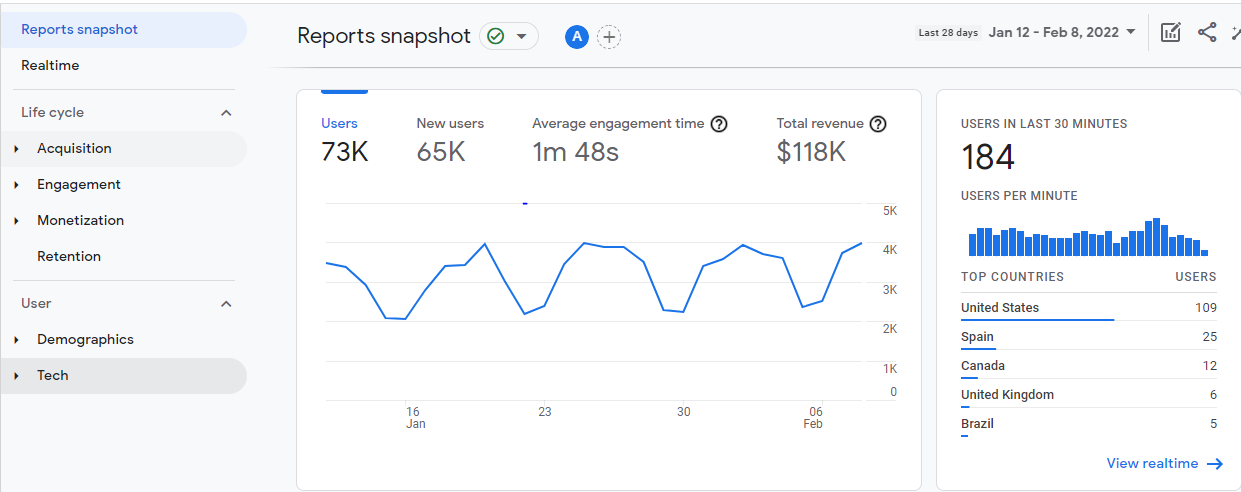
Hootsuite Analytics
Hootsuite Analytics is a tool that pictures a business’ social medial efforts such that the company gets all the necessary information from all platforms in one place. The tool makes it easy and fast for companies to assess their performances and summarize their teams’ stories (Hootsuite, 2022). Hootsuite was developed in 2008 by Ryan Homes (Khan, 2017). The platform’s user interface takes the form of a dashboard that is integrated into some social networks such as Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram. Its essential functions are illustrated on its interface as shown below (Hootsuite, 2022);

Brandwatch
Brandwatch, as a social media analytical tool, tracks online conversations that take place on various platforms such as Facebook, news, Twitter, and blogs. It analyzes the conversations to enable businesses to understand brand perception, consumer insights, trends, and top influencers (Brandwatch, 2022). In addition, the platform allows individuals to understand others in different ways. Brandwatch was founded in 2006 by Giles Palmer in Brighton, England. The products offered by Brandwatch include consumer research, audiences, BuzzSumo, Vizia. Reviews, and APIs. The main functions of Brandwatch are as illustrated in the diagram below (Brandwatch, 2022);
Audiense
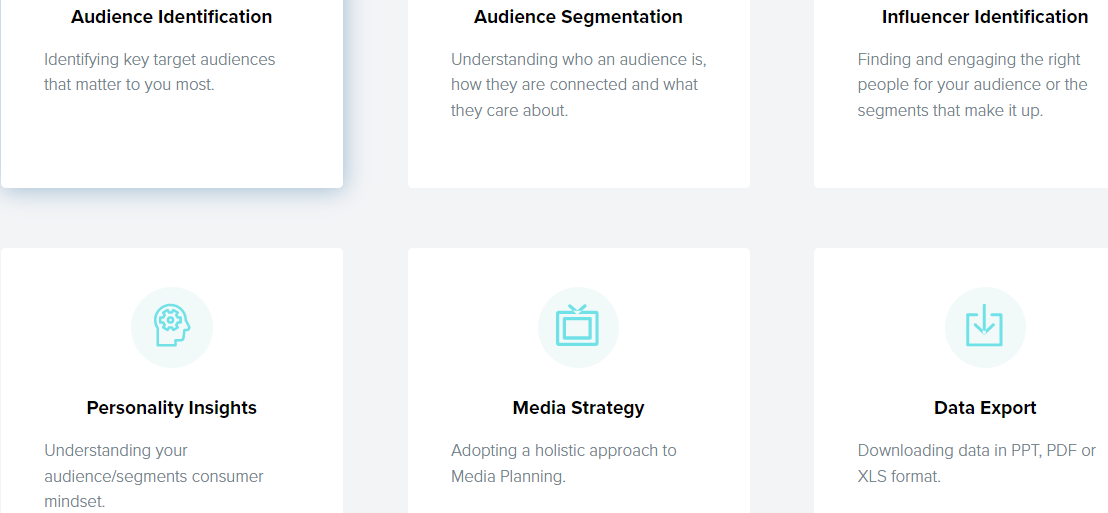
This platform involves making sensible insights concerning a business’ audience. Notably, it helps companies identify their relevant audiences, discover unique and actionable insights, and get informative strategies for growth (Audiense, 2022). Specifically, Audiense analyzes the individuals who react on given updates in social media networks where it acquires some of their data necessary for segmentation. Its services are community management and analysis, chatbots and broadcasts, advanced monitoring and listening, and Twitter-tailored audiences for advertising. Its essential functions are shown on the tool’s interface as shown below (Audiense, 2022);
Falcon.io
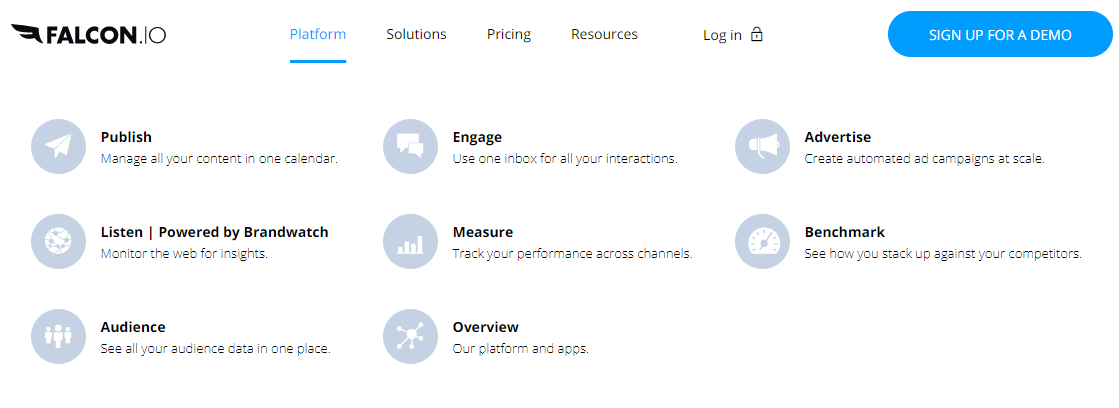
Falcon.io is a tool that offers one of the best platforms for marketing in social media and managing clients’ experiences. It was launched in 2010 in Copenhagen by Ulrik Bo Larsen, its founder (Falcon.io, 2022). The analytic tool enables businesses to earn more revenue by delivering personalized brand experiences from accessing enriched customers’ profiles. In addition, it possesses tools that support social listening, engaging, publishing, managing, and analyzing the clients’ data. Falcon. Io’s interface illustrates its critical functions as shown below (Falcon.io, 2022);
How Social Media Analytics Tools Help Industries Make Profit
Social media analytics helps firms and their industries to improve productivity and increase their chances of earning more profits. Each SMA tool contributes to the profitability of the enterprises that use them. Some tools help companies improve their competitive advantage by providing the most accurate data necessary to make informed decisions (Wang et al., 2017). Particularly, Falcon.io, Audiense, and Brandwatch analytics enable businesses to get detailed insights into their clients’ views and opinions concerning the products and services they offer, which influence their decisions. In addition, Hootsuite enables companies to calculate their Return on Investment in social media marketing. It yields reliable summaries of key performance indices and can advise when to earn more revenue. Finally, Google Analytics helps companies improve target marketing, which is necessary to increase sales, resulting in significant profits.
How Social Media Analytic Tools Help Make Big Data Easier To Use
Big Data comprises structured and unstructured data that should be mined for crucial information. SMA tools help firms analyze Big Data to get helpful information critical for decision making. For instance, Google Analytics makes Big Data easier to use as it aggregates it in various levels that involve the user, session, pageview, and event levels (Semerádová and Weinlich, 2020). In addition, the Google analytics interface contains various menus such as the report menu, which shows the information about the audience, real-time audience interaction with the website, acquisition of traffic, the users’ behavior, and the specific actions they take while at the website.
Hootsuite analytics also makes Big Data easy to use through its functions which involve publishing content, engaging with the clients, creating advertisement campaigns, and monitoring the conversations on the website. Audiense contributes to Big Data by offering a tremendous visual segmentation of a particular audience. Specifically, audiense groups the audience data into various segments based on age, gender, and interests. Both Brandwatch and Falcon.io offer social media listening in which they analyze online conversations about a company or its products. In social media listening, the tools conduct qualitative observations and quantitative analyses of users’ intents and sentiments (Sivarajah et al., 2020). The sentimental analysis makes the collected voluminous conversational data easy to use.
Conclusion and Areas for Future Research
Social media analytics refers to collecting various data from social media sites and analyzing it to help decision-making. Social media analytic tools include Google, Hootsuite, Brandwatch, Audiense, and Falcon.io. The tools handle numerous aspects of social media analytics necessary for business growth and development. Most importantly, the tools help industries that use them improve their profitability. However, studies on the application of social media analytics tools are limited. Therefore, future research should focus on the tools’ utilization and effectiveness in handling social media analytics.
Reference List
Audiense (2022) Unique consumer insights and engagement. Web.
Brandon, D. (2019) ‘Google analytics’, Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges, 34(7), pp.81-82. Web.
Brandwatch (2022) About us. Web.
Falcon.io (2022) Social media marketing platform. Web.
Google Analytics (2022) Features. Web.
Granell, C. and Ostermann, F.O. (2016) ‘Beyond data collection: Objectives and methods of research using VGI and geo-social media for disaster management.’ Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 59, pp.231-243. Web.
Holsapple, C.W., Hsiao, S.H. and Pakath, R. (2018) ‘Business social media analytics: Characterization and conceptual framework.’ Decision Support Systems, 110, pp.32-45. Web.
Hootsuite (2022) ‘Analyze; See your results.’ Web.
Khan, G.F. (2017) ‘Social media analytics’, In Social Media for Government, (pp. 93-118). Springer, Singapore. Web.
Klonner, C., Marx, S., Usón, T., Porto de Albuquerque, J. and Höfle, B. (2016) ‘Volunteered geographic information in natural hazard analysis: a systematic literature review of current approaches with a focus on preparedness and mitigation’, ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 5(7), p.103. Web.
Lee, I. (2018) ‘Social media analytics for enterprises: Typology, methods, and processes’ Business Horizons, 61(2), pp.199-210. Web.
Mirbabaie, M. and Zapatka, E. (2017) Sensemaking in social media crisis communication–A case study on the Brussels bombings in 2016, Web.
Misirlis, N. and Vlachopoulou, M. (2018) ‘Social media metrics and analytics in marketing–S3M: A mapping literature review’, International Journal of Information Management, 38(1), pp.270-276. Web.
Park, D., Kim, W.G. and Choi, S. (2019) Application of social media analytics in tourism crisis communication. Current Issues in Tourism, 22(15), pp.1810-1824. Web.
Semerádová, T. and Weinlich, P. (2020) ‘Using Google Analytics to examine the website traffic’, In Website Quality and Shopping Behavior (pp. 91-112). Springer, Cham.
Sivarajah, U., Irani, Z., Gupta, S., and Mahroof, K. (2020) ‘Role of big data and social media analytics for business-to-business sustainability: A participatory web context’, Industrial Marketing Management, 86, pp.163-179. Web.
Stieglitz, S., Mirbabaie, M., Ross, B. and Neuberger, C. (2018) ‘Social media analytics–Challenges in topic discovery, data collection, and data preparation’, International Journal of Information Management, 39, pp.156-168. Web.
Thelwall, M. (2018) ‘Social media analytics for YouTube comments: Potential and limitations’, International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 21(3), pp.303-316. Web.
Wang, Y., Rod, M., Deng, Q. and Ji, S. (2020) ‘Exploiting business networks in the age of social media: the use and integration of social media analytics in B2B marketing’, Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Web.
Wang, Z. and Ye, X. (2018) ‘Social media analytics for natural disaster management’, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 32(1), pp.49-72. Web.