Introduction
This paper provides a comparison between strategical analysis results, MOP practices, and organizational structures implemented within the companies TESLA and Ritz Carlton. It observes the way the differences between industry requirements for a civil engineering production-based firm and a service sector firm affect the KPI interpretations within the businesses. Additionally, it elaborates on the impact TESLA and Ritz Carlton have in their respective industries and for the global business overall due to their trendsetter status and worldwide recognition.
Business Report
The modern environment of global business and consistent digitalization of the operational processes has unified the majority of medium- and large-scale enterprises in most of their practices. Areas of performance review and strategic planning overlap substantially across industries. Nevertheless, the specific characteristics and requirements within the fields shape the strategic management tools available and the KPI interpretation. This report may therefore be interpreted as a comparative analysis between two firms that may serve as examples for their groups: TESLA and Ritz.
Background Information and Strategic Planning
TESLA was originally established in 2003 with the intention of developing the sector of renewable energy cars to its full potential. The Roadster debuted TESLA’s cutting-edge battery technology and the electric motor in 2008 (Teece, 2018).
From there, TESLA created the Model S, the world’s first luxury all-electric sedan, which has become the greatest car in its class in every category. The company aims to change the perception of electric automobiles, which, according to polls, are typically seen as a sign of elitism. TESLA also makes a unique collection of energy solutions, including the Powerwall, Powerpack, and Solar Roof, which enable homeowners, companies, and utilities to manage renewable energy generation, storage, and consumption. (Teece, 2018). TESLA builds batteries in the numbers necessary to fulfill production targets while also creating thousands of jobs by bringing cell production in-house.
To contrast TESLA’s deeply innovative nature and innate connection to modern technology, one should take into account how Ritz, the other firm this paper examines, originates with the construction of the first glass-made hotel in the world in 1927. Decades later, in 1983, the Ritz-Carlton Hotel Company was officially founded and registered. The firm began to expand, adding additional locations around the United States, led by president and founding father Colgate Holmes.
The success of The Ritz-Carlton Hotel Company drew the attention of the hotel industry in 1998, and Marriott International bought the brand. The Ritz-Carlton has continued to develop since this acquisition, delivering outstanding service and genuine care to their guests all around the world (Marpaung, Pratomo and Wickaconso, 2019). In 2008, the firm launched the first Ritz-Carlton Reserve property, giving a private sanctuary experience in Phulay Bay, Krabi, Thailand, in addition to dozens of additional hotels throughout the world.
SWOT Analysis
One might begin with TESLA Inc.’s strengths, which will cover the company’s good elements that have bolstered TESLA’s position as one of the world’s most dominating firms. The following elements, which are seen to be TESLA’s strong points, have secured the company’s long-term profitability, expansion, and popularity. The firm is recognized as a top employer both within the industry and outside of it, providing an excellent compensation package to its employees.
It was recently named one of the best places to work, attracting young people with new ideas and enthusiasm. The firm was also named one of Forbes’ “America’s Best Employers 2019” in 2019. TESLA’s sales have grown despite its problems. Over 367,500 vehicles were delivered in 2019, making the company rise to the top of the industry. Due to its unrivaled development in innovation and luxury at the same time, the firm has surpassed some of the world’s most prestigious automotive manufacturers, like Mercedes and BMW.
TESLA’s main weakness concerns the manufacturing process complication that arises frequently and is of a complex nature due to the productions’ advanced specifics. Even if TESLA was able to compete with the world’s largest car firms in such a short period of time, its production capabilities would pale in comparison to those of its competitors. The firm only has one factory, which is situated in California and can only produce a limited number of automobiles. Secondly, TESLA’s target market concerns a small group of customers with high-income levels who would be able and willing to purchase a TESLA. The business model image below illustrates the customized eco-friendly production model of the firm.
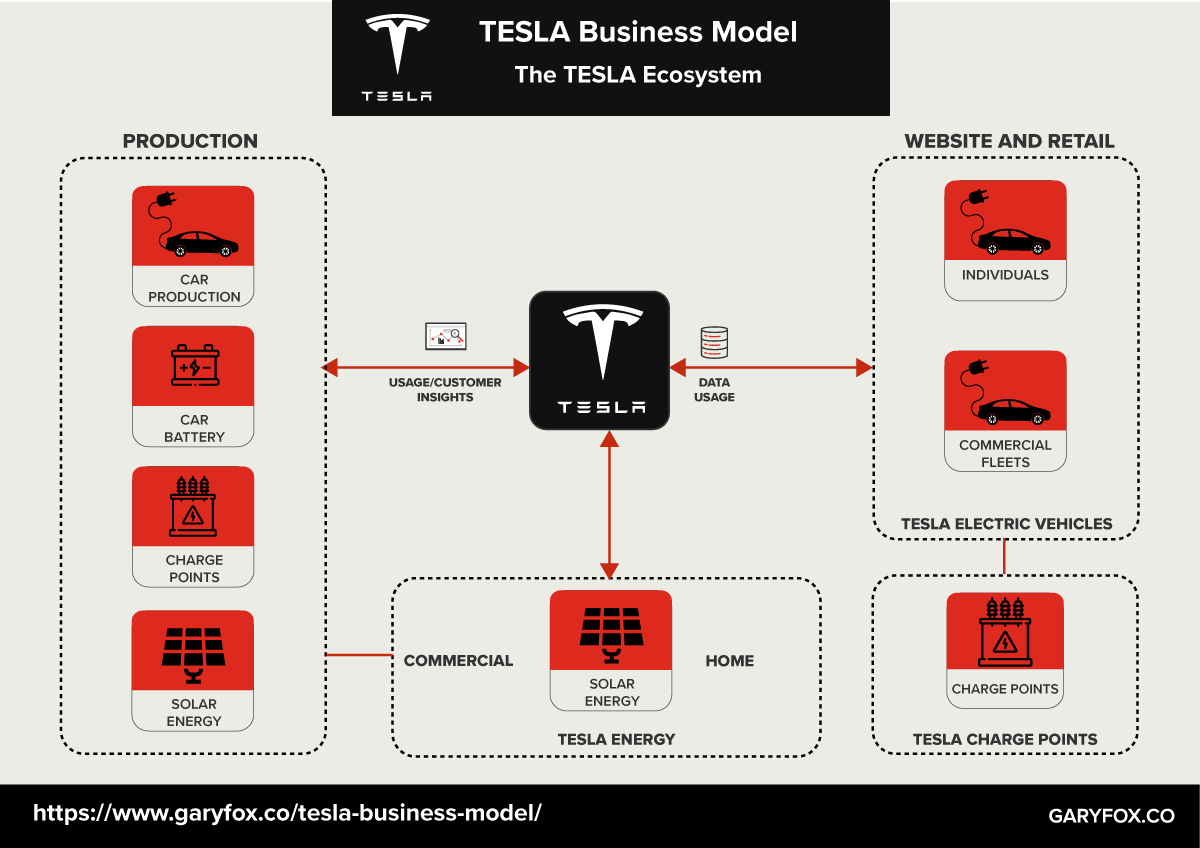
Opportunities for TESLA concern primarily the emerging markets in China and Japan that could be overseen by a U.S. representative to facilitate the negotiations. The demand for sustainable products has risen quickly as people have become more aware of the necessity of switching from fossil fuels to sustainable energy. TESLA is one of the few forerunner businesses in the field of renewable energy and electric vehicles, and demand for its products is increasing every day.
The threats the company is facing are primarily related to the innovative and newly regulated nature of the industry itself. The self-driving sector is reliant on auto-pilot technology that is yet to be fully explored and compared to its alternatives. The volatile nature of the market can, in separate cases, be interpreted as an opportunity. However, considering the budgeting of the company and the scale of the financial loss the firm may face if an experiment goes wrong kindly proceed afterward, suggesting that it is worth it for the long-term partners of the corporation.
Moving on to Ritz Carlton, it is important to specify that the majority of the strategic planning differences between the companies come from their differences in the industries the firms operate in. The competitive landscape and the value propositions for the hotel industry differ substantially from those of the automotive industry, especially the ecological self-driving sector. The strengths of Ritz Carlton as a company include the presence in the right locations, high employee value, high synergy amongst stakeholders, and effective guest feedback.
Ritz Carlton hotels may be found in some of the world’s most well-known, beautiful and travel-friendly places, with the infrastructure built for tourism of all types. Their market research accounts for the national specifics of a location and its target audience, as well as the modern trends in luxury accommodation. Many of the visitors that favor Ritz Carlton hotels are returning customers with a history of established brand loyalty (Marpaung, Pratomo and Wickaconso, 2019). They engage in the form relationship with the management team of the hotel and maintain a form of dialogue in the form of effective feedback and, where possible, adjustments on the administration’s part.
The weaknesses in Ritz Carlton’s business model are primarily related to the fluctuating demands of its consumers that are difficult to track and standardize the general offer accordingly. Customers’ needs differ between segments, countries of origin, family status, and even races, with the managerial team being able to prepare in advance for some of these variations but not others. Each culture may have a distinct concept of luxury, and as a result, the value they place on each component of service may vary. Understanding and supplying what each group wants is very hard for hotel companies like Ritz, which have operations all over the world.
Further difficulties come with how the ever-rising standards of living correlate with increasing complexity of satisfying the rising expectations of the young generation. This tendency, however, provides a simultaneous increase in the range of opportunities available to the Ritz Carlton brand. Luxury goods, such as vehicles, designer labels, and watches, are in high demand across the world.
As customary for the hotel industry and tourism sector in general, competition and local economic turmoils remain the most significant threats for Ritz Carlton as a company. As the major hotel chain, Ritz competes against other well-established brands, such as Best Western and Hilton Hotels Corporation. However, the increasing number and quality of small-scale boutique hotels have turned out to be dangerous competitors as well. Although much less equipped in terms of resources and connections, they provide a more personalized, highly customizable experience that is currently in high demand worldwide. As a result, the strategic planning in Ritz revolves around the potential for increasing their own customization efficiency and adding a personal touch to the firm’s refined current operations.
MOP Practices Review
Maintenance Operations Protocol, commonly referred to as MOP, concerns the uploading, downloading and upgrading of essential software, troubleshooting and remote testing of running operations. In human resources, however, the abbreviation and the concept itself take a different meaning and are therefore relevant across industries for both TESLA and Ritz. In the HR and organizational management context, MOP concerns the running operations degree of internal cohesion and their relationship with the overall strategy of the firm. The five relevant elements include planning and expectation setting, monitoring, development and improvement, periodic rating, and rewarding. These elements were further developed on the basis of the performance management diagram below.
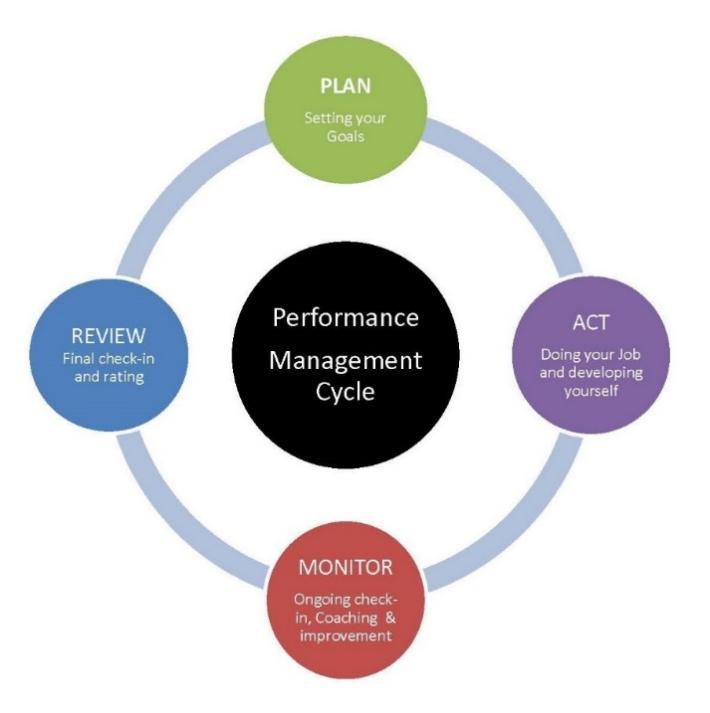
For planning and expectation setting, it is essential that objectives are defined, the mechanisms by which they will be measured must are made clear, and a particular time period is diligently outlined and then followed. Achieving success in performance management necessitates the establishment of defined objectives. Since one of the companies in the analysis is production-focused while the other is service-focused, their tactics of goal setting would naturally differ. Ritz would establish the number of customers they wish to invite, and TESLA would determine how many vehicles it needs to produce within a set period of time.
The monitoring aspect of the performance management system is inevitably included in the set of key performance indicators since it allows one to keep track of the ongoing progress and potential issues. The greatest performance management tools and approaches on the market today may help you track your workers’ continuous growth in a simple and rapid manner (Thoman and Lloyd, 2018). This implies that modern businesses strive to make it easier for their workers to engage in self-assessment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own growth, which is an important trait to develop in an effective employee.
Based on monitoring outcomes, the firms will then engage in further development and performance improvement upon the due consultations with the employees and management held. If an employee is on track to reach their target for the time period set, a wise and successful manager would introduce and promote tools and methods to help the individual surpass and go above their stated objectives. Successful performance management is always striving for more without sacrificing what has already been achieved (Feyerlein, 2017). Arguably, this area of MOP is more relevant for Ritz Carlton employees due to it being situated within the service sector.
When working on the performance management system, it is critical to avoid waiting until judgment day. In the meantime, it is critical to offer some type of feedback or rating to help employees understand whether or not they’re on track to reach their future objective. Some employees perceive their progress more clearly than others, who don’t understand until the last minute that they won’t be able to complete the task at hand. They undervalue their abilities and fail to prepare ahead, making it difficult to review their performance or potential alike. In both the civil engineering sector and other business areas, time management remains a rare skill, although statistically, a person with manufacturing experience is less likely to acutely struggle with it. Between defining the objective and evaluating the target, the successful performance manager learns to offer periodic ratings, which is a practice adopted in both TESLA and Ritz.
Finally, rewarding mechanisms are a beneficial and important KPI as well, being closely linked to the motivation of the employees in the long run. Beyond the obvious financial compensation, the rewards available depend on the industry at hand. TESLA’s insurance package, generous financial benefits and free opportunities for education are unparalleled within the industry. However, Ritz can be praised for its compensation mechanisms as well, as employees of the hotels remain the core part of the service that the company delivers.
Organizational Structure
Structurally speaking, the firms have both similarities and differences at hand, depending on the area of analysis. Ritz Carlton is a worldwide hotel chain, with its operations being heavily reliant on global business management practices and international travel situations. TESLA, on the contrary, is a firm with a singular production location, with international trade coming into the picture only in the form of suppliers. Secondly, the differences between the manufacturing and service sector result in different priorities across the board in relation to resource distribution, the skills required from employees and the value proposition in general (da Costa Fernandes, Pigosso, McAloone and Rozenfend, 2020). Nevertheless, the firms share their positioning as luxury brands with elite clientele, and both engage in premium pricing and a “quality over quantity” mindset in business operations.
From the organizational outlook on structure, it becomes apparent that TESLA relies on the divisional approach, prioritizing flexibility in its operations. The firm somewhat subverts the existing classification of the organizational structures due to the massive leadership in an automotive niche that remains relatively new and unique. However, as the diagram below illustrates, the structure may still be labeled as divisional since the company includes internal departments of energy, HR, communications, legal advice, engineering, production, software and sales. This separation on the basis of specialization fits the firm’s business model of delivering a high-tech product to individual customers on a case-by-case basis, allowing for customization and skill specification.
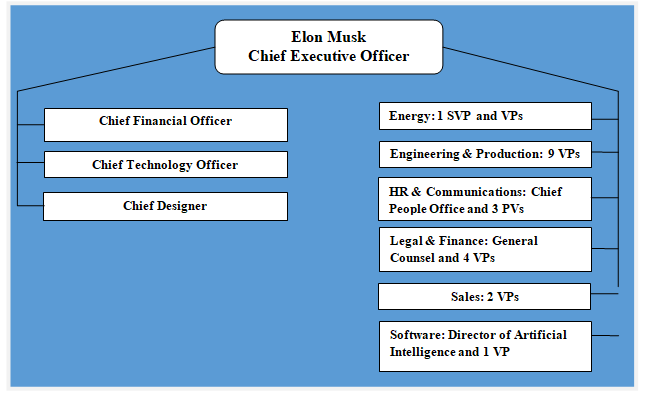
Implications for Technology and Global Commerce
The role of technology for TESLA cannot be overstated, as the firm essentially sells the latest innovations in the automotive industry. Ritz Carlton, however, is reliant on technological advancement as well, with online booking and social media reviews transforming the tourism sector. Similarly, the way both firms attempt to improve the affordability of their products and services while maintaining consistently excellent quality, affects the luxury market in general. The trend-setting power of both TESLA and Ritz Carlton is massive, primarily due to their respective positions as industry leaders. TESLA in particular remains the golden standard in the automotive industry, occupying the overlap between the luxury market segment and the ecological innovations within the field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the focus of the respective fields leads to drastic differences in what particularly constitutes high performance for TESLA and Ritz, but the general measurement guidelines remain the same. Strategic goal setting with regard to the employees’ strengths and weaknesses facilitates the successful implementation of planned operations, reduces the change resistance and increases the competitive advantage. With both firms operating in heavily competitive industries, it is essential for management teams to stay ahead of their tasks and utilize resources effectively.
The main differences in strategic management practices stem from the specific needs relevant to the contrast between a production-focused and a service-focused business. TESLA is heavily reliant on its suppliers and engineers, constant research and development investments and partnerships with science centers and institutes. Its engine, internal construction and the product, in general, need to consistently satisfy and excel the customers’ expectations in a quantifiable way.
Evidently, the luxury tourism industry maintains high standards of its own, yet frequently they are subjective. The core of TESLA’s value proposition lies in product design, excellent quality raw materials and consistent production output, whereas Ritz Carlton primarily sells customer service skills of its hotel personnel. It is then through these areas of specialty that the two firms achieve the KPI objectives and strategic management goals their managerial teams set.
Reference List
da Costa Fernandes, S., Pigosso, D.C., McAloone, T.C. and Rozenfeld, H., 2020. Towards product-service system oriented to a circular economy: A systematic review of value proposition design approaches. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, p.120507. Web.
Feyerlein, D., 2017. Intensify Business Performances of Multinationals: An Introduction to Five Strategic Elements within Performance Management. International Journal of Business and Management, 12(5). Web.
Fox, G., 2021. TESLA Business Model: It’s Just Different, Right!. GARY FOX. Web.
Human Resources. 2021. Diagram of performance management cycle | Human Resources. Web.
Marpaung, A.T., Pratomo, A. and Wicaksono, A., 2019. Implementation of SWOT Analysis in Determining Competitive Strategy On Catering and Conference Services in Hotels., Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Economics, Management, Accounting and Business. Web.
Teece, D.J., 2018. TESLA and the reshaping of the auto industry. Management and Organization Review, 14(3), pp.501-512. Web.
Thoman, D. and Lloyd, R., 2018. A review of the literature on human resource development: Leveraging HR as strategic partner in the high performance organization. Journal of International & Interdisciplinary Business Research, 5(1), pp.147-160. Web.
Research-Methodology. 2021. Tesla Organizational Structure: divisional and flexible – Research-Methodology. Web.