This work is devoted to the analysis of strategic management and strategic competitiveness of the Tesla Company. This paper presents an assessment of the impact of globalization and technological changes on the Tesla Company and its activities. In addition, an industrial organization model and a resource-based model were applied to determine how Tesla can earn an above-average income. Finally, the impact of the company’s mission and stakeholders on overall success was analyzed.
Globalization
The top trend in the development of the modern world and the world economy is globalization. Several reasons prompted Tesla Motors to enter the international market. Firstly, it is worth noting that, according to the company’s website, the mission of the business is to produce and promote a product that would allow more rational use of the natural environment (Hitt). Since environmental issues are global, it is essential to encourage the use of electric vehicles worldwide, not just in the United States.
It is possible to say that globalization has had a positive impact on the company, as it has allowed it to operate outside the United States. In addition to the plants in the USA, the company has a plant under construction in the Netherlands, which will provide a certain degree of supply efficiency (McCain). The most apparent advantage to expect is that there will no longer be a need to transport cars from the US to Europe, saving Tesla Motors costs that would otherwise be spent on logistics (Hitt). Businesses will have better access to local infrastructure, which will make it easier for them to deliver cars to the places where they are needed, simplifying distribution management.
Technology
Due to the demand for fuel that has arisen with the advent of cars, more attention is being paid to alternative energy sources and vehicles. Electric cars have been at the forefront for decades, but with the emergence of new companies and technologies in the last few years, interest and attention have increased (McCain). Due to numerous technological discoveries, Tesla overcame several barriers and brought the quality of electric vehicles to a new level. Indeed, all this has become available thanks to global technological changes, such as automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and much more (Hitt). The high level of nanotechnology development allowed the company to demonstrate a microchip Full Self Driving Chip, responsible for data processing on the proprietary Autopilot system of the new generation (McCain).In the future, the system will be able to keep the car in the occupied lane and automatically go around small bumps and potholes to reduce the degree of tire wear.
Industrial Organization Model
Tesla benefits from its corporate structure in effective management control over multinational operations. In addition, the advantage is the ease of implementing new strategies throughout the organization. Regional divisions support financial reporting and analysis and provide the basis for future regionalization of strategy and tactics in the international automotive market (Hitt). These advantages allow Tesla to use its organizational structure to further global growth and increase competitiveness compared to, for example, Toyota Motor Corporation or Honda Motor Company (Narotam). The organizational structure allows the analyzed company to control the development of competitive advantages centrally.
The disadvantage of Tesla’s corporate structure is stiffness, which limits quick adaptation. For example, global centralization is a structural characteristic that defines the autonomous ability of overseas offices to respond quickly to the challenges they face in their respective regional markets. To eliminate this shortcoming, it is recommended that Tesla Inc. reform its organizational structure to increase the level of autonomy of foreign offices (McCain). A corporate system with a higher degree of decentralization is usually more effective in creating competitiveness than local firms in foreign markets.
Resource-Based Model
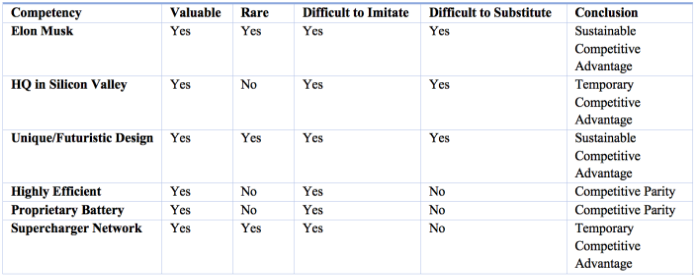
Resource-based representation analysis is used to determine whether competencies within a firm can provide a competitive advantage. Based on Appendix A, Tesla’s most excellent competencies include its innovative CEO Elon Musk and the unique futuristic design of its modern electric vehicles. Moreover, each competence provides a stable competitive advantage since these competencies are not easy to reproduce (Hitt). Temporary competitive benefits include Tesla’s current Silicon Valley headquarters and its Supercharger System, as other companies develop these competencies over time (Narotam). However, the high efficiency of Tesla cars and their branded batteries is competitive since other companies can use hybrid electric vehicles and gasoline cars.
Vision
Tesla’s vision is to create the most attractive car company of the 21st century, contributing to the world’s transition to electric vehicles. The company is approaching this goal by integrating advanced technology into its electric vehicles and related products (McCain). It makes the company popular among consumers, as many are concerned about the environmental problem that Tesla is trying to solve. In addition, people are attracted by the fact that Tesla produces technologies of the future that are unlike anything else.
Mission
Previously, Tesla’s mission was to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable transportation. However, in mid-2016, under the leadership of Elon Musk, the company changed its corporate mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy (McCain). This new statement indicates a small but significant shift in the company’s business to explore the market opportunities of renewable energy sources. This mission also contributes to the corporation’s success, as many people are attracted by the idea of the dominance of electric vehicles in the car market. In addition, in the face of environmental problems, its focus on renewable energy sources also adds to its popularity and success.
Stakeholders
Tesla’s four stakeholder groups are employees, customers, suppliers, and investors. The main motivations of employees are to increase the productivity and productivity of Tesla. Thus, this group of stakeholders belongs to the category of defensive since they help to repel competitors’ attacks (Hitt). Satisfied employees with high motivation contribute to a good image of the company (Narotam). The main motive of the client is to get the best products at a reasonable price, which he can easily afford. Consequently, they fall under the swing category since their solutions constantly change according to Tesla’s automotive products. Therefore, to preserve consumer motives, the Tesla management team develops various strategies to meet their consumer needs.
The main motive of the supplier is to increase the level of productivity of Tesla by providing all kinds of spare parts sufficient to meet the needs of consumers. Consequently, this interested party can be classified as offensive since they have a low threat and high potential for cooperation (Hitt). Therefore, this group of stakeholders can be effectively considered a retention category, as they help the firm maintain its productivity and position in line with the business.
Sources
Michael A. Hitt. 2020. Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases: Competitiveness and Globalization 13th ed. Cengage Learning.
Kishan Narotam. 2021. International Human Resource Management Analysis and Investigation. Tesla Inc. Web.
Cody McCain. 2019. A Strategic Audit of Tesla. University of Nebraska. Web.
Appendix A
Tesla Resource-based Representation Analysis