Executive Summary
Every business must rely on a clear strategic plan which is capable of guiding its activities and the decisions of the management. The current paper explores the strategic plan of PepsiCo, as well as the aspects which shape the goals of the company and its objectives. PepsiCo is a company with a mission and purpose, which can be defined as the desire to generate value for consumers by offering sure quality food and beverages. Essentially, the company positions itself as “the global leader in convenient foods and beverages” (PepsiCo, 2022, para 2). The purpose of PepsiCo influences its strategic decision-making and indicates its aspiration to dominate markets across the globe.
According to the marketing analysis, PepsiCo possesses numerous brands, providing it with a competitive advantage in the market. Specifically, the brands such as Pepsi, Aquafina, Tropicana, and Gatorade all have considerable shares in their respective segments. Based on the research conducted, several proposals were identified which could assist PepsiCo in improving its operations. For instance, the company needs to consider increasing demand for healthy products. Due to the fact that many products produced and sold by PepsiCo cannot be considered healthy, the company failed to get a larger share of the market. At the same time, the company possesses the expertise and resources to develop and begin manufacturing products that promote wellness. Essentially, the company needs to focus on research and development to introduce healthy products for consumers. Additionally, apart from developing new products, the company must consider entering emerging markets which potentially can yield extra profits. Thus, a combination of the two initiatives may help PepsiCo to expand its market presence on a global scale.
At the same time, PepsiCo already has several strategic objectives which it seeks to attain in the near future. Specifically, it has three measurable objectives, namely, focusing on digitalization, monetization of the ecosystem, and optimization of the business. For instance, PepsiCo plans on digitalizing and monetizing its dictation routes to the market by upgrading technology in its numerous facilities. The company will employ business-to-business fintech and software, including solutions such as PerfectDraft (Gios, 2021). Finally, the company seeks to ensure the optimization of its business operations. PepsiCo plans to enhance its resource allocation and utilization approach by increasing investments in markets such as Nigeria and upscaling the beer category in China (Doerr & Page, 2018). The expansion of its beer production is also one of the key objectives of PepsiCo in the coming years. An analysis of the company’s financial statement reveals that PepsiCo will remain profitable even when scaling up its beer operations.
Another important element of PepsiCo’s continuous success in the market is its approach to organizational structure. Specifically, the company’s structure is based on a geographical framework to facilitate addressing challenges arising in local markets (Gaspary et al., 2020). Such a structure meets the company’s global expansion and leadership strategy. The company espouses market divisions, functional corporate groups, and a global hierarchy. For instance, the market division manifests itself in numerous local branches of PepsiCo in Europe and America. Thus, by using the structure, the company successfully addresses the need of the regional markets and is aware of the local demand. At the same time, certain brands of the company, such as Frito-Lay, still have only one division which limits the ability of the business to respond to local markets’ challenges.
PepsiCo has clear objectives for the upcoming years, and in order to achieve them, it needs to rely on an auditing plan. Such a plan will help the company to create smaller tasks and targets for each objective to facilitate their attainment. Additionally, the auditing plan needs to include a reward system and schedule, which will ensure that the employees stay motivated and is able to finish their tasks in time. The plan will also assist the company in analyzing the current progress based on different indicators and components. Moreover, PepsiCo needs to regularly gather customer feedback in order to ensure that the products it sells are in line with the needs of customers. At the same time, the demands of employees and investors should also be taken into consideration. Finally, the company must address factors of collaborative competitiveness and shared management policies and monitor how they are followed by the employees.
PepsiCo also requires a contingency plan which will help it to resolve possible challenges which will emerge in the coming years. Negative situations are always possible, and contingency measures can reduce their impact or prevent them (Reis, 2019). The first step in the contingency plan is identifying all the possible failures and dangers the company may encounter in the future. The second step involves choosing which risks are more important and arranging them according to their priority. The third step implies gaining sufficient resources which will be used in the case of failure or danger. The fourth step involves addressing every single source of risk by creating instructions on how to overcome it. Finally, the company must provide all employees with information on the contingency plan and revisit it whenever a need arises.
Strategic Plan for PepsiCo
In this contemporary environment, a strategic plan plays an integral role in the effective performance of an organization. It uses the current situation in the business environment to define the future (Jayawarna & Dissanayake, 2019). PepsiCo is among organizations that need strategic planning to increase its productivity in the market (Sehrawat, 2019). The SWOT analysis matrix has revealed that the corporation’s strengths are its strong brand, committed workforce, strong corporate social responsibility and many more. On the other hand, some of the weaknesses and threats identified are the increasing perception that carbonated drinks are unhealthy for consumers. In terms of competition, the main rival to PepsiCo is Coca-Cola. Based on this, the corporation should strive to use the strengths and opportunities to eliminate weaknesses and threats. Therefore, PepsiCo should consider growing organically to ensure that its products are healthy and meet consumers’ needs.
The Analysis of the Current Vision and Mission
PepsiCo’s mission and statement indicates its determination to significantly impact its target market through its differentiated products. The company’s mission is to “create more smiles with every sip and every bite” (PepsiCo, 2022, para 1). PepsiCo intends to create value for its customers by making sure that its food and beverages are appetizing and meet its consumers’ needs in the market. The vision of the company is to “be the global leader in convenient foods and beverages by winning with purpose” (PepsiCo, 2022, para 2). In this statement, the organization’s purpose is to be the principal company globally. In addition, the corporation provides the means of achieving the goal by winning the purpose. Therefore, the statements provide the general concept of a company that intends to grow and remain consistent in consumer satisfaction.
The Proposal for an Updated Vision and Mission
Table 1: Vision and Mission Statement
External Factor Evaluation Matrix
Table 2: EFE Matrix
Porter’s 5-Forces Analysis
Table 3: Porter’s Five Forces
Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix
Table 4: IFE Matrix
SWOT Matrix
Table 4: SWOT Analysis
BCG Matrix
Table 6: BCG
Analysis
BCG matrix comprises four components: Dogs, Cash Cows, Stars, and Question marks. Cash Cows represents products with high market share and low market growth rate (Czinkota et al., 2021). Frito lays is a brand that dominates the US market share but has low growth in the global market (PepsiCo, 2022). Stars are products has a high market share in a high growth sector. PepsiCo brands that fall in this segment are Pepsi, Aquafina, Tropicana, and Gatorade. However, Pepsi might shift from the stars to dogs due to intense competition from Coca Cola and increasing preference for healthy drinks. The Question Mark quadrant represents products that are still in the development stage (Czinkota et al., 2021). Brands in this segment are Diet Pepsi and 7up because they have failed to attract consumers’ attention in the market. Finally, dogs are products viewed to have the potential to grow but have failed.
Strategic Direction Choice and Rationalization
PepsiCo should consider growing organically to address some of the issues that reduce the growth of its brands in the market. The corporation is currently a market leader in the food and beverage sector. It has remained true to its mission and vision to become a dominant force in the market. However, the issues that impede the growth of the PepsiCo brand are the increasing demand for healthy products and the failure of some of its brands. This is an indication that the solution lies within the company. The corporation’s leaders should focus on research and development to introduce healthy products for consumers. After developing its products, the company should enter emerging markets to expand its market share on a global scale.
Measurable Objectives
PepsiCo is an international beverage and food manufacturer with an annual $1 billion worth of product portfolio. The company has robust objectives that it intends to accomplish both in the short and long term. In the next three years, PepsiCo intends to advance its concept of sustainability around the world and drive innovation and category leadership to meet the needs of customers. It also hopes to lead the future growth of its industry by reaching out to more customers using its best-in-class portfolio on several occasions. Additionally, PepsiCo intends to use technology and data to connect with its consumers and customers as well as link its customers with resources. The company is also positioning itself to make positive and lasting impacts on social communities around the world and empowering more than its 169,000 employees whom it considers its problem solvers and passionate compatriots.
In terms of measurable objectives, the company’s focus is centered around three areas. These include leading and growing its beer category, digitalization and monetization of its ecosystem, and optimization of its business. Within the next three years, PepsiCo wants to venture into the beer-making category. This will be an all-inclusive beer made of local and natural ingredients (Cardona & Rey, 2022). The company postulates that with the rising consumption of beer, especially among Latin America, Asia, and African markets, this area carries immense opportunities for growth. Specifically, PepsiCo has focused on premium beer, whose growth is twice that of premium spirits. Therefore, PepsiCo’s venture into the beer world over the next three years is a measurable objective.
By digitizing and monetizing its ecosystem, PepsiCo will be expecting to unlock value from its existing assets as well as expand its addressable market. Now, the company has managed to build close to 200 breweries. It expects products from these facilities to reach six million customers and two billion consumers and resultantly generate ten million transactions on a weekly basis. To achieve this, PepsiCo expects to digitalize and monetize its dictation routes to the market. Thus, within three years, the company plans to upgrade its technology capabilities to unlock several ways that will eventually create value for its ecosystem. Towards this end, PepsiCo’s main areas of concern are three holds. First, it plans to develop and utilize business-to-business fintech and software (Gios, 2021). Second, the company intends to use such solutions as PerfectDraft and Ze Delivery to achieve its e-commerce objectives. Finally, PepsiCo intends to use biotech initiatives that will involve several specialists in carrying out scaled fermentation geared towards creating sustainable food production.
The third measurable objective of PepsiCo is to optimize its business. PepsiCo believes that its iconic and profitable brands have given it a unique global ecosystem. Therefore, to increase profitability and continue to drive growth, the company must adopt a disciplined approach to resource allocation and utilization. Over the next three years, hence, the company wants to shift some resources from its mainstream business in the United States, increase investments in such markets as Mozambique and Nigeria as well as upscale the beer category in China (Doerr & Page, 2018). The success of this objective will be measured in terms of the profitability of unit establishments.
Organizational Structure
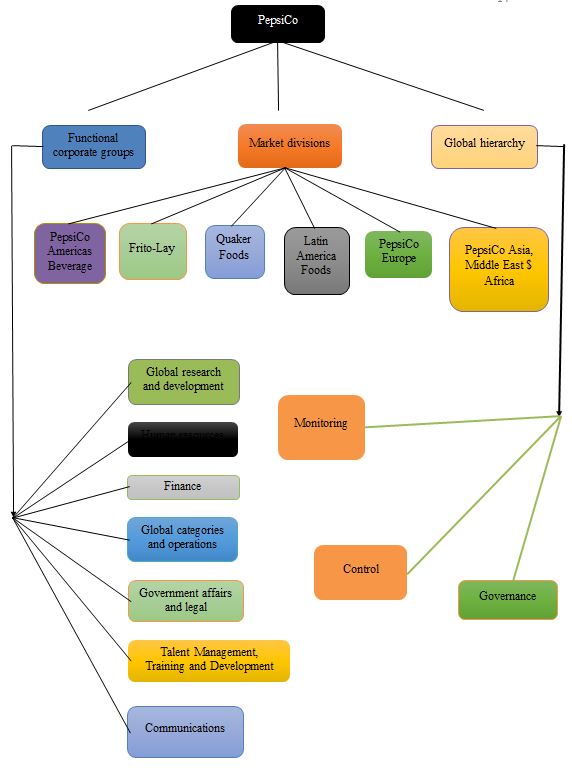
To accomplish these objectives, PepsiCo has a robust organizational structure that assumes a geographical framework as opposed to a hierarchical one as it was in the past. Several times, the organization has seen its organizational structure transformed to mirror the changing conditions of the global market (Gaspary et al., 2020). PepsiCo’s current corporate structure serves to meet the company’s global expansion and leadership aims. These aims reinforce the vision and mission statements of the organization. Moreover, the organizational structure is deliberately designed to support its global growth objective. Indeed, the organizational structure of a company defines the design and system of its business components as well as the interactions of these components towards the fulfillment of its vision and mission. From this organizational structure, the company’s key objective of expanding across the globe can be attained. It is particularly structured to ensure that the organization responds to the changing conditions of the market.
Over the years, PepsiCo has strategically adopted a transformative organizational structure that has abandoned its traditional hierarchical design in place of a more inclusive one. This transformational journey has primarily been occasioned by mergers and acquisitions that the company has entered over time. Subsequently, the current organizational structures have three main features. These include market divisions, functional corporate groups, and global hierarchy, with the market divisions being the most prominent one. The market division has two variables, which are defined by geography and business. The business variable is further subdivided into Frito-Lay and Quick Foods units. Each of these units has only one division maintained in the entire globe (Nene & Pillay, 2019). The company has many divisions for Europe and America as well as other regions of the world. In this market division segment, PepsiCo boasts of PepsiCo Americas Beverages, Frito-Lay, Quaker Foods, Latin America Foods, PepsiCo, Europe, and PepsiCo Asia, Middle East, and Africa.
As regards its functional corporate groups or offices, PepsiCo’s organizational structure primarily features its fundamental business functions. The company has regional, global, and corporate offices where all its affairs are coordinated. Indeed, for efficient implementation of the organization’s policies and strategies, it makes sense to have central command centers. These regional command centers are headed by either a Senior Vice President or an Executive Vice President. Under the functional groups, there are seven further divisions. These include global categories and operations, global research and development, human resources, finance, government affairs and legal, talent management, training and development, and communication.
The company’s hierarchy division particularly comes into play when dealing with organizational operations. It is designed to support control, governance, and monitoring initiatives at the corporate and global levels. For a long time, the company has effectively exploited this division to achieve its top-down monitoring, control, and communication initiatives (Chión et al., 2020). The hierarchical organizational structure division has helped the organization stick to its strategies and policies without much deviation.
Despite its vibrancy, PepsiCo’s organizational structure has both its ups and downs. To begin with, the organizational structure makes it easy for the organization to focus on the needs of its regional market. This is because the organizational structure has market divisions. In addition, the organizational structure helps to support the firm’s corporate control. However, since this organizational structure is not flexible, PepsiCo suffers the disadvantage of limitations (Ike, 2016). For instance, from the discussions above, PepsiCo only has one Frito-Lay division around the whole globe. This comes with limitations that severely reduce its ability to respond effectively to market variations and changes in this division. To solve this problem, PepsiCo resorted to splitting these single global divisions into market divisions that take care of different regions. Through this initiative, PepsiCo hopes to efficiently respond to its market variations around the globe.
Product position Map
A product positioning map is a diagrammatic technique that PepsiCo uses to perpetually map and visually display the position of its various products against its competition. PepsiCo’s main competitor is Coca-Cola, both of which are involved in the manufacture, distribution, and sale of soft drinks and beverages. However, recently PepsiCo has been poised to enter the alcohol manufacturing industry. To predict the effectiveness of this venture, it is significant that a beer positioning map is created.
Projected Income and Loss
From the above financial statement, it is the hope of the company to remain profitable even as it scales up its operations. With the addition of more beer brands, it is expected that revenue obtained from sales will increase drastically.
PepsiCo’s Market Value
The price change over this selected period is represented by 5.54% +9.31
An Auditing Plan/Balanced Scorecard
A company’s effectiveness is determined by its strategic plan and how it implements it. Likewise, an organization’s current state and actions determine its future trajectory. PepsiCo aims to mitigate its weaknesses and risks using its strengths and opportunities. PepsiCo’s main rival is Coca-Cola in the arena of competition. PepsiCo is interested in manufacturing organic components to maintain its customers’ health and wellness concerns. The company has a list of objectives it has to accomplish over the next three years. There are three areas of focus in terms of measurable objectives for the firm. Beer category expansion and leadership in this category, its ecosystems’ monetization and digitization, and business optimization are its strategies in action. PepsiCo plans to join the beer-making market within the next three years. Natural and local ingredients will be used to make this beer, and the recipe can be changed.
PepsiCo is interested in boosting the value of its existing assets while expanding its global reach by digitizing and monetizing its ecosystem. PepsiCo intends to accomplish this goal by digitizing and monetizing its market dictation routes (Sehrawat, 2019). The company plans to improve its technical capabilities within three years to unlock several opportunities for its ecosystem. Consequently, PepsiCo is utilizing biotech projects involving numerous corporations.
The company’s third quantifiable objective is to improve its operations. According to PepsiCo, the company’s well-known and successful brands have created a distinct ecosystem throughout the world (Sehrawat, 2019). As a result, strict adherence to resource allocation must be used to maximize profitability and promote growth. The company plans to relocate part of its resources out of the United States to invest in emerging markets like Mozambique and Nigeria while boosting the beer industry in China operations.
The audit plan will be responsible for tracking the objectives over the next three years. Listing down the objectives will be significant in clarifying what is ahead for the company. Small tasks will be created for the significance of hitting each target and objective set. A reward system and schedule will effectively ensure that all the strategy requirements are met in time within the course of the three years. There might be instances when the company will fall off track of the set strategy. Other cases will be when other tasks take longer than planned to be completed. There will be a need to use motivational skills to tackle the challenges and continue working on the company’s overall goals.
The objective’s success will be assessed based on the unit installations’ profitability. Planned auditing is a list of objectives for evaluating the efficacy and proficiency of acceptable and attainable actions (Turetken et al., 2020). A review strategy will be implemented over the following three years to guarantee that the goals are realized. To achieve a balanced scoreboard, customer loyalty, customer retention, quality, and revenue will be considered. Pay will rise at a comparable market entry rate in the next three years. The project’s progress will be evaluated regularly by analyzing the different indicators and components that characterize the strategy for achieving its objectives. The chief risk plan will protect the affiliation’s obligations.
An emergency approach includes a thorough examination of alternative factors. The factors included crude materials, new sources of dangerous compounds used during the manufacturing process, and lower prices to attract more customers. The company should decide its overall direction and authority by examining the board structure’s conformity with the strategy to ensure they align with the set objectives. A detailed accounting report for the next three years is required for the consumers. Businesses must always compete together to maintain constructive competition with their rivals.
When meeting each customer’s unique needs, they must operate independently and focus on specialized networks and markets. The company’s mission is to make its consumers happy while providing for their health (Jallow, 2021). Therefore, the business must regularly gather customer feedback and ensure that its products always meet the needs of its customers. PepsiCo needs to work together to keep its employees, clients, and investors happy. All three are important shareholders who help keep things running well at the company. The demands of employees, consumers, and investors must be regularly monitored. The company has to keep the investors, employees, and customers’ needs at heart throughout the three years.
The status of the economy directly impacts PepsiCo’s financial situation. The organization has recently increased its global reach and specialized capabilities. Future financial stability could be achieved through modest growth and continued technological advancement (Jackson, 2019). Because of this, PepsiCo’s current practices should address collaborative competitiveness, autonomy, and shared management policies and ensure they are best followed, preserved, and enhanced throughout the years. PepsiCo’s strategy should reduce operating costs while addressing the food industry’s increasing demand for business outsourcing. Keeping a close eye on the relationships between PepsiCo’s various operating companies can help the company save money.
A Contingency Plan
Even if everyone aspires to succeed, failure is inherent in life. Many difficulties can be avoided if appropriate planning is followed, but a few are unavoidable (Pavlov et al., 2018). For example, natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes can wreak havoc on a business. Most valued customers can leave, the database can be hacked, or the system fails. A foresighted businessperson is prepared for a surprise setback.
Management or executives design a contingency plan to help their organization deal with a probable negative situation in the future. Planned contingency measures are put in place to reduce risk and speed up catastrophe recovery (Reis, 2019). The plan can guarantee the continuity of corporate functions. In an unexpected event, a contingency plan provides a method for resuming business. It is a backup strategy, also known as a disaster recovery strategy or Plan B. The contingency plan will involve several steps as listed below:
Step 1: Start by Identifying and Documenting the Most Significant Dangers
PepsiCo cannot manage to prepare for anything if the company does not know what is ahead of them, the dangers there are and the risks ahead. Therefore, as a group, the company should brainstorm and analyze what could go wrong for the firm in the upcoming strategy implementation for the next three years. The company should consider all possible dangers to the company, such as natural calamities, security breaches, and shifts in its workforce and personnel.
For instance, when brainstorming hazards, the team can utilize a mind map to organize and categorize them and then share it with your company for further input or ideas.
Step 2: Prioritization of Risks Based on their Severity
After brainstorming and creating a list of possible hazards, the company should prioritize the risks based on the ones that would have a greater impact on the company. For example, let us assume that the PepsiCo Company’s location is at a lower risk of earthquakes. In that case, one should put it on the back burner in favor of more pressing matters such as competition and profitability challenges.
Step 3: Compilation of Sources that will be Needed in Times of Calamity
In the case of a calamity, PepsiCo should list the critical resources that the company has at its disposal. The resources may include labor, materials, software, and emergency contact information are all needed resources (Ritchie & Jiang, 2019). The list will be effective during calamity to ensure it is dealt with without affecting the business’s productivity. The elements on this list should be ranked in order of significance.
Step 4: Make Arrangements for Every Possible Situation
Contingency plans should be tailored to the specific hazards that the company is facing. Having prioritized a list of potential risks, you should prioritize your tactics and develop contingency plans for the most serious dangers to your organization (Reis, 2019). Loss minimization should be the number one priority for PepsiCo. In an emergency, the contingency plan should provide step-by-step instructions on how to handle the situation. In addition, it should have the most current contact information for the most crucial individuals.
Step 5: Communication of the Approach to the Company’s Staff
As soon as the contingency plans are in place, PepsiCo should ensure that all employees and important stakeholders easily access the documents. Communicating the plan to the responsible parties is key for proper implementation. Contingency plans can be stored in a document management system (Pavlov et al., 2018). An example of such a system is Bit.ai, and the document can be made available to all organization members.
Step 6: The Company Should Revisit its Plan
Having a backup plan is not always a given and effective plan. However, managers can make necessary revisions to a sound contingency plan by inspecting and evaluating it regularly. In addition, new employees, software, procedures, and company practices necessitate revisions to its contingency plan. To prepare for the worst-case scenario, managers who understand the importance of documentation utilize platforms like Bit to create collaborative, interactive, and strong contingency plans for their team.
References
Cardona, P., & Rey, C. (2022). Management by missions: Connecting people to strategy through purpose. Palgrave Macmillan.
Chión, S. J., Charles, V., & Morales, J. (2020). The impact of organisational culture, organisational structure and technological infrastructure on process improvement through knowledge sharing. Business Process Management Journal, 26(6), 1443-1472. Web.
Czinkota, M. R., Kotabe, M., Vrontis, D., & Shams, S. M. (2021). Marketing management. Springer, Cham.
Doerr, J. E., & Page, L. (2018). Measure what matters: How Google, Bono, and the Gates Foundation rock the world with OKRs. Portfolio/Penguin.
Gaspary, E., Moura, G. L., & Wegner, D. (2020). How does the organizational structure influence a work environment for innovation? International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management, 24 (2-3), 132-153.
Gios, L. (2021). Resilience and strategy execution in public organizations. Springer Gabler.
Ike, L. (2016). Management: Principles & Techniques. Xlibris.
Jackson, T. (2019). The post-growth challenge: Secular stagnation, inequality and the limits to growth. Ecological economics, 156, 236-246. Web.
Jallow, D. (2021). A strategic case study on PepsiCo. Available at SSRN 3828353.
Jayawarna, S., & Dissanayake, R. (2019). Strategic planning and organization performance: A review on conceptual and practice perspectives. Archives of Business Research, 7(6), 155-163. Web.
Nene, S. W., & Pillay, A. S. (2019). An Investigation of the impact of organisational structure on organisational performance. Financial Risk, 5(1), 10–24. Web.
PepsiCo. (2022). Mission and Vision. PepsiCo, Inc. Official Website. Web.
Pavlov, A., Ivanov, D., Pavlov, D., & Slinko, A. (2019). Optimization of network redundancy and contingency planning in sustainable and resilient supply chain resource management under conditions of structural dynamics. Annals of Operations Research, 1-30. Web.
Reis, K. (2019). Five things government can do to encourage local food contingency plans. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 62(13), 2295-2312. Web.
Ritchie, B. W., & Jiang, Y. (2019). A review of research on tourism risk, crisis and disaster management: Launching the annals of tourism research curated collection on tourism risk, crisis and disaster management. Annals of Tourism Research, 79, 102812. Web.
Schlegelmilch, B. B. (2022). Global Marketing Strategy. Springer, Cham.
Sehrawat, S. (2019). PepsiCo’s sustainable strategies, Journal of Management, 6(2), 2019, pp. 81–83. Web.
Turetken, O., Jethefer, S., & Ozkan, B. (2020). Internal audit effectiveness: Operationalization and influencing factors. Managerial Auditing Journal, 35(2), 238-271. Web.