Executive Summary
Operations management is an essential function of any organization irrespective of size and motive. All organizations do some or all of the requirements of operations management, even if there is no separate staff or department for this purpose. This paper reviews operations management in business with reference to the Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd., which is situated in Hong Kong. The paper has been divided into three sections, namely, a review of operations management, strategic role/objectives of operations, and the operations strategy in the company. The company has done quite well in this regard but should take steps to improve or even have a specialized department for this purpose. This is mainly to make the company capable of handling challenges during future expansion plans.
Introduction
The term operations management (OM) refers to the process of managing the different activities in an organization. Operations management can be defined as “The maintenance, control, and improvement of organizational activities that are required to produce goods or services for consumers.” (Business Definition for Operations Management. 2008). This implies that operations management is an extremely broad subject and should be taken seriously by all organizations irrespective of size or intent.
All organizations, in fact, have OM built into their systems, even though smaller companies may not have a specialized department or personnel for the purpose. So, smaller organizations like the Thai-Lay Fashion Company will have OM activities even though they do not have a special department or manager for this purpose. This paper will review operations management with respect to the above-mentioned company.
Thai-Lay Fashion is a company based in Hong Kong and is a manufacturer and exporter of garments. The company employees nearly 250 persons and has an annual turnover of nearly HKD 10 million. A variety of garments for adults and children of all sexes are manufactured by the company. The main export market of the company is stored in Europe. The paper will be arranged as per the following topics, namely,
- Overview of operations management,
- the strategic role and objectives of operations,
- Operations strategy, all three with reference to the Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd.
Overview of Operations Management
Two other factors that are closely related to operations management are the operations functions and the operations managers.
Operations Functions
The main activity of a business organization is the transformation of raw materials into finished products or services. Operations functions are the way in which the transformation takes place by facilitating the conversion of raw materials into finished products. “The operations function is the one function directly involved in that transformation, and is responsible for the activities that justify the existence of the firm, both economically and as a value-creating organization in society.” (Operations and Management Science: Department of Operations and Management Sciences. 2008).
It can be seen that this is a very important function for any organization of any size. This function is part of two other important functions in a company, namely, marketing and product or service development. In many cases, there would not be a clear-cut demarcation, and employees may see themselves performing some or all of these functions. This is especially true for a medium-sized company like Thai-Lay Fashion. For example, the design department may sometimes engage themselves in manufacturing also. In short, operations management will have to move in a fine balance with other activities of the company.
It would be worthwhile to mention the different operation functions at Thai-Lay Fashion. They include designing garments, manufacturing, marketing, purchase of materials like yarn and dyes, maintenance of machinery, advertising and design of promotional materials, etc.
Operations managers
Since there is no separate department for operations management in this company, the respective managers of different departments act out the role of operations managers.
Inputs and outputs
All organizations will have inputs that have to be processed or transformed into outputs. Inputs can be mainly classified into three namely materials, information, and customers. In Thai-Lay Fashion, materials include yarn, dyes, thread, etc. Information input here refers to the marketing forecasts by the finance department and design suggestions provided by the customers and the design department of the company, and also customer feedback of the product. There is no customer input here since such a situation will exist only where people are a part of the process, like a hairdresser or a hospital.
So, the inputs using all of the above are ultimately transformed into the finished product or output. The output here is the garments manufactured by the company. The requirements for the transformation from input to output are facilities and personnel. Facilities of the company include the factory and warehouse, the machinery, the storage areas, etc., and personnel include trained workmen, designers, and managers. Output can also be intangible, like consultancy service. Some companies produce both tangible and intangible products. Thai-Lay Fashion has only tangible products. If it starts a consultancy division, the products will include intangible outputs.
Managing processes
There are many processes that help in the transformation of yarn into fabrics. Processes can be defined as “the manner in which decisions are made, and work is performed within any organization.” (Glossary: Processes. 2008). The company is a combination of processes from the design, purchase, and manufacturing departments. Unless all these processes work together, proper production of garments will not take place.
Analyzing business
No organization will exist in a world by itself. It is an integral part of a larger picture which includes suppliers, customers, other service providers, etc. Operations management should take into account all these factors when performing the management functions. For example, the company has a supply chain that starts from the raw material down to the end customers who buy the garments from stores in Europe. It should also be considered that there are internal suppliers and customers for an organization. Here, the manufacturing department will be an internal supplier to the marketing and sales department, who is the internal customer. The internal customers in Thai-Lay are also treated with the same consideration as that of its external customers, namely the stores in Europe.
Hierarchy of operations
The whole process of manufacturing garments is the result of many processes from different departments in the company.
Even inside each department, there will be different processes that will be required to complete a function. For example, manufacturing requires weaving, stitching, sewing, painting, etc., for a garment to be complete. The whole process that involves all these departments and their respective activities must be coordinated for smooth functioning. The concept of internal customers and suppliers also forms a part of this whole process. This structured process of the whole by combining all the parts can be referred to as a hierarchy of operations. (Slack, 1997, p. 67).
Characteristics of operations processes
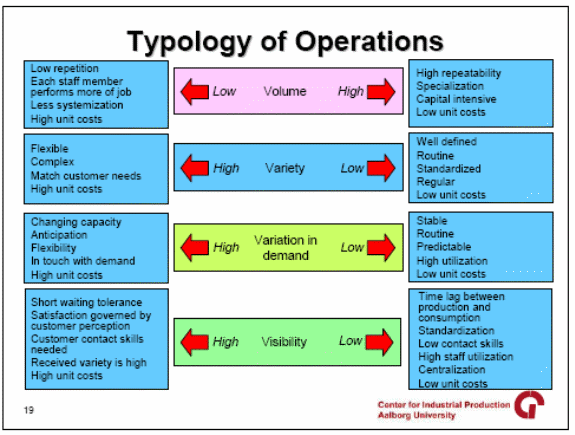
Even though many different processes share similar characteristics, there are four factors with regard to output that set them apart, namely volume, vaVarietyvariation, and visibility. (Operations and Process Management: About Operations and Process Management. 2008).
Volume
Some processes are able to achieve high volumes, whereas other can only produce low volumes. High volumes tend to have lower unit costs than low volume processes. Another characteristic of high volume is that its processes are repeatable, while it may not be possible for low volume processes. Examples of high-volume processes are assembly-line production of certain products. The Ford Model T was probably the first example of high volume production using the principle of repeatability. Thai-Lay Fashion has most products that are of low volume. The process of weaving is a high volume area, whereas the actual manufacture of the garment is a medium or low volume area. This is because garments do not look alike, and hence they cannot be made repeatable.
VaVariety
Some processes are designed to produce a variety of goods, whereas others stick to a small variety. The service provided by a courier company limits itself to the transfer of goods and documents among people and does not have much vaVarietyOn the other hand, a firm of lawyers can provide a variety of services like handling cases civil and criminal cases, preparation of reports, providing legal advice, etc. Thai-Lay Fashion has a lot of vaVarietyince it is in the garment business where customers have different tastes according to age, gender, culture, etc.
Variation
Variation refers to the predictability of the output process. A hotel for holidaymakers will have a high variation in bookings depending on the season. A business-class hotel may get regular bookings throughout the year. Thai-Lay Fashion has reasonable predictability with increased variations during the Christmas season.
Visibility
Visibility is the rate of contact the product has with the customers. A garment will have high visibility once it leaves the premises of the factory and is placed on the shelves of retailers.
The four characteristics and their relationships can be clearly understood from the following chart.
Activities in operations management
For an operative management strategy to be effective, the concerned personnel and managers should involve themselves in certain activities. This is true even if the firm is a medium one like Thai-Lay Fashion. A research article ‘Operations management activities of small, high growth electronics firms’ has listed certain activities that persons in charge of operations management should strictly involve themselves in. The eleven typical activities are
- aggregate planning,
- forecasting,
- facilities layout,
- facilities location,
- job design,
- inventory control,
- product or service design,
- quality and control,
- maintenance,
- production control,
- inventory control.” (White, 1990, p. 5).
Thai-Lay Fashion is actively engaged in all the above except for facilities location and facilities layout.
Importance of Operations Management in Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd.
Operations Management activities in Thai-Lay Fashion have brought forth significant benefits to the company. The company has been able to keep its prices very competitive, customer feedback about products have been increasingly positive and has been able to make optimum use of investment funds. The company is serious about operations management and may even have a separate department once the growth of the company has reached a certain stage.
The strategic role and objectives of operations
For an organization to get the full benefits of its operations management activities, the operations management team has to have a clear picture of its role in the organization. Secondly, operations management should be clearly given specific performance objectives. It is also imperative to know and measure the success arising out of the implementation of the activities of operations management. In other words the operations manager should understand his role in the organization, what exactly he has to do in achieving goals of the organization and his success measured to understand the effectiveness of operations management strategies.
In turn the role of operations management with regard to organizational (business) strategies is three fold. The first is to implement business strategy, second is to support the business strategy and third is to drive the business strategy.
Implementing business strategy
All healthy organizations have effective strategies for survival and growth and it is the duty of all the departments to see that this strategy is implemented. The operations manager (or his equivalent post) should also share this responsibility. For example, Thai-Lay Fashion has immediate plans to buy new machinery and long term plans for strong growth into the Asian market. The maintenance department has to see that the new machine is properly installed and well maintained throughout its working life. The marketing department should do its part in gaining a foothold into the Asian markets.
Supporting business strategy
The operations management team should have the capability to see that the business strategies of the company are implemented according to plan. For example, the design department in Thai-Lay Fashion should have the capability to bring out designs that are suited to the Asian markets.
Drive the strategy
This refers to the long-term implementation of strategies by plans that would automatically sustain them over the years. A system whereby supplier relations are kept at a very high level would be an example of driving the supplier strategy. For this purpose, steps for building supplier relationships should be in-built as a part of the daily function of the purchase department. The operations management function in Thai-Lay Fashion should put more efforts into driving strategies of the company.
Hayes and Wheelwright’s four stages
This model is used to evaluate the competitiveness of functions including that the operations management function.
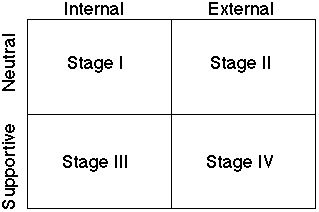
The model developed by Professors Robert H. Hayes and Steven C. Wheelwright of Harvard University gives four stages of competitiveness. Stage one is where the operations management functions is looking internally without any awareness or care of what is happening in the outside world. Functions became fixed and routine. The operations management team will believe that there is nothing new to be done and also that what they are doing is quite satisfactory.
Stage one is referred to being internally neutral. Stage two is slightly better. They look at competitive practices and see that their own standards are matching their competitors. This stage is referred to as externally neutral. Stage three is even better with the operations management practices striving not just to be as good as those of its competitors, but to be the best in the whole industry. Practices work in close alignment with the overall strategies of the organization. This is called internally supportive. Stage four has only a subtle difference from the previous stage where an attempt is made to be world class.
A long term strategy with emphasis on forecasting is also practiced in this stage. Moreover, practices are adaptive to the requirements of the future if the need arises. Stage four is called externally supportive. (Capability and Maturity – Hayes and Wheelwright’s Four Stages). Thai-Lay Fashion can be said to be in the final stages of stage three and moving towards practices that would enable it to be classified as a stage three in operations management practices.
Performance objectives
The company also tries to take all the needs of its stakeholders when formulating operations management practices. The objective here is five fold namely having quality, speed, dependability, flexibility and cost. Thai-Lay Fashion appears to have quality, dependability and flexibility. The company has a strong and effective quality control department. Orders are always dispatched within the time frame. A lot of flexibility within production and design is also possible where changes can be made in design halfway through the production process. With regards to cost it could do better to bring it down a little further to be more competitive especially since it is planning to enter the Asian markets. Average speed for orders is 90 days and efforts should be made to speed this up to at least 60 days.
Operations Strategy
Once what is mentioned in ‘1’ and ‘2’ has been put into practice, the nest step is to formulate an operations strategy. “Major decisions about, and strategic management of: core competencies, capabilities and processes, technologies, resources and key tactical activities necessary in any supply network, in order to create and deliver product and service combinations and the value demanded by a customer.” (Lowson, 2002, p. 57).
A strategy in this context can have the following characteristics namely a top-down approach and a bottom-up approach. It should also take into account the market requirements and the capability of company resources. A top-down approach refers to the alignment of strategies along with overall strategies of the company. A bottom-up approach is the opposite where overall strategies are aligned with operational capability and resources.
Purpose
The purpose of implementing an operations strategy has been explained by Ken Platt of Cambridge University as the five P’s namely, purpose, point of entry, process, project management and participation. Purpose refers to the goals for which operational strategies are implemented. Point of entry refers to the support from within the organization for the implementation of the strategies. The processes which are used for the implementation of strategies should be very clear. A project management strategy should exist within the organization and finally participation of all personnel concerned should be ensured for successful implementation.
Trade-offs
Any organization will have to have a balance between trade offs. For example, in order to increase production of garments, the quality might suffer and this should not happen. The managers at Thai-Lay Fashion are careful that trade-offs are avoided or at least kept to a minimum.
Conclusion
The operations management function in any organization is an important and complicated job. Thai-Lay Fashion Company Ltd does not have a dedicated operations management department or manager, but many of the activities required for this purpose are carried out in the organization in an efficient manner. The company also has a clear-cut operations management strategy though there are areas where the company could improve.
For example, its speed of operations and cost competitiveness could improve especially since the company has plans to expand into new markets. This improvement is essential because a new market will open up a whole set of new challenges to the company. The company could also look into the possibility of having a specialized department for this purpose. But it could be concluded that on the whole, with a little more or time and effort, the company is capable of handling the challenges in the implementation of a successful operations management strategy.
Bibliography
Business Definition for: Operations Management. (2008). BNET Business Dictionary, BNET –The go to Place for Management. Web.
Operations and Management Science: Department of Operations and Management Sciences. (2008). Michigan Ross School of Business. Web.
Glossary: Processes. (2008). [online]. Online Learning Centre, Global Business Today. Web.
SLACk, Nigel. (1997). The Blackwell Encyclopedic Dictionary of Operations Management. Blackwell. P. 67. Web.
Operations and Process Management: About Operations and Process Management. (2008). Businessanalyser. Web.
LIANGSIRI, Jirapha. Typology of operations. [online]. Center for Industrial Production. p. 10. Web.
WHITE, Richard E. (1990). Operations Management Activities of Small, High Growth Electronics Firms: Management Activities. Journal of Small Business Management. All Business – Simple Solutions, Powerful Advice. P. 5. Web.
Capability and Maturity – Hayes and Wheelwright’s Four Stages. University of Cambridge. Web.
Lowson, Robert H. (2002). Strategic Operations Management: The New Competitive Advantage: Operations Strategy Definition 2 – The Wider Value Delivery Strategy. Routledge, P. 57.