Introduction
Barclays Bank is among the largest financial services providers in Europe, America, Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and Australia. The bank deals mainly in offering retail banking, corporate banking, credit and debit cards, wealth management, and investment banking. The bank comprises global corporate and investment banking, international wealth management, and retail banking, each of them has many business units. The report analyzes the bank’s external business environment, financial position, and recommendations.
Background to Barclays Bank
Barclays Bank was formed in 1690 as a multinational financial institution. The bank provides financial services, and its headquarter is based in London, the United Kingdom (UK). The company specializes in operations associated with retail, wholesale, and investment. Barclays Bank commercial activities are partitioned into four parts, which comprise investment banking, corporate banking, wealth management, investment management services, and personal banking. The bank operates in more than 50 countries across the world, with more than 4750 branches (Barclays Bank, 2022). In 1967, the bank emerged as the first to create a cash dispenser in the world. Barclays has employed more than 140,000 people across the globe. The bank is one of the FTSE 100 indexes, with a primary in the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and a secondary listing in the New York Exchange (NYE) (The Banker, 2021). In the past ten years, the bank has strived to improve its performance in the industry through the acquisition of different banking businesses globally.
External Business Environment
Market share and value
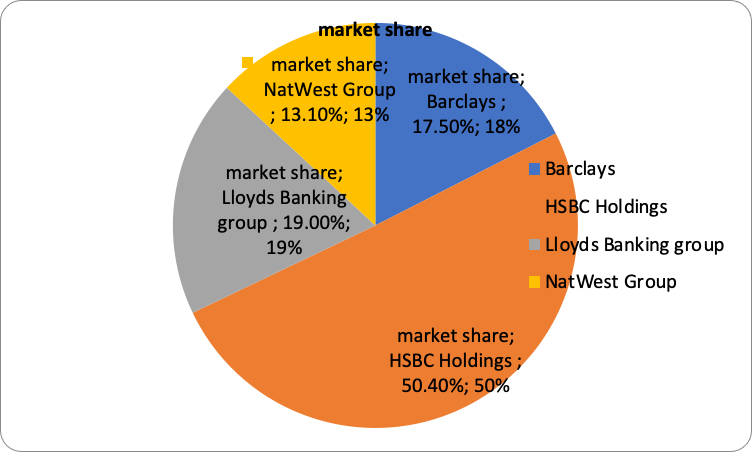
In 2021, Barclays Bank had a market share of 10.50% and ranked third among the largest banks in the UK based on a market capitalization of 37.15 billion Euros. The largest was HSBC Holdings with a market capitalization of 107.2 billion Euros, and Lloyds Banking Group was the second with a market capitalization of 40.33 billion Euros. NatWest Group was ranked fourth with a market capitalization of 27.91 billion Euros (Statista, 2021). The market capitalization places Barclays Bank in the third position overall among the top-performing banks in the UK.
Market Value for the Four Banks
Market Share Based On The Four Banks
The bank industry in the UK in 2022 is £92.3 billion measured by the market size. However, the growth rate for the banking sector in the UK is projected to increase by 5.1% in 2022. The banking industry in the UK has declined over the past five years with an overage of 3.3% per annum between 2017 and 2022 (IBISWorld, 2022). The banking sector in the UK has dropped faster than the Insurance and Financial industry overall. In 2020, banks generated £164.8 billion to the UK economy amounting to 8.6 percent of the GDP. The banking industry was the largest in London, in which 50% of the financial services output was produced (UK Parliament, 2020). The UK banking industry emerged the 3rd largest in the OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) in 2020 based on is portion of national economic output.
Further, performance in the banking industry is influenced by UK’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Growth in the GDP reflects positively on the economy of the country. A sound economy in the UK will raise credit demand as more people can withdraw money from banks and vice versa. The higher savings in banks increases the demand for credit; thus, there is a positive relationship between income per capita (economic development) and the banking industry (Antoni et al., 2019). An increase in the UK’s GDP will exert positive effects on the financial sector and vice versa.
Financial Performance of the Banking Industry
The largest banks in Europe experienced a decline in their market capitalization in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Consequently, the pandemic affected the entire banking sector globally with a fall in the global overall market capitalization in 2020 even though it showed some recovery in 2021. The banking sector in the UK is mostly dominated by the four largest chartered banks (Statista, 2021). However, these banks in recent years have witnessed intense competition from digital players in the industry, for example, Monzo Bank and Starling, to which retail clients tend to switch mostly. The digital challengers have secured more market share weakening the prevalence of the four big retail banks in the UK as per the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) (Barclays Bank, 2022). Prices are declining and consumer choice is growing in what for years was considered a cartel-like sector in which consumers with established banks were reluctant to switch banking services providers. Despite these banks losing consumers to other banks in the UK, HSBC holdings still are the leader in the industry (Hosking and Editor, 2022). HSBC Holdings is the largest in the UK and the entire world based on increased economies of scale.
A PESTLEL Analysis of the Banking Industry
The PESTLE analysis outlines key aspects affecting the banking sector.
Political Factors
Government laws enacted affect the banking industry state in the UK and across the world. The government may intervene in the issues of banking whenever; this leaves the industry vulnerable to political influence. These comprise corruption among political parties, or certain legislative laws like trade restrictions, labor laws, tariffs, and political stability. The banking sector is mostly regulated according to the government regulations in which the banks operate. Since Barclays has several operations in different countries, it is compelled to work as per the government policies, or else it will not carry out its business effectively (Alamanda, 2017). The government of the UK Ring-fencing order can enhance the financial system because smaller and retail corporate banking products and activities are differentiated from some activities outside of the country and European economic area. This will support a faster resolution and recovery plan.
Further, the political stability of the country is often beneficial because the banking sector can concentrate on enhancing its sustainability. While political instabilities in the country may leave the industry speculating the risks and mitigate the current situation. The most significant development was in the regard to the 2016 Brexit vote, which allowed Britain to leave European Union (EU). The risk in the regulatory structure may continue up to 2022, which may lead to compliance problems (Bakhtiyarovich, 2020). It can shift its euro rates exchange group to ensure faster assets and securities clearance that are traded between London, the UK, and other European countries.
Economic Factors
The economy and banks of the nation have interconnected relations with each other. A country with a healthy economy is good for the banking and financial sector, and vice versa. In addition, foreign or local investments are good for an economy as they could create job opportunities. In the 21st century, banks have played a critical role in offering loans to companies and businesses facilitating growth and development in a country. Hence, a healthy economy depends on the smooth management of the banking sector (Bamber and Parry, 2017). Backs cannot manage their operations when the country’s economy is not working. Inflation affects currency and its value leading to instability in the market. Foreign investors will have to re-evaluate things first before offering their funds if the currency value of a given country is high (Barclays Bank, 2022). In addition, to job creation, banks in developing nations support the growth and development of small enterprises.
Sociological Factors
Socio-cultural trends have a great influence on the banking sector. The changing customer preferences and choices would lead to banks and businesses modifying their brand strategies and planning (Comparative financial efficiency analysis for Turkish banking sector,” 2017). For example, millennials tend to utilize credit/debit cards for most of their transactions and their companies would opt to contact them for financial guidance and assistance (Barclays PLC, 2022). In addition, people can go to banks for loans associated with business, academics, and home.
Technological Factors
In the 21st century, technological advancement has led to online banking. Currently, approximately all financial transactions are conducted through online banking. Online banking and technology have transformed service delivery to become easier to reach consumers. In this modern technology world, each bank has a mobile app, which one may use either to pay his or her bills or transfer money. Smartphones have made it easier for customers to scan cheques and the banks can process them from their capacity (Dinçer and Yüksel, 2019). However, technological development and online banking in the sector have raised some critical issues such as confidentiality, privacy, trust, and security (Duncombe, 2018). Nonetheless, checking and double security systems have minimized the risks to a high extent.
Environmental Factors
Factors such as sustainability and eco-friendly have become of great importance for the banking industry. In addition, some banks are investing more capital to develop renewable sources of energy to respond to eco-friendly issues affecting the world. Many banks are turning to the reduced use of paper transactions and the use of solar ATMs with rechargeable batteries. To support a clean environment and efficient utilization of energy, some banks are publishing their fiscal annual reports in the soft copy format (Goel, 2018). This portrays a good brand reputation as it minimizes pollution in several areas.
Legal Factors
Different regulations and laws in different nations affect the banking sector across the world. These regulations and laws affect the financial sector differently despite banks contributing much towards job-creating; they have to encounter the labor laws in each country they operate in across the world. For example, Barclays Bank branches operating in the US economy will have to face several laws that control and regulate the sector such as Glass Steagall Act, the Dodd-Frank Act, and Federal Reserve Act (1913) with other laws in the United States (Hargreaves Lansdown, 2022). Further, governments have introduced several other laws for the protection and safety of consumers in their countries.
Porter’s Five Forces Model in the Banking Industry
Porters’ five forces model examines the industry’s competitiveness based on five distinct areas as explained below:
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers’ bargaining power in the industry is high because the cost of supply accounts for a bigger portion of the total expenditure of a company, the suppliers have no competitors, and when they are few in the market. In this industry, depositors are the major suppliers of banks (Blokdyk, 2018). Deposits from consumers account for the biggest portion of the working capital of banks. Nonetheless, Barclays Bank has a global outreach offering it to a large number of suppliers (Bruijl, 2018). Further, the suppliers still control the interest rates of the bank as the world has become more corporate.
Buyers’ Bargaining Power
Consumers in the banking industry have more power because of more concentration than the sellers. The availability of the information of the market and many options of financial institutions has increased consumer bargaining power (Chik, 2021). However, Barclays Bank was established on the king services and products it provides to its clients. The bank provides insurance services, free credit cards, and e-banking that differentiates it from other key rivals (Kustipia and Wulung, 2019). Generally, in the banking industry, buyers’ power is high because consumers have more power.
Potential New Entrants’ Threat
Markets that have more obstacles to new entrants reduce this threat. Factors that can be considered to create a barrier for new entrants in the market are capital requirements, switching costs, economies of scale, and product differentiation. In the banking sector, statutory financial capital requirements are considered the major obstacles for new entrants (Perera, 2020). A majority of potential new entrants into the industry do not match the capital standards of the bank (Suharti et al., 2018). They target lower-end consumers in the market, which amounts to the largest portion of the global market; therefore, new entrants’ threat in the industry is high.
Threat of Substitutes
Substitute threats in the banking sector are high as a substitute’s presence affects the demand for a given brand in the market. Substitutes’ availability replaces the brand and affects the earnings by lowering the price. The key issues analyzed in the case are, the ease of consumer switching to the substitute services or products, the additional services cost to prevent consumer switching and the threat of obsolescence (Petersen, 2020). Barclays Bank operates in a sophisticated environment because its competitors offer similar services and products. Some of the services and products are insurance, mutual funds, credit cards, loans, and fixed return securities (Süveges, 2019). Nonetheless, a key threat to the bank’s sustainability is the increase in non-banking financial institutions that offer similar products and services.
Competitive Rivalry Extent
In the banking sector, the rate of competition is mostly high. The extent of competition in this sector is determined by the extent of product differentiation, the extent of concentration, growth rate, and the number of players in the industry (Petersen, 2020). However, with the growing number of financial institutions in the UK and across the world, the extent of competition in this sector becomes high.
Financial Position of Barclays Bank
The Importance of Financial Performance in Barclays Bank
The bank’s financial performance demonstrates to investors concerning its general well-being. Financial performance the company’s economic health and management job performance to provide insight into its future (Hargreaves Lansdown, 2022). With a huge global reach, the bank offers innovative services and products to fulfill the needs of its diverse customers and client base (Hashim et al., 2018). Therefore, good financial performance will replicate its mission of providing value for its clients and customers globally.
Director Statement Analysis
C. S. Venkatakrishnan, Barclays Bank Group CEO (Chief Executive Officer) commented that the bank has shown a clear and sustainable growth for the past five years. In 2021, the bank delivered a double-digit RoTE across its businesses and a return of 2.5 billion pounds of excess capital (Hargreaves Lansdown, 2022). The company’s strategic priorities will proceed to develop a diversified business model that they have developed, investing in modern and advanced technical abilities in the consumer businesses, delivering sustainable development and growth across its global corporate and investment bank, and reinforcement of their commitment to helping to change to an eco-friendly economy (Jhingan, 2018). The following as key financial metrics that the CEO based on in 2021 to comment on their future growth and development as a leading bank globally:
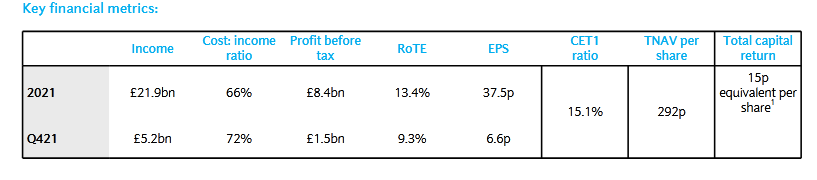
Financial statements and Ratios
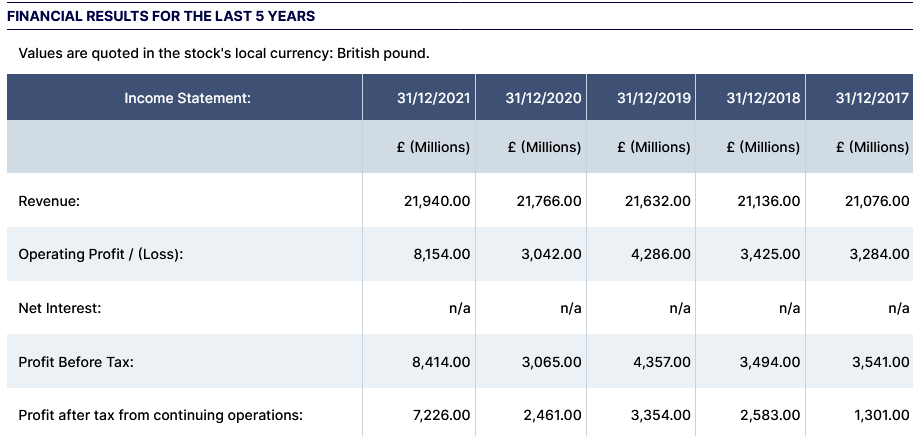
The above figure shows that Barclays Bank’s revenue has been increasing over the past five years from £21,076 million in 2017 to 21,940 million in 2021. In addition, the bank’s operating profits have had an increasing trend over the last five years, increasing from £3,284 million in 2017 to £8,154 million in 2021. This shows that Barclays for the past five years has experienced an improvement in its performance based on increase in profits and revenue.
Financial ratios Analysis
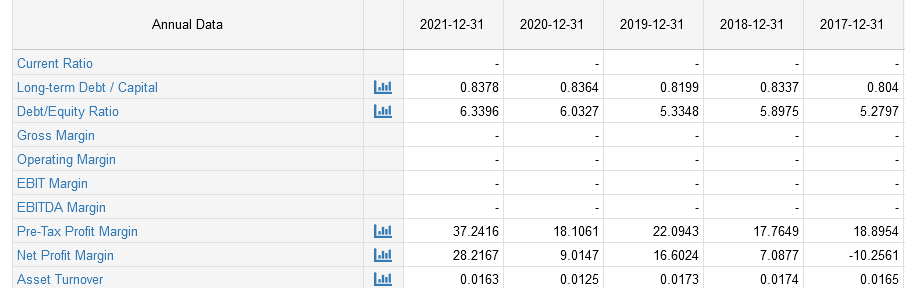
The net profit margin ratio for Barclays Bank as shown in the figure above increased from 2017 at -10.25% to 16.60% in 2019, then drops to 9.01% in 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic that affected the industry in 2020. In 2021, the ratio increased to 28.21% after the industry started to recover from the effects of the pandemic (Kustipia and Wulung, 2019). This shows that the company has performed well despite the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic for the past five years.
The asset turnover ratio for the bank has shown an increasing and decreasing trend. The ratio increased from 0.0165 times in 2017 to 0.0173 times in 2019 then dropped to 0.0125 in 2020. The asset turnover ratio declined in 2020 because of an economic downturn that affected the banking industry because of Coronavirus that affected business operations globally (McKinsey Company, 2018). Again, after some recovery from the pandemic, the ratio has improved to 0.0163 times because of an increase in revenue from £21,076 million in 2017 to £21,940 million in 2021 along with an increase in total assets from £1,133,248 million to 1,384,285 million in 2021 (Minh Sang, 2021). This implies that the bank is utilizing its asset well to generate revenue.
Debt-to-equity ratio as from the figure above shows an increasing trend from 2017 to 2021. 2021. The Company has continued to use more debt to finance its operations leading to a higher debt ratio from 5.28 times to 6.34 times. Barclays Bank’s debts have increased from £1,067,232 in 2017 to £1,314,074 million in 2021 as compared to equity financing increase from £66,016 million in 2017 to £70,211 million in 2021. It implies that the bank uses more debt in its capital structure than equity because debt has a lower cost of capital compared to equity due to its seniority during liquidation (Nagar, 2019). The bank has aggressively financed it growth with debt for the past five years.
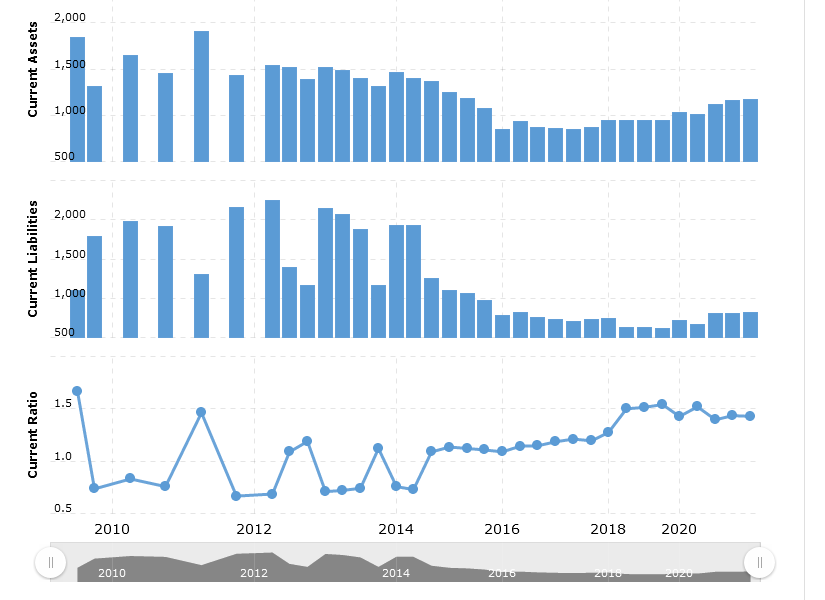
The graphs above show Barclays Bank’s current liabilities, current assets, and current ratio, with an irregular trend. The graph shows that the current ratio has increased from 1.19 times in 2017 to 1.43 times in 2021. This can be attributed to an increase in current assets from £572,298 million in 2017 to £692,567 million in 2021 as compared to current liabilities that increased from £581,063.35 million in 2017 to £646,330.89 million in 2021 (Nagar, 2019). The increase in assets portrays a good performance in financial matters.
Comparing Barclays Bank’s performance with HSBC Holdings, Lloyds, and NatWest Banks
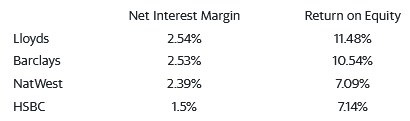
Assessing the quality of four banks’ lending efficiency is based on the net interest margin and return on equity (ROE). Higher numbers in both instances reflect better performance. Lloyds has competitive advantages when it comes to net interest margin and ROE at 2.54% and 11.48% followed by Barclays Bank at 2.53% and 10.54% respectively, NatWest at 2.39%, and 7.09% respectively, and lastly HSBC at 1.5% and 7.14% respectively in 2021 (Wright, 2022). It implies that Barclays has exhibited better performance as compared to others except Lloyds Banking group.
Furthermore, among the four top banks in the UK, Barclays was ranked second with asset growth of 19.9% while Lloyds Banking Group was ranked third recording the highest percentage increase in the Tier 1 capital at 15.27% yearly for the past five years. Generally, the four UK banks experienced an aggregate of 53.08% decline in profits and ranking globally (Wright,2022). The banking sector in the UK has experienced significant challenges over the past three years from 2019 to 2021 with the effects of Brexit uncertainty and the COVID-19 pandemic decreasing their profitability (Tracy, 2019). The UK’s banking industry remains the 5th largest across the globe with an aggregate Tier 1 capital amounting to $437.5 billion.
Costs
The banking sector is clouded with many banks not covering their cost of equity. Financial institutions normally outsource up to 50% of their operating costs even though their supply-chain and procurement capabilities keep pace (Singh, 2017). Financial institutions’ associated services comprise spend areas like ATM, claims, custodial services, armored car, clearance services, fund transfer, banking services, index services (Wright, 2022). Banks have amplified saving opportunities on operation costs by shifting more work to third-party specialists to minimize their operation costs.
Pricing
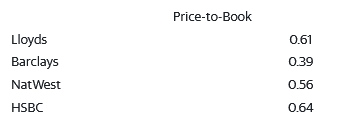
Looking at each bank’s price-to-book ratio which compares the share price of the bank to the equity value each share represents as shown in the table above. A lower ratio is considered to be better (Ntuite, 2018). From the ratios, none of the four banks has an exceptionally high ratio. However, Barclays Bank shares are trading at the lowest price as compared to the book value of the company (Ramlall, 2018). Banking deposit price rates are inelastic based on the pricing strategies employed in banks. When the central bank raises its benchmark rate to control inflation in the country, commercial banks will have to raise interest rates to generate more money. Banks’ logistic prices have increased after the costs of supply-chain increased in c scrambled to shift products during the pandemic (Wright, 2022). The increase in fuel prices has increased the logistic costs affecting banks’ operation costs. This in turn has forced banks to increase interest rates to generate more money.
In the banking industry, retail deposit rates are inelastic because banks typically find it expensive to bid up for deposits to cover the financing gap in the short term. The household deposits’ elasticity based on the interest rate paid is 0.3% implying that deposits have inelastic pricing. However, this differs across banks in the UK, and the forms of shock are conditioned on the retail deposits (Chiu and Hill, 2018). Barclays Bank competitors vary their interest rates to offer a lower interest rate on deposits to increase their competitive advantage.
Barclays Bank’s trading in the foreign exchange markets affects its investments overseas. Currency movements forecasting in a marred with risk, currency may fall or increase in the short-term because of an abrupt political event or an economic data that are unpredictable. Barclays Bank exchange rate expenses are normally approximately 2.75% even though this may change based on the exact amount one wants to transfer. Global transfer of £10,000 with the bank, one would pay £275 as exchange rate costs (Brown, 2022). However, major UK banks such as Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds, and NatWest provide high exchange rates than the country’s high street banks.
Budgeting
Barclays Bank has established its long-term direction by setting specific performance objectives and developing strategies. The bank aims to achieve these objectives under all the relevant external and internal conditions (Okorie and Agu, 2018). Despite an increase in its Debt/Equity ratio the bank projects to meet its debt repayment through increased profits from its strategic investments. Consumer and payments businesses have benefited from the recovery plan (Duncombe, 2018). The increase in interest rates directly increases the yield on the massive cash holdings because of business activities and customer balances, and the proceeds directly go to earnings. Higher interest rates make banks to benefit mostly for brokerages, regional banks and commercial banks (Tsui, 2019). Banks make more cash, when the interest rates are high because they take advantage of the difference between their interest pay to consumers and the interest banks generate by investing.
Risk

In analyzing risk for each bank as shown above look at the common equity tier 1(CET1) ratio of each bank. This ratio shows the core capital of the bank as a percentage of its assets weighted by risk (Pruteanu-Podpiera et al., 2018). The ratio determines how well the bank could hold up during challenging economic times. A higher ratio shows the bank carries less risk and a ratio below 4.5% raises concern about the bank (Rodriguez-Lozano, 2019). All the four UK banks Lloyds, Barclays, NatWest, and HSBC have high ratios even though Barclays Bank is leading with a ratio of 18.2%.
Investment
Barclays Bank is building and delivering enhanced products and services across the globe as modern technology transforms consumer financial services for its customers. The company has leveraged its payments interconnection and enhanced its efficiency. The bank has invested in digital capabilities to enhance service for consumers and unlock new income sources. Barclays Bank is realizing value from investment in payments across Group to deliver an additional income of £900 million between 2020 and 2023 (Rodriguez-Lozano, 2019). The bank is also expanding its unsecured lending in the US, UK and Europe via corporate partnerships (Tsui, 2019). The company has illustrated a sustainable and clear path to growth for the period, delivering a double-digit Return on tangible equity (RoTE) across its operating investments and generating £2.5 billion in surplus capital in 2021.
Profitability
Barclays Bank shows an improvement in its earnings from 2017 to 2021 with its profits increasing from -£ 1,283 million to £7,179 million in 2021. The profitability ratio based on net profit margin shows an increase from -10.25% in 2017 to 28.21% in 2021. This shows that the company is recovering from the pandemic that lead to an economic crisis in the sector in 2020 (Wright, 2022). The profits have increased due to an increase in digital capabilities that enhances performance and operations in the bank.
Recommendations Based on the Information in Task 1 and 2
Growth technique: Barclays Bank’s strategies for conquering prospects and difficulties have been well executed in its mandate to enable it to grow and expand in the banking sector. The company should continue to establish a solid global reach through expansion, mergers, and acquisition of potential small financial institutions in the sector. The case study analysis shows that Barclays should have more flexibility in strategic planning to permit swift adjustments to its intended strategy given the intense competition in this banking industry. This way the company will have a competitive advantage over the emerging digital challenges in the industry and its core competitors Lloyds, HSBC, and NatWest. The bank can deploy a defensive strategy to maintain valuable consumers who may be taken by competitors.
The company needs to protect its profitability, growth, expectations, and brand to keep a good reputation and competitive advantage over other brands in the banking sector. Profits in the industry moves up and down because of interest rates fluctuation. When interest rates increase the banking industry profitability increases and vice versa. The industry’s portfolio performance is also driven by earning of other industries; hence, when an economy is healthy and other businesses are expanding, this increases revenue and profits. Banks can also be affected with economic crisis such as the current COVID-19 pandemic that curtailed bank operations leading to a decline in earnings. However, growth in mobile banking, online banking, investment banking and banking as a service has enhanced profitability in banks.
Reference List
Alamanda, A. R. (2017). Analysis of Islamic intellectual capital performance in Islamic banking industry: Study in Southeast Asia countries. 1st International Conference on Islamic Economics, Business, and Philanthropy.
Ament, F. (2020). FinTech strategies. How do FinTech start-UPS position themselves in the banking sector? GRIN Verlag.
Antoni, Aimon, H., Nasfi, Ramadonna, Y., and Subhan, M. (2019). The effect of internal and external factors on bank investment credit’s demands. Jurnal Ekonomi Malaysia, 53(2).
Bakhtiyarovich, K. R. (2020). Analysis of financial performance of private banks in Uzbekistan. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(5), 3713-3722.
Bamber, M., and Parry, S. (2017). Accounting and finance for managers: A decision-making approach. Kogan Page.
Bamber, M., and Parry, S. (2020). Accounting and finance for managers: A business decision making approach. Kogan Page.
Barclays Bank. (2022). Barclays corporate strategy. Barclays Corporate Communications | Barclays. Web.
Barclays PLC. (2022). Barclays PLC (BARC) financial ratios. Investing.com. Web.
Blokdyk, G. (2018). Porter’s Five Forces analysis: A complete guide. Create space Independent Publishing Platform.
Brown, A. (2022). Bank exchange rates revealed (Barclays HSBC Natwest & more). Key Currency. Web.
Bruijl, G. H. (2018). The relevance of Porter’s Five Forces in today’s innovative and changing business environment. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Chik, J. (2021). Analysis of the boiler and heat exchanger manufacturing industry in the US using Porter’s Five Forces framework. Alberta Academic Review, 4(2), 1-18.
Chiu, C. and Hill, J. (2018). The rate elasticity of retail deposits in the United Kingdom: A macroeconomic investigation. International Journal of Central Banking, 3(53), 1-46.
Comparative financial efficiency analysis for Turkish banking sector. (2017). Industrial Engineering Non-Traditional Applications in International Settings, 185-203.
Dinçer, H., and Yüksel, S. (2019). Handbook of research on decision-making techniques in financial marketing. IGI Global.
Duncombe, W. (2018). Lecture notes in public budgeting and financial management. World Scientific.
Goel, S. (2018). Financial statements analysis: Cases from corporate India. Routledge.
Hargreaves Lansdown. (2022). Share dealing charges of barclays plc (BARC). Web.
Hashim, S. L., Ramlan, H., and Vetiveran, S. A. (2018). Assessing the performance of commercial banks in Malaysia: Financial ratio analysis. The European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences.
Hosking, P., and Editor, F. (2022). Digital banks eat into the Big Four’s market share. The Times & The Sunday Times. Web.
IBISWorld. (2022). Industry market research, reports, and statistics. IBISWorld – Industry Market Research, Reports, & Statistics. Web.
Jhingan, A. K. (2018). Financial ratio analysis: (Enhance your financial skills and learn how to evaluate financial performance).
Kustipia, R., and Wulung, S. R. (2019). Porter’s Five Forces analysis: Potential of extreme night culinary tourism. Proceedings of the 1st NHI Tourism Forum.
McKinsey Company. (2018). A winning partnership: Financial institutions and strategic suppliers. McKinsey & Company. Web.
Minh Sang, N. (2021). Capital adequacy ratio and a bank’s financial stability in Vietnam. Banks and Bank Systems, 16(4), 61-71. Nagar, N. (2019). Financial analysis of banks.
Ntuite, S. R. (2018). Analysis of financial performance of commercial banks in Rwanda: A case study of BPR and I&M bank (BCR). Period of study 2008 to 2013. GRIN Verlag.
Okorie, M. C., and Agu, D. O. (2018). Does banking sector reform buy efficiency of banking sector operations? ? Evidence from recent nigerias banking sector. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 5(2), 264-278. Perera, R. (2020). Understanding Porter’s Five Forces analysis. Nerdynaut.
Petersen, L. (2020). Suitability and further development of Porter’s Five Forces model against the background of digital transformation. GRIN Verlag.
Pruteanu-Podpiera, A., Weill, L., and Schobert, F. (2018). Banking competition and efficiency: A micro-data analysis on the Czech banking industry. Global Banking Crises and Emerging Markets, 52-74.
Ramlall, I. (2018). Banking sector and financial stability. The Banking Sector Under Financial Stability, 13-27.
Rodriguez-Lozano, G. (2019). The colombian banking sector: Analysis from relative efficiency. Accounting and Finance – New Perspectives on Banking, Financial Statements and Reporting.
Singh, B. (2017). Financial analysis of SBI: A study with special reference to Indian banking industry. International Journal of Contemporary Research and Review.
Statista. (2021). Biggest banks in UK by market capitalization 2020. Web.
Suharti, T., Yudhawati, D., and Azzahra, S. N. (2018). Analysis of financial ratio for measuring the average of the banking industry ratio listed in LQ45. Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science.
Süveges, G. B. (2019). Porter’s Five Forces analysis of the district heat sector. MultiScience – XXXIII. microCAD International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference.
The Banker. (2021). UK press release: HSBC only European bank in global top 10. The Banker – Unrivalled coverage of global finance & banking. Web.
Tracy, A. (2019). Ratio analysis fundamentals: How 17 financial ratios can allow you to analyse any business on the planet. RatioAnalysis.net.
Tsui, K. I. (2019). Analysis of internet banking services for Hong Kong banking industry : The case of Hong Kong bank.
UK Parliament. (2020). Financial services: Contribution to the UK economy. House of Commons Library. Web.
Wright, S. (2022). Lloyds vs barclays vs NatWest vs HSBC — which share price is the most attractive? Yahoo Finance – stock market live, quotes, business & finance news. Web.