Abstract
There is no way one can now doubt that emerging technology is not significant in the current society especially in business and healthcare. Basically the way people carry out their busyness, and live their lives would be totally different were it not for the ever changing technology. The emerging technology has hade a very big impact on business today. Business associates are able to communicate across the world without having to incur other unnecessary costs like traveling outside their offices. Web-conferencing and teleconferencing are the order of the day. The emergent technologies are not only limited to the business but also impact on the normal life – society at large. In medication, more sophisticated technology has evolved to assist caregivers in a number of ways. Robotics is particularly important in assisting doctors carry out very intricate surgical procedures. Robots are made by Nanorobotics technology. It’s with this in mind that this paper will address the impact of emerging technologies, specifically Nanotechnology and robotics in surgery on business and on Society. The first part of the paper addresses these technologies in brief as a way of introduction while the second part will discuss the technologies in relation to the specific sectors of application – business and society. The paper will include concepts, ideas, benefits and analyses from journals and other relevant sources.
Introduction
The advancement in technology that the world is witnessing today is very important because it affects the lives of people directly. This could either be in healthcare, communication, businesses, and just life in general. As a result of the expedite process that are being employed with the emerging technologies, production and delivery of products is very easy, fat and convenient than the way it was before. Due to the greater sophistication of technology in Nanotechnology, the carte delivery in medicine is bound to be very good in the near future. This is because nanotechnology has been able to exploit knowledge from, genetics biotechnology and other aspects the technologies.
Surgery and other surgical related processes will be safer to carry out when robots are used for surgery. Basically robots and nanorobotics technology is increasingly finding use in medicine. Nanotechnology is hence very critical in this paper.
Definitions
Walter F. Deal defines Nanotechnology as a way of manipulating or self assembly of separate atoms, or groups of molecules into structure that fall within the dimensions of 1 to 100 nanometers to be able to make devices that have vastly new or completely different characteristics (Deal, 2002, p 21). However also important to realize that there has been a lot of changes in the field of nanotechnology and that the old definition by Walter any not address all the aspect of what this technology can achieve(Deal, 2002, p 21). Nanotechnology is therefore a scientific study of extremely tiny particles measured in nanometers and has unique characteristics depending on their arrangement. They can also be manipulated by experts so that they behave in a certain way (Deal, 2002, p 21).
Robots are becoming very useful in the technical activities that require precision, high risk and those taking so much time. Davies B describes Robots as mechatronics that are controlled by computers to carry out a wide range of tasks (Davies, 2005, p 129). In medicine, there are use to carry out surgical procedures as programmed to do, robots have sensors that assist them, in their operations. A more explicit definition in surgery could be that of Paolo Fiorini in 2009 explaining that unifying minimally invasive technologies from surgery with tele-operative technology that enable surgery to be performed dexterously by manipulation of the tools in the body of a patient through very small incisions (Fiorini, 2009, p 45).
Emerging technologies: Impact of Robotics
Robots are computer powered machines that are used in surgery to help surgeons to perform surgical procedures. In the past, robots were used basically to hold the equipments while humans did the surgery (Taylor & Dalton, 2000, p. 35). However, nowadays, robots are actively involved in the process of Surgery. A new era is emerging in medicine in nanotechnology and nanodevice (Finlay, 2008 para 3). Robots offer better surgery processes that are less invasive or at time long distance operations. It’s anticipated that the future presents more benefits.
Impact of Robotics on Business
As business is improved due to advancement in communication means, business in the field of robotics for surgery will experience equal growth. This is because exchange of information around the world has allowed sharing and technology spreads very fast (Finlay, 2008 para 3). In the year 2009, World robotics website revealed that there was an increase in the sale of robot units by a margin of 33 percent in one year from 2008 to 2009. Such findings can be extended to the yearly increase in sale of robots for the entire nation as being 33% and this has a direct effect on the new technology being introduced (Taylor & Dalton, 2000, p. 35).
Indirect impact is associated with services organization like logistic and management firms, security firms and shipping services. Furthermore, when the growth is so rapid, spending is increased. This can have an influence on the government’s resources (Finlay, 2008 para 4).
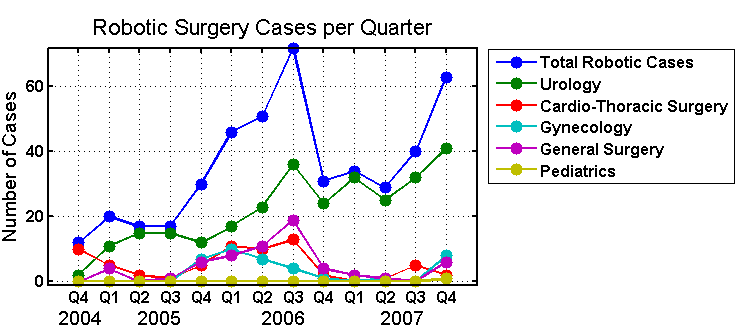
The Number of Robotics Used in processes of Surgery is progressively getting high in general. This means that businesses that deal with these equipment and technology are likely to experience equal momentum. Business in Robotics is going to boom.
The developing nations are a very good place to invest in new technology since they are also expected to make technology leap rater than go through a very slow process of developing such technologies which may take up a lot of years and money (Cavalcanti, 2003, p 78).
Impact of Robotics in Surgery on the Society
Currently, there are many robots and their enforcements being developed for surgery. The minimally invasive processes of doing surgery are being encouraged. Eberhard Karl University has developed a robot that has two arms and is manipulated by a professional surgeon. The operations are operated by professionals (Howe & Matsuoka, 1999, p. 211). Allowing endoscopists to oversee the process and even tele-operate them mean that the system is highly feasible. However professionals also think that the systems cam expand to apply to other sectors of medication. There are other laboratories that have adopted models for haptic feedback in real time while carrying out the surgery that is cleanly invasive (Howe & Matsuoka, 1999, p. 215). The technique also combines visuals and receives feedback to help the robot assisted process.
One of greatest developments is the Zeus system and the Da Vinci system all of which have similar capacities though employ different strategies in robot surgery. They have a video assisted visual screen and are computer enhanced. Da Vinci was developed from telepresence machines invented for high security operation of NASA and the United States (Lanfranco et al, 2004, p 14).
Zeus systems have consoles that are controlled by professional. The gadget has two arms that replicate the normal hands of a surgeon. However there is a third arm that has a voice controlled robot endoscope for visualization (Lanfranco et al, 2004, p 14).
When robotics was introduced in surgery, a new trend in medical delivery was initiated. The introduction is targeting to improve the dexterity in a restricted space for the process of surgery and reduced spills and contamination due to open surgeries (Satava, 2002, p 10). The endoscopic surgeries are the most performed by these improvements and as such they are the one with better success stories. The incorporation of three dimensional visions is very good in making the conventional open surgeries have minima l incisions. Nonetheless when the other internal organs are not visible, then more information has to be researched in order to have basis an informed decision. The delicate internal organs have to be protected (Satava, 2002, p 10). One of the best ways to do this is to use the minimally invasive methods since the processes that use excessive force could severely damage the body tissues (Satava et al, 2001, p. 489).
There are several benefits that robotics have brought to the fields of surgery in medical care delivery. One is that there is reduced number of personnel that are needed for one procedure to be carried out. The robots take up the duties of several personae in the surgery room (Lanfranco et al, 2004, p 14). This means that in future even fewer people will be required in the surgery rooms to carry out an efficient surgery. The surgery distance is reduced so much. Incorporation of the telecommunication technology and the speed of information transfer in the emerging technology, surgery can be carried out even when people are long distances apart (Satava et al, 2001, p. 489). This is to say that a surgeon can do the surgery from another location mile apart from the location of the patient. As the robot surgery has few incisions, and invasions, there is minimal trauma on the patient and thus translates to more rapid recovery (Satava, 2002, p 10). It’s sensible that small incisions that are inflicted by robot surgery heal faster. Holistic recovery of the patient is therefore faster and this can only be said to be beneficial in reducing the medical risks, excessive pain and any other complications (Satava, 2002, p 10).
Specifically, laparoscopy surgery is very critical when it comes to robotics. Emerging technology has enabled professionals in this field to overcome some very critical obstacles. Robotics increase handiness, recover hand-eye synchronization and an ergonomic arrangement and allow better vision (Satava, 2002, p 10).
Accessing information and sharing it at appropriate time in the medical care is very important. Having one record to every one mean that there would be a lot of delays, confusion, and disorganization and overcrowding (Davies, 2005, p 129). For these reasons the healthcare would turn chaotic. Several issues will be very difficult to solve; patient information like where tracked patient populations, illnesses, ands side effects and lab results are needed at once in different departments (Adhami & Coste-Marine, 2002, p 2965). Patient safety will be compromised because several health conditions have different degrees of severity and priority should be given to serious cases so as to be able to save lives. Adapting EMR can solve such problems as data can be accessed from anywhere in the hospital setting and even e-prescribing done (Adhami & Coste-Mariene, 2002, p 2965).
Issues like its safety, cost and convenience the process will bring about is very enticing and worth the investment. EMR will ensure that the patient’s safety is guaranteed while at the same time eliminating the bulk of paper documents, refilling, storage and waster of time as one move from place to place shifting fields. Surgery can be done long distance by tele-operation (Adhami & Coste-Mariene, 2002, p 2965).
Impact of Nanotechnology on Business
The evolution of new technology is very critical and has been observe to impact a lot of aspects of human life. The GDP’s of various nation have been greatly influenced by the technology whiles others have seen better service delivery (Davies, 2005, p 129). Nanotechnology is gaining popularity since the world is in the midst of a model that change in technology is increased exponentially. Nanotechnology is likely to impact on the Business of many nations (Bachand & Montemagno, 2000, p 179).
Nanotechnology is simply manipulating matter at an atomic or molecular level. This is being observed as large-systems tactical competence that can allow a society that is highly productive. This therefore means that nanotechnology could be able to transform the sustainability and the wealth of these countries. A major concern is to take create machines that are designed to tackles future challenges (Bachand & Montemagno, 2000, p 179). As the technology advances, there is need for global markets to reassess the technology and the economies and industries on standards that have never been experienced before.
A study by the global Futures College to investigate the readiness and awareness of the business persons concerning the economic impact and business benefit of nanotechnology was carried out in 1999. Several interviews were carried out across a very wide range of business personalities in different sectors of economy ranging from health, manufacturing, information communication technology and real estate (Bachand & Montemagno, 2000, p 179). Global future institute is involved in advisory services to companies and governments on the impact of technology on the market, clients and economy. Areas covered range from communication, robotics and life sciences.
The findings from the research indicated that awareness and rates of being ready were very low. Still, about 80 percent could define nanotechnology superficially. It’s also evident that nanotechnology is still in its infancy and should be allowed to grow (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2005, p 117). Assessment of the awareness and readiness in this context was very critical since before results could be drawn, there was need to assess the accelerated change and its impact on business ahead of time. Since of this technology is a real issue, being ready and aware directly linked to possible use in future; integral to this research (Bachand & Montemagno, 2000, p 179).
Considering the relative and varied heights of social adaptation, some scenarios have been investigated to offer further understanding of the importance of nanotechnology on business (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2005, p 117).
It’s evident that nanotechnology integrates expansively into economy do to high rates of readiness, efficient planning and increased investments by business owners. As indicated, the viability of these emerging technologies is not easily accomplished as the technologies are still developing. Almost every aspect of humanity is affected (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2005, p 117). About 35 nations have initiated nanotechnology according to Roco and the investments increased from $430 million in 1997 to $3billion in 2003. It is estimated that at this rate, it would be over $ 1 trillion by 2015. The benefit cannot be assessed commercially immediately by the signs fro development are very important. Sales are expected to increase as the technology is sold.
Major aspects that are to be observed include global; trading leadership, integrated education, low labor problems and unemployment, sustainable economy, global patent headship, higher industrial competitiveness and plenty capital liquidity (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2002, p743). Future outlook is very practicable; creating an ever increasing dominance in major markets and industries that result in investments and innovations. Nanotechnology assured accelerated progress and confidence in growth of economy and improved quality of life to the entire country (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2002, p743).
As readiness remains low, there are also inadequate strategic plans by businesses. There has been a very slow and nation-wide adoption of the new technologies. There is no full government polices across the world that address investment in national nanotechnology. Some of the challenges in attaining adequate business success include lack of skill, inadequate training or poorly educated, and liquidity insufficient (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2002, p743).
Impact of Nanotechnology on the Society
Nanotechnology impact can be evaluated in a number of ways on the society. As indicated early the problems of getting nanotechnology include lack of a very comprehensive adoption, integration and preparedness hence resulting in reduced post-industrial growth, negative competitiveness that translates to reduction in growth of the economy (Cavalcanti & Freitas, 2002, p743). It’s expected that then technology when fully adopted will cause a very massive investment can economic growth. Problems of unemployment should be solved. Nanotechnology has a vast impact on society. This ranges from the concept previously addressed about awareness, ignorance is also very high and hence people find it very difficult to make decisions with basis of use, merits and controlling surrounding (Finlay, 2008 para 2).
Knowles E quotes that opinion poll in UK conducted by Royal Society revealed that about 29 percent were aware of nanotechnology. Only 19 percent could define the terminology (Knowles, 2006, p 25). This is worth noting since a country like the UK is expected to be knowledgeable but very few people know about the new technologies. In many nations, societies are influences by the type of politics that they play. This in turn is reflected by the voting patterns. The policies could be very favorable to the growth and research; however, lacking awareness of existence of such technology distorts the progress (Knowles, 2006, p 25).
Technology is spreading faster than the public awareness. This means that the problems have to be aligned with the ethical reasons, general understanding and regulation by the government (Sayers, et al 2005, p1572). Financing the priorities is proper since nanomaterials are present in consumer products most of the time whereas general knowledge concerning materials could be detrimental to a people’s health (Knowles, 2006, p 25). Environmental factors are very important in ensuring that environmental factors are addressed especially emission of carbon gases.
Ubiquitous access to information and creation of harmony between life and service delivery is assured by Nanotechnology. Protection of environment, superior service to patients and access to information is guaranteed.
Positive link to society is associated with investments and sales projections for nanotechnology products. When this happen, opportunities in employment, education and further research will go up; it’s important to be able to maintain a balance between bad effects and positive outcomes (Knowles, 2006, p 25). For instance, nanotechnology in medical services can be very important to people in developing nation, this could be very expensive and at times even non-existent.
Basically nanotechnology applies atoms almost every aspect of human necessities. Medical services will be sophisticated and improved as people will also be able to manage themselves from Home (Knowles, 2006, p 25)
Conclusion
The safety of patients and care delivery is a very important aspect in the current society. This is because of the increased concern about patient autonomy and right to treatment. Surgery is a very important procedure for patients. Great care in needed and the advancement in technology have assured that. Nanotechnology and robotics in surgery carry unrivalled merits. Nanotechnology will completely revolutionize care delivery as the benefits are imaginable yet the technology is just picking (emerging). There are some unknown risks especially to the environment, humanity and law regulation. Robotics has influenced business positively and improved surgical processes. However despite the hailed benefits, it’s important to take caution of the projected benefits since other external factors like political, economy and social concerns may go overboard and jeopardize these successes.
Reference List
Adhami L & Coste-Mariene E. 2002. “Positioning Tele-Operated Surgical Robots for Collision Free Optimal Operation”, In Proc. Of IEEE ICRA’02 Int’l Conf. On Robotics and Automation, Washington, DC, USA, Vol. 3, Pp. 2962-2969
Bachand G.D & Montemagno, C.D. 2000. “Constructing Organic/Inorganic NEMS Devices Powered by Biomolecular Motors,” Biomedical Micro devices, 2:179 – 184
Cavalcanti C & Freitas R.A 2005. “Nanorobotics Control Design: A Collective Behavior Approach for Medicine”, IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, Vol. 4, No. 2
Cavalcanti A. 2003, “Assembly Automation with Evolutionary Nanorobots and Sensor-Based Control applied to Nanomedicine”, IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, Vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 78 – 87.
Cavalcanti A. & Freitas R.A Jr. 2002, “Autonomous Multi-Robot sensor-based cooperation for nanomedicine,” Int’l J. Nonlinear Science Numerical Simulation, Vol. 3, No.4, pp.743-746
Davies B. 2005. A Review of Robotics in Surgery: Mechatronics in Medicine Group, Department Of Mechanical Engineering, Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Copyright of Proceedings of Institution of Mechanical Engineers. P 129
Deal W.F 2002. Under The Microscope: Nanotechnology. The Technology Teacher Journal. Resource in Technology. Ebsco Publishing. P 21
Finlay P.A 2008. Robotics in Surgery. Electronics Channel. At The Engineering Our Health-Advances in Medical Engineering Eeesta Prestige Seminar.
Fiorini P. 2009. Robotic Surgery: Past Results and Current Developments. University Of Verona. Advanced Technologies For Enhanced Quality Of Life.
Howe D.R & Matsuoka Y. 1999. Robotics for Surgery. Annual Reviews. Biomedical Engineering 01: 211 – 240
Knowles E. 2006. Emerging Issues, Nanotechnology: Evolving Occupational Safety, Health and Environmental Issues. Professional Safety Journal. American Professionals of Safety Engineers. P 25
Lanfranco A, Castellanos A, Desai J & Meyers W. 2004. Robotic Surgery. A Current Perspective. Ann Surg. 239 (1): 14 – 21
Satava RM. 2002. Surgical Robotics: The Early Chronicles: A Personal Historical Perspective. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 12: 6–16.
Satava RM, Et Al. 2001. Robotic Surgery: State Of The Art and Future Trends. Contemp Surg.; 57:489 – 499.
Sayers, C., Lai, A., & Paul, R.P. 2005. Visual Imagery for Sub-Sea Tele-Programming. IEEE International Conf. On Robotics and Automation, 2: 1568 – 1574.
Taylor, K., & Dalton, B. 2000. Internet Robots: A New Robotics Nich. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, 7 (1) 35–40