This essay sample focuses on Tesla communication strategy. Here, you’ll find Tesla’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats, and issues as well as other useful information. Learn more about Tesla internal communication strategy with our sample!
Tesla Communication Strategy Essay Introduction
Founded in 2003, Tesla Motors is an American automobile manufacturing company. The development of the brand is owed to the efforts of engineers from Silicon Valley. Its headquarters are located in Palo Alto, California (Tesla Motors, 2014). The company developed its first model, Roadster, with the objective of setting way for the development of an electric car as an alternative to gasoline propelled cars (Hardester 2010, p. 43).
Since this early innovation, Tesla Motors has experienced a problem with sales of products with zero marketing communication budgets. Upon the adoption of communication strategies for pushing its sales higher through the creation of the brand awareness, the company has an opportunity of developing a brand loyalty. In fact, Tesla Motors is the only company that produces high performance and lucrative fully electric sedans in the US.
After proving that electric technology was a possible impulsion of vehicles, Tesla Motors progressed to release Model S into the market in 2012 (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 44).This model targeted the lucrative sedan market segment, which is also the target market segment for the proposed marketing communication plan. Tesla Motors markets its model S brand as a luxurious, technological, and high performing brand.
The organisation also engages in the design and sale of electric trains to various automakers, including Mercedes Benz and Toyota among others. However, this paper does not focus on this product lines. Rather, its objective is on the analysis of the company and its marketing communications. It suggests online communication platform as a possible way of enhancing communication of the organisation’s brand in the effort to boost sales from 20,000 units in 2012-2013 to 35, 000 units in 2014-2015 fiscal year.
Market Definition and Parameters
The market segment for Tesla Motors is mid-sized with highly performing luxurious sedans. The company has the capability to succeed in this market segment upon considering that the Model S is not only purely eclectic, but also a highly performing eco-friendly automobile (Mangram, 2012, p. 300).
In this market, the company does not have any close parallel competitor. Indeed, the closest organisations that compete with it in the electric luxury sedan segment include Nissan through Nissan Leaf and Chevy through its product, Chevy Volt (Tesla, 2013). Nevertheless, they both present low threats. They offer lower performance electric cars in comparison with Model S.
Model S particularly fits well in the mid-size luxury automobile market. Forbes magazine conducted a research on the sales of different luxurious automobiles. It reported an increase in sales volume of luxurious vehicles for a period of 5 years. As shown in appendix 1, this increase was highest in 2012 by about 20 percent compared to 2011 (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 44).
This finding suggests an increasing demand for luxury vehicles, especially as the economy recovers from the aftermaths of the global financial crisis. However, amid the increment in demand, organisations that offer a brand with high performance and efficiency are likely to make more sales because luxury products market segments value product utility and conformance to specifications while making buying decisions (Simon, 2007, p. 126; Yelkur, 2011, p. 110).
The market definition for luxurious a vehicle can perhaps be best accomplished by considering forecast for the expected sales level. Appendix 2 exemplifies one of such approaches of forecasting purchasing behaviour in the US for consumers with household incomes amounting to $100, 000 and above. From the appendix, downturns in 2009 and at the beginning of 2010 are evident. Declines are also evident in July to august 2011. They can be explained by uncertainties that are associated with debt ceiling fears and downgrading of the US credit. Upon considering that data of market dynamics in the lucrative vehicles category is forecasted for a period of 6 months, the trend line implies greater expectations for Model S.
Market Dynamics and Trends
While developing a marketing plan for Model S, it is important to consider marketing dynamics and performance trend for electric cars in the marketplace. Appendix 3 shows potential for increased demand for greener vehicles. This data depicts the changing preferences among consumers, especially those who are environmentally conscious. Changing fluctuation in oil prices may also create a higher demand for purely electric vehicles such as Model S. In the US, this segment accounts for only 3.38 percent in the whole industry of electric cars, including hybrid vehicles (Lim, 2014, p. 1).
Changing the perception among consumers in terms of their role in protecting the environment from pollution that is associated with green gas emissions and/or the rising demand for luxury items constitutes a reliable indicator for better performance and embracement of luxury electric vehicles such as Model S. However, the success of this model in the marketplace depends on competitive forces and the capacity of the Tesla Motors to capitalise on its opportunities and strengths to overcome its weakness and threats. This claim suggests that a complete analysis of the marketing trends and dynamics requires an aggressive investigation using Porter’s five forces and SWOT description.
SWOT description
Strengths
- Has a strong brand that is built around the perception of high performance, reliability, and luxury,
- It has devoted customers, and
- It demonstrates an uncompromising attitude towards its future success in terms of creativity and innovation.
Weaknesses
- It depends on external suppliers, an unknown brand, and a dynamic new technology for its operations,
- It eliminates the use of fossil fuels in the propulsion of automobiles, and
- The new technology poses the challenge of uncertainties associated with negative preconceptions about the performance of the electric vehicle in comparison with the oil or gas engines.
Opportunities
- The existing external environment, which can make the organisation improve its performance,
- The increasing number of people who are becoming cautious over degradation of the natural environment,
- Unstoppable growth when fully electric car market bursts, and
- It can break free any negative notions and preconceptions about electric cars.
Threats
- Incumbent automobile makers,
- The twin threat of introducing a new company and a new product in the market, and
- Dependence of info-structure.
For the viability of marketing plans, SWOT description for new or existing brand is necessary with the aim of determining whether an organisation has the capacity to place the product in the market (Menon, 2006, p. 30). This approach calls for the strategic planning approach for evaluating the strengths, restrictions, prospects, and threats that a business establishment encounters (Hill & Westbrook, 2007, p. 50).
Tesla Motors has managed to establish a strong brand that is built around the perception of high performance, reliability, and luxury. Mangram (2012) confirms that “the model demonstrates how technology can be deployed in the development of alternative automobile products with high performance and high safety features” (p. 300). Tesla Motors also possesses incredibly devoted customers. It also has an uncompromising attitude towards its future success in terms of creativity and innovation.
Although Tesla Motors has strengths that can favour the success of the Model S, it has some weaknesses. It depends on external suppliers, an unknown brand, and a dynamic new technology for its operations (Mangram, 2012, p. 300). Model S eliminates the use of fossil fuels in the propulsion of automobiles. Apart for the brand being new in the market, assuming it is not well known by all potential customers, the new technology poses the challenge of uncertainties associated with negative preconceptions about the performance of the electric vehicle in comparison with the oil or gas engines.
Opportunities include the existing external environment, which while utilised well, can help an organisation to improve its performance (Hill & Westbrook, 2007, p. 51). One of the major opportunities for success of the Model S encompasses the increasing number of people who are becoming cautious over degradation of the natural environment due to high carbon emissions that are associated with the rising number of automobiles.
With already developed superior features, Model S has the opportunity for unstoppable growth when fully electric car market bursts. Tesla has a capability of breaking free any negative notions and preconceptions about electric cars. Indeed, hybrid varieties and various other eco-friendly vehicles currently in the market have performance compromises.
Incumbent automobile makers pose a significant threat to Tesla Motors. They have a well-established and protected brand, which may enable them secure higher sales even if they may resort to the production of inferior fully electric vehicles. Motavalli (2013) reveals that “Audi, Volkswagen, Lexus, and BMW among other automakers are in their advanced stages of developing fully electric cars” (p. 20). Tesla Motors also suffers from the twin problem of introducing a new company and a new product in the market.
Competitor Analysis (Porter five forces)
Threats of New Entry
- High costs that are involved in setting an electric car production system imply that Tesla Motors experiences low threats of new entrants,
- The market target segment for Model S customers encompasses people who are looking for luxurious products,
- New entrants lack reputation, and
- Hence, they suffer from incapacity to outdo those with already well-established customer loyalties.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
- Tesla experiences high bargaining power from its suppliers since it does not purchase commodity type of goods,
- Relies on suppliers from different places and in different areas of specialisation to ensure sustained manufacturing processes,
- More than 33 suppliers did business with Tesla Motors to facilitate the production of Model S in 2013, and
- Tesla Motors’ suppliers can set their prices at higher levels without considering the unwillingness of the organisation to pay.
Rivalry among existing competitors
- The market demand influences the organisation’s market price due to the lower number of competitors who offer products with similar performance, technology, and luxury characteristics,
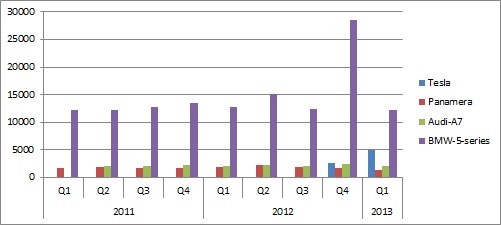
- Appendix 2 illustrates the extent of rivalry in the electric car industry
Buyers’ Bargaining Power
- Tesla Motors’ buyers have a low bargaining power
- Tesla positions its Model S brand as a luxurious and high-performance product.
- High-cost technology that is involved in its production drives the prices of Model S higher compared to gas and oil cars that have an equal carriage capacity.
Threats of Substitute Products/Services
- Threats posed by substitute products are low,
- The company is the only automobile maker that specialises in the production of zero green gas emission cars, and
- Therefore, eco-friendly customers who also love sports vehicles have Model S as the only option
Industry environment is a risk to an organisation in terms of threats of new entrants, supplier and buyer bargaining powers, industry rivalry, and threats posed by substitutes. Tesla experiences high bargaining power from its competitors, as it does not purchase commodity type of goods. It depends on suppliers who are derived from different places and in different areas of specialisation to ensure sustained manufacturing processes.
Mark (2013) informs that “more than 33 suppliers did business with Tesla Motors to facilitate the production of Model S in 2013” (p. 1). This move suggests that in case of failure of the organisation to pay a specific amount of money as demanded by a given supplier, the entire production process becomes halted. This situation disadvantages Tesla Motors since its suppliers can set their prices at higher levels without considering the unwillingness of the organisation to pay.
Buyers possess a low bargaining power. Tesla positions its Model S brand as a luxurious and high-performance product. High-cost technology that is involved in its production drives the prices of Model S higher compared to gas and oil cars that have an equal carriage capacity. The market demand influences the organisation’s market price due to the lower number of competitors who offer products with similar performance, technology, and luxury characteristics (Ashtiani et al., 2011, p. 452).
High costs that are involved in setting an electric car production system imply that Tesla Motors experiences low threats of new entrants. The demanding technology in the production makes capital requirements prohibitive to small-scale automakers. The market target segment for Model S customers encompasses people who are looking for luxurious products.
Such people consider quality and performance essential attributes of product before arriving at purchasing decisions (Farris, Neil & Pfeifer, 2010, p. 211; Freshwater, Sherwood & Drury, 2006, p. 300). This observation highlights the significance of good reputation as a major component in branding luxury products. New entrants lack reputation. Hence, they suffer from incapacity to outdo those with already well-established customer loyalties.
While the industry loyalty for Tesla Motors is high, threats posed by substitute products are low. Tesla Motors constitutes the only automobile maker that specialises in the production of zero green gas emission cars (Mangram 2012). This case implies that eco-friendly customers who also love sports vehicles have Model S as the only option.
However, even though Tesla Motors is the only organisation that is currently producing EV Model, several other well-established automakers are focusing their attention on research and designs of EVs in the effort to have a share of the market in the future as trend in the adoption of the model continues to pick. Appendix 4 illustrates the extent of rivalry in the electric car industry.
Overview of the selected Brand
Upon considering that Tesla Motors is the only organisation that produces fully electric vehicles, it has good opportunities for building its reputation to establish significant customer loyalties. This success depends on the ability of the organisation to establish effective marketing communication strategies. Unfortunately, Tesla had no budget for its marketing, although it had attained revenue growth of above 75 percent by 2010-2011 fiscal year and 102 percent in the 2011-2012 fiscal year amounting to $ 413m (Karamitsios 2013). Incorporating brand communication strategies can help in pushing Model S into the market.
However, without specific marketing communication budget, Tesla Motors attempts to brand itself as ‘Apple automaker’ akin its use of technology in production (Mangram, 2012, p. 300). Upon considering that it is a new brand, it needs building a strong brand identity. Taking the benchmark of Apple Company is perhaps an important starting point. However, the creation of consumer awareness about the brand remains significant for increased performance.
This strategy needs to be accompanied by the production of more innovative products. Through budgetary allocations to initiate brand communication over new and traditional media, Tesla Motors can increase its brand identity across the globe. Perhaps, this step is the biggest strategic marketing opportunity available to the organisation.
Strategic Marketing Opportunities
In its marketing initiatives, Tesla Motors needs to consider introducing creative strategies in order to manage customer relationships. Keeping potential clients up to date with information is of important methods of maintaining positive relationships with customers (Hill & Ettenson, 2005, p. 88; Holt & Quelch, 2009, p. 70).Tesla Motors needs to update its customers constantly with new features for Model S so that they can update their vehicles using the internet.
These attempts would be done for the commitment of financial resources in communication. Although the strategy increases the cost of running Tesla Motors, it is justifiable in the context of Fornell’s (2002) assertion, “marketers are quick to recognise that the value of the customer asset is the sum of the discounted net contribution margins of the customer over time” (p.11). The claim here is that attempting to build customer relationships comes at a cost, which Tesla Motors must be willing to incur, notwithstanding its past loss experiences.
Ensuring that Tesla Motors’ website is up to date with the information on innovative and technological developments that are aimed at making Model S offer even higher customer experience is critical in the development of the brand image of the organisation.
Potential customers are likely buy products from a manufacturer whose information on what is available in-house is easily accessible (Roth, 2008, p. 310; Saxena, 2012, p. 40). This claim suggests that through the commitment of financial resources in online communication, Tesla Motors acquires a higher probability to capture the loyalty of both the existing and potential clients to gain competitive advantage.
Advertising to potential customers of Model S encompasses a major milestone towards enhancing the performance of Tesla Motors. However, retention of the clients is a function of how well the products satisfy their needs, in this, case luxury and technological innovativeness and performance. This claim underlines the significance of the utility of a product in terms of helping build good customer relationships (Kotler et al., 2009, p. 201).
Potential clients can also arrive at their decisions to seek products from an organisation that engages in online communication based on how the communications personnel handle them and/or how the sales personnel handle them at the physical premises of the organisation (Rust, Zeithaml & Lemon, 2004, p. 114). In the quest to build positive customer relationships, it is vital for an effort to be made to select people who can represent the interests of the organisation in the most pragmatic way.
Customers not only buy a product, but also pay for the brand image. According to Keller (1998), brand image is “a perception of customers when they see a brand reflected by brand associations in their mind” (p.27). These associations are multidimensional. They contain a myriad of attitudes or dimensions, which are emotionally instigated in relation to customer perceptions on brand quality and the degree to which the brand satisfies customer needs (Zineldin, 2000, p. 15). In case of Tesla Motors, the brand image can be enhanced using the power of the internet as the main approach for developing and creating awareness of the brand.
Using the internet as the means of creating the brand image of Model S implies that it can serve the dual purpose of distribution and communication. Using social networks, websites, and traditional media such as TV and contests among others as shown in table 1 makes it possible to influence the demand for the Model S. Internet aids in helping an organisation ‘focus on enabling customers find information about products’ (Fields, 2010, p.14). Brand image cannot be satisfactorily developed if potential clients are not aware of the existence of an organisation that offers products.
In the effort to create alertness of the existence of an organisation, social media is incredibly helpful. Such a strategy for building positive brand image is opposed to traditional approaches of brand communication in which organisations mainly focused on controlling what was said about their products and brands by dominating communication channels with carefully planned messaging (Anbu & Mavuso, 2012, p.3 12).
However, in the modern business environment, control of messages is immensely difficult since the ability of customers to access information through online interactions has become incredibly sophisticated. This sophistication entails online communication through B2B (business to customer) platforms. Therefore, Tesla Motors needs to the deploying latest developments in web 2.0 applications in enhancing communication to its market segment both cheaply and effectively.
Quantification of Marketing Objectives
The objective of engaging in both traditional media and online communication for the Models S is to achieve a sales target of 35, 000 units over 2014-2015 fiscal year. This sales level is achievable upon considering that the company receives more than 1 million people who visit its stalls in 2013, with 25 percent of them testing Model S (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 70). This observation suggests that with increased promotion of the product, it is possible to increase the number of people who visit the stall either physically or through an online platform, later making purchasing decisions.
Tesla Motors can currently produce 20, 000 cars at 20 percent capacity utilisation (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 70). This observation implies that initiating a marketing communications plan for marketing 35, 000 cars annually is achievable within the range of the available resources. Indeed, increasing production potential can help the organisation take the advantage of economies of scale to lower costs, which in turn increase its profitability levels.
The overall objectives of the marketing communications plan are increasing sales, enhancing Tesla Motors brand awareness, and/or driving potential consumers to access the organisation’s online communication platforms. The sales target of 35,000 units per year is feasible upon consideration of the past sales level of the organisation. Tesla (2013) data indicates that “when customers receive their ordered car, the organisation acquires 3 more reservations from each customer” (p. 1). In this extent, verbal communication has proved that communication can aid in boosting the sales levels of Tesla Motors.
Financial Analysis
To achieve the objectives of the marketing communications plan, $45M is required. The organisation has a financial resource to funds such as the marketing communications initiative. In 2013, it sold 20,000 units at $75,000 (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 73). This figure translates to $1500. The market communications budget will only cost 3% of the total sales in 2013. From the paradigm of cost-benefit analysis, the commitment of these resources is a viable decision upon considering that it will yield an increase of 15, 000 automobile sales in 2014-2015 fiscal year.
Selling the vehicles at $75,000, Tesla will make sales amounting to $2625M. Therefore, at the end of the fiscal year, a $45M communication budget will represent only 1.7% of the total sales. This finding shows a long-term gain in investing in communication to drive the sales potentials for the organisation until it produces at full capacity. Table 1 below summarises the financial requirements for implementation of the marketing communications plan.
Budget for the Proposed Marketing Communication Plan
Objectives and the scope of the marketing campaign
The idea of Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) has become an integral process in marketing in the current decade. It alludes to the procedure that advertisers utilize to arrange, create, execute and assess composed, quantifiable, powerful brand correspondence programs over the long run to focus on various segments of people (Yelkur, 2011, p. 108). It is currently broadly accepted that the incorporation of all types of advertising interchanges is fundamental for business achievement.
Indeed, the IMC methodology contends that shoppers see different interchanges by the same brand per say, instead of as individual messages, addressing them in better places and diverse ways. The real advantage of IMC is that a steady flow of messages is passed on to all intended interest groups by method for every accessible type of contact and message channels (Yin, 2009, p. 67). As a consequence of the consistency in the middle of instruments and messages, IMC has a tendency to be more viable and effective than customary marketing correspondences.
Tesla Motors considers its future performance to oscillate around the better placement of Model S in the marketplace. Currently, it employs an excess of 2000 people across all its fully owned subsidiaries that are situated in Asia, North America, and Europe. It also opened a new outlet in Toronto in 2012 in a bid to market itself in the Canadian market. This long-term strategic goal is not only to offer highly performing automobiles to average consumers, but also vehicles that have zero emissions.
Tesla Motors remains the only organisation that offers serial produced luxury electric sports cars. It anticipates launching its Model X this year, 2014. It plans to develop a large number of recharging stations across the world whilst making a significant progress in terms of innovation of battery technologies as an attempt to boost the dependability of its products (Roy, 2012, p. 60).
The company has experienced losses since its inception until 2013 when it began to make profits through sales of 20,000 units with an average price of $75,000 each. The company depended on the ‘word of mouth’ communication between people who came to purchase a vehicle and/or potential clients who interacted with them, to create awareness of its brand. Thus, the 20,000-unit sales level was achieved with zero allocation of financial resources on marketing communications.
The current marketing communication plan proposes that with a budget of $45M, Tesla Motors can increase its sales from 20,000 units to 35,000 units in 2014-2015 by incorporating online and traditional media marketing communication strategies (Roth, 2008, p. 77). This way, the company can clear misconceptions and doubts on the usefulness of the Model S. This strategy can help in terms of solidification of Tesla Motors’ brand equity. The objective of the plan is to increase sales, enhance Tesla Motors’ brand awareness, and/or drive potential consumer traffic into the organisation’s online communication platform.
There are seven key subjects which are normal for IMC. These subjects are: correspondence, marking, relationship administration, cross-useful arranging, mix, cooperative energy and business sector introduction (Reynolds & Valentine, 2011, p. 320). These speak to a critical part of the IMC idea; however, one is especially prominent – relationship administration.
Developing from a prior practice of advertisers corresponding with customers on a monolog premise, it is presently a generally acknowledged principle that connections need to be overseen in the long haul. IMC coordinates an awesome extent of the advertising exertion towards keeping up and overseeing long haul connections with all partners (Okoro, 2012, p. 135).
This gives a strong premise to business gainfulness and long haul achievement, and Tesla Motors needs to give careful consideration to the way it is dealing with its client connection. The new battle for Tesla Motors will have all commonplace IMC attributes, and, vitally, will be gone for enhancing a decent relationship and passionate bond with buyers, rather than simply depending on substantial advancement.
Integrated marketing communications performance objectives
The centered basic supply retailer, Tesla Motors, is at present confronted with solid rivalry from the other related players in the same line of production. As of late, some players were propelled, making the business significantly more defenseless against brand-exchanging and unfaithful client conduct. Tesla Motors is not in a sufficiently viable position to have the capacity to contend head-to-head with the other competitors.
Notwithstanding, it can settle on a decision – to either draw in a single competitor’s clients or to concentrate on the other competitors’ clients. Tesla Motors need to construct their decision of heading with respect to what might be most steady with the sought brand picture and personality. Audi is a fairly powerless contender however their objective client is basically distinctive to Tesla Motors – the little brand is focusing on the cost cognizant, by vigorously advancing low costs of its item run.
Then again, BMW is focusing on a more complex, prosperous sort of client – an objective which is steadier with Tesla Motors’ image picture. Being in an association with other competitors right now, it would bode well for Tesla Motors to continue pushing for a bigger bit of the premium section, as opposed to profoundly alter its key course and change the brand character to its exceptionally center (Matha & Boehm, 2008, p. 245).
With the end goal, Tesla Motors should accomplish a practically identical level of intensity on the online staple business sector, it needs to embrace a painstakingly arranged and executed IMC battle, went for situating it singularly as the main competitor for BMW, instead of a contender of the majority of the top four competitors in the meantime.
By concentrating its endeavors on a barely characterized target market, Tesla Motors does not just has a superior possibility of coming to its business goals, additionally, it would accomplish a superior designation of assets in doing as such. Currently, Tesla Motors is still in a semi-association with other firms, which is situated to terminate by the year 2017. In any case, the associated firms have officially rebranded to and have started conveying inside the marketing zone, which implies they are currently contending straight on with Tesla Motors for the consideration of the working class market (Lussier, 2005, p. 37).
Tesla Motors’ present suggestion is in light of high caliber of items sold, the complexity of site innovation and premium client administration. The brand has figured out how to gain from other enormous chains errors, by offering brilliant administration, which is one of the primary client disillusionments with the increased shopping for cars; most clients would typically grumble about deficient item substitutions or issues with conveyance times.
Accordingly, the premium valuing of the organization can be supported, particularly when contrasted with any semblance of Tesla Motors or even BMW, which is yet to get the online basic need retail business right. Utilizing Tesla Motors now highlights as a discussion piece at working class preferences and perpetually in sanctioning terms. Tesla Motors is not about as large as Audi, and it is more extravagant; however, the nature of administration does emerge (Lovvorn & Chen, 2011, p. 276).
Notwithstanding phenomenal client administration, Tesla Motors is additionally anticipating offering interesting items, which cannot be found with any of the top competitors. In the year 2014, the company identified with the other top players and resorted to large supplies rather than little or medium-sized suppliers hoping to market a good quality automobile that is not offered by the other competitors (Lee, 2008, p. 62). This endeavor would help in further upgrading Tesla Motors’ premium notoriety and issuing it a state of separation in a generally jumbled business.
Brand positioning
Right now, Tesla Motors focuses on a fairly wide client section, and can be regarded as lacking concentration because of the premium cost of its various offers, whilst advancing itself as less expensive than the others competitors’. The brand is right now focusing on clients who might ordinarily shop at Tesla Motors. This inexorably prompts a certain level of perplexity as to what Tesla Motors remains for, and an integrated marketing communication crusade would need to focus on this. It could hence be presumed that the centered retailer now targets high profile clients; what’s more, needs to tight this down to all the other clients in light of a legitimate concern for better characterizing its market suggestion, hence, expanding its deals in the long haul (Kvale & Brinkmann, 2009, p. 134).
With a specific end goal to better picture the current condition of the basic supply showcase, a situating guide can be outlined, characterizing where brands stand against two key criteria: cost and nature of administration. Price identifies with the offering cost of item ranges and additionally conveyance charges while the nature of administrations is basically focused on the rate of item substitution on a normal purchase and accessibility and dependability of conveyance.
Various perceptions can be made when investigating the staple retail situating guide. In the first place, some of the competitors are at present in a helpless state, due to rebranding and getting accessibility to M25 clients as of late. Client audits online have focused on the absence of refinement and poor tantamount nature of administrations, which could be ascribed to the generally recently settled online administration. Furthermore, other competitors as of late propelled online administration, in association with Tesla Motors. This is additionally as yet battling to rival built up players, yet in any case, it can possibly develop and move from the low superiority to the high superiority, while keeping costs low, as its principle image articulation.
At long last, Tesla Motors is in a somewhat shaky situating state, in spite of its nature of administration being regarded as magnificent. It has been utilizing low-cost capacity advancement while in the meantime as yet being connected with higher evaluating, equivalent to that of the competitors. This can result to negative ramifications on the brand, and ought to be tended to keep in mind the end goal to evade further client perplexity, and advantage from an engaged situating (Kouzes & Posner, 2003, p. 38; Kouzes & Posner, 2012, p. 324).
Tesla Motors’ business, regardless of being one the world’s greatest automobile manufacturers, is still powerless against rivalry from family unit names, for example, BMW and Audi. Their principle leeway is that they work physical stores, which clients are acquainted with and are thusly more prone to trust these brands’ administration.
On the other hand, this test can be overwhelmed by essentially dodging direct rivalry with these retailers. BMW and Audi are usually connected with lower costs and are accordingly pulling in an alternate sort of clients. In the meantime, Tesla Motors, having been connected with many clients, because of their long haul association, is more inclined to draw in the competitors’ clients, instead of simply looking for ones who rely on discounts.
The test that Tesla Motors is confronted with is persuading potential clients that it remains for high caliber at a premium value, and is pretty much as solid as any physical store, however, with a more proficient online business model. This can be accomplished by utilizing a painstakingly arranged IMC battle directed to probable clients. Cautious knowledge into the objective client profile would help in distinguishing key customer conduct and inclinations, which need to be tended to by Tesla Motors (Kolenda, 2001, p. 108).
Brand target
As settled in the talk as such, Tesla Motors’ present objective needs to be all the more barely characterized all together for the retailer to have the capacity to better address client needs and accomplish a more strong brand situating according to the customer. Its current low-cost offer advancement joined with a premium valued conveyance administration produces disarray among customers, which brings about the view of untrustworthiness and absence of reliability.
Concentrating on a limited target business is the initial phase in creating a brand, which addresses better-characterized client needs. Right now, Tesla Motors is endeavoring to achieve customers of a vast age reach and social evaluation classification. This is mostly because of its endeavor at a value war with enormous names, for example, BMW. This may bring about wealthier high class clients to be put off and to scrutinize Tesla Motors’ amazing administration claims (Kline, 2010, p. 211).
All together for the retailer to pull in and hold high profile clients, it needs to move the concentration far from its value reductions, and towards the premium nature of its administration. This is not another system for Tesla Motors, yet in any case, it has not been investigated to its maximum capacity. The initial phase in understanding this system would be to characterize the objective market that the integrated marketing communication campaign will address. Right now, Tesla Motors just covers 70% of the available market.
Then again, Tesla Motors is especially solid in California, where the quantity of individuals with a higher economic wellbeing, is more ideal for the business. Along these lines, it would be reasonable for an integrated marketing communication campaign to be focused at California-based people of the higher social class. So as to measure the objective business for Tesla Motors’ new integrated marketing communications campaign, information from the most recent survey done in 2011 by the Office for National Statistics to establish the total number of the population has been separated and broke down. The total population for the Californian territory proposes that roughly 3.5 million individuals fit in with the high profile social class. This represents about 26.5% of the aggregate populace of the city (Keller, 2006, p. 208).
Customer profile
The normal client that Tesla Motors is presently focusing on is hard to characterize because of the company’s fairly unfocused methodology. The gathered information proposes that the normal automobile customers is between 25 and 34 years of age, and are mostly males. Nonetheless, Tesla Motors’ present situating may be pulling in youthful, and also more seasoned, prosperous clients driving occupied ways of life.
A recently dispatched integrated marketing communications crusade ought to focus on a very much characterized sought client profile with a specific end goal to accomplish better concentration and convey a clearer message. Utilizing the normal competitors’ customer profile as a perspective, a Tesla Motors’ purchaser profile can be created, with the accompanying qualities: The age is between 30 and 50 years, gender is either male or female, upper middle class social class and above. The normal client would have not less than a 45 hours of work every.
They would lean toward great administration and convenient conveyances – planned at helpful times through the time period as opposed to drive online requests, where helpful time spaces are less inclined to be accessible (Kantabutra & Avery, 2010, p. 40). This shopper has a deliberately arranged out week after week timetable, and feels better on the off chance that they know precisely when their week by week shopping will be, as opposed to needing to do unpredictable top-up shopping at a neighborhood motor store various times through the week.
The customer behavior and decision making
Kouzes and Posner (2003), in their study clarified that “the acquiring propensity for a customer is attached to his essence of the item, impression of the item, and his way of life” (p. 46). The purchasing conduct of the purchaser is impacted by various inside and outer variables; this makes it an unpredictable marvel by and large (Kolenda, 2001, p. 56). The buying propensity for the purchaser is separated into five stages as stipulated below:
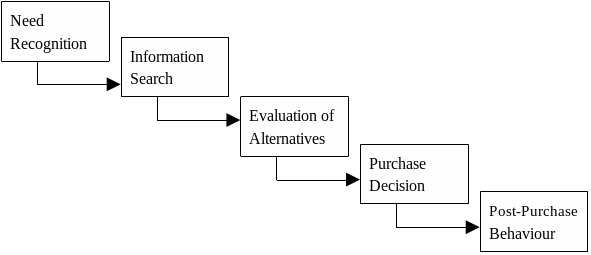
The above graph outlines the stages included in the buying propensities for the consumers. It admires the way that the consumers settle on choices in a five stage model.
Relationship between nature of the brand and consumers’ decision
It is critical for any business enterprise to have a reasonable picture of what the client anticipates from them (Kouzes & Posner, 2012, p. 22; Kline, 2010, p. 6). The consumers’ decision on the nature of a brand is altogether different from their decisions concerning picking merchandise or items. This is on account of the brands are considerably more not quite the same as wares. Merchandise are unmistakable and can be touched, while brands are not substantial; merchandise are perishable, the brand is not, and so on (Kantabutra & Avery, 2010, p. 40). In this way, these difficulties are faced by the clients when looking at brands and items.
Intangibility of the brand
Brands cannot be felt, or touched, or tasted, or seen, unlike products or items, (Keller, 2006, p. 206). Clients are known to settle on decisions, taking into account both unmistakable and impalpable components. Measurements like the nature of the nourishment or administration, and the cost of the item in connection to the administration are a few cases of elusive variables that impact the choice making methodology of the consumers (Kang & Singh, 2006, p. 200). Tesla Motors ordinarily select to focus on substantial components that are gone for impacting the clients’ choice making. The substantial measurements that they embrace are: great climate of the automobile shop, quality of service, enhanced offices, etc. (Daft, 2005, p. 330).
Variability of the brand
A brand differs from one supplier to another, furthermore from a client to another (Annabelle, 2006, p. 862). Because of this variability, consumers have a tough undertaking to settle on choices to pick one service provider over another (Aquinas, 2006, p. 60). Tesla Motors’ proprietors likewise have a tough errand of keeping up an unfaltering level of operation regarding the nature of the sustenance or administration (Avery, 2004, p. 43). For instance, if an organization’s employee gets a complaint from a customer, the complaint will influence him/her to provide low quality services consequently (Avolio, Walumbwa & Weber, 2009, p. 430).
Inseparability of the brand
A company’s proprietor will gauge the efficiency of the brand only after he/she has sold the service. On the other hand, a customer will gauge the efficiency of the brand only after he/she has bought it (Bass, 2005, p. 22; Bell, 2005, p. 120). The level of professionalism of the company’s employees will give the customers an insight in regards to the brand quality. In the same context, the feedback or responses received from customers will give the company’s proprietors a perception in regards to the customers’ satisfaction regarding the company’s brand (Aquinas, 2006, p. 9; Daft, 2005, p. 36).
Perishability of the brand
Consumers can buy physical items at any given time because of the way that they can be put away and sold whenever a consumer gets some information about their accessibility. Then again, it is impractical to store a brand. At the point when a brand is not sold, it means the way that the brand does not exist in any case (Clawson, 2011, p. 253).
One way of illustrating this is to take, for instance, a customer who has made a reservation and fails to show up. The restaurant will fail to serve other customers when the restaurant becomes full because they are anticipating the arrival of the customer who reserved the table. Due to the fact that the nature of the customers is uncertain, the restaurant proprietors find it challenging to find the balance between the supply and demand for their services.
The model of decision-making by the consumers
Very many scholars have come up with different interpretations of the model of decision-making by the consumers. This model gives an explanation of the steps that any consumer takes just immediately after seeing the product up to the time he/she makes the decision to purchase the product.
Due to the fact that services vary from one organization to another, the process by which consumers make their decisions when it comes to using a service is far much different from the process by which they make their decisions when purchasing a physical product. Collins (2001) in his study came up with “a five-stage model of the consumer decision-making process” (p. 31). These stages are discussed in the section below.
Acknowledging the need
The process starts with the need recognition whereby the consumers define their needs. The needs can be created due to both internal and external factors. An example of an internal factor is when the consumer decides to eat because he/she is hungry. An example of an external factor is when the need of the consumer is created when he sees an advert about a product. It is important for Tesla Motors to be familiar with the factors that capture the interests of their segment clients.
These needs can be related to a setup of a company. The physiological needs of the customers will motivate them to use a particular company. The business owner or workers then treat the customers with a good quality service which gives them a sense of belongingness and safety. In addition, customers prefer to choose a particular company that is in line with their esteem; thus, giving them a status in the society (Clawson, 2011, p. 253; Aquinas, 2006, p. 9).
The consumer acknowledges the fact that indeed there is a need that exists. To the consumers, the need is the problem that drives them to find solutions for the same (Flint, 2012, p. 24; Gratton & Jones, 2004, p. 33; Jha, 2014, p. 68). According to Clawson (2011) “there is a hierarchy of human needs which includes: the physiological needs, the need for safety, the need for belongingness, the need for self-esteem, and finally the need for self-actualization” (p. 48). These needs were ranked in regards to the order of importance.
The search for information
Logical consumers will want to have a good knowledge about the product or service plus the added features before taking the step to buy it. By digging into the information about the product, an association or attitude between the consumer and the product/service is developed. It is this association/attitude that will determine whether the consumer will like the service (Bass, 2005, p. 16). In this stage the consumer is motivated to know more about the product/service of interest.
After that the consumer evaluates the available existing alternatives whereby he can compare prices and quality. The consumer then makes the decision to make the purchase. In the final stage, the post-purchase decision, the consumer will gauge their prospects about the product/service against the performance of the product (Bell, 2005, p. 13; Clawson, 2011, p. 23). The information can be sought from friends, colleagues or even the media.
Exploring on the possible alternatives
When a customer has already identified a need and has gathered enough information about the need, he/she will look for other possible options that exist in regards to the category of the need the customer has. In this instance, the customer will explore on the various characteristics of the need to help him/her make a decision. In the context of a restaurant, the specific attributes that are explored by the customer include: varieties of automobiles available, the prices, the colour of the cars, and so on. This explains the primary reason why one automobile company is chosen over another (Flint, 2012, p. 24; Gratton & Jones, 2004, p. 33; Jha, 2014, p. 68).
The purchase
After the successful consideration of the top three stages, the customer will make his/her mind to purchase the service from the preferred vendor and consume it. In the context of a brand, the process of purchase and consumption are complementary; they happen together. At this stage the customer is very confident because he/she has enough and relevant information about the service (Clawson, 2011, p. 253; Aquinas, 2006, p. 9; Flint, 2012, p. 64).
Evaluation of the service after the purchase
Service providers are required to have in mind this process of decision-making in order to know and understand what the consumers’ needs are in each stage. This will also help them in making useful strategies in the near future (Flint, 2012, p. 24; Gratton & Jones, 2004, p. 33; Jha, 2014, p. 68). Rational consumers will want to evaluate if their expectations have been satisfied by the service after purchase and consumption.
When the customer is satisfied, he/she is likely to make the brand the top choice. The customer is also very likely to become very loyal to the brand and refer a friend to the same automobile company. In future, the customer will not feel overburdened to pay more for the service because he/she has full confidence (Clawson, 2011, p. 253; Aquinas, 2006, p. 9; Bass, 2005, p. 72). The decision-making process by the consumers is affected by the influence of others.
A customer can decide to choose a particular brand because his/her friends normally frequent there. The young adults normally have a habit of exchanging ideas with their friends regarding new brands that have come up in order to get their advice. When a particular brand is regarded highly by friends, the customer is most likely to prefer it. Advertising also influences the decision-making process of the customers. It creates more awareness about the product since it is the biggest form of communication. Other factors include the packaging of the service and the convenience of the service.
Objectives of the Integral Marketing communications
In view of the examination of Tesla Motors’ present method, brand qualities and shortcomings, aggressive business position, and possible key course for the future, another incorporated advertising correspondences crusade can be created. The main concentration of the Tesla Motors’ IMC campaign will be on two levels – first and foremost, to convey an engaged, exceptional brand picture to possible clients and secondly, to construct passionate customer brand association by advancing the psychosocial advantages of its consolidated faithfulness plan.
The crusade will go for satisfaction of the accompanying goals inside of a 12-month period, beginning June 2015.
Corporate targets
- To be the fastest growing automobile production firm through acquisition of new clients;
- To re-assemble brand personality to dispense with current brand picture related disarray among customers.
Business targets
- To expand total turnover by 25% in the one year period;
- To develop the present dynamic client base by 20% in the one year period;
- To build piece of the overall industry by 1% in the one year period.
Advertising and communications targets
- To improve the brand’s premium, by moving concentration far from its value coordinating action;
- To plainly characterize brand character and make a convincing message to bolster it;
- To make a passionate bond with potential clients, by emphasizing the advantages of the brand for the clients.
Proposal for communications and campaign strategy
Message Development
Altogether, for Tesla Motors new incorporated campaign to be effective in accomplishing the set destinations, it needs to be completely adjusted regarding the methods and the execution. The automobile company can possibly make a perfect association between the brand and the purchaser, however that would just be conceivable if the centre procedure supporting the battle is completely actualized all through the entire organization, with a specific end goal to accomplish full coordination of exercises and operations working towards the same objective aimed at the business achievement.
Tesla Motors’ two primary marking correspondence objectives are to convey a premium picture, and to stress the psychosocial advantages of its dedication plan, and the retailer by and large. These two objectives, in spite of being independently recognized, can be accomplished all the while, through painstakingly executed incorporated campaign, which is high quality, while connecting with the customers on an enthusiastic level (Abbas & Asghar, 2010, p. 35; Kline, 2010, p. 120).
Presently, Tesla Motors’ business is composed around the thought of providing valuable services to the clients. This is reliable with the marketing campaigns which have not been exceptionally effective previously, as they have produced perplexity and suspicion among customers. That is the reason why another focal sorting out thought needs to be produced, which will bolster the vital change of brand picture and will assume a focal part in the new incorporated marketing crusade.
The new thought and trademark will characterize the adjustments in the key course for the business, and will help in wiping out perplexity about the brand later on. The newly coordinated advertising crusade will be implemented under the thought of time, instead of expense, sparing the point of interest of the business and will go for setting up a passionate association with the objective buyers, who are in the upper middle class.
These buyers are associated with a substantial work timetable and minimal extra time to go through with their friends and family. An accentuation on the significance of not needing to make a compromise between investing valuable energy with your friends and family and running the family unit will be placed, focusing on the way that Telsa Motors nurtures its clients, lasting through the year. The brand’s motto of the company is expected to change (Adetule, 2011, p. 33).
The new motto of the company will be updated on the Tesla Motors’ website. Also, the motto will be printed on the company’s official vehicles and on all direct correspondence with buyers. The motto will bolster every promoting correspondence to help in accomplishing a predictable brand picture over all channels.
As the US economy is gradually recouping and turning out to be steadier, purchasers and the upper middle class specifically are less inclined to be keen on value reductions and more inclined to contemplate premium, yet basic and effective ordinary answers for their absence of extra time. That is the reason why Tesla Motors’ modified image picture is prone to engage the objective customer portion, and make a state of separation in a jumbled business.
The new trademark of Tesla Motors will bolster a particular incorporated promoting correspondences crusade which will incorporate various diverse executions, bound together by the basic subject of valuable moments. The campaign will concentrate on the significance of valuable minutes with the family or accomplice, and how these can be more regular and more agreeable for Tesla Motors steadfast clients.
Push and pull marketing
Push marketing involves advertising and circulation networks and is gone for persuading outsiders to advance the organization advertising. Push techniques incorporate exchange shows, displays, engaging suppliers, and making a production network to encourage circulation (Anbu & Mavuso, 2012, p. 312). Such a methodology is, for the most part, treasured to producers hoping to construct a conveyance system for their items (Blanchard & Cathy, 2002, p. 46).
On account of Tesla Motors, it being an automobile company as opposed to an organization offering a solitary item, it does not fundamentally need to actualize a push procedure of marketing in the customary sense. Due to the fact that push methodologies are principally concerned with pushing a solitary item through different circulation channels to the buyer, such methodologies are not significant to Tesla Motors as the organization is in control of its own appropriation and is indeed more inclined to be an objective of push procedures, instead of a dynamic implementer of such.
Push promoting ordinarily includes building associations with wholesalers to backing the vicinity of an item available in-store or on the web. In any case, as a merchant itself, Tesla Motors is the last purpose of contact in the middle of the brand and the customer and is hence in charge of its own business identity.
With the goal for Tesla Motors to be a favoured wholesaler for premium items, it needs to have interest for such items by shoppers. By making the automobile company more obvious to customers, and a favoured shopping destination for vehicles, a pull marketing technique would help build interest for the company’s sourced items and would, therefore, make free suppliers more intrigued by building an association with Tesla Motors.
It is, thus, of basic significance for Tesla Motors to execute a pull marketing method keeping in mind the end goal to continue adding to the business, on both the supply and the demand side. The pull marketing showcasing is the demonstration of executing promoting and special methods that are intended to tempt the prospect to purchase your item or administration (Ferch & Spears, 2011, p. 64). Pull marketing showcasing is coordinated at buyers, as opposed to promoting or conveyance channels, welcoming them to look for the item or the benefit themselves through alluring promoting and/or persuasive exercises.
Tesla Motors can take advantage unequivocally from the usage of different pull marketing procedures, thus, exercises would elevate the company to the objective buyer and make it more unmistakable, which could conceivably prompt client securing and maintenance. As of now, Tesla Motors is expanding its client base at a relentless level; even though it needs a correspondence push so as to plant it in the purchaser minds for the long haul.
Numerous internet shopping-favouring shoppers might not have offered thought to Tesla Motors, and an in number coordinated promoting interchanges campaign in light of the drawn procedures. This would assume an indispensable part in expanding levels of thought and transformation. The previously stated examination of the importance of push marketing and pull marketing procedures to Tesla Motors’ new campaign prompts the determination that a pull marketing procedure would be most fitting for the automobile company for the motivation behind re-marking and client procurement.
A pull marketing method can be executed through different components, for example, promoting in distinctive structures, public relations, direct advertising, advanced promoting, and that’s just the beginning (Fornell, 2002, p. 18).
Evaluation of advertising and correspondence
Customary promotion
Marketing is any paid non-individual interchanges through different media by a recognized organization, non-benefit association or person (Frost & Walker, 2007, p. 28). The primary advantage of this way to deal with interchanges is that it furnishes the publicist with complete control of what message and feeling to bestow into the promotion.
Any brand can advance its advantages in a powerful manner to purchasers and endeavour at drawing in them with a message of useful and/or enthusiastic qualities, to expand brand/item thought and deals. As a consequence of good purchaser and contender knowledge, brands can make promoting which displays them in the best conceivable light, to engage potential clients. Media stations, techniques and innovative yield are all measured and are chosen by the brand/organization, making the outcome useful much of the time.
On the other hand, it has been contended that regardless of the brands’ best goals to put in the most convincing and positive message into their publicizing, shoppers may translate the message diversely to what it is proposed to be interpreted as. The translation of boosts and signs in the environment is reliant on numerous individual qualities of the message beneficiary which is the reason the same boost may be understood diversely by diverse individuals.
This likewise remains constant in promoting, as in spite of promoters’ earnest attempts; outer element outside their ability to control may influence a shopper’s key message deciphering process and result in unfavourable disposition towards the brand.
Keeping in mind the end goal to survey the suitability of distinctive sorts of promoting to Tesla Motors’ new campaign, a more intensive examination at the conduct of the intended interest group needs to be taken. The automobile company’s new targets are 30-50-year-old, upper middle-class people with substantial work timetables and minimal leisure time.
People conveying these attributes would invest the majority of their energy outside of the home, and could accordingly be seen as prime time TV watchers. Radio promoting may be seen as less appealing a possibility for various reasons. Firstly, Tesla Motors’ new targets are California-based people, which imply that a substantial number of this gathering would in all probability be general workers, and would not be utilizing an individual engine vehicle regularly.
This, thus, implies that they fall outside of the typical radio promoting target bunch. Besides, radio publicizing, in spite of being a less expensive mass reputation alternative, is viewed as outdated and obsolete, which is the reason it would not resound with Tesla Motors’ more advanced, computerized picture. Print publicizing may be especially fit for the online retailer’s new battle, as it considers the focusing of workers, and it likewise has the capability of conveying messages capably through the great nature of imaginative work. Print publicizing is an extremely regular segment of the incorporated promoting specialized tool, as it has a high crowd achieve and can be a good avenue for key message correspondence (Gallos, 2008, p. 312).
Direct advertising
Direct promoting is broadly utilized by organizations for both the client obtaining and maintenance purposes. It can have a constructive outcome on deals if executed through the channels most pertinent to the objective shopper bunch. Characterizing the objective here is vital to great execution, as assets could undoubtedly be squandered, if narrowed on an insignificant channel. For instance, 18-24-year old customers would be better reached through email showcasing, as opposed to standard mail. Additionally, elderly buyers would react better to standard mail, rather than email promoting.
Direct advertising is most likely worth investigating as a major aspect of a more extensive incorporated showcasing interchanges campaign, as it can accomplish great client procurement levels with high reaction rates and great engagement. Reaction rates can increase uniformly to the level of the centre of the campaign by using different client databases giving nitty-gritty client profiling to suit the particular needs of the crusade.
There are two sorts of client database records that can be utilized as a part of direct advertising, for instance, cold and warm. Cold records give data on customers by gathering them into general classifications, for example, age or occupation. Then again, warm records separate customer profiles by particular qualities, for example, magazine memberships, acquiring propensities, and so on. The last are considerably more valuable for accomplishing particular campaign goals, as they help in sectioning the market all the more correctly, and focusing on the purchasers all the more adequately (Gitman, 2000, p. 251).
Digital promotion
Advanced promoting has turned out to be greatly applicable in the previous 10 years with the ascent of advancement in innovation and far-reaching access to the internet. Most families today profit by no less than one gadget which join with the Internet and an extensive number of family units have more than one gadget, for example, portable PC, tablet, or cell phone, which issues them access to the internet. This has opened up unlimited open doors for advertisers to achieve buyers with customized advanced substance in progressively imaginative ways.
For instance, the advertisers in association with distinctive organizations can now target purchasers by utilizing GPRS information got by their cell phones, and send them instant messages about brand advancements in the zone shoppers are in. An amazingly advanced kind of direct computerized promoting, notwithstanding some moral concerns it may have raised. For an automobile firm like Tesla Motors, advanced showcasing would be particularly significant as it would reverberate with brand picture and the business’ innovative capacities (Harteis, 2012, p. 97).
Public relations
Advertising crusades can be created for various purposes. While conventional promoting focuses on one partner particularly (the shopper), public relations ought to consider all the pertinent partners to a business, drawn out on a partner matrix which helps in distinguishing their association and significance to the business. Public relations exercises include, however, are not restricted to newspapers, occasions and public deeds. Public relations can be valuable for business from various perspectives, some of them being, in times of emergency, new item dispatch, changes in the business framework, extension, and so forth.
In spite of public relation’s high adequacy in imparting news about the business to the overall population, it would not so much be pertinent to Tesla Motors’ amended system over the accompanying one year, as the business is not experiencing huge changes. It would be more practical for Tesla Motors to centre its assets on different channels of correspondence, which would all the more adequately interpret its adjustment in brand picture, and help towards increasing great earned media consideration (Hughes, Ginnett & Curphy, 2012, p. 127).
Delivery of the integrated marketing communications
In this segment, an itemized clarification of the integrated marketing communications campaign conveyance will be furnished with each of the advertising specialized devices exclusively investigated top to bottom, to furnish the scholar with a decent comprehension of the thinking behind the execution procedure of the crusade. Subsequent to having decided the monetary allowance confinements of the crusade, the discourse will move onto concentrating on every individually specialized instrument in the order: Conventional advertising, direct marketing and advanced marketing. The segment will finish up with an expert timing arrangement and expense suggestions.
The budget for the integrated marketing communications
The initial phase in building up a coordinated advertising correspondences campaign for Tesla Motors is to emphasize the limitations of the financial backing, with a specific end goal to have the capacity to precisely arrange the applicable correspondences exercises and evaluate their suitability regarding expenses and campaign endpoints fulfilment. Utilizing the PITA figuring strategy, the accompanying parameters of the campaign have been recognized and have added to precisely deciding a sensible spending plan for the integrated marketing communications campaign.
The objective Population (P) of this campaign is 600,000 people. (California based inside of the applicable age and social evaluation classification). The Incidence (I), is accepted at 1 in 10 individuals of the objective gathering will turn into a Tesla Motors client upon introduction to the crusade). The quantity of Times (T) of purchasing Tesla Motors’ item joining to its steadfastness plan is 1. The cost of Tesla Motors offer is $300 for one-year membership.
By getting the product of these parameters and dividing them by the normal return on investment of the campaign, taking into account a normal standard rate of return on investment for campaigns of this size, the financial budget is computed at a sum of $4,000,000 for the integral marketing communications campaign. The table below provides the summary.
Conventional advertising
As far as conventional promoting, Tesla Motors’ new campaign will use TV, print and out of home channels, keeping in mind the end goal to get a high crowd achieve and brand presentation. Television and out of home promotion have a tendency to be substantially more extravagant than whatever other correspondences medium, which is the reason they have to be a piece of a deliberately outlined media arrangement, which considers these expense suggestions (Jerisat, 2004, p. 231). The three publicizing channels will be utilized overwhelmingly as a part of the initial half year of the campaign at the same time, so as to pull in the consideration of potential clients towards the campaign.
With such a media surge, the key message of the campaign will be conveyed well over the distinctive channels in coordination and will possibly produce larger amounts of thought rather than having blasts of diverse sorts of publicizing all through the entire one year period without full mix (Johnson, 2008, p. 88). The objective of the customary promoting endeavours will be 50 percent of the general campaign target of 35,000, implying that before the end of the campaign, conventional publicizing alone ought to have brought about the securing of 35,000 new clients.
Creative brief
The initial phase in outlining the campaign’s promoting movement is to set up a creative brief which will layout the situating explanation of the brand, key message focuses, and the exceptional selling scheme, which will be imparted over each of the three channels. The reconsidered exceptional selling scheme of the brand will be ‘the quality automobile provider’ which typifies the updated brand picture of an automobile company concentrating on the nature of administration, as opposed to value coordinating method (Hughes, Ginnett & Curphy, 2012, p. 127).
This is further upheld by an updated situating proclamation: ‘For occupied, white collar class buyers who need a service that would spare them time and exertion, Tesla Motors is an automobile company which offers excellent, bother free. Not at all like different stores, the company in light of an exceedingly productive request satisfaction and conveyance framework, sources all the customer requests precisely on time.
After seeing the ads, purchasers ought to not just see the premium brand picture of Tesla Motors; additionally, they feel that Tesla Motors is dependable and is there to help make their lives simpler. Key message focuses which the promoting will convey are as per the following: reliability, premium benefit, timely conveyance, easy to explore the site and broad-range of the products.
For TV publicizing, a half minute spot will be made, conveying the key message of Tesla Motors’ new campaign with a premium look and feel targeted for building up an enthusiastic bond with target customers. The spot will be branded as ‘Valuable Moments’ and will highlight an unpretentious correlation between the confused and upsetting nature of shopping at other automobile stores and the casual, effortless nature of shopping from Tesla stores.. Toward the end of the advertisement, Tesla Motors will be mentioned, uncovering the purpose behind the casual state of mind exhibited in the notice.
Advertisement plan
The incorporated advertising correspondences campaign’s print publicizing will keep running for an aggregate of one month, conveyed over two productions. The LA Times piece will keep running for an aggregate of 5 weeks, for 5 working days weekly amid the first week of each month, starting in June 2015. In any case, as opposed to running until September, the advertisement will be put in the production for 2 weeks in August, as the occasion month is for the most part connected with more elevated amounts of shopping movement.
In the initial two weeks of August, the commercial will endeavour to persuade buyers of the advantages of doing their car shopping at Tesla Motors, as opposed to other stores, and accentuating on the unwavering quality of Tesla Motors’ request satisfaction and conveyance framework. The LA Magazine’s piece will be set onto the distributions back page in the second and third weeks of August to harmonize with the occasion month shopping patterns.
Out of home advertising
Tesla Motors will place an out of home publicizing on boards in occupied regions crosswise over California to pull in more consideration reliably with whatever remains of the incorporated exercises inside of the battle. Inventive advancement will be straightforward and advanced, abstaining from adding of pointless multifaceted nature to the key message.
Bulletins are by and large consideration-getting, particularly if deliberately situated in territories portrayed by high number of individuals coordinating a battle’s objective group; however, they are not a decent medium for complex informing, which is the reason effortlessness would be fundamental to the imaginative technique crosswise over the mode of promoting.
The imaginative thought of the board promotions will be predictable with that utilized as a part of other media for Tesla Motors’ campaign. The notion of ‘valuable moments conveyed to you by Tesla Motors’ will be represented through various scenes. Boards will be set in the highly business-populated territories of California with one 96-sheet (40ft x 10ft) board per range in a three-month program, beginning June 2015, with the beginning of the bigger Tesla Motors’ campaign.
Timetable
As specified in the previous sections, Tesla Motors’ brodcasting movement will occur amid the initial half year of the campaign, close by other marketing interchanges exercises, with a specific end goal to bring issues to light about the brand, produce interest towards it, and in the long run lead to client procurement. About 50 percent of Tesla Motors’ procurement focus on (35,000 people) will be procured as an aftereffect of the battle’s conventional publicizing endeavours.
Direct advertising
As opposed to utilizing conventional direct advertising as a part of the type of standard mail, Tesla Motors campaign will attempt email advertising exercises as it is a speedier and less expensive choice, however, being quick, effective and special. Moreover, Tesla Motors’ objective are caught up with working people who should likely be monitoring their online letter box consistently and giving careful consideration to the messages they get, instead of conventional regular postal mail.
These individuals are liable to as of now be searching for efficient open doors on the web, which is the reason they are thought to be additionally eager to connect with email promoting instead of standard mail. The results of an all-around executed email promoting battle can be effectively assessed and a return on investment followed, keeping in mind the end goal to quantify the accomplishment of the marketing campaign (Hughes, Ginnett & Curphy, 2012, p. 127).
Direct advertising strategy
With a specific end goal to achieve its objective, Tesla Motors will lease an email catalogue containing the email locations of customers classified by area and age, which have picked into get business messages, which will further help to accomplish the securing focus, as it would minimize the danger of beneficiaries erasing Tesla Motors’ email without really opening it.
The email catalogue will be leased from an email advertising consultancy gaining practical experience in email marketing administrations and list rentals. The objective for this phase of Tesla Motors’ campaign will be gone for securing 35% of the general campaign procurement target, which are 35,000 individuals. The email advertising methodology ought to result in 20,000 new clients joining to Tesla Motors’ dependability plan.
Imaginative methodology
Tesla Motors’ messages will be precisely intended to not just contain all the significant data about the brand and its steadfastness but also to convey this data in a fascinating and interesting way with visual components and clickable connections, eluding the beneficiary straightforwardly to the Tesla Motors’ website. Essentially, the email needs to have a consideration-drawing title as the subject line, which tells the beneficiary what he/she ought to expect after opening the email. The title ought to contain a particular advantage aimed at drawing all the attentions of the customers.
Predictions and the campaign costs
To satisfy the objective of 20,000 client acquisitions through email advertising, it is important to lease a cold rundown of people falling into the objective group classification. The below table contains exceptional pick in email locations ought to produce a reaction rate of 1%, and a transformation rate of 1 in 4 customers. As the message in the email body will urge beneficiaries to snap a connection and register to Tesla Motors’ dedication plan as opposed to having them ask for more data physically, this methodology won’t cause any satisfaction expenses connected with answering to offer-related questions.
The objective of the email advertising phase of the campaign is 20,000 individuals, which implies that 8,000,000 individuals need to be reached, of whom 80,000 need to navigate to Tesla Motors’ site utilizing the connection given. The aggregate expense of this methodology, taking into account an expected expense for every email including rundown rental and duplicate improvement, will be $400,000. Likewise, post-testing of the email advertising crusade will cause expenses of roughly 10% of the expense of the campaign itself, $40,000. With included VAT, the aggregate expense of the marketing campaign will come up to just shy of $500,000.
Evaluation of the campaign outcomes
In this segment assessment strategies will be talked about and evaluated by fitness for evaluating the execution of the diverse methodologies inside of the coordinated advertising correspondences campaign. Customary promoting estimation and assessment technique will be trailed by a joined assessment approach for the advanced and direct advertising exercises inside of the campaign. In spite of the fact that Tesla Motors has qualities that can support the achievement of the Model S, it has a few shortcomings.
It relies on upon outer suppliers, an obscure brand, and an element new innovation for its operations (Mangram, 2012, p. 300). The ‘Model S’ takes out the utilization of fossil fills in the drive of autos. Separated for the brand being new in the business sector, expecting it is not no doubt understood by every single potential client, the new innovation represents the test of instabilities connected with negative previously established inclinations about the execution of the electric vehicle in examination with the oil or gas motors.
Opportunities incorporate the current outside chances, which while used well, can help an association to enhance its execution (Hill & Westbrook, 2007, p. 51). One of the significant open doors for achievement of the Model S includes the expanding number of individuals who are getting to be careful over debasement of the common habitat because of high carbon discharges that are connected with the rising number of cars. With effectively created predominant components, Model S has the open door for relentless development when completely electric auto business sector blasts. Tesla has a capacity of loosening up any negative ideas and previously established inclinations about electric autos.
Conventional marketing
Analysis and assessment are of extraordinary significance in the execution of a marketing campaign as they prompt changes in execution, lessened expenses and an all the more tweaked adaptation of the current advertising. With a specific end goal to survey the adequacy of messages and figure out whether the customary promoting phase of the campaign has accomplished the built up objectives, advertisement message exploration ought to be completed all through campaign phases.
On the trial stage, the commercials’ potential and regions of change will be investigated. To test ideas and designs of promotions for three diverse media, for instance, television sets, newspapers, and out of home, a total of 30 top to bottom meetings with delegates of the intended interest group will be carried out. The subjective information will give us significant data on the level of comprehension of key messages, purposes of interest and/or perplexity, acknowledgment and review rate.
There are four fundamental goals of the marketing campaign, for instance,
- To examine if the important messages are comprehended by the target buyers,
- To find out the commercial that is most loved by the buyers,
- To scrutinise at purposes of interest and/or disarray, and
- To assess the review.
Constant research ought to additionally be done all through the campaign keeping in mind the end goal to assess the viability of the picked media. For these objects, Brand International is prescribed as it has a vast day by day test size and empowers the estimation of quality, consideration and courtesy. To screen the effect of customary promoting on the measure of the advertising campaign to Tesla Motors’ website, the administrations of ComScore, the main web innovation organization, are prescribed. ComScore gathers and measures data about online movement and will furnish Tesla Motors with quantities of remarkable visits, returning guests, length of remain focused page, stage utilized and so forth all through the marketing campaign.
Following the rolling out of the campaign, the execution of the entire marketing campaign is assessed by measures, for example, knowledge of the brand, online movement and deals. For online movement assessment, information and experiences given by the internet company will be utilized. The knowledge of the brand will be assessed utilizing Brand International’s information.
Deals and their recurrence patterns will be measured through statistical tools as it is savvier than different systems. Econometrics will help to segregate and evaluate drivers of the key performance indicators, for example, publicizing, which is of specific significance, monetary patterns, value blend, and so on. On a littler scale, it will help focus the return on investment by relating the surge in sales to the interest in distinctive media and assess media commitment.
Direct and digital marketing
A prescribed device for dissecting the execution of both pennant promotions and email advertising is Google Analytics. The administration helps by creating specific codes for tracking the diverse marketing campaign correspondences which take into consideration their assessment independently.
This, therefore, prompts a superior comprehension of how fruitful individual routines are and can have clear ramifications on purposes of change. By determining the outcomes with Google Analytics, Tesla Motors can constantly enhance its return on investment and construct more grounded, more successful web vicinity. To track the flag advertisements’ execution, the Analytics created a URL for tracking which will be given to the advertising newspaper alongside the pennant promotion itself.
The immediate messages conveyed to potential clients would likewise contain an Analytics created for tracking the URL set up of a normal connection to Tesla Motors’ website. The Google Analytics tool will consistently monitor the execution of the marketing campaign by the accompanying parameters such as, number of website visits, optimum time on location, the number of new visits, and so forth. After the marketing campaigns have been commenced, their adequacy will be assessed by the satisfaction of the various goals.
The business sector portion for Tesla Motors is average sized with exceedingly performing sumptuous cars. The organization has the capacity to succeed in this business sector portion after considering that the Model S is absolutely mixed, as well as very performing eco-accommodating vehicles (Mangram, 2012, p. 300). In this market, the organization does not have any nearby parallel contender.
Without a doubt, the nearest associations that contend with it in the electric extravagance car fragment incorporate Nissan through Nissan Leaf and Chevy through its item, Chevy Volt (Tesla, 2013). All things considered, they both present low dangers. They offer lower execution electric autos in correlation with Model S. The Model S especially fits well in the moderate size extravagance auto market. Forbes magazine led an exploration on the offers of diverse lavish cars. It reported an increment in deals volume of lavish vehicles for a time of 5 years.
As demonstrated in addendum 1, this increment was most elevated in 2012 by around 20 percent contrasted with 2011 (Karamitsios, 2013, p. 44).This discovering proposes an expanding interest for extravagance vehicles, particularly as the economy recoups from the aftermaths of the worldwide monetary emergency. In any case, in the midst of the augmentation sought after, associations that offer a brand with elite and effectiveness are prone to make more deals on the grounds that extravagance items business sector portions esteem item utility and conformance to details while settling on purchasing choices (Simon, 2007, p. 126; Yelkur, 2011, p. 110).
The market definition for an extravagant vehicle can maybe be best fulfilled by considering conjecture for the normal deals level. Reference section 2 epitomizes one of such methodologies of anticipating obtaining conduct in the US for buyers with family unit livelihoods adding up to $100, 000 or more. From the reference section, downturns in 2009 and toward the start of 2010 are apparent.
Decreases are likewise clear in July to august 2011. They can be clarified by vulnerabilities that are connected with obligation roof reasons for alarm and downsizing of the US credit. After considering that information of business sector progress in the lucrative vehicles classification is anticipated for a time of 6 months, the pattern line infers more prominent desires for Model S.
References
Abbas, W & Asghar, I 2010, ‘The role of leadership in organizational change: Relating the successful organizational change to visionary and innovative leadership’, Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 1-49.
Adetule, J 2011, Handbook on management theories, Author House, Bloomington.
Anbu, J & Mavuso, M 2012, ‘Old Wine in New Wine Skin: Marketing Library Services Through SMS-Based Alert Services’, Library Hi Tech, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 310-320.
Annabelle, M 2006, ‘Notes from a Small Island: Researching Organizational Behaviour in Healthcare from a UK Perspective’, Journal of Organizational Behaviour, vol.27, no.7, pp. 851-867.
Aquinas, P 2006, Organizational behaviour: Concepts realities applications and challenges, Excel Books, New Delhi.
Ashtiani, C, Cullen, G, Davis, P, Greenwald, J, Hardigan, P, Eladio, K & Zimmerman, D 2011, Plug in electric vehicles: A practical plan for progress, School of Public and Environmental Affairs at Indiana University, Indiana.
Avery, C 2004, Understanding leadership, Sage Publications, London, UK.
Avolio, B, Walumbwa, F & Weber, J 2009, ‘Leadership: Current theories, research, and future directions’, Annual Review of Psychology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 421-449.
Bass, B 2005, Transformational Leadership, Simon and Schuster, New York.
Bell, J 2005, Doing your research project: a guide for first-time researchers in education, health and social science, Open university press, Maidenhead.
Blanchard, H & Cathy, S 2002, The generosity factor: Discover the joy of giving your time, talent, and treasure, Zondervan Press, Grand Rapids.
Clawson, J 2011, Level Three Leadership: Getting Below the Surface, Prentice Hall, New York.
Collins, J 2001, Level 5 leadership: The triumph of humility and fierce resolve, Harvard Business Review, Boston.
Daft, R 2005, The leadership experience, Thomson South-Western, Mason, OH.
Farris, P, Neil, P & Pfeifer, D 2010, Marketing metrics: The definitive guide to measuring marketing performance, Pearson Education, Inc., New Jersey, NJ.
Ferch, R & Spears, L 2011, The spirit of servant-leadership, Paulist Press, New York.
Fields, E 2010, ‘A Unique Twitter Use For Reference Services’, Library Hi Tech News, vol. 6, no. 7, pp. 14-15.
Flint, B 2012, The journey to competitive advantage through servant leadership: Building the company every person dreams of working for and every president has a vision of leading, West Bow Press, Bloomington.
Fornell, C 2002, ‘A National Customer Satisfaction Barometer: The Swedish Experience’, Journal of Marketing, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 6-21.
Freshwater, D, Sherwood, G & Drury, V 2006, ‘International research collaboration: Issues, benefits and challenges of the global network’, Journal of Research in marketing, vol. 11, no.4, pp. 295-303.
Frost, J & Walker, M 2007, ‘Leadership culture – cross cultural leadership’, Engineering Management, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 27-29.
Gallos, J 2008, Business leadership: A Jossey-Bass reader, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Gitman, L 2000, Principles of managerial finance, Addison-Wesley Longman, Inc., New York.
Gratton, C & Jones, I 2004, Research methods for sport studies, Psychology Press, Chicago.
Hardester, E 2010, The profitability of the electric car (Thesis), Brigham Young University, Brigham.
Harteis, C 2012, ‘When workplace learning fails: Individual and organizational limitations? Exemplarily demonstrated by the issue of responsibility in work life’, International Journal of Human Resources Development and Management, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 92-107.
Hill, S & Ettenson, T 2005, ‘Achieving the ideal brand portfolio’, Sloan Management Review, vol. 2, no.1, pp. 85-90.
Hill, T & Westbrook, R 2007, ‘SWOT Analysis: It’s Time for a Product Recall’, Long Range Planning, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 46–52.
Holt, A & Quelch, T 2009, ‘How global brands compete’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 68-75.
Hughes, R, Ginnett, R & Curphy, G 2012, Leadership: Enhancing the lessons of experience, McGraw-Hill Irwin, New York.
Jerisat, J 2004, Governance in a globalizing world, P2, Tampa, Florida, USA.
Jha, H 2014, Social research methods, McGraw-Hill Education, New Delhi.
Johnson, H 2008, ‘Mental models and transformative learning: The key to leadership development’, Human Resource Development Quarterly, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 85-89.
Kang, L & Singh, R 2006, ‘Stress at Work: An Assessment of the Magnitude of Various Organisational Stressors’, Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 190-202.
Kantabutra, S & Avery, G 2010, ‘The power of vision: statements that reason at’, Journal of Business Strategy, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 37-45.
Karamitsios, A 2013, Open Innovation in EVs: A Case Study of Tesla Motors, Routledge, New York, NY.
Keller, L1998, Strategy Brand Management: Building, Measuring, and Managing Brand Equity, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, NJ.
Keller, R 2006, ‘Transformational leadership, initiating structure & substitutes for leadership: A longitudinal study of research & development project team performance’, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 91, no. 1, pp. 202-210.
Kline, J 2010, Ethics for International Business: Decision-Making in a Global Political Economy, Routledge, New York.
Kolenda, C 2001, Leadership: The warrior’s art, Army War College Foundation Press, Carlisle.
Kotler, P, Adam, S, Denise, S & Armstrong 2009, Principles of Marketing, Prentice Hall, Australia.
Kouzes, J & Posner, B 2003, Encouraging the heart: A leader’s guide to rewarding and recognizing others, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Kouzes, J & Posner, B 2012, The Leadership Challenge, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Kvale, S & Brinkmann, S 2009, Interviews: Learning The craft Of Qualitative Research Interviewing, Sage, London.
Lee, P 2008, ‘A review of the theories of corporate social responsibility: its evolutionary path and the road ahead’, International Journal of Management Review, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 53-73.
Lim, T 2014, Model S: Revolution for the Masses. Web.
Lovvorn, A & Chen, J 2011, ‘Developing a global mindset: The relationship between an international assignment and cultural intelligence’, International Journal of Business and Social Science, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 275-282.
Lussier, R 2005, Human relations in organization, McGraw- Hill Irwin, New York, NY.
Mangram, M 2012, ‘The globalisation of Tesla motors. a strategic marketing plan analysis’, Journal Of Communication Management, vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 289-312.
Mark, K 2013, Suppliers to the 2013 Tesla Model S, Web.
Matha, B & Boehm, M 2008, Beyond the babble: Leadership communication that drives results, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Menon, A 2006, ‘Antecedents and Consequences of Marketing Strategy Making,’ Journal of Marketing, vol. 63, no. 2, pp. 18–40.
Motavalli, J 2013, ‘As it increases production, Tesla worried about battery supply’, The New York Times, pp. 19-20.
Okoro, E 2012, ‘Cross-cultural etiquette and communication in global business: Toward a strategic framework for managing corporate expansion’, International Journal of Business and Management, vol. 7, no. 16, pp. 130-138.
Reynolds, S & Valentine, D 2011, Guide to Cross-Cultural Communication, Prentice Hall publishing, Upper Saddle River.
Roth, H 2008, The challenge of the Global Brand: Handbook on Brand And Experience Management, Columbia Business School, Columbia.
Roy, S 2012, ‘Digital mastery: The skills needed for effective virtual leadership’, International Journal of e-Collaboration, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 56-66.
Rust, T, Zeithaml, A & Lemon, N 2004, ‘Customer centred brand management’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 82, no. 4, pp. 110-118.
Saxena, S 2012, ‘Challenges and Strategies for Global Branding’, Journal of Business and Management, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 38-43.
Simon, H 2007, ‘Rational decision making in business organisations’, American Economic Review, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 123-129.
Tesla 2013, Tesla Motors Inc. 2012 Annual Report, Palo Alto, EDGAR.
Tesla Motors 2014, About Tesla, Web.
Yelkur, R 2011, ‘Customer satisfaction and service marketing mix’, Journal of professional services marketing, vol. 21, no.1, pp. 105-115.
Yin, R 2009, Case Study Research: Design and Methods, SAGE Publications, New York.
Zineldin, M 2000, ‘Beyond relationship marketing: Technological marketing’, Marketing Intelligence & Planning, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 9-23.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Total Sales of Mid-sized Luxury Sedans in Units in the US
Appendix 2: Affluent Consumer for Electric Cars with over $100,000
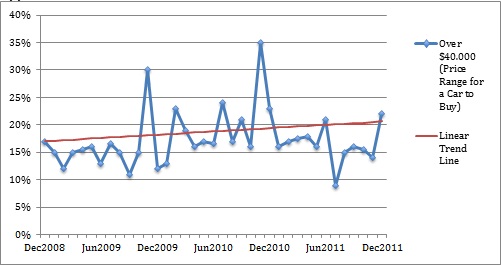
Appendix 3: Changing Demand for Greener Vehicles in the US
Appendix 4: Model S Sales In Units and its Major Competitors