Introduction
It is important to note that an e-commerce business heavily depends on a properly structured and organized information systems infrastructure. The availability of such systems enables the automation of many important and repetitive tasks, but it needs to be incorporated with precision and in accordance with the key objectives of the company. As a chief technology officer or CTO of a startup, the goal is growth within the next two years by becoming an online traditional store-based retailer primarily focused on the B2C format.
Background
The hypothetical e-commerce startup is called Health Tactical, which specializes in selling groceries and common goods with an emphasis on health aspects. The e-commerce store will feature products of great interest to people highly engaged in improving their health and well-being. Considering the fact that the area of nutrition science is rather confusing and complex, with many differential trends being presented, the goal is to accommodate all of these groups by offering them solutions in a convenient website platform. On top of the organic food products, e-commerce will also have additional goods interesting for health-focused individuals. The company will be mainly comprised of chief managers, such as the CEO and CTO, as well as ten employees, with an expected expansion of the employee size to 30. The revenue is expected to grow from $5 million to $30 million within two years. The current two-story standalone building will serve as a hub for the company’s servers, computers, and employees.
It is important to note that the company will not be selling its own foods, supplements, and products but will build a network of suppliers with local butchers, farmers, and overseas supplement manufacturers, as well as other retailers. For example, for the Carnivore and Paleo sections, the meat will be essential, which is why local butchers will be contacted to operate as a supplier for customers. The supplementation and another diet/lifestyle-related products will be the most lucrative aspect of the business since they will be sold alongside organic and healthy foods, but these do not have specific risk elements associated with regular food products due to storage and transportation convenience. The supplements will be highly useful for all categories because health-conscious individuals are well aware of the dietary imbalances in vitamins, minerals, protein, and healthy fats. For instance, individuals interested in prolonged fasting might want access to easy-to-consume zero-calorie drinks to supplement the absent minerals and vitamins. Another example would be vegan people, who are unable to supplement vitamin B12 through plant-based foods (Jin, Line, Lee, 1, p. 2111). In other words, health-conscious customers always tend to have some awareness or caution about specific nutrients absent in their regular diets.
The website will be mainly an easy and automated ‘middleman’ to connect various suppliers with customers interested in a specific health trend. The platform can also integrate social media networks to ease the communication process as well as registration procedures. In addition, it is important to note that the e-commerce business has a massive potential to grow by implementing vertical integration in the future. Since it is rather challenging to ensure that the business has enough room to store and distribute its own products within two years in such a small building, the emphasis will be put on perfecting the website, acquiring customers, and promoting the brand. However, in the long term, the business will be able to reinvest in storage and transportation facilities in order to sell its own goods, such as foods, supplements, and other health products. The end goal will be to conduct a full vertical integration starting from having farmland, cattle, and supplement manufacturing facilities.
The business, as a form of e-commerce, taps into a major consumer need for healthy products within the convenience element of a specific dietary regimen or lifestyle. Various YouTube, TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook health advocates and influencers will be used to market the platform. There are many echo chambers of individuals interested in the specific dietary lifestyle with their own convictions and science behind it. Although it is possible that any diet leads to health improvement due to a mere reduction in processed foods and refined sugar consumption, heavy meat-eaters and vegans tend to have their data to confirm their convictions. As a platform, the business is not interested in advocating for a specific dietary choice, but rather it is a convenient tool for such groups of individuals who do not want to go to a regular shop and selectively read, examine, calculate, and search for foods, supplements, and health products, which fit their dietary lifestyle. The platform will provide a simple interface for health-conscious individuals who seek to be presented with all foods, supplements, and health products allowed or preferred for their dietary needs.
Business Type, Customers, and Demographics
The e-commerce company Health Tactical will be of B2C type with B2B format applicable only to the suppliers. The core business model is centered around being sensitive and responsive to different health trends and newly emerging as well as already popular diets. The website will feature the categorization of products not only by their type but also by their relevance to a particular dietary style. The key categories will include Paleo, Atkins, Carnivore, Vegan, Vegetarian, Low Fat, Low Carb, Fruitarian, Intermittent Fasting, Water Fasting, Keto, and the Mediterranean diet. The customers will be mainly health-conscious individuals concerned with improving their health through consuming certain food types. It should be noted that “for health-conscious consumers, the availability of healthy food significantly affects the evaluation of the consumption experience in terms of both cognitive and affective response mechanisms” (Jin, Line, Lee, 1, p. 2103). In addition, individuals are becoming more interested in online and technical solutions for their health by relying on devices and online availability of consumables (Garge, Balakrishna, Datta, 2). Therefore, the business is focused on catching and predicting various diet or food trends to incorporate on the website alongside the core lifestyle eating patterns.
The core demographics are comprised of health-conscious individuals interested in what they consume, the science behind a diet, and maintaining a normal weight range. It is reported that “consumers who are health conscious regarding their lifestyle and diets derive high utility values from the nutritional information of the product” (Ghvanidze, Velikova, Dodd, Oldewage-Theron, 3, p. 863). Although there is no single adherence to a particular group, millennials aged between 25 and 34 will comprise the bulk of customers since they are the most health-conscious group (Buchholz, 4). After the millennials, Gen Z and Gen Y will be of prime interest since they, too, rely on reliable online sources to get a framework and science behind each dietary style. Therefore, such an interest in health, in combination with the internet’s influence and spread of major diets, provides the basis to provide healthy foods, supplements, and many other products with a simple categorization style in order to remove the tedious aspect of selecting foods in accordance with a specific diet’s requirements.
One of the most interesting aspects of health-conscious consumers is the fact that most of them are willing to spend more on organic and properly grown foods rather than corn-fed meat or GMO farm produce. In addition, local butchers and farmers tend to lack proper access to the larger consumer base because they need assistance in reaching a greater customer base due to the inherent nature of the restricted locality. The platform will serve as a connecting tool with a value of convenience for health-conscious individuals and customer providers for the local farmers with butchers. The most lucrative aspect of the business will be supplemented because the organic food market is already expensive by design, which is why the profit margin of food products will not be significant. However, the platform will have a powerful and key feature in its cart option to calculate the total amount of nutrients, such as macros, vitamins, and minerals, and offer supplements as a solution to fill the gaps. A customer will be asked for a specific age, body weight, and daily activity information during the registration process or as an option to track the nutritional information of their purchase.
Key Elements for The Company’s Information Systems Infrastructure
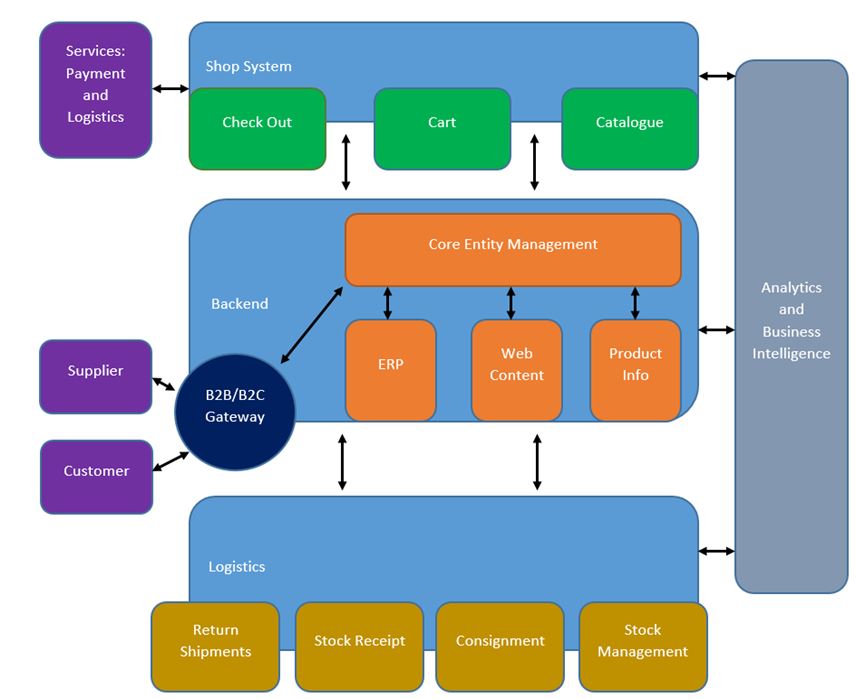
The key elements of the company’s information systems infrastructure include four major compartments. These involve shop systems, backend, logistics, and analytics with business intelligence or BI. The shop system will be integrated to contain the product catalog, cart function, and check-out procedure capabilities. It will be interacting with three different subsystems, such as services of payment and logistics, analytics and BI, and the backend. The latter will be comprised of web content, product information, and enterprise resource planning or ERP connected to the core entity management of the backend. Customers and suppliers will interact with the backend through the relevant B2C and B2B gateway. The logistics element will be comprised of return shipments, stock receipt, consignment, and stock management functional elements. Analytics and BI will be interconnected with the shop system, backend, and logistics in order to ensure that data is being stored, categorized, and analyzed. A high-level block diagram for the company’s information systems infrastructure can be accessed in Figure 1 below.
It is important to point out that e-commerce is a commercial activity, the purpose of which is considered to be the acquisition of benefits and is based on the complex automation of the paid cycle through the introduction of computer networks. The economic prerequisite for e-commerce is the objective need to reduce the losses that appear in paid cycles. The formation of e-commerce is directly dependent on the spread of the internet. The company trades directly with the consumer, and the basis is the retail sale of goods. The customer can simplify and speed up the purchase procedure by making a commercial transaction. The consumer does not need to go to the store to select the desired product because it is enough to view the characteristics on the supplier’s website, select the desired product, and order with delivery. The internet gives the seller the opportunity to track demand. Minimizing the number of intermediaries in organizing sales is the main advantage of this e-commerce model. Future implementations of this model are likely, such as web storefronts, online stores, and online trading systems.
Initially, it is important to use web storefronts before the entire website is complete, as they are relatively inexpensive and fairly easy-to-implement sites that provide a product catalog. Ordering goods and invoicing are among the functions of the web storefront. However, the processing of the order is carried out by a human sales manager. His or her responsibilities include organizing interaction with the warehouse, delivering goods, confirming payment for the purchase, studying demand, conducting marketing and promotional activities, and doing analytical work. Thus, the manager performs the implementation of the sales process with the internal business processes of the company. An online store-enabled commerce organization is more suitable for a firm that wishes to control the entire e-commerce process and seeks to reduce transaction costs. Compared to a storefront, creating a store is more expensive, and with proper organization, these costs pay off faster. Customer requests are processed by the application server, which, in turn, communicates with the data warehouse and the electronic payment system.
Technically, an online store is a combination of a web storefront and an electronic trading system. This system carries out automatic processing of incoming orders, such as storage at the base, control of payment, or delivery of the product. In the next stage, there will be a transition to the format of an online store that offers to place an order and receive information about the product around the clock by all available means. The latter includes an electronic catalog on the website, by phone, e-mail, social networks, and other internet communication channels. The buyer receives all the accompanying documents when purchasing a product, as in a regular store. The warranty card or written explanation of how to obtain warranty service for this product is important, and in some cases, it also includes a written explanation of how to return or exchange the purchased product. Unlike web storefronts, in an online store, the manager only controls the operation of the system, and therefore, the online store can work in automatic mode.
Gantt Chart
List of Key Elements
Website Development
- Frontend and Design
- Backend: Core Entity Management + ERP, Web Content, Product Info
- B2B/B2C Gateway: Supplier and Customer interaction
- Shop System: Check Out, Cart, Catalogue – interaction with Services: Payment and Logistics
- Analytics and Business Intelligence: Big Data, analytics, and customer information
- Logistics: Return Shipments, Stock Receipt, Consignment, Stock Management
The combination of all elements
- Launch of the e-commerce website
- Enabling the integration of suppliers into the system
- Marketing
- Sales
Conclusion
In conclusion, Health Tactical will be an e-commerce health product retail website with an emphasis on convenience and dietary categorization, as well as nutrient tracking options. The local butchers and farmers will be the suppliers of the food products, but the profits will be made from supplements and other health products. The information systems infrastructure will be comprised of shop systems, backend, logistics, and analytics with business intelligence or BI.
Sources
Naehyun (Paul) Jin, Nathaniel Discepoli Line, Sang-Mook Lee. 2017. The Health Conscious Restaurant Consumer: Understanding The Experiential and Behavioral Effects of Health Concern. pp. 2103-2120. Web.
Gopi Krishna Garge, Chitra Balakrishna, Soumya Kanti Datta. 2018. Consumer Health Care: Current Trends in Consumer Health Monitoring. pp. 38-46. Web.
Sophie Ghvanidze, Natalia Velikova, Tim Dodd, Wilna Oldewage-Theron. 2017. A Discrete Choice Experiment of the Impact of Consumers’ Environmental Values, Ethical Concerns, And Health Consciousness On Food Choices: A Cross-Cultural Analysis. pp. 863-881. Web.
Katharina Buchholz. 2019. Vast Majority of Americans Interested in Healthy Foods. Web.