Introduction
When people arrived and connected to the internet, incoming connection requests were detected. Incoming requests, more so from unknown locations, may be an indication that someone is trying to gain unauthorized entry into your server. This could be dangerous as it might be a cyber-attack, or someone is attempting to get vital information from you. Therefore, a specialized tool should be in place to always detect any form of infiltration into the system through various ports or protocols.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Problem identification.
- Establishing a concept of the possible origin.
- Testing the idea of likely cause.
- Establishing a plan of action and identification of likely effects.
- Implementation of the plan or escalation.
- Verification of the whole system’s functionalities.
- Document findings, actions, and results.
Tool and Description
Protocol analyzers previously referred to as network monitors, might help solve the issue. Commercial sniffers such as Wireshark and Omnipeek may help solve the problem by collecting any packets on the network. With this sort of tool, for instance, you might be able to see all the packets that went into setting up a connection.
Tool Operational Use Case
Using Wireshark, the whole network can be monitored to ensure that everything is working as intended and that nobody is trying to get entrée via a port. However, suppose somebody or anything attempts to gain access through a port. In that case, the analyzers in Wireshark will recognize this, and as a network administrator, they may limit communication over this port. Thereby blocking any undesirable opponent on their network who is initiating harm.
Tool Functionality
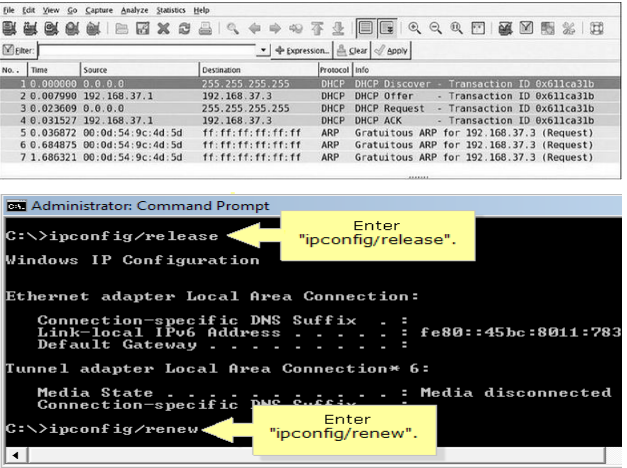
A protocol analyzer or sniffer, such as Wireshark, will record and display network packets in real-time for network administrators. For instance, below is a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol capture of a network administrator releasing and renewing their Internet Protocol address from the server. When you type the executable commands (ipconfig/release and ipconfig/renew) into the command window, the sniffer catches the release and renews Internet Protocol address commands that was requested by this computer from the DHCP server.