A PESTEL analysis, which examines the conditions of an industry’s external environment, was performed on U.S. smartphone industry. The analysis revealed that this industry has strong governmental involvement and economic influence. There are U.S. agencies that exist just to protect consumers from unfair or fraudulent businesses, and to regulate the manufacture and operation of certain products and devices such as cell phones and other electronic devices which communicate by emitting and receiving radio waves (Federal Trade Commission, 2021).
On the cultural front, U.S. firms have quickly transformed their segmentation strategies due to how globalization has influenced culture, ethnicity, gender, generation, income, and other factors (The Pew Charitable Trusts, n.d.). A positive attribute in the U.S. is the reliability, availability, and overall quality of infrastructure (Best, 2020). Climate change, however, may be a concern with the range of extreme temperatures, some of which are extremely destructive and may pose a risk to communications infrastructure, manufacturing, and logistics (NOAA, 2021).
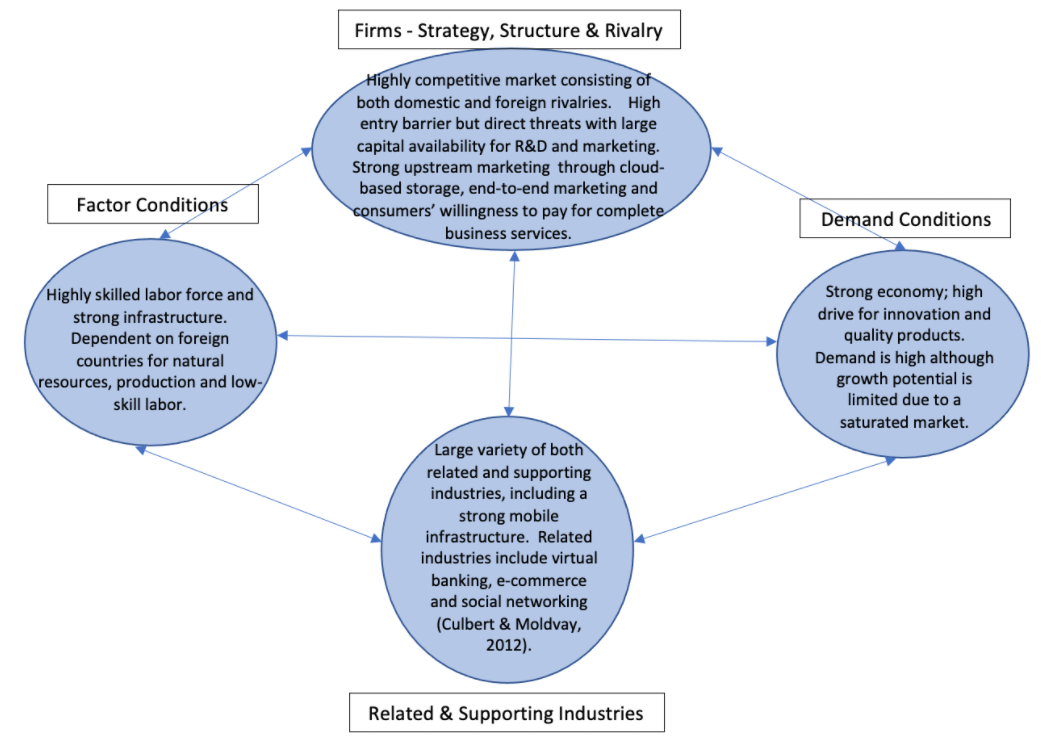
A Diamond Model analysis was also performed to examine the smartphone industry from a different perspective. The analysis revealed that the industry has a highly skilled labor force but is dependent on foreign countries for low-skill labor. There is a high drive for innovation and quality products but new entry threat is low due to a saturated market. However, there are direct threats with large capital companies who can invest heavily in R&D and marketing. Smartphones have many related industries, mainly, mobile telecommunication, banking, and social networking.
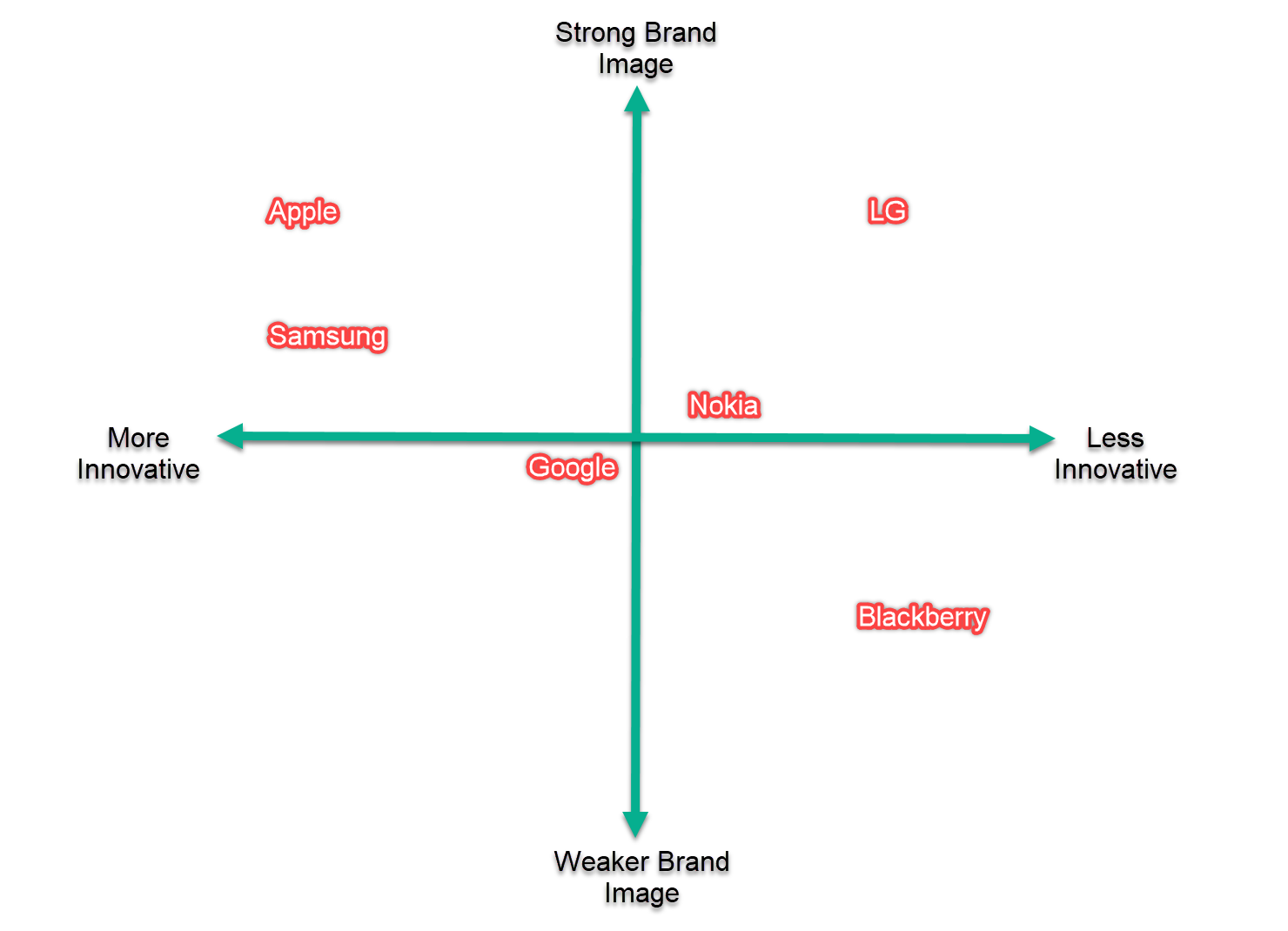
The strategic problem with the smartphone industry in the U.S. is that penetration has reached 85%, which leaves little opportunity for other competitors to enter this market space. Samsung is by far Apple’s top competitor, however LG, Blackberry, Nokia, and Google were included in a competitive analysis and evaluated on innovation, expertise, customer service, delivery time, regulations, and safety. The competitive positioning map shows that Apple ranks the highest in brand image and innovation. However, their highest competitor, Samsung, is just as innovative and with only a slightly weaker brand image. This creates a competitive environment where Apple must continually strive to maintain their lead in these areas.
Porter’s Five Forces is a framework that was completed to analyze Apple’s competitive environment. It revealed that the threat of new entrants is weak in that they would not only need substantial capital but would also need to pursue the endeavor of establishing brand recognition within an industry that already has several strongly branded companies (Beers, 2020). In addition, the threat of substitutes is low as similar products have limited capabilities compared to Apple’s products. However, as noted in the competitive analysis, the level of established competition within this sector is high. The bargaining power of buyers is weak but the strong of suppliers; buyer power is weak due to consumers investment in a diverse suite of integrated Apple products which would make switching costs very high (Maverick, 2019), and bargaining power of suppliers is high as the vast majority of processor chipsets are manufactured by only two companies (Lee, 2021).
In light of this market saturation, a TOWS matrix and SBU analysis were created to identify the cash-flow (also known as ‘cash-cow’) and question mark strategies. Based on these strategies, I am recommending a marketing strategy to pay for the implementation of these strategies. Once implemented, I expect a 35% ROI and 50% revenue from services segment increase over the next 5 years.
Strategic Problem
Smartphone penetration in the U.S. has reached 85% (O’Dea, 2021), leaving very little room for further penetration by competitors in the known market space. Firms in the “high tech industry are competing against each other to increase their market presence while continuing to face challenges like slim operating margins, high capital expenditure, shortening product lifecycle and managing a global supply chain” (Kamann et al., 2011, p. 5). In a fully saturated zero-sum market, companies need to accelerate innovation in order to win new market share away from their competitors especially in a market such as this where the majority of consumers are not particularly price sensitive.
PESTEL Analysis
The PESTEL analysis opens the door for an organization to see the conditions of an industry’s external environment, which will help dictate their actions and performance. The PESTEL is an acronym that symbolizes the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Environmental, and Legal analytics that can impact a business.
Political
In terms of the political environment, the government is heavily involved. For the high-tech industry, the government can pass and change legislation over privacy, surveillance, censorship, security, and antitrust laws at any time. The U.S. government’s impact has been so pronounced that big tech companies have turned to nonmarket strategies to yield some influence. “A new report from consumer advocacy nonprofit Public Citizen says that big tech companies are now the biggest lobbyists, and that the money they spend on influencing government policy has allowed them ‘to harm consumers, workers, and other businesses alike’” (Lovejoy, 2021). With the passing of time and as technology evolves, corporations may overstep their boundaries, which would mean that the tech industry can anticipate that the actions of government bodies will continue to influence the decisions and behavior of firms. In other words, political pressure due to changes in legislation and regulations can be expected.
Economic
As much as political factors can affect corporate strategies, the same impact can be articulated with economic factors. The U.S. growth rate, inflation, deflation, interest rates, and exchange rates can have drastic consequences to a firm’s overall strategy. Within the United States and globally for that matter, the Great Recession created a sharp decline in the economic activity of the country for which has not been seen since the Great Depression. Forbes “analyzed data from the Great Recession and found that tech companies that acted swiftly to counteract the downturn ascended to the tops of their markets, but that nearly half of market leaders slipped to the back of the pack” (Montgomery, 2020). Additionally, a change within macroeconomic factors, such as an increase of the level of unemployment, can indicate increased lost wages, and manifest a reduction in consumer buying power. Since then, the economy has grown; however, the constant vigilance and mitigation to the changing characteristics of economic conditions needs to be continuous (NOAA, 2021).
Sociocultural
The term continuous is also applicable within the sociocultural factors in the PESTEL model. “Sociocultural factors capture a society’s cultures, norms, and values. Because sociocultural factors not only are constantly in flux but also differ across groups, strategic leaders need to closely monitor such trends and consider the implications for firm strategy” (Rothaermel, 2021, p. 78). In the advent of globalization, demographic trends in age, ethnicity, socioeconomic class, gender, generation, income, among other factors, have quickly transformed firms’ segmentation categories and strategies in the United States. “Societal changes drive public policy. These shifts include an aging population; the growth of high tech and service sector jobs; evolving views on race, ethnicity, and immigration; and changes in family structure” (The Pew Charitable Trusts, n.d.). Regardless of the industry involved, it is imperative that corporations repeatedly scan, monitor, and evaluate external factors and trends, which can create both opportunities and threats.
Technological
The U.S. ranks high in overall availability and quality of infrastructure. Municipal water and sewer services, power utilities, communications and broadband internet, and reliable transportation infrastructure are all readily available in almost all portions of the country, though there are regional differences in availability and quality as could be expected (Best, 2020). The vast majority of the landmass of the U.S. is covered by LTE rated cell service from one of the nation’s four largest wireless carriers: AT&T, T-Mobile, UScellular, and Verizon (FCC, 2021) which constitutes LTE coverage for 98% of the population (Heisler, 2015) and over 99.9% of the population have at least a 3G connection (SDG, 2017). Ninety-seven percent of Americans own a cell phone of some kind with 85% of Americans owning what would be considered a smartphone (Pew, 2021).
Environmental
The overall climate in the U.S. is relatively temperate with a range at the extremes from the Alaskan tundra to the tropical climate in Florida and Hawaii (Weather and Climate, 2021). The U.S. does experience some destructive extremes in weather, most notably hurricanes in the southeastern coastal states, which have been on the rise since 1970 (NOAA, 2021). The U.S. does have some significant issues with pollution with overall air quality being problematic in many places. Additionally, there has been an ongoing municipal water crisis in Michigan for many years which has highlighted the problems with some of the aging infrastructure present in the country (Tiseao, 2020). The U.S. ranks 24th on the Environmental Performance Index which suggests that, while there are some pollution issues present in the country, overall the US does better than many other countries with regard to environmental protection and pollution (Yale University, 2021).
Legal
The U.S. has a very robust degree of protection for Intellectual Property to deter counterfeiting and industrial espionage thereby preserving the drive for ingenuity and entrepreneurship that the country is renowned for (U.S. Department of State, 2021). There is also a significant body of labor law and anti-discrimination law present in the U.S. that prevents discriminatory practices, abusive and dangerous working conditions, child labor, and other undesirable conditions that may be present in other labor markets around the world (U.S. Department of Labor, 2021). There also exist in the United States agencies that protect consumers from unfair or fraudulent businesses (Federal Trade Commission, 2021), from monopolistic business practices (Federal Trade Commission, 2021), and from false reporting of operating results and finances (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, 2020). The Food and Drug administration and the Federal Communications Commission share joint responsibility in the regulation of cell phones and similar electronic devices that emit and receive radio frequencies (FDA, 2021).
Competitive Analysis
Apple
Mission & Vision
Apple’s current mission is “to bring the best user experience to customers through innovative hardware, software and services” while their vision is “to make the best products on earth and to leave the world better than we found it.” (Abbott, 2021) Despite frequent changes in their mission and vision statements, one thing always remains the same – quality products and services for its customers.
Company Profile
Apple was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne and has been a global leader in the technology industry. The company, based in California, is known globally for its innovative solutions for computer software, electronics, and online services. (Apple Mission Statement 2021: Apple Mission & Vision Analysis 2021) Apple is one of the ‘Big Four’ tech companies as they not only design and sell consumer electronics such as the iPhone and Apple watch but also for developing computer software and offering online services as well. They have 80,000 employees as of 2020 (Apple: Job Creation, 2021). At the end of Q1 on December 26, 2020, Apple reported a record $111.4 billion in revenues driven by strong iPhone sales with a record $65.6 billion from iPhone sales. (Abbott, 2021)
The core values adopted by Apple go a long way in maintaining its consistent growth. The company’s core values include Accessibility, Education, Environment, Inclusion & Diversity, Privacy and Supplier Responsibility.
The company’s focus on innovation is a leading source of competitive advantage. The other areas where Apple has been able to achieve a strong competitive advantage include marketing and product quality.
Strengths
- Proprietary ecosystem: The ecosystem is successful due to the ease of use of products and how well they integrate with each other and the services of the company.
- Brand Recognition & Customer Loyalty: Apple is recognized world-wide but also demands loyalty due to the way it sells its products.
- Management and Culture: Apple has transformed into a behemoth not only focusing on the iPhone but expanding into Wearables, Services, and more all while building a strong corporate culture. There’s a reason the company is consistently ranked one of the best places to work year after year.
- Domination of the advanced consumer electronics supply chain. Apple has “effectively created a closed ecosystem, controlling every part of the supply chain from design to retail” (Clarke & Boersma, 2018).
Weaknesses
- Overreliance on iPhone Revenue: 50% of Apples revenue in 2020 was from iPhone sales. If for some reason (economic, political, social, etc.) Apple can’t sell as many phones in a particular quarter or year, it will likely have a material impact on results.
- Declining Global Smartphone Market Share: Over the last 3 years, Apple’s global smartphone market share has stayed relatively flat while other carriers continue to take share.
- Few Successful Product Innovations Introduced Over the Past Decade: Historically Apple has been considered one of the most innovative technology companies in the world for releasing breakthrough products like the iPod, iPhone, and iPad yet in the past decade when it comes to product innovation they have slowed down significantly only introducing AirPods and the M1 processer. Apple needs to do more for product innovation to stay successful especially as hardware products become more commoditized.
- Apple’s ethical decision making has come under question multiple times due to the nature of their supply chain putting the burden of cost and production onto the laborers through low wages and unsafe conditions (Clarke & Boersma, 2018).
VRIO Analysis
LG
Mission & Vision
“One of the first things a strategic leader must do is to shape an organization’s vision, mission, and values, as each of these plays an important role in anchoring a winning strategy” (Rothaermel, 2021, p. 34). As this author articulates, companies with a good strategy generates value for society. This is what LG portrays in their mission and vision. The essence of LG means “Life Good.” Their vision and mission are to maintain a hard-earned reputation for bringing added value to the lives of consumers. They do so by constantly researching and introducing a full range of innovative, greener products and services (Comparably, 2021). This mission/vision allows them to maintain a dynamic strategic fit to the ever-changing external environment.
Company Profile
Goldstar Co. (now LG Electronics) was established in October 1958 in South Korea. Their first trademark was for electrical machinery and urea resin products. They produced the first Korean radio and within a few years began establishing themselves in key industries within the cosmetic, laundry soap, telephone, and electricity meters. By 1965, they had produced the first domestic refrigerator and shortly expanded by producing televisions, air conditioners, elevators, escalators, and even washing machines.
Through the years of 1970-1994, the company experienced a high-growth period through state-of-the-art technology development and internal management capabilities. They produced the first Korean cassette recorder, started mass producing color televisions, created the first electronic Korean VCR and also moved towards computers, video cameras, and microprocessors (LG Communication Center, n.d.).
The LG brand name became incorporated in 1995. Today, they are a global conglomerate corporation that employs 75,000 employees throughout 118 nations and 71 unique companies (LG Electronics, 2019). LG is constantly pursuing innovations and solutions within the home appliance and air solution industry, the home entertainment industry, and vehicle component solutions industry.
LG’s strategic activity system has been developed to respond to changing environments. “Strategic leaders…need to adapt their firm’s activity system by upgrading value-creating activities in response to changing environments. To gain and sustain competitive advantage, strategic leaders may add new activities, remove activities that are no longer relevant, and upgrade activities…” (Rothaermel, 2021, p. 143). And this is exactly what LG did. Within their first-quarter 2021 financial results, they experienced the highest quarterly results in the company’s history with consolidated sales of 16.90 billion and an operating profit of 1.36 billion. “Compared with the first quarter a year ago, revenues grew by 27.7 percent and profitability soared by 39.1 percent, reflecting very strong demand for LG home appliances and home entertainment products…” (LG, 2021). LG was able to accomplish this performance growth through their corporate strategy of diversification. While they experienced an operating loss within their mobile communications SBU with a deterioration of 28 percent from the same quarter a year ago, the combined growth of the LG Home Entertainment Co., the LG Home Appliance & Air Solution Co., and the LG Vehicle Component Solutions Co. was an increase in sales of 102 percent (LG, 2021). This performance shows the relevance and importance of strategic corporate strategy.
Strengths
- Strong Brand Recognition – LG has grown into a well-known global company and has a strong reputation to back them. “For its luxury brand, LG Signature uses the brand’s focus on innovation and takes it to a higher level by optimizing the artistry of design” (Light, 2019).
- Recognized as a high-quality brand.
- Extensive differentiation in product mix and distribution network.
- Ethical Decision Making – LG’s Code of Ethics encompasses two key corporate principles, ‘Creating value for customers’ and ‘Respecting human dignity’, “and as such we will continuously pursue mutual benefits for our stakeholders on the basis of trust and cooperation. LG is committed to act uprightly and make value judgments in accordance to the code of ethics” (LG Code of Ethics, n.d.). This commitment can also be seen in their vision within corporate social responsibility to constantly research greener products and services. With an emphasis of sustainability and ethical decision making, this can be viewed as a company strength.
Weaknesses
- Low Market Share on cellphone market — “LG’s U.S. market share currently stands at about 10%, research firms Gartner and Counterpoint estimated” (Patnaik & Mehta, 2021).
- Continued Loss in Profit Margins – Experiencing years of losses in the smartphone market due to intense competition.
Due to the intense competition on the cellphone market with companies such as Samsung and Apple, LG has decided to leave the smartphone production business. The “strategic decision to exit the incredibly competitive mobile phone sector will enable the company to focus resources in growth areas such as electric vehicle components, connected devices, smart homes, robotics, artificial intelligence and business-to-business solutions” (Toh, 2021). This aspect might be in favor of Apple inc. since this company develops the most attractive to the new customers production.
VRIO Analysis
Samsung
Mission & Vision
Samsung follows a simple business philosophy: to devote its talent and technology to creating superior products and services that contribute to a better global society. To achieve this, Samsung sets a high value on its people and technologies. Samsung believes that living by strong values is the key to good business. That’s why these core values, along with a rigorous code of conduct, are at the heart of every decision the company makes. In an expression of its commitment to corporate social responsibility as a world leading company, Samsung Electronics announced the “Five Samsung Business Principles” in 2005. The principles serve as the foundation for its global code of conduct in compliance with legal and ethical standards and the fulfillment of its corporate social responsibilities (“Samsung Mission & Values”, 2021).
Company Profile
The Samsung Group is a South Korea-based conglomerate, operating globally, that includes several subsidiaries. It’s one of the largest businesses in Korea, producing nearly one-fifth of the country’s total exports with a primary focus on electronics, heavy industry, construction, and defense. Other major subsidiaries of Samsung include insurance, advertising, and entertainment (Burris, 2020). Samsung has around 267,937 employees as of 2020 (Eun-jin, 2021). For the 2020 fiscal year, Samsung reported KRW 236.81 trillion [approximately $211.5 billion] in revenue and KRW 35.99 trillion [approximately $32.1 billion] in operating profit (Sajid, 2021). This was weaker than anticipated due to the ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic but was still a growth of 2.7% from the previous year (Byford, 2021).
Samsung was founded in 1938 by Lee Byung-chul as a grocery store – trading and exporting goods produced in and around Taugu city. In the 1960’s, Samsung entered the electronics industry with the formation of several electronics-focused divisions. The company then entered the telecommunications hardware industry in the 1980’s, initially building switchboards but expanding into telephone and fax systems and eventually mobile phone manufacturing. Soon after the death of founder Lee Byung-chul in 1987, Samsung Semiconductor and Telecommunications merged with Samsung Electronics. The merged organization focused on home appliances, telecommunications, and semiconductors. The next decade brought additional growth and achievements. Samsung soon became a world leader in chip production, formed Samsung Motors, and began producing digital TVs (Burris, 2020).
Samsung entered the phone market in the early 2000’s with the SPH-1300, an early touch-screen prototype phone. They then acquired companies that developed technologies for electronic devices in the early 2010’s, releasing the Galaxy phone in 2011. The year 2012 marked Samsung becoming the world’s largest mobile phone maker. They made several acquisitions in the following years, including organizations that would help it expand its offerings in medical technology, smart TVs, OLED displays, home automation, printing solutions, cloud solutions, payment solutions, and artificial intelligence (Burris, 2020).
Strengths
- Very high research and development (R&D) expenditure resulting in one of the strongest patent portfolios among technology companies (Jurevicius, 2020)
- Dominates the Smartphone Market (Parker, 2020)
- Product innovation and design capabilities. (Jurevicius, 2020)
- Strong global brand tied to consumer electronics (Martin, 2019)
- Synergistic support among divisions or subsidiaries (Martin, 2019)
- Ecologically Friendly Innovations (Parker, 2020)
- Stronghold in the Asian Markets, particularly India and China (Parker, 2020)
Weaknesses
- Heavily dependent on the American Markets (Parker, 2020)
- Product Failures that have eroded confidence and trust in the company (Parker, 2020)
- Lack of a competitive comprehensive platform for hardware, software, and services (Martin, 2019)
- Too Large Product Diversity (Haque, 2021)
- Despite a heavy emphasis on ethics and corporate social responsibility on their website, Samsung continues to be exploitative and unethical due to the exploitation of their workers and consumers – facing multiple lawsuits due to misleading ethical claims (Singh, 2020).
VRIO Analysis
Blackberry
Mission & Vision
Blackberry’s mission is “to be the world’s leading provider of end-to-end mobility solutions that are the most secure and trusted” while their vision is “securing a connected future you can trust.” (BlackBerry, 2021)
Company Profile
BlackBerry Limited was incorporated in 1984 and is headquartered in Waterloo, Canada. The company also operates leased facilities of over 1,285,000 square feet in North America, Europe, Middle East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific (BlackBerry, 2021). These facilities house 3,497 employees of which approximately 51% are in Canada, 32% in the U.S., and 17% outside of North America (BlackBerry, 2021).
The company uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to deliver solutions for cybersecurity, safety, and data privacy and endpoint security management, encryption, and embedded systems (Yahoo, 2021). They provide intelligent security software and services to enterprises and governments worldwide and software vendor developers who integrate the security features of BlackBerry right into their own mobile and web applications (Yahoo, 2021). BlackBerry annual gross profit for 2021 was $643 million, a 15.73% decline from 2020 (BlackBerry, 2021).
In 2021, Blackberry owned approximately 38,000 worldwide patents and applications (Blackberry, 2021). On the horizon, Blackberry will develop a cybersecurity curriculum for the University of Windsor’s graduate master’s program in applied computing (Yahoo, 2021). They also have an agreement with Amazon Web Services, Inc. to develop and market BlackBerry’s IVY, an intelligent vehicle data platform (Yahoo, 2021).
Blackberry, which was the pioneer in mobile-based technologies with its best selling original Smartphones, has been in the news for all the wrong reasons. First, the company known as Research in Motion (RIM), which made and marketed the Blackberries, missed the emerging Smartphone revolution though it was one of the pioneers of mobile computing. Next, the company was unable to read the market and hence, it lost market share to Apple and Samsung.
Strengths
- Good reputation among corporate users of mobiles over its competitors because of its proprietary technology (MSG, 2020).
- Can be used with any mobile carriers anywhere which facilitates easy mobility and portability (Blackberry, 2021).
- Devices are more secure than competitors include security features within the devices that are unmatched by any other mobile maker, including Samsung and Apple (MSG, 2020)
- Devices include an encrypted military grade security platform which makes it the phone of choice for agencies dealing with sensitive information, such as the FBI, CIA, The White House, and the State Department (MSG, 2020).
- Committed to operating in sustainable way by maintaining a variety of programs to identify, execute, and maintain sustainable initiatives and to reduce the environmental impact of its products throughout the product lifecycle (BlackBerry, 2021).
Weaknesses
- Single-track focused on corporate users needing enhanced security features as its unique selling proposition (MSG, 2020).
- Utilization of Blackberry services requires an install of expensive enterprise software, crowding out small businesses (MSG, 2020).
- Obsessive focus on corporate users provided competitors, such as Apple and Samsung, the opportunity to obtain a large consumer base and eventually took away corporate customers.
- Slow to keep up with innovation, such converting to a full touchscreen rather than opting to stick with the Querty keyboard (Muldrew, 2020).
VRIO Analysis
*Effective applied to entire organization (not just mobile telecom)
Nokia
Mission & Vision
The mission of Nokia is “we create the technology that connects the world” (Nokia, 2020). Their vision is “Nokia wants to create a new world; to transform a big planet to a small village. Their vision is to create, build, and encourage people from all countries to communicate with each other in order to create a world where everybody is connected”
Company Profile
Nokia was formed in 1865 by Fredrik Idestam as a paper mill in Espoo, Finland (Nokia, 2021). Through time, the company adapted to consumers’ demand, shifting their manufacturing focus from rubber products, to cabling and eventually landing on technology, primarily televisions and mobile phones. In addition, Nokia develops several types of network infrastructures as well as cloud software solutions (CNN, 2021)
Pekka Lundmark replaced Rajeev Suri as chief executive officer in 2020 (Kauranen, 2020). They currently maintain over 92,000 employees with several locations on every continent, less Africa and Antarctica (Yahoo, 2021). The company prides itself for its robust research and development, which has invested most of its efforts to 5G technologies since Lundmark has been the company’s leader (Morris, 2020).
The technology firm has fallen from its prominence of the late 1990s and early 2000s, but with a new CEO, intends to change that. Current stock prices are 10% the value they were during their peak in 2000, but long-term outlook anticipates a positive return earnings per share and expansion into African markets (Yahoo, 2021). Over the past 5 years, their revenue has been fairly consistent, without showing any defined trends (Marketwatch, 2021). Nokia has a strong history of acquiring and selling off portions of its business, and Lundmark hopes to further their focus on specific portions of the mobile market rather than the complete end to end product Suri envisioned (Morris, 2020).
These days, the company might be considered as a leading force in a highly competitive 5G technologies’ market. The company has overshadowed its main competitors from China and Europe. As a result, the company might consider its internet technologies business as the most profitable and perspective one. In addition, due to the expectation overbeating, the company has announced new margin targeting and dividend payments program to assure the organic but fast growth (Saigol, 2022).
Strengths
- One of several Finnish companies that perform well in the technology market despite the country’s size (Koduvayur, 2021).
- $30b company valuation and stock is outperforming predictions (Tyler, 2021).
- Early entrant to 5G infrastructure and well-established creates competitive advantage (Hardesty, 2021).
- Social responsibility is integrated throughout their business model to encompass all ethical areas including responsible sourcing and green initiatives (Nokia, 2020).
Weaknesses
- Random event of stock performance failure is high (Tyler, 2021).
- Has historically failed to keep up with competition in emerging markets despite entering the industry with a competitive advantage (i.e., smart phone technology) (Gifford, 2020).
VRIO Analysis
Mission & Vision
Google’s mission is “…to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful (Google, 2021)” and their vision is “to provide access to the world’s information in one click” which they achieve by adhering to several core principles and values including: great isn’t good enough; focus on the user, all else will follow; it’s best to do one thing really well; fast is better than slow; democracy on the web works; you can make money without doing evil; there’s always more information; the need for information crosses all borders; you can be serious without a suit; and you don’t need to be at your desk (Comparably, 2021).
Company Profile
Google LLC is a global technology company that operates world-wide and specializes in products and services related to information and the internet such as their search engine, advertising tools, cloud computing, software, and hardware (Bloomberg, 2021). Alphabet, Google’s parent company, has consistently grown revenue between 13% and 23% per year for the last 5 years from 2016-2020 with record revenue of $182.5 billion and record profit of $40.3 billion in 2020 with the vast majority of revenue and profits, around 81%, being derived from Google advertising services (Form 10-K 2020, 2020).
Google began as a partnership between Larry Page and Sergey Brin at Stanford University where they built an algorithmic search engine that they initially named “Backrub” but which would later be rebranded as “Google”. In 1998, Andy Bechtolsheim bought into the business and Google Inc. was officially incorporated in Menlo Park, California (Google, 2021). In the intervening years between their start in 1998 and present day, Google has evolved vastly beyond its start as a search engine and has become one of the premier tech companies of our time and one of the largest companies in the world.
Google branched out into media with its purchase of YouTube in 2006 and subsequently began to refine and perfect their online advertisement tools which are used today almost ubiquitously around the internet. Google has also pioneered such services and products that have mass appeal such as Google Maps, Gmail, the Chrome web browser, and the Android mobile phone operating system (TRT World, 2018). Android currently accounts for 72.84% of the mobile operating system market to Apple iOS’s 26.34% which has remained (more or less) unchanged over the last 10 years in comparison to the growth in popularity seen by Android (O’Dea, 2021).
Google entered the smartphone market in 2010 partnering HTC and Samsung to manufacture the Nexus line of phones to run on their Android platform. These phones were in more of a cost leadership position and appealed to users by giving them less adulterated access to the Android operating system but were never marketed or adopted by the broader market of consumers (Chokkattu, 2016). In 2016, however, Google really entered into the smartphone market when they revealed that they were building and manufacturing their own devices and launched the Pixel line of smartphones that we still have in the market today (Soloman, 2016).
Today, Google phones only account for about 2% of mobile device sales compared to Samsung at 27.1% and Apple at 53.07%. Google employs a hybrid cost leader and differentiation strategy with regard to their devices, offering high quality and feature rich devices at a much lower cost than the two dominant leaders, Samsung and Apple, but they consistently fail to outstrip these competitors in rankings (Spoonauer, 2021) (Hoyle & La, 2021) (Seifert, Bohn, & Johnson, 2021). The majority of the market is more than willing to tolerate high prices on phones (Shibu, 2020) especially with so many carriers offering plans to finance them and simply include it as a monthly line item on their phone bill. With Pixel phones at the top of the pricing spectrum for Android based phones other than the front-running Samsung, they don’t seem to be offering the differentiation needed to gain significant market share.
Strengths
- Extremely high market share for the Android operating system (O’Dea, 2021)
- Strong financials, solid profitability and growth (Alphabet Inc., 2021)
- Proprietary algorithms and search quality led to 92% search engine market share worldwide (Statcounter, 2021)
- Business built largely on multiple facets of internet traffic monetization which is slated to increase steadily for the foreseeable future (Alphabet Inc., 2021)
- Usability, stability, and compatibility led to 64.94% web browser market share (Statcounter, 2021)
- Dominant capability in software, web services, and web-search
- Alphabet is rated highly with regard to environmental responsibility (Censible, 2021) and issues the largest sustainability bond in history in 2020 (Emily Holbrook, 2020)
- One of the most efficient business ‘ecosystems’ in the world with highly marginal products (Alphabet Inc., 2021)
Weaknesses
- Focus on software development and web-based products has detracted from competitive marketing in their mobile device products
- With 90% of Google’s revenues coming from ads, they are vulnerable to fluctuations in demand or industry disruption (Sun L., 2018)
- Alphabet is rated very poorly with regard to ethical business practices and corporate governance (Censible, 2021) and there have been a number of ethical issues raised by the public including a lack of accountability due to Brin and Page owning 13% of the stock but carrying 51% of the voting power and human rights issues regarding their business in China (Tiku, 2019)
VRIO Analysis
Competitive Positioning Map
Five Forces Analysis
Apple has grown to become one of the world’s most valuable companies and respected brands within the consumer electronics and mobile device industry which has become nothing if not ubiquitous within the US market. Analyzing this industry using Porter’s Five Forces Model reveals that the domestic market is maturing and demonstrates hostile forces with regard to new entrants to the market. The bargaining power of buyers is weak, suppliers of critical components are few in number and very strong, and the threat of substitutes is very low.
Potential Entrants
As technology becomes more complex and specialized, potential new entrants would face very high costs to become established within the industry and achieve brand recognition. The new entrant would need to have a massive amount of capital just to spend on research and development and manufacturing prior to even bringing its products to market (Beers, 2020) as Apple and its major competitors are all already large and well-established. Another challenge new entrants would face is trying to establish brand recognition within an industry that already has several companies, such as Apple, Google, and Samsung, who have established very strong brand recognition.
Competition among existing companies
Apple and Samsung dominate the competitive environment, and these companies expend significant capital on innovation and marketing. The threat of marketplace competition is a key consideration in the mature domestic market which shows a projected CAGR of only 1.69% until 2026 (Mordor Intelligence, 2021). In a low growth market competition is high and most company growth must come from captured market share or increasing prices. One thing unique to Apple though is the relatively high switching cost. Although it does not require a substantial investment for a consumer to switch from Apple’s iPad to an Amazon kindle for example, the customer would lose access to anything they had already purchased through the App store as the platforms used are completely different, whereas consumers switching from one Android manufacturer to another would not experience these switching costs.
Substitutes
This market force is relatively low for Apple since most potential substitute products have limited capabilities compared to Apple’s products. An example would be of a landline telephone compared to an iPhone that has the capability to do much more than just make telephone calls. As Apple achieves product differentiation, they can mitigate the threat of substitute products. And as they continue to target innovation, they can stay ahead of the competition.
Bargaining power of buyers
The element of a high switching cost weakens the bargaining power of buyers and since there are so many customers in this market, no individual customer has any real power over the company (Maverick, 2019).
Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is a fairly strong force in the consumer electronics industry and specifically in mobile devices. The vast majority, or about 71%, of processor chipsets are manufactured by only two companies: TSMC and Samsung (Lee, 2021). With regard to competition this adds an interesting dynamic insofar as the fact that Samsung has vertically integrated to produce their own processor chipsets and Apple may switch their business from TSMC to Samsung for manufacturing of their new M1 chipset (Jeet, 2020).
Diamond Model
Michael Porter’s Diamond Model is a tool developed to determine the competitive advantage of a chosen market, based on the factors of its environment (James, 2020). The analysis being conducted is the high technology market in the United States, so the conditions described below are based on these specifications. As a first-world country, the United States is a global economic leader, but the Diamond Model takes labor force, manufacturing capabilities, and access to natural resources into account as well. Because of these variables, the high technology market is driven primarily by a strong economy and protected by high entry barriers, but lacks the low-skill labor that countries like China possess (Perlberg, 2013). The market will remain strong for the competitors within the United States; nonetheless, it is thanks to government intervention preventing threats, such as Huawei, from entering it (Keane, 2021).
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis is an important element in the strategic development of a company since it predetermines the knowledge of information about the influential parties involved in the business and capable of affecting it. According to Rothaermel (2021), stakeholders are “organizations, groups, and individuals that can affect or be affected by a firm’s actions” (p. 13). The interests of the external stakeholders include obtaining products and services for customers, ensuring taxation for the government, obtaining revenue and reliable cooperation for suppliers, and competitors’ interests are in the market forces understanding and trend recognition. Internal stakeholders’ interests are in obtaining employment and salary for employees, return on investment for investors, and sustained profitability and industry dominance for leadership.
Stakeholder Strategy & Globalization
Corporate Strategy
TOWS matrix
Business Level Strategy
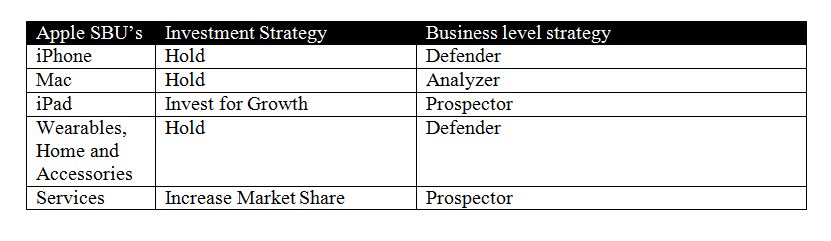
Strategic Business Unit Analysis
Investment & Business Level Strategy
World Market Strategy
Apple Inc. exhibits a strong global market presence strategy with operations based in multiple countries. The company uses a global standardization strategy trying to ensure constant image of the products across markets.
Functional Strategy
Marketing
The marketing strategy at Apple Inc. is agreed with the business strategy and predetermined by its corporate strategy of product diversification. The marketing approach uses market segmentation with medium- and higher-income populations most actively addressed. In addition, the company designs its marketing strategy to promote its services and products among prospective customers in the fields of business and education (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2020). In line with the business strategy, the company integrates product quality and the uniqueness of customer experience into its marketing practices.
Operations
The operations management strategy is closely interrelated with the corporate strategy and the world market strategy, which are centered around the approach of differentiation, which might be labeled as the flexibility strategy. The company strives to develop and produce unique, ground-breaking innovative electronic devices, which is viewed as one of the most important elements in the competitive advantage (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2020). Thus, with the differentiation approach to operations management, the company arranges its designing, production, and distribution of multiple products and services.
Management Information Systems
The management information systems at Apple Inc. constitute a significant competitive advantage since the company allocates resources to ensure that technologies assist its operations and overall company management.
Apple has to manage a significant amount of customer data between all of its SBU’s therefore a customer relationship management (CRM) system should be implemented to ensure consistency across all areas. With expansion of current products to new markets, a CRM will enable consolidation of customer information and documents it into a single database for easier access and management. It will assist with data collection, dissipation, and analysis of information which can be further used for decision making and improvements.
Research & Development
The R&D strategy at Apple Inc. is incremental, which means that the company gradually builds the innovative nature of its products through deliberate and growing investment in research and development. The strategy is aligned with the differentiation approach for consistent quality-assurance and uniqueness of customer experience. The management of company finances is distributed throughout the organizational department with the aim of serving the overall organizational goal of delivering innovative and high-quality products and services with an exceptional customer experience guaranteed.
Financial Resources
Apple’s financial statement indicates that the revenue increases steadily (“Condensed consolidated statements of operations (unaudited),” 2021). As a result of this strong financial position and historical financial performance, profits from standard business operations will be more than sufficient to finance the execution of this strategy. In addition, Apple can continue to re-invest profits to increase their earnings.
Human Resources
Apple Inc. uses a strategy that allows for retaining talented employees to use their potential for the benefits of the company and ensure a balance between their work and life. The company cherishes creativity and innovation, which are the priorities when recruiting employees. As for the leadership style used by the management and the CEO of the corporation, it might be characterized as a democratic leadership style. The personality of the leader plays a significant role in setting an example and leading a high-standard corporate culture.
An adhocracy culture within the organization would best foster innovation, knowledge and idea sharing, and creative problem solving. The adhocracy culture is characterized by a significant focus on creative exchange and innovation as well as an encouragement of individuals to engage in entrepreneurial ventures in pursuit of the attainment of organizational goals.
Organizational Structure
In terms of organizational structure, Apple employs a multidivisional structure type, which is also named ‘M-form,’ where position-based reporting prevail. In particular, the company expand its organizational hierarchy in horizontal, vertical, and geographic vector (Rothaermel, 2021). The structure of the company is aligned with the global standardization world market strategy, which implies a multidivisional structure with product divisions and centralized decision-making. In addition, the organizational structure is characterized by a subdivision of departments depending on products and services. In particular, products include iPhone, Mac, iPad, and wearables and home accessories; services include advertising, Apple Care, cloud services, digital content, and payment services (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2020). An organic structure is applied, meaning that the information processing efficiency is maximized (Rothaermel, 2021; Tasnim, 2018). Thus, the organization has a complex structure, which is competently regulated and managed using proper structural management approaches. More specifically, the chief executive officer, vice presidents, design, and operating officers, are responsible for various product-based branches. It is certain that the multidivisional structure of such an expanded company benefits from applying the group-based model.
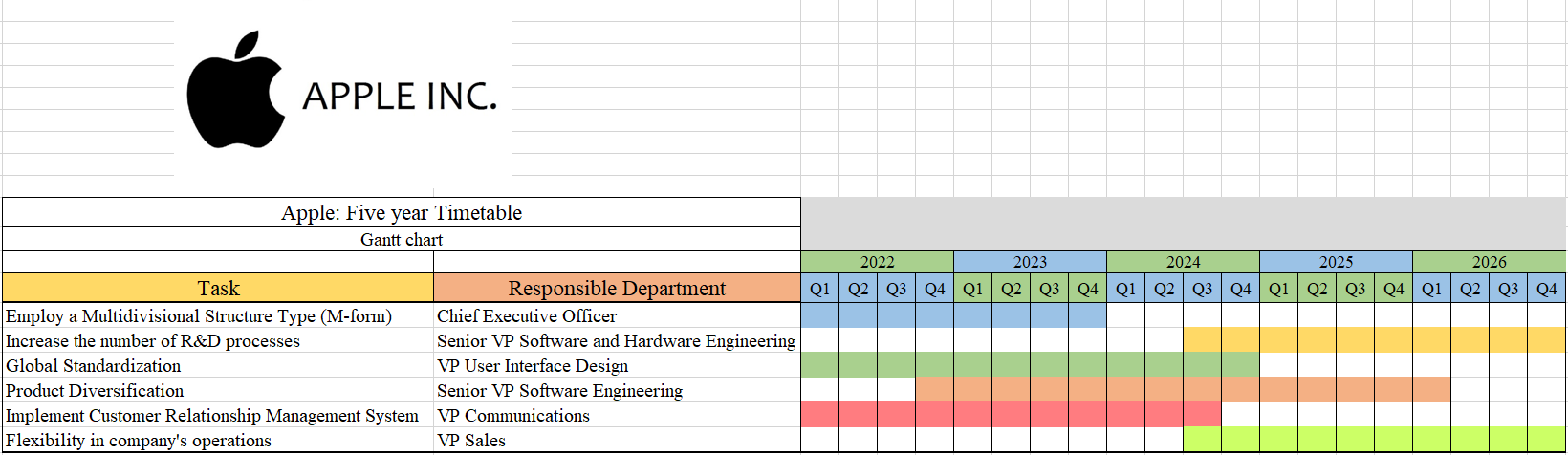
Timeline Table
Milestone Table
Evaluation and Control
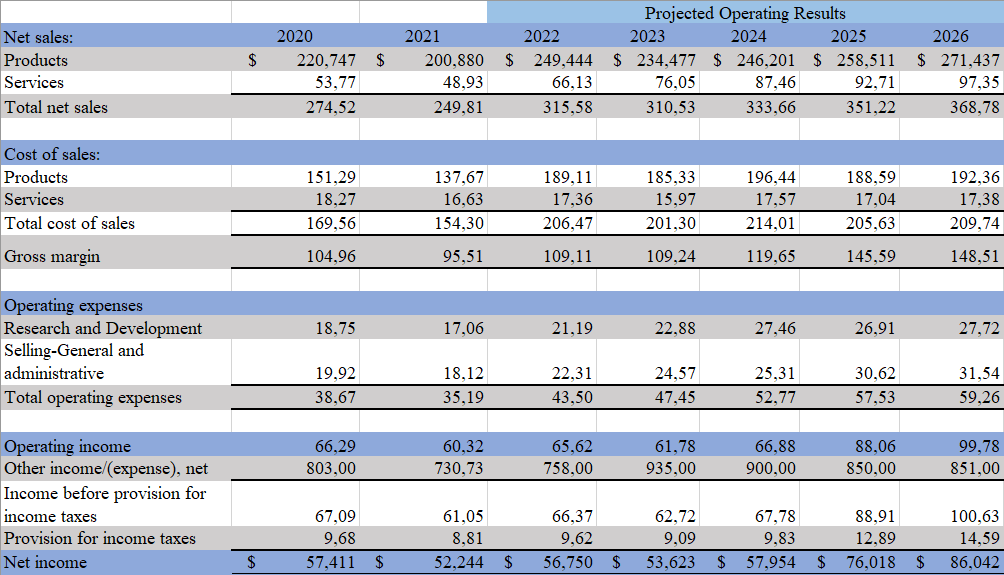
Profit and Losses Statement
Apple inc. has a positive anticipation for net income increase due to the effective global standardization strategy application and a high level of organizational efficiency. The profit and losses (P&L) statement is demonstrated on the figure 5.
Benchmarking
Using the benchmarking approach, one might evaluate the necessity of the proposed strategy improvement implementation on the background of the performance of competing organizations. For example, given that Samsung is a rival in the low- and middle-income market, Apple should apply resources to the research and development of SBU to minimize costs and ensure the affordability of its products, which is achieved through the flexibility strategy. When it comes to Microsoft, the company’s flexibility and compatibility with other software force Apple Inc.’s to re-invest its profits in research and development to ensure its software compatibility to increase the competitive advantage.
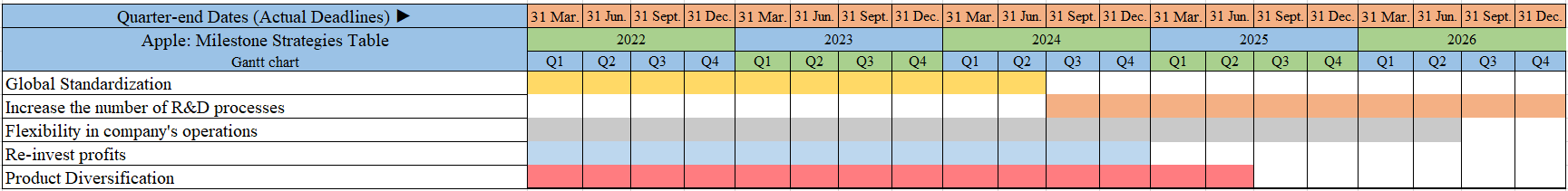
Strategy Audit: Milestone Table
When implementing the improvements to the strategy of Apple Inc., a plan should be used in order to align the recommendations with allocated budget ranges and the duration of implementation. In addition, it is relevant to foresee the challenges that might be faced by the organization when implementing the strategy changes and the ways of mitigating or overcoming those challenges. The milestone table presented in Figure 6 demonstrates all these elements in order to visualize the scope of strategic change generated on the basis of the conducted analysis. The budget plan is aligned with the anticipated P&L statement. For instance, in year 3, the company plans to allocate more sources to decrease the cost of production. As a result, the company’s profit would rise by nearly eight percent due to effective costs optimization. During the strategy development, there was used a ‘SMART’ model was that enables to definition specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and timely goals. As a result, the correctly settled strategy would increase Apple inc. efficiency of achieving the planned goals on a long-term basis. When it comes to ethical decision making, Apple inc. is interested in supporting the fair competitiveness in the industry. This claim might be supported by the company’s strategy of developing the presence on affiliated markets instead of concentrating the market share in some specific segments to achieve monopolistic presence in the niche.
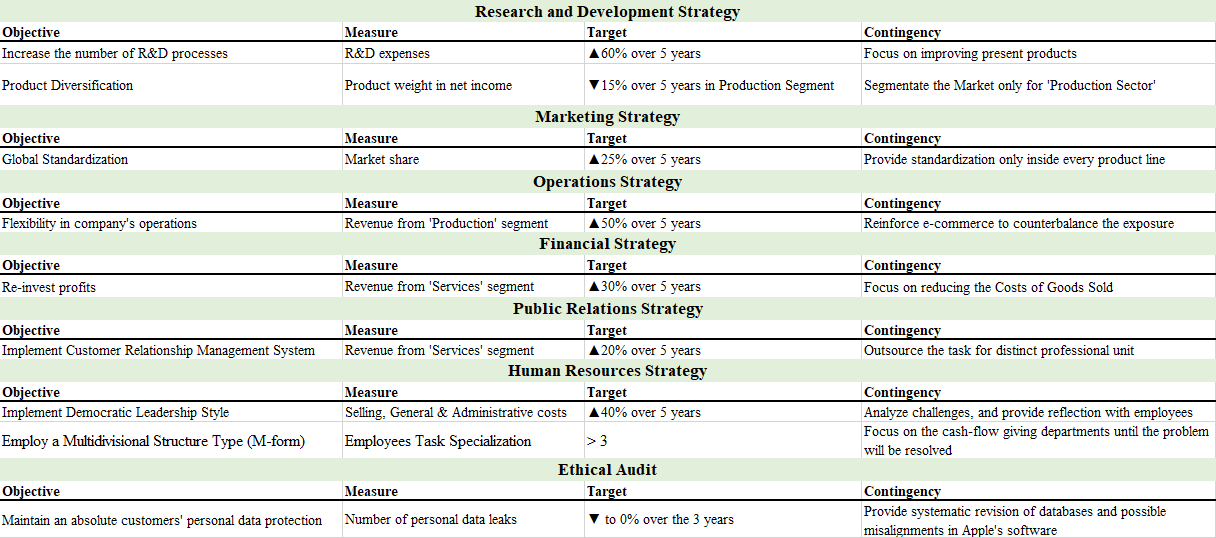
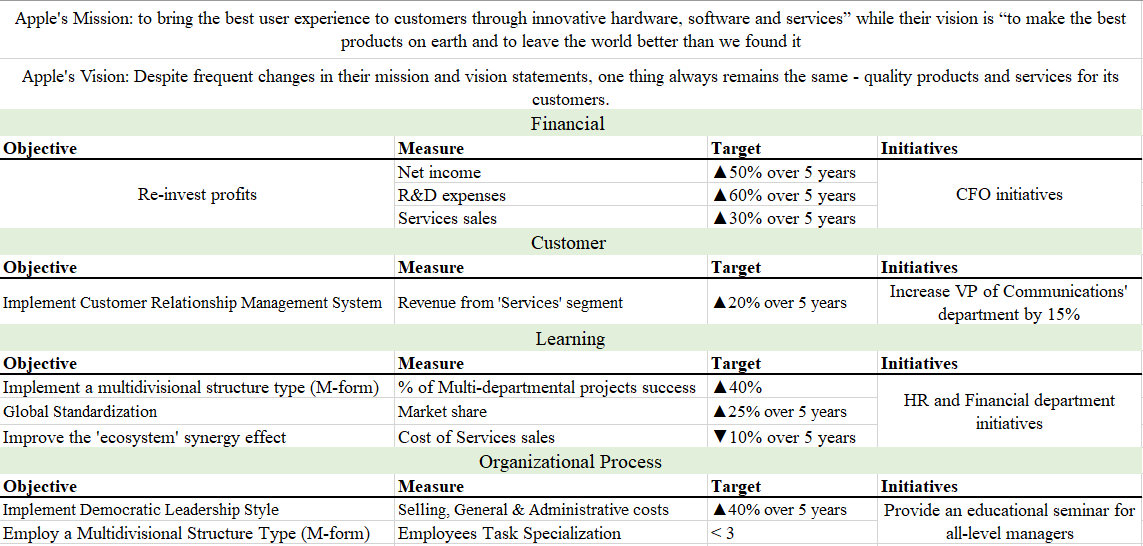
Kaplan’s Scorecard
Using a balanced scorecard, one might evaluate and develop a competitive advantage obtainment strategy. Figure 7 and 7a demonstrates the scoreboard for Apple, including the forces predetermining its competitive advantage. To maintain it, Apple needs to meet the vision of shareholders, who see the company as a reliable profit-generating organization. The company should implement it’s competency and incrementing R&D strategy to create value in improved customer experience and meet customer views of Apple as a premium-product brand.
In summation, the proposed recommendations for Apple Inc. are validated by the results of the conducted analysis of the company’s environment and internal strategies. The proposed milestones are approximate and might need adjustment during the project planning and implementation stages. Overall, the changes are anticipated to generate a more stable competitive advantage for Apple Inc. under the conditions of the threats of the external environment and existing rivals in the industry.
References
Abbott, A. (2021). Apple Mission Statement, Vision, & Core Values. Business Strategy Hub. Web.
Alphabet. (2020). Form 10-K 2020. Web.
Alphabet Inc. (2021). Form Q10 – Q2 2021. Web.
Apple: Job Creation (2021) Apple. Web.
Beers, B. (2020). What Are the Key Barriers to Entry in Electronics? Web.
Best, R. d. (2020). Infrastructure in the U.S. – Statistics & Facts. Web.
Bloomberg. (2021). Google LLC. Web.
Burris, M. (2020) The History of Samsung (1938-Present). Lifewire. Web.
Byford, S. (2021) Samsung’s profits rose in 2020 despite the pandemic. The Verge. Web.
Censible. (2021). Alphabet. Web.
Chokkattu, J. (2016). 14 devices, 6 years, 1 name: Revisiting every Google Nexus ever built. Web.
Clarke, T.; Boersma, S. (2018) A hostage situation: Why Apple won’t address its unethical supply chain. The Conversation. Web.
CNN. (2021). NOK – Nokia Oyj Company Profile. CNNMoney. Web.
Comparably. (2021). Google Mission, Vision & Values. Web.
Comparably. (2021). Nokia mission, vision & values. Comparably. Web.
Comparably. (2021). LG mission, vision & values. Web.
Culbert, K., & Moldvay, C. (2012). How the Smartphone is Revolutionizing 10 Industries. News Powered by Cision. Web.
Eun-jin, K. (2021) Number of Samsung Electronics Employees Overseas Dwindles by 23,000 in 2020. Business Korea. Web.
FCC. (2021). Mobile LTE Coverage Map. Web.
FDA. (2021). Cell Phones. Web.
Federal Trade Commission. (2021). Bureau of Competition. Web.
Federal Trade Commission. (2021). Bureau of Consumer Protection. Web.
Gifford, C. (2020). Stuck on repeat: At NOKIA, is history doomed to repeat itself? The New Economy. Web.
Google. (2021). About. Web.
Google. (2021). Our Story. Web.
Haque, F. (2021) SWOT Analysis of Samsung. The Strategy Watch. Web.
Hardesty, L. (2021). Nokia’s network infrastructure had ‘fantastic’ Q1 2021. FierceTelecom. Web.
Harvey, M. (2020). VRIN/VRIO analysis of apple. Essay48. Web.
Heisler, Y. (2015). A huge 4G milestone: LTE is now available for 98% of Americans. Web.
Holbrook, E. (2020). Google Issues Largest Corporate Sustainability Bond of Any Company in History. Web.
Hoyle, A., & La, L. (2021). Best phone to buy in 2021. Web.
James, M. (2021). What is the Porter Diamond? Investopedia. Web.
Jeet. (2020). Samsung Electronics could become Apple Silicon manufacturer. Web.
Jurevicius, O. (2020) SWOT analysis of Samsung (6 Key Strengths in 2020). Strategic Management Insight. Web.
Kamann, G., Gill, N., & Sen, A. (2011). The changing dynamics of the global high tech industry. Capgemini. Web.
Kauranen, A. (2020). Nokia replaces CEO with Fortum boss Lundmark to revive 5g business. Reuters. Web.
Keane, S. (2021). Huawei ban timeline: Chinese company SETTLES patent lawsuits with Verizon. CNET. Web.
Koduvayur, R. (2021). Council post: Challenges and opportunities for the marketing industry In Finland. Forbes. Web.
Lee, Y. N. (2021). 2 charts show how much the world depends on Taiwan for semiconductors. Web.
Light, L. (2019). LG: From low class to high class. Forbes. Web.
LG. (2021). LG announces first-quarter 2021 financial results. Web.
LG Communication Center. (n.d.). History. LG. Web.
LG Electronics. (2019). LG Overview. Web.
Lovejoy, B. (2021). Big tech now biggest lobbyists, says report, but Apple mentioned only in passing. 9to5Mac. Web.
Management Study Guide. (2020). SWOT Analysis of Blackberry. MSG. Web.
Marketwatch. (2021). NOK: Nokia Corp.. ADR annual income statement. MarketWatch. Web.
Martin, V. (2019) Samsung SWOT Analysis & Recommendations. Panmore Institute. Web.
Maverick, J. (2019). Analyzing Porter’s 5 Forces on Apple (AAPL). Web.
Mission-statement.com. (2021). Apple mission STATEMENT 2021: Apple Mission & Vision Analysis. Apple Mission Statement 2021 | Apple Mission & Vision Analysis. Web.
Monash, C. (2019). Political issues around big tech companies. Monash Research. Web.
Montgomery, M. (2020). Lessons for tech entrepreneurs from the great recession. Forbes. Web.
Mordor Intelligence. (2021). SMARTPHONES MARKET – GROWTH, TRENDS, COVID-19 IMPACT, AND FORECASTS (2021 – 2026). Web.
Morris, I. (2020). Nokia CEO lays OUT 5G turnaround plan as shares tank. Light Reading. Web.
Muldrew, E. (2020). What happened to BlackBerry? – Edward Muldrew. Medium. Web.
NOAA. (2021). U.S. Climate Extremes Index (CEI). Web.
Nokia. People & Planet 2020. Web.
Nokia. (2021). Our history. Nokia. Web.
O’Dea, S. (2021). Market share of mobile operating systems worldwide 2012-2021. Web.
O’Dea, S. (2021). Smartphones in the U.S. – Statistics & facts. Statista. Web.
Parker, B. (2020) Samsung SWOT Analysis 2020 | SWOT Analysis of Samsung. Business Strategy Hub. Web.
Patnaik, S., & Mehta, C. (2021). LG’s smartphone exit: Who stands to gain? Reuters. Web.
Perlberg, S. (2013). 10 reasons why America will continue to dominate the global economy for years. Business Insider. Web.
Pethe, S. (2021). Nokia vs. Ericsson: WHICH 5G stock is a better pick? Nasdaq. Web.
Pew. (2021). Mobile Fact Sheet. Web.
Rothaermel, F. T. (2021). Strategic Management (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Sajid, I. (2021) Samsung posts Q4 profit despite pandemic challenges. Anadolu Agency. Web.
Saigol, L. (2022). Nokia Reinstates Dividend, Sets New, Long-Term Margins Target. Barron’s. Web.
Samsung. (2021). Leadership & Mission: Samsungabout us: Samsungsamsung us. Samsung US. Web.
SDG. (2017). Percentage of the U.S. population covered by at least a 3G mobile network. Web.
Seifert, D., Bohn, D., & Johnson, A. (2021). THE BEST PHONE TO BUY RIGHT NOW. Web.
Shibu, S. (2020). What Are People Willing to Pay for the iPhone 12? Web.
Singh, S. (2020) Is Samsung an Ethical Company? A Philosophical Examination. Soapboxie. Web.
Soloman, H. (2016). Google enters competitive smartphone market by making its own, called Pixel. Web.
Spoonauer, M. (2021). Best phones in 2021: The top smartphones rated. Web.
Statcounter. (2021). Search Engine Market Share Worldwide. Web.
Sun, L. (2018). SWOT Analysis of Google Inc. Web.
Suri, R. (2020). How do we build a better world after this crisis is over? Nokia. Web.
The Pew Charitable Trusts. (n.d.). Social and demographic trends. Web.
Tiku, N. (2019). Alphabet Shareholders Demand Accountability. Web.
Tiseao, I. (2020). Environmental pollution in the U.S. – Statistics & Facts. Web.
Toh, M. (2021). LG was a smartphone pioneer. Now it’s quitting the business. CNN. Web.
TRT World. (2018). The evolution of Google: 20 years and counting. Web.
Tyler, C. (2021). Buy nokia stock for the strengths, not the memes. InvestorPlace. Web.
US Department of Labor. (2021). Summary of the Major Laws of the Department of Labor. Web.
US Department of State. (2021). Intellectual Property Enforcement. Web.
US Securities and Exchnage Commission. (2020). Exchange Act Reporting and Registration. Web.
Yahoo. (2021). Nokia corporation Sponsored (nok) company profile & facts. Yahoo! Finance. Web.
Weather and Climate. (2021). Climate and Average Weather in United States of America. Web.
Yahoo. (2021). Yahoo Finance – Blackberry Company Profile. Yahoo Finance. Web.
Yale University. (2021). 2020 EPI Results. Web.