Data Management in Business
How does a relational database organize data, and how does it differ from an object-oriented database?
A relational database can be described as a collection of data that is organized through a system of tables which grants easy access to various types of information while an object-oriented database utilizes objects as representations of data in order to create the system of classification within the database. Some of the inherent advantages of object oriented databases as compared to a relational database comes in the form of far easier methods of navigation, a lesser amount of code is required, there is reduced pagination, and the objects within the database do not require aspects related to assembly and disassembly of coding time.
On the other hand it must be noted that there are vastly more tools available for relational databases, the inherent standards of this type of database infrastructure is more stable and support for a relational database is far more certain and simpler thus reducing the need for constant changes to be implemented.
What is the role of information policy and data administration in the management of organizational data resources?
It is important to note that data administration often entails the implementation of processes that are considered industry standard (meaning that they conform to a certain structure and method of operation) so as to ensure that the operational capacity of the company’s database is running at peak capacity and works in a manner that can be easily cross compatible with a myriad of different systems and components as determined by the database administrator.
It is based on this that the processes utilized to store and retrieve data as well as the inherent restrictions placed on data access and creation are governed by the information policy that is established within the company. By having an information policy in place this ensures that the management of organizational data resources is not subject to constant problems related to the dissemination of the wrong types of information, access to critical systems by unauthorized personnel as well as the creation of new forms of data that have not been subject to approval by upper management. In summary, information policies act as safeguards against potential misuse of the company’s database.
Why is data quality assurance so important for a business?
It is important to note that businesses operate not only on the basis of supply and demand but also do so through by quantifying data in order to predict current business trends, store information and develop market strategies in order to better position the operational performance of the company to comply and take advantage of changes within the market. It is based on this that data quality assurance becomes an almost integral aspect of business since inconsistencies, anomalies and even errors in the data presented can and often will result in problems related to database administration which can cost a company millions of dollars in lost transactions or even fines from vendors.
One example of this was seen in 2010 wherein Convergys, a global leader in relationship management and business processing, experienced a database error due to data inconsistencies within its network. As a result the company lost an estimated $1 million within a single day due to contractual obligations with AT&T that it was unable to meet due to its network being unable to field the necessary customer service calls as a direct result of the data anomaly. It is this and other such examples that the profiling of data through data quality assurance becomes all the more necessary especially in an era where businesses are reliant on error free methods of operation.
Telecommunications networks and Internet in Business
What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies?
The principal components of telecommunication networks consist of terminals, links and nodes from which various forms of information and methods of communication are conducted on a daily basis. The first proponent of a telecommunication network, namely the terminal, acts as a means by which a company, customer, or employee is able to access the network in order to send or receive data.
This can consist of a wide variety of possible forms such as a computer terminal, a mobile phone, a tablet pc or even your basic fax machine/landline phone. Without this component in place a user will be unable to send or receive information and is thus an integral part of the telecommunication process. It must be noted though that unlike the other proponents of a network, such as links and nodes, terminals are user specific and as such there are inherent limitations to the type of data and method of communication that can be conducted over such devices.
For example, while a fax machine can send or receive phone calls and receive faxes it is unable to manifest aspects of data related to computer files. The second component of a telecommunication network is the link. This aspect of a telecommunication network can consist of either an actual physical link between a terminal and the network (i.e. a fiber optic cable) or a logical link (i.e. a data uplink, point to point link etc.).
It is through a link that a terminal is able to connect to a network and from there send or receive data to and from a myriad of sources. Lastly, a node acts a redistribution point for information wherein data sent from a terminal is sent to a node and from there the information is transferred to an endpoint which usually takes the form of another terminal. For computer networks this often takes the form of server or data hub while for telecommunication networks this manifests itself as a router.
How do the Internet and Internet technology work, and how do they support communication and e-business?
The internet can basically be considered a gateway from which businesses can easily access a diverse consumer base while at the same time creating a faster and more efficient method by which it is able to contact a myriad of suppliers, employees and distributors. One way of seeing how the internet supports businesses can be seen in the process of E-commerce. E- Commerce, an abbreviation of the term electronic commerce, is a way in which business transactions such as the buying and selling of products is conducted over the internet. Due to its the widespread proliferation with thousands of users being added to the online browsing population on a daily basis the breadth and depth of the internet is not to be underestimated.
With estimates placing the number of users in the hundreds of millions companies have started to capitalize on this trend by moving traditional operations such as advertising and retail to online mediums in order to attract customers to their products. Originally E-commerce was limited to operations such as electronic data exchanges, electronic funds transfers as well as ordinary bank to bank communications.
It wasn’t meant as a means of purchase but rather as a means to which banks could easily and effectively communicate with one another in order to facilitate the transfer of funds from one country to another. One other original purpose of the original e-commerce system was its use as a means to send invoices and purchase orders between businesses in order to better facilitate customer transactions. With the advent of credit cards, ATM’s and the rise in the popularity of the internet following the creation of the Windows 95 operating system and the changeover from slow dial up connections to faster broadband systems the concept of E-commerce as a means of direct customer selling took off.
Sites such as Ebay and Amazon.com were the vanguards of an online sales industry that resulted in a plethora of websites all dedicated to buying or selling products in one form or another. When dealing with online retail operations it must be noted that such methods of selling to customers do not suffer from the regular limitations that affects in-store selling. With an online store a company is able to save money on employee salaries, benefits and bonuses since the entire process has been automated using computers resulting in the potential for a greater product to profit ratio due to the lower costs involved in operations.
In fact most online retail stores employee skeleton crews of website editors, procurement specialists and online marketers which enable the company to run a website with fewer employees needed yet are able to display their products in a much more efficient and attractive way than in a store and are able reach a much larger market due to online marketing campaigns.
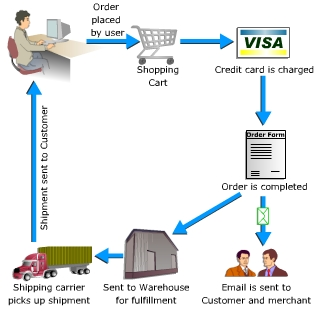
Information Security in Business Organizations
What are the components of an organizational framework for security and control?
An organizational structure for security and control often involves aspects related to compliance management (in order to ensure that the indicated security protocols are followed), security program management (which is necessary in implementing the necessary standards for security), incident management (in order to handle problems as they occur), host and network security controls and lastly software architecture, strategy and consulting. It is only when such aspects are method that something can be considered a proper framework for security and control.
What are the most important tools and technologies for safeguarding information resources?
Preventing malicious access to database resources is one of the responsibilities of a database manager and often times one of the most difficult to accomplish due to the ever changing security environment that we find ourselves in at the present. It is based on this that the following tools and technologies should be taken into consideration when safeguarding the information within your company’s database.
The first is the most widely utilized and implemented tool in database security management today: the username and password. Through the use of an alphanumeric username and password word that is unique to individual users this in effect restricts access to certain aspects of the company’s information system. The inherent problem with this is that even if limited access is granted a user can still go online and download various types of malicious software which could in the end compromise the integrity of the system and grant access to third parties. It is due to this that another resource that is often utilized by companies in order to safeguard their data is to install an assortment of firewalls, anti-virus programs and website restrictions.
Enterprise software and information systems
How do supply chain management systems coordinate planning, production, and logistics with suppliers?
In order to coordinate aspects related to planning, production, and logistics with suppliers, supply chain management systems often utilize the following functionalities in order to address such issues: The first is the customer requirement processing functionality which examines the needs of customers versus the current capabilities of the company. By examining what is necessary versus what is required the system in effect determines how much to order and where to allocate it.
This is where the purchase order processing functionality enters into the picture wherein through this particular function individual suppliers are contacted in order to have goods sent to the correct locations at the right time. The third level of functionality involves inventory management which entails an examination of the current stocks of the company’s supplies and products in order to determine what will be necessary in the upcoming quarters.
Another function is the supplier management/sourcing functionality which involves a classification of the different sources of materials for the company and the necessary means of obtaining it. Lastly comes the warehouse management functionality which as its name implies involves the storage and delivery of current company products and resources.
What are the challenges posed by enterprise applications?
One of the problems connected to enterprise software is the inherent cost related to their creation. Unlike other types of software that companies purchase in order to solve various problems within their company, enterprise software is often created “in-house” and thus has a far higher cost as compared to simply buying the software solution from another company. It thus becomes a question as to why companies would chose to create enterprise software solutions with the high costs associated with their creation.
One of the reasons behind this is connected to the concept of proprietary and how developing software that is meant to enhance and address specific problems within the company can actually become an advantage in the long run since software of this particular nature can create a certain degree of added value for a company’s clients. One company in particular that proves the effectiveness of such a method of operation is Accenture which has developed a plethora of in-house accounting software solutions that has resulted in the company becoming a veritable behemoth in the accounting world due to its focus on providing clients with cost effective solutions for their accounting needs.
On the other hand, it must be noted that there are inherent problems with issues related to cross compatibility of enterprise software especially in cases where a company merges its systems with another. This was seen in the case of Cingular when it was bought by AT&T resulting in the merger of proprietary in-house Cingular systems such as C.A.R.E with the Telegence systems utilized within AT&T. The end result is usually an arduous process of re-coding, evaluation and re-coding once more in order to combine both systems in order to merge them in such a way that it does not cause problems for the company’s information architecture.
One of the last problems involving enterprise software is the sheer amount of complexity found in the coding process of the tools. This means that should the creator of the software leave for another company it often takes a considerable amount of time for the new person in charge to familiarize himself/herself with the software which can often result in subsequent operational problems and delays within the company should something need to be fixed.