Introduction: The Non-Alcoholic Beverage Company Portfolio
The paper regards the non-alcoholic beverages sustainability in the context of company analysis. The major principles of organizational hierarchy development, as well as finance raising and human resources management, are discussed. Moreover, the work views the questions of equipment sustainability and production procedures.
Non-Alcoholic Beverage Company: Operations Plan
The non-alcoholic production targets a broad range of hot and soft drinks. The complexity of the industrial processes is stipulated by such factors as ingredients variability, equipment diversity, and health care concerns. Therefore, selling non-alcoholic beverage products requires an elaborate operational plan.
Key Aspects of Operation
The industry’s success is partly dependent upon the facilities and tools that sustain the production. Besides, it is crucial to outline the major production processes since they organize the work procedures.
The company management possesses some basic equipment that supports drinks production. Specifically, it uses two powerful non-alcoholic beverage mixers that mix up approximately 400 gallons. Besides, the industrial corporation owns some bottling tools. These are two bottling machines that assist in capping and filling bottles. Additionally, the company operates four vehicles, three computers, graphic software, and a willing beverage machine. The total financial value of the industry equipment equals approximately $900,000.
Non-alcoholic beverage production goes through certain stages. Mainly, one may outline such industrial processes as raw materials gathering, water treatment, which predetermines demineralization and content restrictions, bottles filling, etc.
The labor force utilization is to be conducted by the company in six months. It implies a stipulation of such processes as materials gathering and technological processing. In general, the non-beverage industry jobs include positions of a mechanic and manual workers, filling and packaging operators.
Cost and Time Efficiencies
The non-alcoholic beverage industry is characterized by high-cost efficiency. For instance, the major sales of the production reach approximately $800 billion per year. A tendency of the active beverage purchasing may be traced in Western Europe as well as North America (Non-alcoholic beverage manufacturing industry profile, 2015).
The estimations of the company’s cost allocations prove that there is a positive expectancy of the industry’s development. First, the startup embraced an effective production strategy that presupposes selling the product for $2 a bottle, which is profitable since the costs that are spent for its production equal $0.56 a bottle. The latter presents a sum of inventory expenditures, which includes glass bottles, cardboard cartons, metal caps, and NAB ingredients. Moreover, the management does not plan to spend the company’s finance on the personal expenses for the first six months of work. Consequently, the industry will earn a total sum that will greatly exceed the initial investments.
The company will need six months to become firmly incorporated into the global beverage market. Since the preliminary inventory investment is counted on 24,000 units, it is rational to use the six-month term for the accomplishment of the plan. The regular workweek lasts forty hours. Consequently, according to the simple calculations, 25 beverage bottles per hour have to be produced during the period. Taking into consideration the worker’s count, it is an accomplishable task that can stipulate a favorable industry development.
Competitive Advantages
The major competitor players on the non-alcohol beverage market are such companies as Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, Inc. Both industries cooperate with such powerful market leaders as Starbucks and Unilever. Moreover, the non-alcoholic beverage mammoths maintain favorable price policies, which ensure their enormous success among the consumers. The core advantage of our company that may become a competitor-eliminating factor is an orientation of the industry upon non-carbonated soft drinks. Since health concern produces a tremendous impact on the general consumption rates, the new industry is taking the direction of a healthy lifestyle promoter and plans to produce the drinks without artificial sweeteners. Moreover, the industry lowers the average prices for drinks, according to the cost-efficiency plan, which will contribute to the company’s success.
Problems Addressed and Overcame
The primary problem that is faced by a developing non-alcohol beverage industry is the introduction of its main product – non-carbonated drinks. Due to the established tradition, carbonated soft drinks have long been the dominators of the beverage industry. Thus, the market size of these products equaled $337.8 billion in 2013, which made it a leading drink kind on the global market. Therefore, it is a challenge for the company to create a strong promotion for the new type of healthy beverages. The developing industry management plans to reach the goal through the tight association with the American Beverage Association that is an influential body in the world of beverage production since it establishes the principal industry tendencies.
The Advantages Rationale
The non-alcoholic beverage company disposes of the key inventory equipment. Concerning the materials that embrace production ingredients and packing facilities, the developing industry purchases the amount that will suffice for the six-month term, so that to trace the progress. Due to the uniqueness of the company’s production, it is not planned to rent the facilities, for the industry aims to create an innovative beverage interface.
The supplies that are needed for further production support include refrigerators, vans, and other subsidiary facilities. These materials are to be rented, for the developing company can not afford to invest in an innovative production until it is promoted and established on a global market. Because the supplies require continued maintenance, it is agreed to hire two workers who will handle the facilities cleaning and constant technical support.
The industries that promote drink production are fast-growing and pursue constant developments and product extensions. The new company develops a product that is claimed to become a healthy alternative to harmful carbonated drinks. Moreover, the company prepares a production of a few additional drink hits. These are an innovative batch of vegetable juices and healthy energy drinks. Therefore, the company’s core strategy targets the promotion of healthy drinks.
Beverage Company Technology Plan
The industry targets drinks that are based primarily on fruits and vegetables. The major processes require workforce distribution because production includes various procedures. Thus, the staffing sector is subdivided into three core parts: the processing workers, those who are responsible for gathering and peeling, packing, and filling employees.
The work procedure implies the accomplishment of three major tasks: ingredients preparation, core production, canning, and bottling. In the first stage, the workers handle washing, peeling, and thermal processing of fruits and vegetables. This type of work is of mundane nature but requires special physical training as well as patience and concentration.
The second process implies water treating as well as actual drinks preparation, according to the established recipes. Since the company uses an innovative approach to beverages production, this stage demands perfect proficiency and knowledge of the recipes. This step is the most challenging. That is why it is decided to establish a constant administrators’ control over product processing and drink preparation.
The last stage of the complicated procedure is quite demanding as well. The developing industry promotes the usage of environment-friendly reusable containers. Specifically, it introduces glass and stainless steel bottles that serve as healthy alternatives to plastic materials. Thus, despite the fact that the process of filling and canning is highly automated and requires neither many efforts nor special training, there is a tendency of breaking the bottles out of inattention. That is why the process demands a huge concentration.
Technology Assessment: Connecting the Needs to the Opportunities
The industry embraces both on-premise and cloud software usage. According to Ian Gotts (2015), cloud handling possesses three core advantages: cost saving, innovation, and flexibility (para. 3). Thus, industry management makes a decision to operate the primary production processes through cloud computing. However, small operations are to be managed with the help of on-premise software. The hardware needs of the company are ensured with the assistance of four powerful computing systems that belong to the hereditary inventory.
There is a strong necessity to satisfy the telecommunication needs of the company, due to its promotion orientation and collaboration with the partners as well as internal information exchanges. Therefore, the industrial body is supported by the active telephone line as well as internet services that promote constant contacting. Finally, the company ensures in-house personnel training by coordinating the employees’ work as well as outsourced education, which helps the workers to master the innovative production techniques.
Management and Organization Plan
Due to the status of the company, it does not dispose of a huge board of human resources. Nevertheless, all the types of the industry’s operations can be conducted by a team of qualified workers. Mainly, the key management is comprised of the owner of the company and Melinda Cates, who is a creator of the industry as well as Stephen Job, who is responsible for technological support and the NAB production specialist, Ian Glass. The board and advisory members are headed by Mary Cates, who specializes in the standards support, consumer serving, and planning procedures.
The management style is democratic. The team’s work is based on understanding and collective decision-making. Due to the underdevelopment of the company, it maintains a flat management structure, which promotes tight cooperation between the staff members.
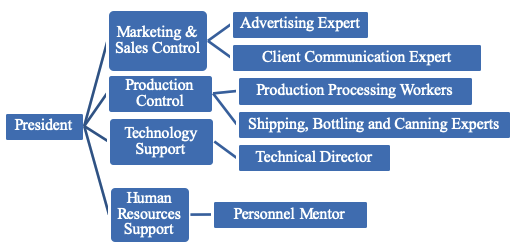
Since the management of the company takes an orientation upon the hierarchy development, it is crucial to outline its constituent elements so that to perceive the long-term aims that were set by the industrial body. Thus, according to the future management hierarchy, the administrators of the company emphasize such work sectors as marketing and sales, human resources, production, and technology (Figure 1). According to the cohorts, the core responsibilities are assigned to such workers as advertising and client communication experts, production processing workers, personnel trainers, technology experts as well as bottling and canning specialists.
Conclusion: Innovation in the Beverage Industry
The non-beverage industry faces many challenges since its work is affected by health concerns as well as low-quality management. The company’s working principles that are described in this paper refer to mutual understanding, collaboration, and innovation. Therefore, the production has a high potential and can become a dominator on the beverage world market.
References
Gotts, I. (2015). The cloud vs. on-premises software: What you need to consider for your business. Insider. Web.
Nonalcoholic beverage manufacturing industry profile. (2015). Web.