Executive Summary
This business report analyzes and rates Tesla in comparison to its rivals in the auto industry, as well as its business model, tactics, culture, available resources, and other vital aspects. With the help of SWOT analysis, it became evident what strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are now in play. The most important results demonstrate that Tesla needs to ramp up manufacturing for the mass market, expand their pricing points, and keep researching and developing autonomous driving. Tesla’s vertical integration model helps them reduce their reliance on outside vendors and keep prices down without sacrificing quality. Climate change, political instability, a lack of resources, and the availability of workers are all discussed as potential obstacles. Porter’s Five Forces model and the BCG matrix were two more techniques used to analyze Tesla’s market position and entry obstacles. Problems, like high startup costs and intense competition, were highlighted by the model. The matrix revealed the difficulties in implementing solar power, energy storage, and supplementary technologies.
Business Strategy
Tesla Inc., formerly known as Tesla Motors Inc., was established in 2003 in Palo Alto, California, USA (Liu et al., 2022). The company manufactures and distributes fully electric automobiles, solar power storage and generation solutions, and solar power itself. Electric vehicles are at the center of Tesla’s business model, emphasizing the company’s control over product supply. Tesla entered the market with luxury vehicles aimed squarely at the well-off. When it gained greater recognition and credibility as a proven concept, it entered the more crowded market for entry-level-priced versions. Tesla’s business strategy relies on the company’s ability to sell and service its electric vehicles directly to customers and establish a nationwide network of charging stations for its customers. As a part of their business strategy, Tesla requires deposits from customers an entire year, two, or even three years before the vehicle is even produced or delivered. Unlike many other companies, Tesla does not use franchise retailers. In many of the world’s largest cities, they have their own galleries where they choose to offer their merchandise.
Stakeholder Environment, External Environment, and Organization
Many stakeholders are invested in Tesla because of the company’s success and the radical changes it could bring to the transportation industry. Customers of Tesla care most about product quality, price, and ease of access to charging stations for electric vehicles. In terms of suppliers, Tesla seeks those committed to social and environmental responsibility and is constantly mapping its complicated supply chains to understand its channels better and conduct audits (Tesla Inc., n.d). Tesla has encouraged its consumers to play a guardian role by boosting stakeholder engagement and grassroots advocacy in situations where stakeholder interest exceeds that of shareholders, such as extending charging facilities and reducing charging fees. Through its Impact 2020 program, Tesla has acknowledged its clientele as a critical stakeholder group and made strides toward its sustainability targets (Raj, 2022).
Politics, law, technology, and society all play a role in shaping Tesla’s external environment. To begin, governments on a global scale have made no effort to hide their support for a harmful regulatory regime. For example, California’s Air Resources Board created zero-emission rules, which fourteen states across the United States have adopted (Center for Climate and Energy Solutions, 2022). Second, urban transport options with a shortened average driving range per person per trip, smaller durations, and faster response times will be in more demand in areas with high population concentrations. From a technical standpoint, batteries are responsible for the total price of a vehicle. As a result of the first phase of the super battery factory’s economies of scale, Model Y’s newest LFP battery now costs under $100 per kWh, a reduction of 58% (Yang et al., 2021). Consequently, Tesla is highly susceptible to changes in the cost and popularity of battery technology.
The organization, particularly the Board of Directors of Tesla, Inc., demands a lot from their team members and themselves in their roles. Strong corporate governance is an essential part of this ethos. The Board of Directors is responsible for protecting the interests of the company’s shareholders and supervising the executive team. The Board of Directors abides by the policies and regulations established in several documents to carry out its functions. Audit, disclosure procedures, compensation, and a code of ethics are all covered by these rules, all designed to benefit the company or mandated by law (Tesla Inc., n.d).
SWOT Analysis
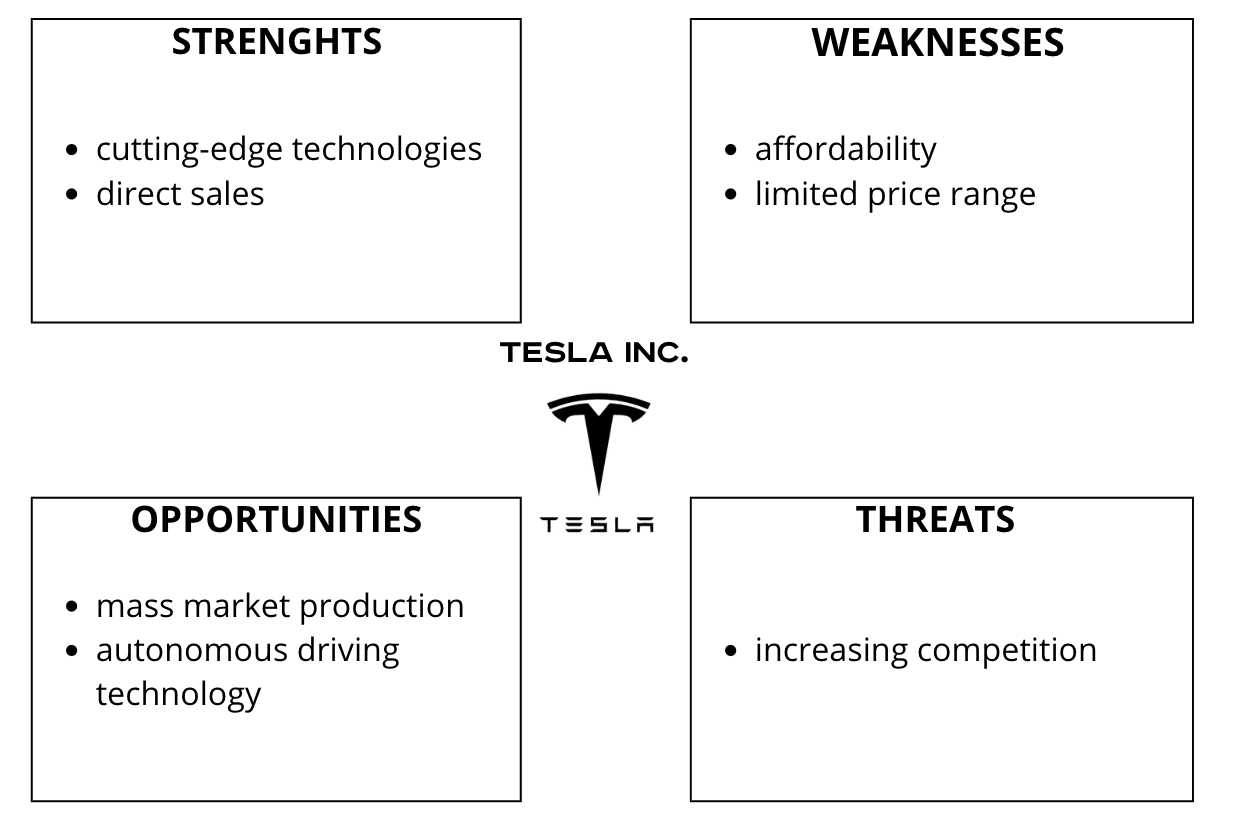
Tesla’s competitive edge is the novel notion it aims to provide: high-end electric vehicles that do not break the bank, as presented in Figure 1. To give just one example of Tesla’s pioneering spirit, the business was the first to mass-produce a totally electric sports car (Tesla Inc., n.d). Advantages include cutting-edge technology, which is included in all three of Tesla’s market segments. Unlike competitors, Tesla sells its vehicles directly to customers. This streamlines communication between Tesla and its consumers and allows the company to cut costs. Nevertheless, many Tesla supporters are turned off by the company’s high automobile prices. Despite widespread interest and support, few people can actually afford a Tesla. For instance, the base price of a 2023 Tesla Model X is estimated to be over $105,000, with a fully loaded Model X Plaid costing more than $140,000 (Tucker, 2022). Tesla is taking a big chance by selling the more reasonably priced Model 3 to the middle class. Consequently, Tesla faces substantial losses unless the company expands its price range.
Increasing production to a mass market level is Tesla’s greatest opportunity. Since there is a higher demand than supply for a more inexpensive Model 3, prices are expected to rise. Tesla has manufactured a total of 226,517 Model 3s as of April 9, 2019, with weekly output averaging around 5,540 vehicles (Marshall & Davies, 2019). Furthermore, the company’s introduction of autonomous driving technology, and notably its potential direction, presents an opening. If they successfully implement this technology, it will have far-reaching implications for the transportation sector and beyond. The primary threat is competitive pressure, which will increase when established automakers release more advanced electric cars. There are now more reasonably priced options for those interested in purchasing an electric vehicle; for instance, Nissan sells electric vehicles for around $30,000 USD (Nissan USA, n.d). To give just one example, since 2020, Toyota has been offering over 10 different kinds of fully electric cars on the market (Toyota United Kingdom, 2022).
Tesla Inc. Organizational Structure
Tesla’s organizational structure combines functional elements with hierarchical ones. Musk’s aversion to delegating authority has given rise to a flatter organizational structure at Tesla, in which employees outnumber supervisors. Tesla may be highly adaptable or show little structure at all, depending on the circumstances (Cuofano, 2022). Consequently, Tesla’s dominant structure works effectively, where there may be a sales department, another with engineers, and so on. Most of the company’s domestic and global affairs are managed by functional heads situated in Austin, Texas (Cuofano, 2022). Two core business units are supported by each functional group, the automotive unit and energy generation and storage, and four regional units report financially.
Tesla Inc. Corporate Reorganization
In an email addressed to staff in 2018, Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced the business was reorganized to “flatten corporate structure” and “enhance communication” (Thompson, 2018). Another objective of the reorganization was to cut down on Tesla’s use of external contractors. By consolidating duties where it made sense and eliminating those that were not essential to the company’s objective, Tesla was able to streamline their management structure and increase transparency as part of their restructuring. In addition, despite Tesla’s difficulties in ramping up Model 3 manufacturing since its introduction, the business has continued to hire hourly and salaried positions related to Model 3 manufacture as a part of reorganization efforts (Thompson, 2018).
Brand Reputation
When people think of electric car manufacturers, they think of Tesla. With such a strong reputation, the corporation has a leg up on competitors looking to break into the market. An electric vehicle producer is bound to get noticed in today’s environmentally conscious market. There is widespread agreement that conventional gasoline-powered cars produce excessive carbon and severely pollute the environment (Liu et al., 2022). As a result, Tesla has built a reputation as an eco-friendly brand. Therefore, the corporation has advantages in several key areas, including pricing, billing, corporate reputation, differentiation strategy, and environmental considerations.
Political, Societal, Economic, and Technological Considerations
Tesla’s expansion could be affected by macroeconomic issues (Kissinger, 2019). Exploring the economic aspects of free trade deals with other countries can help boost the chances of expanding into new locations. Most middle-class people in the nations it is infiltrating would contemplate buying cars they can afford; therefore, their purchasing power is a vital factor to consider. Regarding technology, Tesla has already spent considerable time and money on research and development in robotics, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence. Since they are pursuing vertical integration, it makes sense for them to invest in Robotics and AI to increase productivity. Internet of Things-enabled, self-driving cars are the wave of the future in vehicles.
Tesla has a distribution base in Beijing, China, and an administrative body in Amsterdam, Netherlands, demonstrating the company’s global reach and expansion into new markets (Kissinger, 2019). Political unrest in the nations in which it operates is another potential obstacle since it could lead to supply chain destabilization and, ultimately, a loss of revenue. In addition, Tesla works with a wide range of international sourcing partners whose output is affected by factors including the domestic political climate and the country’s diplomatic ties to the United States.
Tesla Inc. Competition
Despite Tesla’s reputation as an electric car innovator, the company’s centuries-old rivals have quickly caught up to the advancements. Moreover, their cheaper rates may eventually entice Tesla consumers. However, Tesla’s primary competitive opportunity lies in its ability to generate market-competitive major innovations at affordable prices, shattering existing market structures’ monopolies and opening up new markets (Wang et al., 2021). Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, Audi, Toyota Motor Corporation, Ford Motor Company, Nissan, and General Motors Company are some of Tesla’s biggest direct competitors. Since all three companies are developing autonomous vehicle technology, Tesla is also in indirect rivalry with Uber and Google. For instance, Uber’s vision is to become a comprehensive solution for fueling local businesses around the world, and one step toward this aim is the concept of self-driving cars. A substantial substitute risk is also present due to the availability of other mobility options, such as public transportation, bicycles, and taxis, in addition to electric and conventional vehicles.
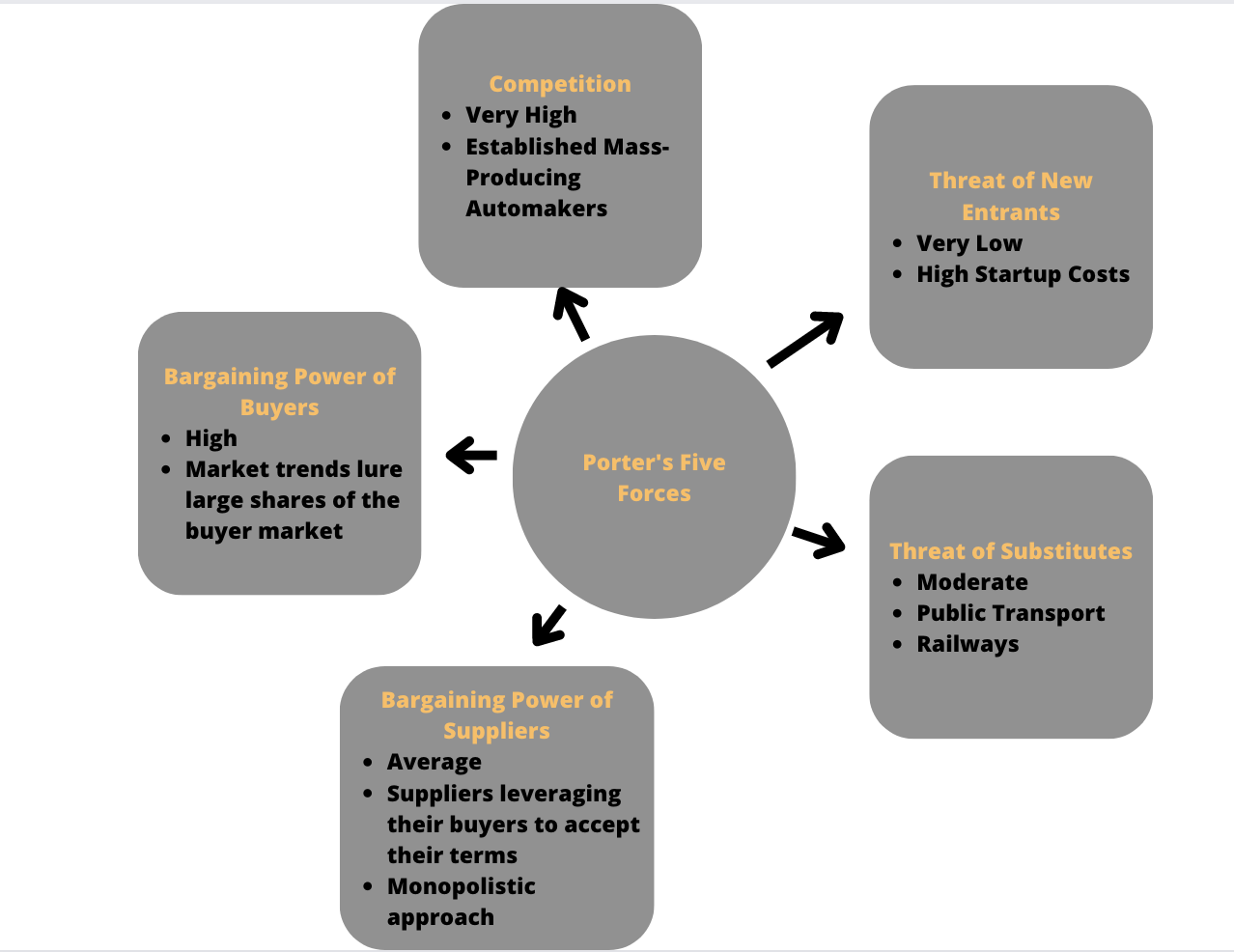
Barriers to Entry Using Porter’s Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces model identifies and analyzes the five main influences that shape any industry. Competition in the industry, the potential of new entrants, the power of suppliers, the power of customers, and the threat of substitute products are the elements that shape every sector, as presented in Figure 2. Adjustments to a new company’s entry strategy may be necessary in light of these five forces. According to the Five Forces research, the high startup costs associated with the automobile industry represent a significant opportunity barrier for new entrants (Kissinger, 2019). With such a hefty entry cost, the industry is effectively closed to potential entrants. Concerning the rivalry aspect, mass-producing automakers have a long history of being fierce competitors. Therefore, even if a new company manages to allocate startup costs, stiff competition is yet another barrier facing potential industry newcomers ahead.
Tesla Inc. Resources
Tesla’s ability to attract and retain talented workers is one of the company’s strongest suits. By collaborating with Elon Musk’s other businesses like SpaceX, Hyperloop, etc., Tesla has benefited greatly from the pooled resources of both employees and technological know-how. Since it embraces open innovation, Tesla has been able to collaborate with pioneering customers and suppliers outside of the conventional auto industry. The overall number of Tesla employees in 2021 was 99,290, an increase of 40.33 percent from the previous year (MacroTrends, 2022). In order to help employees feel more at home at Tesla, the business supports a wide variety of Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) (Tesla Inc., n.d.).
In terms of viable physical resources, there are now five Gigafactories. Giga Nevada, Giga New York, and Giga Texas are the three locations in the United States (Baldwin, 2022). Tesla’s Powerwall and other battery packs and storage technology products are manufactured in Nevada. From its base in Buffalo, Giga New York manufactures Powerpack batteries, solar panels, and components for charging points. The new Austin center and manufacturing facility, Giga Texas, is where all models are built (Baldwin, 2022). The company manufactures Model Ys in two overseas plants: China and Germany (Baldwin, 2022). Giga Berlin plans to produce battery packs and powertrains in addition to its existing Model 3s, while Giga Shanghai focuses on building Model 3s.
For its early growth, Tesla relied substantially on loan financing. Positive retained earnings are a result of a recent uptick in Tesla’s business performance. In December 2021, Tesla’s debt was nearly equal to its equity (Gorton & Estevez, 2022). Tesla’s economic health has significantly improved over the past few years, even though it has not always been stable. While the company’s cash on hand shrank in 2021, it still made a profit of more than $2.6 billion in Q4 alone (Gorton & Estevez, 2022). Tesla is challenged to maintain its current level of productivity while simultaneously cutting costs and increasing output.
Tesla Inc. Financial Performance
The history of financial growth at Tesla Inc. is long and substantial. Tesla stock closed in 2012 at $33.87 (Nasdaq, 2022). The price per share reached about $340 by the end of 2017 (Nasdaq, 2022). Before Tesla’s first stock split in 2020, when shares were split five-for-one, a single share had reached $500 (Nasdaq, 2022). The price of a share of Tesla stock is predicted to reach $1,077.60 by the end of the first quarter of 2022 (Gorton & Estevez, 2022). Elon Musk, the co-founder of PayPal, saw potential in the company early on and contributed millions in seed capital. Tesla is well-known for its inability to generate a profit for many years despite extensive investments in high-priced machinery, large production facilities, and efficient production methods. The company’s long-term plan is beginning to pay off now. By the end of 2021, Tesla had turned a positive $331 million in retained earnings from a negative $5.4 billion in 2020 (United States Securities and Exchange Commission, 2021). As Tesla has become more profitable, it can secure cheaper loan funding in the future.
Tesla Inc. Sustainable Competitive Advantage
The company’s wide portfolio of technologies could facilitate the introduction of cheaper automobiles to the market. This provides the organization with a significant technological and competitive edge, setting the stage for sustained and rapid expansion. Tesla’s primary competence is in developing its engine and battery pack technology. Because of its extreme rarity and strategic value, this is the single most important aspect. Costing a lot of money and requiring a lot of technological know-how, this skill is difficult to replicate. Its business model is designed to maximize profits by exploiting this technology for both internal and external car production (Han, 2021). Therefore, it can be reasoned that the technology behind the engine and the battery pack represents a significant and lasting competitive edge.
Tesla Inc. CEO and Senior Leadership
Elon Musk, a co-founder and the current CEO of Tesla Inc is a charismatic figure who has successfully brought attention to himself and his company. Inventive and constantly in need of making something new, Musk is a true creator. Even when he was not the CEO, Elon Musk played a pivotal role at Tesla. Musk led the company’s Series A funding round in 2004 while he served as chairman (Gorton & Estevez, 2022). In a 2006 blog post, he revealed the company’s stated goal of transitioning to a “solar electric economy” and went into greater depth about Tesla’s lofty goals for the future (Tesla Inc., n.d). Musk has always taken bold action with Tesla and openly stated his intentions for the brand. Senior Vice President of PowerTrain and Energy Engineering at Tesla, Drew Baglino, has issued a call to action to Tesla’s supply network and all other industries to speed up the development of new battery technologies (Tesla Inc., n.d).
Tesla Inc. Mission, Vision, and Values
“Create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world’s transition to electric vehicles” is a direct quote from Tesla’s vision statement (Cuofano, 2022b). They plan to integrate their existing electric vehicles, batteries, and renewable energy storage and generation in the future. And yet, its stated mission is “to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible” (Cuofano, 2022b). The primary goal was to demonstrate that battery-powered vehicles were competitive with or even superior to their gasoline-powered counterparts. Since Elon Musk took over as CEO, the company has implemented a plan to make Tesla’s base price more aligned with the competition. Although the current market for Tesla vehicles is diverse, the company is still focused on scaling its operations to meet demand. For some, it is still about ecology, but for others, it is about social standing, saving money on gas, or both.
Tesla Inc. Crisis Management
Even the best-run firms cannot escape every unpleasant occurrence, but crisis management, preparation, and response can help prevent long-term damage. Since a video showing one of the company’s electric cars caught on fire on the edge of a Washington highway became popular on YouTube, Tesla Motors has been criticized. Chief Executive Officer Elon Musk has been on a media blitz, expertly weaving his key points on safety into interviews and public comments. CEO Elon Musk blogged that the business has altered the software of the Model S car (Bernstein, 2022). Such changes enabled the car to not ride as close to the ground at highway speeds, decreasing the likelihood that the car batteries would be damaged and catch fire from road debris. Musk’s rapid response to the issue rescued Tesla’s reputation for producing safe vehicles.
Tesla Inc. Positioning Using BCG Matrix
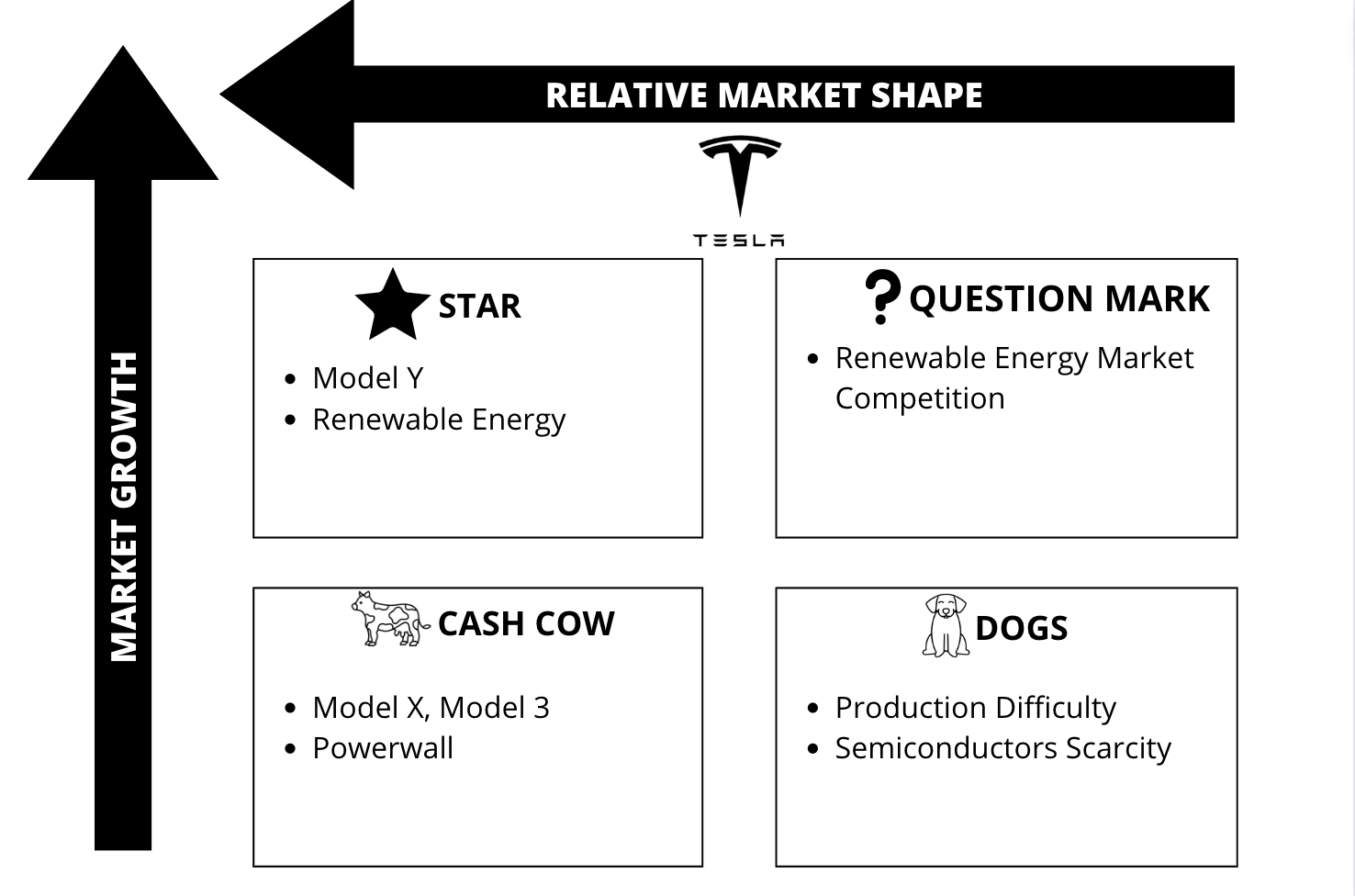
Tesla’s standout offerings are the electric automobiles it develops and manufactures and the renewable energy it generates. Tesla is at the forefront of the sustainability movement, and the company’s whole product line is designed with the planet’s well-being in mind. About 200,000 Model Ys were sold by the company during the third quarter of 2021, increasing the total number of vehicles sold by the company to over 500,000 (McKerracher, 2022). This puts the Model Y comfortably within the top best-selling automobiles in the world. Thus, the star items that symbolize an expanding market are clean energy and Tesla’s Model Y, as presented in Figure 3. Products that generate high profits year after year, although a stagnant market, are called cash cows. Indeed, this holds true for all other types of relatively inexpensive automobiles. Also included is the Powerwall, as this battery is suitable for home use. Powerwall is a solar battery storage device that can keep the lights on in the event of a grid failure (Tesla Inc., n.d).
The corporation is facing challenges associated with solar power, energy storage, and other ancillary technologies. The investment size needed to turn a profit from these types of services is bigger. Price and demand swings and the unpredictability of renewable energy sources characterize the current energy environment (Jebli et al., 2021). More and more businesses are showing interest in the ecological industry. Even while there are hardly any “dogs” in the Tesla lineup, the production difficulty of particular models can seriously damage demand when competition is heating up. As an example, Tesla needs help to meet its fourth-quarter sales targets due to a global scarcity of semiconductors (Kolodny, 2022).
Tesla Inc. Organizational Culture
Matching individual values with those of the company is a key factor in fostering long-term success and Tesla’s culture. The peculiarity of Tesla’s organizational culture lies in its dedication to a wide range of social objectives, including conserving natural resources and the environment (Cardenas, 2022). Providing sustainable energy to domestic, corporate, and industrial markets is important to Tesla’s organizational initiatives, as is reducing reliance on traditional transportation through the promotion of zero-emission solutions (Cardenas, 2022). That is why Tesla’s organizational vision and tactics are well-suited to balancing the company’s culture and social duties.
References
Baldwin, R. (2022). What you need to know about Tesla’s gigafactories. Capital One. Web.
Bernstein, E. (2022). Tesla’s new crisis management tactic as NHTSA launches investigation. Bernstein Crisis Management. Web.
Cardenas, B. (2022). Tesla case study: Complete assessment of social/organizational culture, leadership, teams, communication, talent/knowledge management & recommendations. LinkedIn. Web.
Center for Climate and Energy Solutions. (2022). U.S. state clean vehicle policies and incentives. Web.
Cuofano, G. (2022a). What is Tesla’s organizational structure? Tesla organizational structure in a nutshell. FourWeekMBA. Web.
Cuofano, G. (2022b). Tesla mission statement and vision statement analysis 2022. FourWeekMBA. Web.
Gorton, D., & Estevez, E. (2022). Tesla stock: Capital structure analysis. Investopedia. Web.
Han, J. (2021). How does Tesla Motors achieve competitive advantage in the global automobile industry? Journal of Next-Generation Convergence Information Services Technology, 10(5), 573–582. Web.
Jebli, I., Belouadha, F. Z., Kabbaj, M. I., & Tilioua, A. (2021). Prediction of solar energy guided by Pearson correlation using machine learning. Energy, 224, 120109. Web.
Kissinger, D. (2019). Tesla Inc. five forces analysis (Porter’s model) & recommendations. Panmore Institute. Web.
Kolodny, L. (2022). Tesla cut a steering component from some cars to deal with chip shortage, sources say. CNBC. Web.
Liu, Y., Shen, Y., Zhang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2022). A comprehensive analysis of Tesla. In 2022 2nd International Conference on Financial Management and Economic Transition (FMET 2022). pp. 344-356. Atlantis Press.
MacroTrends. (2022). Tesla: Number of employees 2010-2022. MacroTrends. Web.
Marshall, A., & Davies, A. (2019). Tesla’s Model 3 is now selling for $35,000. Wired. Web.
McKerracher, C. (2022). Tesla’s Model Y passes perennial top-sellers in global rankings. Bloomberg. Web.
Nasdaq. (2022). Tesla, Inc. common stock. Web.
Nissan USA. (n.d). 2023 Nissan LEAF: All-electric vehicle. Nissan. Web.
Raj, V. (2022). Corporate governance: Shareholders vs. stakeholders – Divergence and common ground. SSRN Electronic Journal, 12(1), 1-4. Web.
Tesla Inc. (n.d.). About. Tesla. Web.
Tesla Inc. (n.d.). Careers. Tesla. Web.
Tesla Inc. (n.d). Corporate governance. Web.
Tesla Inc. (n.d). Powerwall. Tesla. Web.
Thompson, C. (2018). Elon Musk reveals new details about how Tesla is restructuring. Business Insider Nederland. Web.
Toyota United Kingdom. (2022). Electric. Toyota GB. Web.
Tucker, S. (2022). New 2023 Tesla Model X reviews, pricing & specs. KBB. Web.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission. (2021). Tesla Inc. form 10-K. Web.
Wang, J., Duan, Y., & Liu, G. (2021). A study of specific open innovation issues from perspectives of open source and resources—The series cases of Tesla. Sustainability, 14(1), 142. Web.
Yang, X. G., Liu, T., & Wang, C. Y. (2021). Thermally modulated lithium iron phosphate batteries for mass-market electric vehicles. Nature Energy, 6(2), 176–185. Web.