Introduction
WiMAX is the cellular version. Its stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX). There has been a great evolution in wireless communications over the last few years. WiMAX is an emerging wireless technology used for deploying broadband wireless metropolitan area networks (WMAN). WiMAX is a wireless technology that offers many features with a lot of flexibility. WiMAX has replaced many of the existing telecommunication technologies and provides last-mile connectivity with higher speed at longer distances, from 30 to 50 miles and its transfer rate is up to 70 Mbps. 4G is the 4th generation cellular wireless principle. It uses the technique of packet switching mode of transmission (Wang, Kondi & Luthra, 2009).
This works by first breaking down information to be transmitted into packets. Each packet is uniquely identified by a number and is transmitted differently. At the destination, the packets are re-arrange to get the information received. This really helps in identifying errors in that missing packets can easily be discovered. It offers multi-carrier transmissions. It provides mobile internet access. It is nowadays available in the market.
It provides very fast and reliable internet access. It covers large miles because it is wireless. It provides a high speed and a wide range of bandwidth. It is currently integrated with cellular phones. With the release of 4G iPhones mobile devices, there has been an increased use of the internet. This 4G technology came to replace 3G and 2G standards.
There are two types of WiMAX fixed and mobile WiMAX. FDD requires two spatially segregated channels, one for the uplink and one for the downlink. Many regulators assign spectrum in paired channels and require the utilization of FDD. While the TDD uses one channel for uplink and downlink transmissions. Widely used in license-exempt bands, it is increasingly allowed in licensed bands as well. Vendors and network operators that focus on data services generally prefer TDD, while FDD dominates in cellular communications. The choice between the two is often dictated by regulatory constraints (Dubendorf, 2003).
Fixed WiMAX supports both TDD and FDD to ensure a wide market appeal, although we expect TDD to dominate where there is a choice, as it is best suited to data applications (although it can support voice applications as well). While Mobile WiMAX currently supports only TDD operations, TDD facilitates support for MIMO and beamforming, which gives WiMAX a performance advantage over 3G FDD-based technologies like EV-DO and WCDMA that do not yet support them. It has been seen that fixed WIMAX provides high-speed internet access. 4G has a high quality of service. It assists multimedia applications, high-speed data, and even mobile TV (Shi, 2004).
WiMAX and its Enhancements in Communication
The implications of this technology as a communications platform for 4G range from Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), streaming and real-time video, and support for advanced social networking applications that feature real-time chat. The development of WiMAX technologies continues to be accelerated by the rapid adoption of Web 2.0 technologies and with them, the exponential growth of social networking applications as well.
As the bandwidth required to support Web 2.0-based technologies including Extensible Markup Language is limited over wireless devices, the need for WiMAX compression techniques that increase the performance of increasingly complex applications is needed. 4G can be used across multiple networks irrespective of their locations. It makes everything almost possible. This will enable the company to communicate with various suppliers and customers wherever they are.
Nuaymi (2007) indicated that the multimedia support application will make it possible for photographs and different images to be sent over the transmission channels. People are able to have a real picture of what they are purchasing. This is possible because of the use of 3D graphics which has a clear perspective of how everything looks like. Below is a diagram of how WiMAX works:
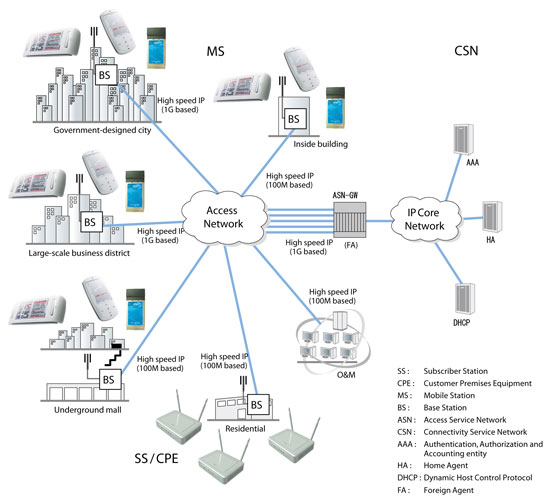
The 4G technology also provides a platform for chatting online. Several stakeholders of the company can communicate anywhere using the chat application. They can share ideas and make sound decisions according to what they have agreed on. The technological innovations in WiMAX are having a significant impact on the business and societal uses of wireless devices and the applications being produced to enrich their use and adoption.
In conjunction with the rapid development of 4G is the location-independent technology of Evolution-Data Optimized (EV-DO) which has the high-speed capability and rides on a Carrier Detection Multiple Access signal which can manage both voice and data traffic. According to Zhang, Zheng & Ma (2008), the potential of EV-DO in the context of 4G over WiMAX is significant because it alleviates the need for intermediary carriers in a communications network. 4G technology provides very fast connections which do not need any cabling since it is wireless. Institutions using this technology will only pay some subscriptions per month to the service providers. There is no traveling made hence fuel is conserved.
Competition
EV-DO technology and 4G combined with WiMAX would in effect create a strong catalyst of consolidation in the telecommunications industry globally. This would have the net effect of leading to a proliferation of lower-cost devices for accessing the Internet which would, in turn, mean application depth and functionality would have to correspondingly increase rapidly. The need for extensive levels of XML compression to support greater depth of functionality in mobile-based applications would be critical for the hundreds of millions of users globally to be able to use the applications developed (Hung, 2009).
This is a fascinating dynamic in the telecommunications market and would eventually re-order the approach to services bundling that is dominating the sales of notebook computers today. Berndt (2008) 4G applications have been evident to be almost the fastest mobile technology available today. It offers a wide range of interoperability with currently available wireless standards. This makes it possible for residential and suppliers and even customers to communicate faster. This will enhance the pace of doing business. 4G solutions provide all these applications which enable instant communications. This increases the reliability and availability of good communication in the business environment. Most of the businesses nowadays are being done through the web.
The World Wide Web, therefore, provides several applications which enhance businesses. Companies should therefore adopt this 4G over WIMAX technology in order to increase their profitability. Telecommunications providers are currently charging a monthly fee for 3G access to their networks and in exchange for a multi-year commitment, provide a net book at a significantly reduced rate.
Clearly this does not benefit the consumer over the long-term, instead benefiting the service providers with highly profitable services with very little incremental costs per user. 4G not only provide fast communication but it also supports home and mobile benefits. This technology has been seen to slowly outweigh and replace other technologies in the market. Several people are able to surf wherever they are and communicate with their family, friends and even their business partners.
This happens because of the use of 4G technology. This technology connects many homes and work places. Everything can now be done online e.g. booking of flights, hotel rooms and even buses for travelling. This therefore improves the living standards of the people to a digital world where almost anything can be done while at home.
In 4G data is sent through signals using several aligned towers. These towers communicate and transmit information to an intended receiver. This technology has been integrated with the current 4G cellular phones in the market. This makes 4G to be even more accessible and reliable than other forms of wireless technologies. Almost everyone is able to surf using their phones using this technology. They can also be able to make payment for anything they want to purchase using this technology through the same mobile phones. 4G is not as expensive as we might expect. It will even cut down several cost previously incurred in cabling of other networks.
What is needed is just a modem which enable a connection to the internet to be set and then one is able to browse and anything from the internet. Since it reduces the cost of data transmission and the cost of gas used to make various travels in marketing the products. Therefore implementing this 4G technology over WIMAX will greatly reduce cost incurred for several bills in the country (Kyriazakos, Soldatos & Karetsos, 2008). WiMAX will however over time change the market dynamics in favor of the consumer, which will in turn require exceptional levels of performance gains on XML optimization and compression of applications operating over these networks are to deliver sufficient performance. WiMAX is also augmented in performance through the use of AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)-based programming languages (Zhang, Schiffman et al 2009) that provide for selective updates of only those components that have changed over time.
Technology
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access which is better known as WiMAX has added a new revolution to the world of wireless and communication technologies. With standard published by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802 committee in the year 2004, the 802.16 working group defined WiMAX in two phases. Through Revision D, definition for fixed application was provided while Revision E added the mobility chapter and was published in 2005. WiMAX technology operates in 2.5GHz, 3.5GHz and 5.8GHz frequency bands under license provided by government authorities of the concerned nation.
As compared to other Wi-Fi technology WIMAX covers a longer range of distance. It covers very many kilometres using spectrum to deliver connections to a particular network. Wi-Fi utilizes unlicensed spectrum unlike the WIMAX. WIMAX is connection oriented while Wi-Fi is both connectionless and connection oriented protocols e.g. CSMA. WIMAX is able to connect several homes and offices all over the world. This makes it to be preferred to Wi-Fi.
WIMAX provides a subscriber unit which can be positioned at a corner of the building to as to get the best connectivity and reception. 4G actually have interesting features than Wi-Fi and 3G technologies. 4G allows video conferencing and other excellent forms of communication. Below is a WiMAX network diagram:
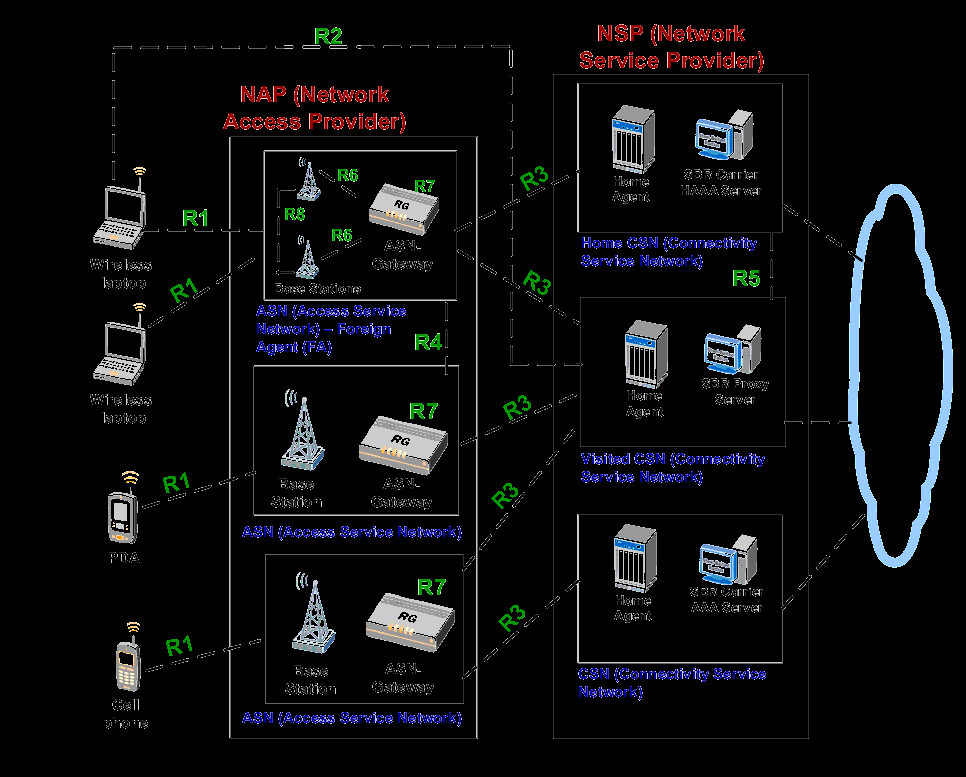
WiMAX has been based on RF technology effective for transferring data through carriers of width more than or equal to 5MHz. The multiplexing technique used in this case is that of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) which contrasts with CDMA based 3G technology requiring a carrier of width less than 5MHz. WiMAX is basically a standard based technology with application in wireless networking that could provide broadband connections over larger distances.
The use of 4G over WIMAX has several advantages to a country using it. The data transfer rate in 4G technology is quiet high and attractive. 4G enables a full time on line mobile connection. It is a fully packet switched digital broadband connection. 4G has far much higher bandwidth than other wireless technologies unlike WIMAX. Jacobsson, Niemegeers & Groot, (2010) indicated that 4G technology is ten times as faster than the 3G networks currently being used. It is normally termed as internet protocol solution. This is merely because of its ability of 4G to combine voice, multimedia message and data and transmits with very high data rates. This quantifies the fact that 4G should be implemented over WIMAX.
WiMAX technology has its several usages of applications such as the “last mile”. This is for the broadband connections at home and for those who use it for business purposes. It’s also hotspots which makes it favorable for the business connections. The technology is capable enough for implementing wireless metropolitan area network or MAN with connectivity speed in the range of 70 Mbps.
The WiMAX base station has a coverage area between 5 and 10 km and the system is developed like cellular system. Base stations in this case don’t require high tower based installation or any other elevated structure. The complete installed unit at the customer’s end is nothing more than a device similar to that of satellite TV setup which connects the customer with the base station. The signal received by the box is routed to the computer through Ethernet cable.
Impacts of WiMAX
According to Berndt (2008) 4G applications have been evident to be almost the fastest mobile technology available today. It offers a wide range of interoperability with currently available wireless standards. This makes it possible for residential and suppliers and even customers to communicate faster. This will enhance the pace of doing business. The suppliers and the vendors are able to communicate through emailing and use of instant messages.
4G WIMAX solutions provide all these application which enables instant communications. This increase reliability and availability of a good communication in the business environment. Most of the businesses nowadays are being done through the web. The World Wide Web therefore provides several applications which enhance businesses. Companies should therefore adopt this 4G WIMAX technology in order to increase their profitability.
Benefits of WiMAX
WiMAX displays a high degree of interoperability. It is a standards-based technology that is actively supported by most vendors. Interoperability is ensured by the certification program managed by the WiMAX Forum which tests whether products from different vendors are capable of operating successfully in the same network. Interoperability brings greater flexibility to operators in the selection of vendors, subscriber equipment form factors and base station configurations.
WiMAX also reduces cost. Wide support for WiMAX from vendors and operators will lead to lower prices overall, as economies of scale kick in and components become mass-produced. This greatly improves the business case for service providers, especially in countries like India where the expected ARPU is low and subscriber equipment needs to be affordable—that is, below $100—to achieve profitability in the residential market.
The average speed of 4G witnessed in the market survey is very high. It showed a download speed of up to 6 Mbps. This therefore lowers cost previously incurred in 3G downloads. The upload speed ranged from 0.5–1 Mbps. It has made faster the delivery of customer services. It provides several consumer applications which are quiet desirable. It enables social networks and You Tube videos to be downloaded at a very high speed and a reduced cost. Users of this technology can also download movies and music as they please (Rao & Radhamani, 2008).
WIMAX has an increased performance. WiMAX is a leading-edge technology that takes advantage of OFDM and OFDMA modulation, wide RF channels, advanced antenna technologies like MIMO and beam forming, and sophisticated QoS functionality. As a result, WiMAX enables operators to use their spectrum holdings efficiently and promises high throughput and capacity, coupled with low latency and great flexibility in traffic management.
It enables unlimited surfing to the internet. Companies using this technology save money previously used to settle the very expensive telephone bills. This technology if integrated in all the processes in the country will boost the economy. This technology will also attract foreign investment since the investors want a reliable internet access to manage and monitor their daily businesses. This will be a great boost to the country’s economy.
There is also reduced complexity. WiMAX, like 4G is an all-IP technology based on a core network that is not tied to the complexity and higher cost of legacy technologies, and that can be easily integrated with other IP networks. Sprint 4G provides a high productivity. It also offers simplicity and quality to a customer. A research was carried out in Baltimore market about the use of 4G technology in business. The research showed that 4G is 10 times faster and efficient as compared to 3G connections under the same conditions. There are several 4G single mode embedded devices e.g. laptops and modems.
The research also showed that people preferred using WIMAX technology because of its renowned benefits. The ability of 4G to carry streaming videos to every part of the world is quiet desirable. Sprint has experience in economic boom with the use of this WIMAX technology. It has fastened shopping abilities of customers. It has also improved communication between Sprint and its suppliers (Ahson & Ilyas, 2007).
Limitations of WiMAX
Although the implementation of WIMAX by several institutions around the world shows much promising results, it cannot fail to have some shortcomings. Berndt (2008) indicated that the major limitation is the coverage area. Although WIMAX is wireless and cover a wide range of distance, there are still many areas which are not yet covered. Places in the rural part of the world are no served by this wireless technology. Metropolitan areas are also left out.
The hype brought by 4G technology gives the public some expectations which are not realistic. Since despite of it availability anywhere anytime, it is not as reliable as wired internet. The technology required in implementing this technology is expensive. The carriers required and the 4G handset are still very expensive in the market. WIMAX uses complex modulation schemes. This increases the data throughput in the PCS spectrum which in turn making the power consumption to rise.
WIMAX Customer Devices
WIMAX is an IEEE specification. It is known as 802.16e. It is normally designed to support very high data transmission speeds. It implements OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access). The hardware requirements may include high throughput transmitters and receiver antenna. This is what makes the 4G wireless system architectures. There is also the need for high programmable processors.
These are used to set up 4G base stations. Switches are also required. They link LTE network devices and provide connections to the wireless base stations. In order to enable this applications to function well a complex operating system is needed. Some additional applications like flash player and Bluetooth are also required (Hart & Kalaichelvan, 2007). As WiMAX modems are built to open standards, they can be provided by a number of different suppliers and in a number of different form factors. The following are customer devices needed:
- Stand-alone WiMAX Modems:This is used for the activation of stationery.
- Internal Interfaces: This has linked the WiMAX and the Wi-Fi abilities. This relates to the Echo Peak which has been established in a dozen of several PC makes. There have been intentions to bring on board the multiband WiMAX so as to be on the same level with the Wi-Fi.
- Wi-Fi/WiMAX Routers: This is a move to enhance the combinations of the Wi-Fi routers and WiMAX.
References
Ahson, S. & Ilyas, M. (2007). WiMAX: applications. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Berndt, H. (2008). Towards 4G technologies: services with initiative. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Dubendorf, V.A. (2003). Wireless data technologies. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Hart, L. & Kalaichelvan, K. (2007). WiMAX Explained. New York: Cengage Learning.
Hung, P.C.K. (2009). Services and Business Computing Solutions with XML: Applications for Quality Management and Best Processes. Hershey: IGI Global snippet.
Jacobsson, M. Niemegeer, I. & Groot, S.H. (2010). Personal Networks: Wireless Networking for Personal Devices. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Kyriazakos, S. Soldatos, L. & Karetsos, G. (2008). 4g Mobile and Wireless Communications Technologies. London: River Publishers.
Nuaymi, L. (2007). WiMAX: technology for broadband wireless access ITPro collection. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons
Rao, R.K. & Radhamani, G. (2008). WiMAX: a wireless technology revolution. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Shi, N. (2004). Wireless communications and mobile commerce. Hershey: Idea Group Inc (IGI).
Wang, H. Kondi, L. & Luthra, A. (2009). 4G Wireless Video Communications. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. & Ma, M. (2008). Handbook of research on wireless security. Hershey: Idea Group Inc (IGI).