Introduction
In the modern world, globalization has led to an increase in passenger travel from one part of the globe to another. Improvement and development of transport infrastructure across the nations is a critical influencer contributing to the ease of movement. With reference to the stated advancement above, the tourism and hospitality industry is fundamentally benefiting and expanding its market operations. Currently, many organizations offer travel services, lodging, hotels, restaurants, amusement parks, tourist guides, and other related forms of entertainment. The industry is well known for its cultural incorporation since it entails dealing with individuals from different cultural backgrounds. It is one of the performing sectors of the economy. Thus it generates a considerable amount of revenue for the respective countries. Tourism and hospitality organizations require effective management because of its aspect of encompassing and depending on the local and international communities that bear significantly varied beliefs and ways of living. Developing practical cross-cultural management practices within an organization is essential in promoting cohesion, diversity and togetherness amongst the stakeholders of the particular business company.
Theories of Cross-Cultural Management (CCM)
In every business setting, management is a core determinant of performance. Tourism and hospitality organizations are diverse and employ people from different cultural backgrounds. To achieve better outcomes and job satisfaction, managers are tasked with ensuring individuals are treated based on their cultural contexts. Better cross-cultural management is vital for the tourism industry since the entities are global and involves interaction with persons from varied cultures. Several theories have been developed to explain the cross-cultural aspect of organizations. They include interpretative, positivist, critical and postmodern approaches of CCM.
Interpretative Theory
Based on this model, culture is seen as an interpretative framework that different groups of people share, especially individuals with similar socialization. The theory is aimed at sense-making through sharing experiences of the cultures. According to the idea, attention is given to various meanings so that proper sense can be drawn from them (Jiang, Croucher and Ji, 2021). The model is critical in tourism and hospitality management, where people from varied cultural backgrounds work. It is important for the managers to ensure there are some shared consensuses amongst the people. The model is effective since it focuses on the main issues of cultures that can easily affect employees. Therefore, it is critical in analysing the cross-cultural perspective of an organization. Despite its efficacy, the study is based on personal opinion which makes it less relevant at some points.
Positivist Theory
The Positivist model of CCM views cultures as separate, self-contained and stable phenomena that consist of entirely different observable, manipulatable and measurable features. According to this theory, beliefs and norms are understood in accordance with the cultural dimension. CCM practices and comparison of various national scores effectively enable managers to properly understand the management difference when dealing with people from diverse backgrounds (Shuck, Kim and Fletcher, 2021). The model is ideal and scientific which makes it ignore some critical aspects of transcultural in business organization. Therefore, the model does not provide deep insight into societal beliefs.
The emergence of Cultural Diversity in Hospitality
Cultural diversity is a contemporary issue in the hospitality and tourism industry. It is facilitated by the growing globalization where people from different traditional backgrounds work together in a given organization (Paudel et al., 2021). Generally, this sector involves the movement of individuals from their original settings to adventure in places of their interest leading to multicultural nature. The concept of cultural diversity entails having a group of people with varied perspectives of culture within the same system.
Cultural diversity plays a significant role in binding different groups of employees in the organizations together. An entity that embraces this perspective allows workers to pursue their inspirations with limited attacks on race, nationality, gender, health status, sexual orientation or any other form of judgment. Currently, most managers have adopted to embrace the culture of assortment to enhance productivity. In the tourism and hospitality industry, employees have an excellent opportunity to interact with passengers from different beliefs and norms (Birnbaum et al., 2021). Therefore, it is necessary for the team to understand and appreciate various cultures they encounter. Managers should ensure workers are well trained to accommodate a variety of visitors. The hospitality workforce is vast and diversified, thus making it essential to employ personnel from different nationalities to promote diversity in the organization.
Since tourism and hospitality is a diverse sector that entails interaction with different people from various cultural backgrounds, workforce diversity is vital in enhancing service delivery. Having employees who understand other cultures make it easier to accommodate all kinds of visitors irrespective of their beliefs and perceptions. It also facilitates easy problem solving because employees have a different point of view if they contribute, leading to finding the solution to the issues troubling the organization.
Apart from promoting employees’ productivity, cultural diversity is essential in enabling organizations to retain the necessary and significant talents that can benefit the entity. A system that accommodates workers irrespective of tribe or status improves, attract and maintain professionals, thus allowing the business enterprise to have a quality workforce (Jones, Chace and Wright, 2021). It also facilitates corporation and sharing opinions which are essential in enhancing the skills and knowledge of workers. Furthermore, workplace cultural diversity increases the creativity of staff members, which is vital for the tourism and hospitality industry. Diversification allows people to learn from each other, making them informed and thus able to service customers that belong to the already learned standards.
Implementation of Models of Cross-Cultural Human Resource Management
Generally, tourism and hospitality organizations have significant roles to play in implementing cross-cultural model into their systems. First, they should promote workforce diversity whereby they employ workers from different nationalities with varied cultures during recruitment. Tourism organization should ensure they employ both genders as workers. This will ensure women and men do not feel neglected thus increasing their workplace confidence. When people with distinct values interact, they learn from one another, thus promoting the level of comprehension.
Secondly, the organization’s management should ensure they offer consistent training to increase cultural awareness amongst workers. Exposing employees to different cultural beliefs enables them to understand and appreciate the existence of such norms, thus making it easier for them to incorporate them within the diverse working industry. The companies should organize workshops to teach staff various aspects of the organization. This will ensure employees better understand the cultural context of the firm, thus improving their performance.
Third, organizations can implement effective cross-cultural communication within the workplace. A proper culture of passing information ensures that everyone within the entity understands the message. The management should ensure there is one common language that people can use to express their views. If other staff does not understand, a reliable interpreter should be made available to facilitate communication. The approach will allow maximum comprehension and appreciation of the people irrespective of their cultural background.
The emergence of International Human Resource Management (IHRM)
Currently, most businesses operate globally, and the tourism and hospitality industry is no exception. The sector is diverse and conducts its activities across borders, thus calling for the IHRM. The practice was initiated following the need to meet the expectations of shareholders. Since most organizations take advantage of emerging markets, proper human resource management is necessary to ensure the prosperity of the business enterprise (Fedyk et al., 2021). IHRM is aimed at ensuring proper allocation and utilization of the available resources to raise the value of the firm both at the regional and international levels.
The need to overcome competition at the national level is a contributing factor to developing the IHRM. The system effectively ensures the organizations are capable of achieving their international objectives by creating a pool of employees with relevant skills necessary in the sector. The practice allows tourism and hospitality entities to gain a competitive advantage over their rivals. IHRM is an important aspect of the corporate strategy because it facilitates staffing, training, and motivating the personnel to enhance the performance and success of the business organization. It is also effective in enabling the management to establish better compensation plans for the employees working overseas. Similarly, IHRM plays a significant role in promoting an understanding of different cultures that arise in the international context of tourism (Fedyk et al., 2021). IHRM is necessary for tourism organizations because it can easily promote workforce diversity, language, economic and cultural diversification. These aspects are essential for the performance of global businesses thus, they require an international perspective to understand and manage the entities towards the set objectives.
Importance of Leadership and Management Skills
The hospitality and tourism industry is a vast sector with a variety of services attracting people and employees from different backgrounds. It is a sensitive business since it deals majorly with a multicultural perspective. It, therefore, requires well-defined leadership and proper management skills to enable managers of the entities to facilitate a smooth operation that guarantees customers and workers a high level of satisfaction (Kršlak and Ljevo, 2021). With the growing influence of globalization, effective governance is necessary to ensure the company’s objectives are met.
Good leadership is essential in promoting mutual respect amongst workers in the organization. Tourism organizations employees many personnel, thus making it easier to experience a high disagreement rate between individuals. Therefore, managers are supposed to ensure there is an optimal correlation in the workplace by discouraging discrimination and other behaviors, which can result in hatred. The supervisors ensure there is unity and understanding that enhance collaboration and teamwork in the business.
Similarly, management skills such as problem-solving are essential for international tourism organizations because they enable leaders to effectively explore the causes of possible issues and then develop appropriate measures to curb them. For instance, if there is racial discrimination amongst workers in the company, managers can successfully use their abilities to determine the reasons for such behaviors, thus formulating a formative action towards the accused individuals.
Good leadership is also essential in enhancing the morale of employees, which improve the overall performance of the organization. Generally, there is high demand for talents in international markets; therefore, for a company to maintain available human resources, managers are often involved in practices such as appreciation and recognition of workers based on their efforts. When staff members feel valued by the firm, they commit and deliver the best services to the organization, giving the corporation a competitive advantage in the international market.
Moreover, tourism organizations have several departments that perform arrays of services. Good leaders encourage micromanagement practices where various divisions are assigned to different individuals. The approach of delegating duties makes employees feel part of the company, thus making them enjoy the work environment (Hoang et al., 2021). With limited supervision, staff members would gain the trust of the business organization, thus creating a loyal team that promotes the productivity of the firm.
Important Models of Motivation and Teamwork
In the tourism and hospitality industry, organizations need a high level of teamwork and cooperation from the employees to ensure optimal service delivery. Motivated workers enjoy their job functions, which leads to productivity and increased output. Collaboration is also essential in ensuring all the available skills and creativities are maximized to the benefit of the company. The sector recognizes the significance of motivating workers in the organization since the hotel workers are engaged in providing services to the guest every time.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
There are several motivation models that are significant to the tourism and hospitality industry. First is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs which states that employees have five necessities to satisfy as they continue working (Ștefan, Popa and Albu, 2020). According to this concept, hotel worker requires adequate salary to sustain their wellbeing. Second, they also wish for job security and working in a conducive environment. Third, individuals desire to belong to a given team where they feel valued. Fourth, professionals aim for recognition at the workplace to boost their morale and self-esteem. Lastly, after enduring and servicing the company effectively, workers would want to be growth-oriented and participate in the management of crucial roles. Despite the arguments, the model does not take into consideration other cultures that might have different wants. Similarly, it lacks empirical justification on how to rank the needs. When these aspects are met, the organization will be more productive because staff will be encouraged to work effectively.
Herzberg’s Model
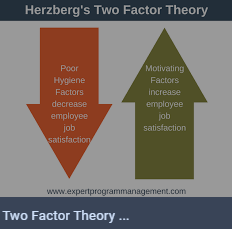
Another motivation model is Herzberg’s theory which states that employees’ morale is accelerated by hygiene and motivators. Hotel workers are known to work for long hours in the organization. They require a proper work environment with considerable salaries to boost their enthusiasm. The theory bases its argument on two main factors which play vital role in influencing satisfaction. Despite the contribution of the model, it has drawback, for example, the model did not use comprehensive measure of satisfaction. Even though the idea has some weakness, it is still applicable in evaluating motivation of workers.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding cross-culture management in tourism and hospitality management is essential in enhancing the organization’s performance. Cultural diversity is important in the sector because it enables firms to explore different skills and capabilities from various people. Globalization has resulted in the emergence of IHRM, which is necessary for international business performance. IHRM ensures that recruitment, language and diversity are well incorporated into the management to facilitate the achievement of business objectives. Furthermore, leadership and proper management skills are significant in the industry because they improve problem-solving abilities and other issues that can affect the company’s performance. Good leadership boosts the morale of workers, thus making it possible for the organization to retain most of its talent in the market. Staff motivation and teamwork are vital in promoting the performance of tourism firms. There are different ways by which a corporation can inspire and encourage collaboration in the organization. Recognition, considerable wages and job security are some of the motivating factors that keep workers aligned and committed to the achievement of business objectives.
Reference List
Birnbaum, H.J., Stephens, N.M., Townsend, S.S. and Hamedani, M.G., (2021) ‘A diversity ideology intervention: Multiculturalism reduces the racial achievement gap,’ Social Psychological and Personality Science, 12(5), pp.751-759. Web.
Fedyk, W., Sołtysik, M., Oleśniewicz, P., Borzyszkowski, J. and Weinland, J., (2021) ‘Human resources management as a factor determining the organizational effectiveness of DMOs: A case study of RTOs in Poland,’ International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. Web.
Hoang, G., Wilson-Evered, E., Lockstone-Binney, L. and Luu, T.T., (2021) ‘Empowering leadership in hospitality and tourism management: A systematic literature review,’ International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. Web.
Jiang, F., Croucher, S.M. and Ji, D., (2021) ‘Historicizing the concept of transcultural communication,’ Journal of Transcultural Communication, 1(1), pp.1-4. Web.
Jones, G., Chace, B.C. and Wright, J., 2021 ‘Cultural diversity drives innovation: Modeling in the global pharmaceutical industry,’ International Journal of Innovation Science. Web.
Kršlak, S.Š. and Ljevo, N., (2021) ‘Organizational creativity in the function of improving the competitive advantage of tourism companies in Bosnia and Herzegovina,’ Journal of Advanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(1), pp.81-91. Web.
Paudel, U.R., Puri, S., Parajuli, S., Devkota, N. and Bhandari, U., (2021) ‘Measuring cultural diversity impact in hospitality industry leadership: Managerial communication perspective from Five Star Hotels in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal,’ Journal of Tourism & Adventure, 4(1), pp.75-88. Web.
Shuck, B., Kim, W. and Fletcher, L., (2021) ‘Engagement at 30: a retrospective and look forward through an international cross-cultural context,’ Human Resource Development International, 24(5), pp.465-467. Web.
Ștefan, S.C., Popa, Ș.C. and Albu, C.F., (2020) ‘Implications of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory on healthcare employees’ performance,’ Transylvanian Review of Administrative Sciences, 16(59), pp.124-143. Web.
Appendices
Appendix A: Cultural Diversity

Appendix B: Motivation Model

Appendix C: Herzberg’s Model