Abstract
Math anxiety is supposed to be the feeling of nervousness for Young people when they have to solve mathematical problems. The paper discusses if young people have math anxiety from elementary school or it develops later as they grow. It gradually analyses all aspects related to this problem among children and later tries to give some solutions to cure this anxiety.
Introduction
Social research is a scientific study of society, and it is performed by sociologists. Sociological research explains the issues which affect us as individuals and as members of any group. This kind of research is helpful in establishing the relationship between personal troubles and public issues. It also helps us in understanding how our social background can influence our educational achievement. “Research is the purposive and rigorous investigation that aims to generate new knowledge… Social research is about discovery, expanding all horizons of the known, confidence, new ideas and new conclusions about all aspects of life” (Saratakos 2004:4 as cited in Sociological Research, n.d.).
There are some ways of doing research, such as questionnaires. It is very important to choose any research tool on the basis of its advantages and disadvantages. The foundation of sociological research depends upon some terms- methodology, methods, theory, and epistemology. Crotty has explained the meaning of all the terms as follows:
- Methods are the technique to collect data, which is related to the hypothesis.
- The methodology is the plan of action in which some particular methods are used to get results.
- The theoretical perspective is the philosophical standpoint that provides a context for the process.
- Epistemology is the theory of knowledge which is implanted in the methodology (Crotty 2003:3 as cited in Sociological Research, n.d.).
Studying sociology is very important since it helps people to understand the world around them in different ways. Those different approaches influence the research and form the views of the researchers, and in this way, the best result can be obtained.
Research problem statement
The present research is based on Math anxiety and the effect it has on children with a learning disability.
Aim of the research
The main aim of the research is to find out if Math anxiety has an effect on children with a learning disability. It also aims to find if young people have math anxiety from elementary school, or it develops later as they grow. It also concentrates on surveying different groups of kids studying in different grades.
Research Hypothesis
Knowing about the causes of math anxiety at the earlier stage and its solution for the young generation.
Literature Review
Math anxiety is a pessimistic response to situations where one has to do mathematical tasks, and it is taken as a threat to one’s confidence. Some people call math anxiety as a feeling of nervousness, rational ineffectiveness, and vulnerability when it comes to solving mathematical problems or to work with numbers (Rubinsten & Tannock, 2010).
The arithmetic word problem is considered to be a significant problem in the elementary school mathematics curriculum in connection with developing general problem-solving skills (Leh & Jitendra, 2012).Though many studies have been done on the subject of math anxiety, yet it is difficult to find out when math anxiety in young kids emerged. “Indeed, most studies of math anxiety have focused on middle school or high school students, and the few published studies investigating math anxiety in elementary school have focused on children who are in fourth grade or beyond” (Bush, 1991;Chiu & Henry, 1990; Suinn et al., 1988, as cited in Ramirez et al., 2013, p.188).
Ramirez et al. (2013) examined math anxiety in young children and tried to find out whether it is present in elementary school in first and second-grade students too. “It is important to address math anxiety at the earliest possible ages because early math anxiety may ‘snowball’ in ways that lead to increased anxiety, dislike, and avoidance of math” (Wigfield & Meece, 1988 as cited in Ramirez et al., 2013, p.188).
Ramirez et al. (2013) has revealed that “Math anxiety may negatively impact math performance by co-opting the limited working memory (WM) resources that are crucial for successful math problem solving, which we refer to as ‘WM disruption’ (Ashcraft & Kirk, 2001; Ashcraft & Moore, 2009; Engle, 2002; Young, Wu, & Menon, 2012, as cited in Ramirez et al., 2013, p.188). It is hypothesized that young children with high WM can perform poorly in math because of math anxiety.
The ecological model of human development tells about the ecological subsystem, and the central part of this subsystem is the family. In a child’s development and learning, home and family play an important role. According to the ecological model, a child also influences his family. As a consequence, a disabled child affects his family in a special way. According to the National Joint Committee on Learning Disabilities (1997, p. 29 as cited in Dyson, 2010),
“Learning disability applies to a heterogeneous group of disorders manifested by significant difficulties in the acquisition and use of listening, speaking, reading, writing, reasoning, or mathematical abilities. These disorders are intrinsic to the individual, presumed to be due to central nervous system dysfunction, and may occur across the life span” (p. 44).
The families of children with more visible disabilities like sensory, intellectual, physical, etc. have more child-related stress than the families which do not have disabled children. Dyson (1997) mentions that two different studies done to find out the stress level of these children’s parents gave two different results- one study revealed the same stress level of mothers and fathers of such children, but another study revealed that mothers of such children were more stressed and due to this they had poor health.
Researches show that siblings of the children with learning difficulties also get affected by them. Dyson (1999) got mixed results after doing studies for four years. At the same time, siblings of children with developmental disabilities showed worse self-concept than their opposite numbers of siblings who had no developmental disabilities (Dyson, 2010).
Studies are being done to create the basis for recommending interference to lessen the dominance of learning disability (LD). It is important for the core elements of primary grade curriculum, which is essential for future academic development: in reading, comprehension, and word level skill; in math, word problems, and number combinations. Studies reveal that the students having a reading problem or math problem can progress in a better way if they are provided with effective tutoring. Such tutoring classes can be conducted 3-4 times per week for 30-45 minutes per session, and it should go for 12-20 weeks (Fuchs et al. 2012).
If the students with severe learning difficulty get high-quality tutoring, they easily catch up to their classmates, and also this kind of tutoring create a strong foundation for them to experience continuing success (Fuchs et al. 2012).
Peer tutoring is also considered one of the most effective strategies for mathematic instructions. The planned guidance format of peer tutoring helps students who have difficulty in this subject. Peer tutoring does not involve any professional teachers rather it involves various social groups who help each other in learning and learning themselves by teaching (Tsuei, 2014).
According to Vygotsky, the role of private speech is very important for the development of higher psychological functions like executive functioning, planning and behavioral self-regulation. A lot of different features of children’s private speech have been investigated by the researchers, which consists of children’s task performance and on-task behavior. “The use of input through the auditory channel to form connections between the phonological features of numbers has been discussed as an approach to learning number facts” (Robinson, Menchetti, & Torgesen, 2002 as cited in Ostad, 2011, p.292).
Some other studies reveal that verbal and visual strategies improve problem solving skills in children who have math difficulties (Kolloffel, Eysink, de Jong, & Wilhelm, 2009;
Montague, 2008; Van Garderen, 2007; Xin, 2008as cited in Swanson et al 2013).Reading and generative strategies have been found very effective in improving comprehension. Generative learning helps the students to paraphrase the text either orally or in writing before they respond to questions about any text. This strategy helps the students to understand the material deeply.
Methodology
This section will provide an overview of the methodology and the data collection tools used in doing the survey about Math anxiety, and the effect it has on children with a learning disability
The present research is a qualitative as well as quantitative analysis of the given topic. It uses a descriptive survey design to investigate the effect of math anxiety on children with a learning disability. The findings provide a detailed analysis of the data from a given population to determine the status of math anxiety.
According to Dawson (2009), it is important to know the difference between qualitative and quantitative methods before research methodology starts (Research Methodology: An Introduction, n.d.).
Qualitative research involves subjective data. Dawson (2009) mentions that qualitative research focuses on behaviour, attitude and experience through the methods like interviews. Since attitudes, behaviour and experiences are very important so this kind of research tries to get in depth feeling and opinion from the people who participate in the survey (Research Methodology: An Introduction, n.d.).
Research Methodology
This part of research deals with research methodology that was employed in conducting the study. It, therefore, covers the research locale, research design, target population, sample selection, research instruments, conducting, reliability of research instruments, validity of the research instruments, data collection procedures, data analysis, and reporting.
The research methodology that was used in the study is the combination of qualitative as well as quantitative research methods. By using this methodology, the hypotheses of the research questions can be measured, determined, and analysed. The method also helped in determining the quantity and consistency of results.
Moreover, the survey provided important statistical quantitative data to compliment and confirm the findings presented by qualitative data.
The statistical survey provides standardized information about the research subject. It is a well-organized way to gather information regarding the understanding of a subject by a large number of respondents. For the purpose of this study, Likert scale, a bipolar scaling method, is used to construct the questionnaire.
Likert scale is used to construct questionnaires to get psychometric replies from the people. It aims at obtaining the degree of agreement or knowing the preferences of the respondents. These scales do not use comparative techniques, but rather evaluate a single feature. The level of agreement has to be shown with the statements in an ordinal scale (Bertram, n.d.).
The design is best suited for this study. The purpose of the study is to study the effect of math anxiety on children with a learning disability.
Quantitative research methodology is used because data (perceived effectiveness) being tested in this study was through various sources which support it. The study is guided by the actual data collected from the respondents, and the purpose of the study is to analyze them.
The study involved the use of the questionnaires. These were prepared in advance, and the questions were reviewed to find their relevancy in the concept being investigated. The language used in the questionnaires was relatively moderate to be understood by the people and the procedure was understood.
Population and Sampling Procedure
The population of interest for this study is 20 students from different schools. A large no of participants is used in the sample. Since this is a descriptive design, sampling is a significant process because of the need to obtain an accurate representation of the population (Heck, 2004).
Instrumentation
Survey questionnaires were used as the research instrument. The survey was a face-to-face interview. In a face to face interview, all the participants were provided with survey questionnaires in order to determine their perceived level of explaining their views on math anxiety and its effect on them. The survey instrument was based on the general type of questions related to their understanding about math anxiety. There were two types of questions open-ended and closed, targeting different groups from different schools.
Reliability
The data collection method that was used needed to be clearly defined and described; in terms of the how instrument has been tested and validated by past studies (Sunderman et al., 2004). The strategy for obtaining good measures for the study involves upholding the relevance and appropriateness of the study for the data collected and the purpose of the study. Thus, the instrument section clearly defined the processes for this method, which will enable future researchers to duplicate the study.
In order to uphold the reliability of this study, the participants were selected according to their various grades. The questionnaires targeted students from different schools as per the setting of its questions.
Data Collection Procedures
The research captured both primary and secondary data to get proper answers of the research questions. For this study in depth interview was chosen as data collection method. The questionnaire was used for in depth interview. Each participant was asked 5 open ended and 5 close ended questions. Every question was explained by the researcher to make sure that the respondent understood the question and was comfortable to answer. This survey lasted for half an hour.
Ethic Issues
The qualitative research has different ethical problem in comparison to quantitative research. The ethical conflict occurs in connection to how a researcher approaches a group and what kind of effect he may have on the participants. Respondents were made aware of the purpose of the study, the researchers agreed not to reveal the identities of the participants and not to disclose their personal information for ethical reasons. All the respondents were made sure that their views on any questions would be kept confidential. This was to win their trust so the quality of data could be good.
Primary Research Findings
This dissertation presents the finding of the primary research. The primary research was conducted by making questionnaires and those questionnaires were distributed among 20 participants. The participants were divided in two groups- middle school and high school. This research was carried out to collect data. Each participant was explained clearly each and every question.
The results of the interview are shown below:
When asking about if they were afraid of going to math class and hesitate in asking questions, most of them from middle as well as high school students gave their affirmation that they felt nervousness and anxiety in math class. Numbers always made them dizzy.
Fifty percent of them said they feared math test though other fifty percent of the students said that they did not fear math test rather they were much worried about math test results. Middle school and high school students both confirmed that math was going to get tougher according to level of standards and it was tough to remember math formulas.
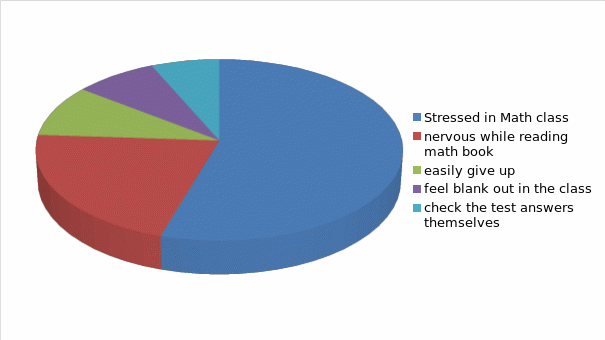
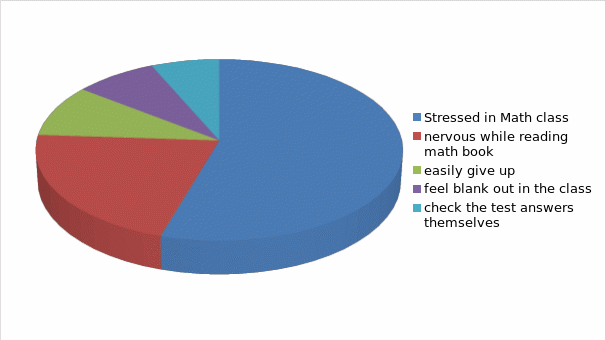
The above mentioned data shows that 59 percent of the students got stressed in math class and forgot equations. 23 percent of the students stopped reading the math book when they felt nervous about the subject. 10 percent of them easily gave up when they did not find the solution of the problem. 9 percent of the students felt blank out to identify any math problem and its solution. 7 percent of the students tried to check the test answers.
Conclusion
It has been observed that middle school and high school students face lots of problem to score better in math. This is due to math anxiety among such students. It is troublesome to have math anxiety since it influences negatively math grades and math knowledge in young people. In present time where the world is increasingly connected, it is very important that young people construct self-confidence in their ability to do mathematics since insufficiency in this area can create lots of obstacles in many aspects of life.
Questionnaire
Type A: Open ended Questions
- Are you afraid of going to math class?
- Do you hesitate in asking questions in math class?
- Do you fear math test most than any other test?
- Do you always think that math is going to get tougher as you go in high standard?
- Do you feel that it is difficult for you remember math formulas?
Type B: Tick any one of options
References
Bertram, D (n. d). Likert Scales…are the meaning of life, CPSC 681 – Topic Report. Web.
Dyson, L. (2010) Unanticipated effects of children with learning disabilities on their families, Learning Disability Quarterly. 33 (1), 43-55. Web.
Fuchs, S.L., Fuchs, D.& Compton, D.L. (2012). Intervention effects for students with Comorbid forms of learning disability: Understanding the needs. Journal of Learning Disabilities. 46 (6), 534–548. Web.
Heck, R. (2004) Studying educational and social policy: Theoretical concepts and research methods. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. Web.
Leh, J.M. & Jitendra, A.K. (2012) Effects of Computer-mediated versus teacher-mediated Instruction on the Mathematical word problem-solving performance of Third-grade students with Mathematical difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly 36 (2), 68–79. Web.
Ostad, S.A. (2011). Private speech use in Arithmetical calculation: Contributory role of phonological awareness in children with and without Mathematical difficulties. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 46 (4), 291–303. Web.
Ramirez, G., Gunderson, E.A., Levine, S.C. & Beilock. S.L. (2013) Math anxiety, working memory, and Math achievement in early elementary school. Journal of Cognition and Development, 14 (2), 187-202. Web.
Research methodology: An Introduction (n.d.) Web.
Rubinsten, O. & Tannock, R. (2010) Mathematics anxiety in children with developmental dyscalculia, Behavioral and Brain Functions, 6, 46. Web.
Sociological research (n.d.), Chapter 3. Web.
Sunderman, G.L., Tracey, C.A., Kim, J. & Orfield, G. (2004), Listening to teachers: realities and no child left behind. Harvard Civil Rights Project.
Swanson, H.L., Moran, A., Lussier,C. & Fung, W. (2014) The effect of explicit and direct generative strategy training and working memory on word problem-solving accuracy in children at risk for Math difficulties. Learning Disability Quarterly, 37 (2), 111–123. Web.
Tsuei, M. (2014). Mathematics synchronous peer tutoring system for students with learning disabilities. Educational Technology & Society, 17 (1), 115–127. Web.