Introduction
Cells are made in such a way that they are able to communicate with each other. This communication takes place through messages that are sent in regard to the various shapes taken by proteins. The mechanism of sending signals by various cells therefore is significant as it enhances that message from the surface of the cell gets to reach the nucleus of the cell. The proteins responsible for sending the various signals play an important role in ensuring that a cell is able to retain its shaped. In case there are changes that occur in the signaling proteins, such changes may cause problems. Mutation is a common change that occurs in signaling cells and usually results in interference on the signals that are sent to the cell and consequently cancer may occur within the cell. Oncogenes are the genes responsible for causing transformation of the cell once mutation has taken place.
Main body
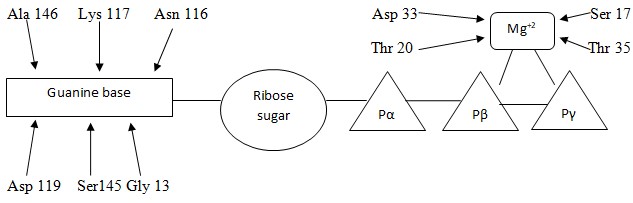
G proteins are a large family of proteins with various subfamilies. Ras Proteins are one of the various subfamilies of G Proteins. These proteins have a comprehensive structure in terms of dimensions and have various atoms which facilitate the functioning of these atoms. One such atom is Mg+2 which is responsible bringing atoms of oxygen thus ensuring that nucleotides are bound. Usually, a ras protein is bound to GDP when the protein is in its natural state. When signals are released by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), these signals play an important role in ensuring that GDP is released and hence ensuring that GTP is bound to the protein. These signals are halted when hydrolization of GTP to GDP takes place. All the parts that are instrumental in ensuring binding of nucleotide are normally similar in all proteins under the G proteins family. The exchange time for either GTP to G proteins or GDP to G protein varies and may last from a few minutes to several days. GTP brings about a change in the arrangement of proteins and this leads to an activation of mitogen flow. Consequently, phosphorylation takes place and the message that was sent will have been delivered
Protein Fold
A keen look at the structure of the ras protein for the interior shows that it has helices which are five in number which are to be found on the top most part of the protein. In addition, there are strands which are six in number and are right handed. The residues of hydrophobic and hydrophilic processes have been identified in the diagram below using different colours with the hydrophobic residues being represented by blue colour while the hydrophilic is represented by the red colour. In he figure below, the residues which are hydrophobic are directed towards he inside while the hydrophilic are facing towards the outside of the molecule. This kind of distribution is referred to as amphipathic distribution. Key variations exist between the helices that have been exposed on the surface and those that are buried inside the protein. The arrow in the diagram points at helices that are to be found within the structure. Usually, the helices that are buried have more patches that are hydrophobic ion nature and this results to greater stability.
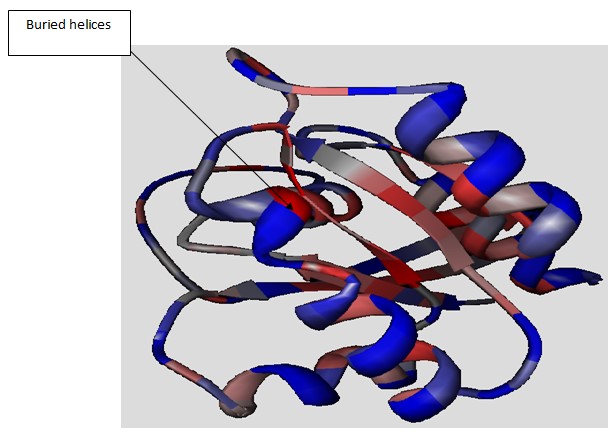
Surface Properties of Ras Proteins
The surface of the ras protein is hydrophilic in nature. This is because there are many amino acids on the surface of this protein and a good number of them are hydrophilic. These amino acids include Arginine 128, Aspartic acid 47, lysine 88 and Glutamine 43. A closer look at the molecule indicates that the inner part also has hydrophobic amino acids and so are the sides of the molecule.

As already mentioned the intrinsic activity of GTPase possessed by ras protein is responsible for the conversion of GTP to GDP through hydrolysis of gamma phosphate from the GTP making it possible for the ras protein to automatically change from an active to an inactive mode. The regulation of proteins and the exchange factors is done through upstream which is a process that starts at the receptor level which is to be found in the membrane of the cell. Due to the regulation that takes place at the membrane of the cells, consequently as stimulations of cells takes place the level ras GTP in the cell increases.
The Ligand Binding Site
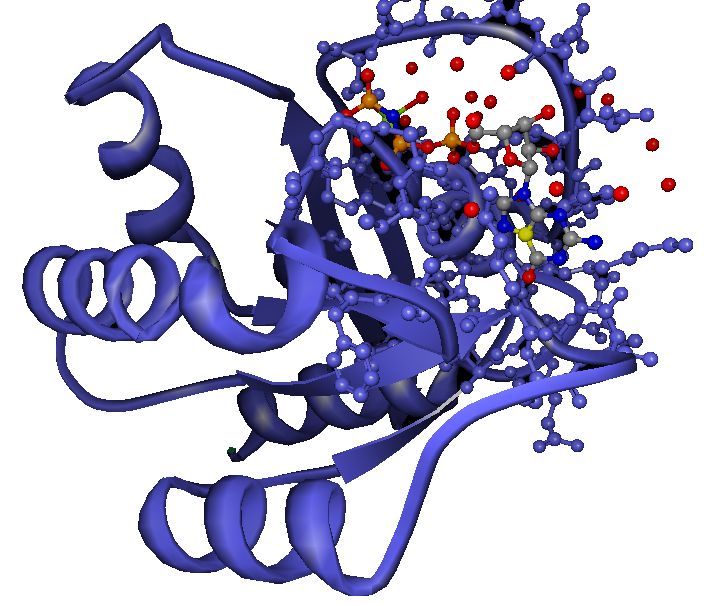
When a ras GTP is in its active mode, it has the tendency of binding itself to another effector which could be one or several effectors molecules. As a result of the binding, the signals are relayed to the molecules on the down side also known as downstream and finally the signals get to the factors responsible for transcription which have the effect of altering the expression of RNA that are found in the nucleus.
It is therefore correct to state that the functioning of the ras protein takes place within a cascade that is controlled by signals. The amount of signals as well as their levels that pas through the ras protein is highly dependent on how balanced the ras GDP and the ras GTP are in the cell. Activities that are likely to cause balance that is directed towards ras GTP usually will prevent activities that are known as downstream activities. On the other hand, activities that causes a balance that is directed on the ras GTP side causes an activation of downstream activities.
Simply put therefore, ras protein is type of protein whose main purpose is to oversee the growth of a cell. The cycle of a cell undergoes four phases of growth namely the G1phase of growth which is then followed by the S phase of growth. Under the S phase, the DNA found in the cell is doubled. The next stage is known as G2 and the final phase of growth is known as mitosis which involves the division of a fully-grown cell to form a new one.
Conclusion
The ras protein has the ability to bring modifications to the cycle of a cell. When a cell is normal, the ras protein will go back to a state of being inactive after replacing GTP to GDP. However, in case of mutation the ras protein remains in an active state stimulating even more growth of the cell without control and the result is that cancer is likely to occur in such a cell.
