Introduction
Background of the Study
Founded in 1907, the United Parcel Service (UPS) is an American-based logistics company. The company relies on its information management systems to undertake most of its operations. This report provides an information management plan for the year 2019.
How to use this Report
The data presented in this plan differ from those of previously published IT management reports because of changes in company programs and developments in innovation. Therefore, it should be assessed in the context of the company’s current internal and external environment.
Terms of Reference
- Due to the network effects of implementing the strategic proposals outlined in this report, it is necessary for team members to work in synchrony.
- A UPS-appointed steering committee should coordinate activities relating to this IT management plan.
Variation to Terms of Reference
- The terms of reference may be reviewed in consultation with the company’s chief executive officer as well as a board of directors
Project Constraints/ Assumptions
Constraints
- The project has to be completed within a fixed period
- The existing system should not be interrupted when implementing this plan
Assumptions
- Dedicated personnel from the company’s information technology department will implement this strategic plan
- There are adequate resources to implement each aspect of the information technology plan
The Business Model
Statement of Business Direction
The information management plan will be used to improve organizational performance by meeting the logistical needs of different groups of clients. The operations of UPS are also designed to make the enterprise financially sound by improving employee buy-in through a broad employee ownership formula. Employees are expected to support the organization’s processes because they will receive a long-term competitive return on their investments. Inspiring employees to do their best will also maximize employee support.
Operational Concerns, Problems, and Needs
- Managing overheads
- Monitoring Performance
- Responding to competition
- Listening to feedback
- Regulation and compliance
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
Table 1 below presents a summary of UPS’s SWOT analysis.
Table 1. SWOT Analysis (Developed by Author).
Business Constraints
- Physical/Resource Constraints
- Market Constraints
- Policy Constraints
- Material Constraints
External Constraints/Deadlines
Competition from business rivals and the prevailing legal environment are the main external constraints affecting this IT management plan.
Internal Constraints/Deadlines
The implementation of this IT management plan could be constrained by the company’s culture and the internal policies and procedures governing its processes.
Technical Constraints
The limited availability of technical staff to implement the IT plan is another constraint of the IT management plan. There should also be a proper IT infrastructure to implement some of the recommendations outlined in this plan.
Business Aims and Objectives
Aim: Serving the logistical needs of customers and providing excellence and valuable services
Objectives
- Maintain a financially sound company with a high level of employee buy-in
- Inspire employees and business partners to serve customer needs
- Leading by example as a strong, sustainable, responsible, and caring organization
Critical Success Factors (CSF)
- Timely deliveries
- Safe deliveries
- Excellent reputation
- Competitively priced services
- High levels of customer satisfaction
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Employee retention rate
- Employer of choice index
- Transportation intensity index
- Energy consumption rate
- Lost time injury frequency (UPS Sustainability, 2014)
Current Situation Assessment
Structure and Design
Conceptual data model (strategic model/matrix)
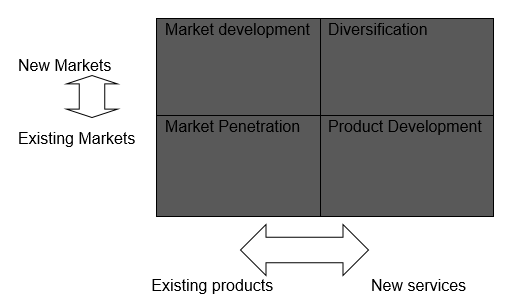
AT UPS, the strategic model mix is hinged on four key pillars: market development, diversification, market penetration, and product development. This marketing mix model cuts across current and existing markets as well as existing and new products and services. Table 2 below highlights the composition of this matrix.
Information gaps
- Data proliferation
- Data analysis gaps
- Data integration challenges
- Lack of support by senior management
Data Storage
Legacy systems will be evaluated based on how well they complement the use of newer methods of data management. Those that have a low level of alignment will be eliminated. Comparatively, the customer relationship system will be premised on an assessment of customer feedback. Online surveys will also be undertaken to assess customer satisfaction standards. Data movements across these systems will happen via an integrated application for monitoring the overall organization’s performance. The entity source system-mapping document is outlined in figure 1. The assessment of information systems and architecture will be undertaken by assessing online transaction processing systems (OLTP), operational data stores (ODS), data warehouses, and data marts. These four key areas of assessment will be assessed based on their speed of efficiency and user-friendliness.
Enterprise data management strategy
The enterprise data management strategy will be premised on six key pillars: performance assessment, a definition of deliverables, determination of standards policies, stakeholder education, investment in the right people, and quality.
Data Movement
Data movement will be undertaken virtually because there will be no physical transfer of documents. However, there will be physical safeguards to restrict the movement of unauthorized personnel in and out of the company’s rooms that host IT facilities. Master, data will be collected and distributed to other systems through data consolidation, federation, and propagation using point-to-point transfers.
Data Security and Recovery Strategy
UPS’s data recovery strategy will be developed for purposes of improving systems applications and data management. The priorities for IT recovery will be aligned with the goals of the business. Similarly, the recovery time for the IT plan will also be matched with the recovery time for business functions, as recommended by Peppard and Ward (2016). Since some of UPS’s business applications cannot accommodate long periods of downtime, they will rely on dual data centers which will ensure process continuity if one system is down.
Metadata
The process of managing metadata will involve the identification and layout of policies and procedures. Here, the role of all project team members will be highlighted in the management plan. The personnel will be accredited and possess the right skills in data analytics to be included in the overall plan. Data management tools that will be used include spreadsheets and Oval Edge. The information gap that these tools will help to address will be poor coordination in data management.
Data Quality
Data quality management will be undertaken by tracking the effectiveness of data quality improvement initiatives. UPS has the capability to undertake this function because of its advanced data analytical systems.
Project Management Methodology
The software development lifecycle will include five key steps: planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. The requirements analysis will be conducted through a technical feasibility study, which will identify how to implement the plan with minimal risks. Data quality requirements will be assessed using an SRS (Software Requirements Specification), while quality assurance will be observed by investigating whether there are product defects, or not.
Human Resource Strategy
The roles and responsibilities of the human resource personnel will be documented on the company’s duty roster for all employees to read and understand. The roles and responsibilities will also be consistent with information management requirements because the skills and qualifications of each employee will be matched with their job requirements. Table 3 below explains the roles of key members of the implementation team.
Table 3. Human Resource Strategy (Source: Developed by Author).
Management Information Requirements
The management information plan needs to be aligned with the requirements of the existing system. In other words, the information has to be obtained from a reliable source before it is considered for use. So far, UPS is undertaking several new projects and new information requirements will be aligned with those of old projects.
Business Intelligence Strategy
The business intelligence strategy will be implemented by understanding how to use existing company strengths to exploit market opportunities. In line with this understanding, metadata management will be pivotal to the business intelligence strategy because the information will be centralized and assessed using meta-analytical techniques. Therefore, analytical software is a tool to execute this plan, while the skills that will be required to undertake the plan will be premised on the technical requirements of project implementation. Overall, this strategy will be aimed at bridging information gaps that cause poor coordination.
Change Management Strategy
The change management process will be operationalized by reviewing how current organizational processes address future needs. Comparatively, the release management process will only be initiated when all the project objectives are completed. Current resources at UPS are adequate to undertake information management projects.
Information Management Policies
Information management policies that characterize the IT management plan will be assessed based on international standards of operation. These global standards will cover different aspects of information management, including the structure and design of the IT management plan, data storage standards, data movement best practices, data security, metadata analysis, data quality management, human resource policies, and change management policies. Gaps between existing and international standards of operation will be assessed by evaluating how best each strategy meets the IT management goals. Those that support the accomplishment of such goals will be preferred to those that do not.
Data Management Strategy
The data management plan will be predicated on accomplishing the overall goals of the IT management plan, which is to enhance service delivery at UPS. As mentioned in this report, some of the tools that will be involved include relevant software and IT infrastructure (hardware). The main roles and responsibilities for executing the overall plan will be distributed to three main members of the project team, who are the business analyst, project team member, and project manager. Lastly, policies, standards, and best practices will be benchmarked with international standards of operation.
Information Management Policy
The information management policy will be based on accreditation whereby only authorized people should be privy to the activities in the information management plan. This strategy is aimed at safeguarding business processes from security breaches.
Information Management Strategy
Outline Solution
Information management framework
The information management framework should be designed in a manner that aids in the accomplishment of organizational goals. This way, there will be a better understanding of the scope of data to be collected and their effects in supporting the realization of the organization’s goals. In cases where large data need to be managed, a phased approach of incremental variables should be adopted.
Data management framework
The data management strategy will be initiated if there is a loss of function in the computer room environment, hardware (networks, servers, etc), connectivity to a service provider, software applications, and data restoration programs. Therefore, the data management framework will be premised on the proper functioning of these key elements of the company’s information technology strategy.
Project management framework
As part of the data recovery plan, there will be an internal data recovery strategy, which will be operationalized because UPS has access to more than one facility. The hardware that will run the alternate facilities will be configured to use similar hardware and software configurations. If data is backed up off-site, information will be restored from the offsite location, thereby allowing for business process continuity. The resources that will be used to implement this strategy are listed below:
- Computer Security resource center
- Contingency planning guide
- Guide to testing and training
- Developing an information security awareness program
Human resource strategy
There will be an in-house consultative expert to manage enterprise data. Investing in the right people will help to identify the right technologies to use.
Change management methodologies
It is important to educate and inform stakeholders about impending changes to gain their support for new policies. Doing so will ensure that stakeholders understand the change management process and techniques that would be used to execute the strategies.
Business intelligence framework
The business intelligence framework will involve a definition of data flows and the establishment of common data types that need to be included in the overall model. The information assessment strategy should match the type of data available for review.
Release management
Existing standards, policies, and procedures will be used to keep data where it needs to be. The goal is to minimize the possibility of corruption and security breaches. Employees should use the same standards, policies, and procedures to meet the current operation criteria. These policies and procedures should also be used to improve adherence to regulatory standards that govern the operations of UPS.
Implications on Business and IT Department
The UPS Worldship program will be used to facilitate the fast and efficient delivery of goods and services across the UPS network (UPS Sustainability, 2018). It will also help in customized documentation by increasing the speed and effectiveness of delivering packages across the UPS network. At the same time, the strategy will make it possible to customize business rules, thereby influencing shipment characteristics, such as transportation modes and delivery times. This strategy will also make it possible to manage transportation expenses across the entire value chain.
Logical Dependencies
The development of the information technology strategy will depend on the accurate identification of users because the target audience will dictate whether native or hybrid strategies will be adopted. The development of the information technology strategy will also involve a determination of the methodology that will be chosen to develop new applications. Agile and waterfall methodologies are under consideration (UPS Sustainability, 2018). In the waterfall methodology, the parameters for development have to be established first before a step-by-step method is adopted in application development. Comparatively, the agile method technology allows work to be developed simultaneously across different sections of application development. Therefore, different sections of the application should support each other.
Recommended Implementation Method
The UPS Shipping Application Programming Interface (API) will be central in implementing the e-commerce strategy. It will also be pivotal in integrating the company’s shipping functionality into its enterprise system. This strategy will reduce the need for undertaking manual processes of information analysis, thereby providing seamless management of shipping processes.
Hardware, Communications, and Software Requirements
Identifying required hardware, communications, and software requirements will depend on an analysis of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the UPS. The goal will be to understand the business environment – a process that is vital in decision-making. The aim of undertaking this strategy is to improve resource allocation plans to maximize strengths and minimize organizational weaknesses.
Metadata and Data Quality Support Considerations
The use of a virtual marketplace to undertake business functions has created a new platform for increasing corporate revenue and the level of competition for UPS. To address some of these challenges, the UPS marketplace shipping strategy will be seamlessly integrated with major online marketplaces. This way, the customers will have greater access to a shipper they trust and that will provide them with the service they require.
Change Management and Control
The change management control of the proposed IT plan should be overseen by UPS’s IT director because his department has developed most of the applications that will be used in the model. In other words, there is no need to contract third parties to undertake change management and control. This strategy is aimed at reducing the overheads. These functions of the IT plan should also be merged with those of the marketing department because the latter will help identify the go-to-market strategy.
In this collaborative framework, questions relating to the platforms to target and how to convey the company message will be explored. Additionally, to make the overall strategy visible to users in the market, UPS should leverage application and banner advertisements. Using coupons and ad-specific offers will also be employed as part of the overall business strategy.
Configuration Management
Configuration management should be done through the identification of users. Since users are diverse, it is essential to identify those who will appreciate the products offered. Different demographic characteristics will be used to distinguish these customers. They include age, gender, and occupation. This strategy will be instrumental in personalizing the company’s services to meet the needs of each customer segment.
Information Management Plan
Planning Assumptions
- Dedicated personnel from the company’s information technology department will help to implement this strategic plan.
- There are adequate resources to implement each aspect of the information technology plan.
Phasing – Mobile Strategy
Information management will be integrated into the organization’s overall plan through a mobile strategy. This strategy will involve the use of mobile technology in the operationalization of UPS’s corporate strategy. The overall mobile strategy that will be used in the organization will contain several key steps, which will be aimed at improving the user experience. The first step involves the alignment of the mobile strategy with the organization’s vision. Here, emphasis will not only be on designing a mobile phone application that would bring business to the company but also one that would exist in the long run. In line with the vision of aligning the company’s mobile strategy with its overall vision, the mobile app will also be designed in a manner that the end-user processes reach the target users of the applications.
Another step of the mobile strategy would be to define the pitch. Here, there will be a proper definition of the new applications. In this part of the strategy, the new strategies will be established as the locus of IT control.
For example, mobile applications could make payments much easier to complete. Alternatively, a “loyalty point” feature could be introduced on the mobile platform by allowing frequent UPS users the added benefit of enjoying extra services at discounted prices because of their loyalty to the company. The goal of implementing this strategy is to improve brand loyalty. The last stage of the mobile strategy will involve a determination of the testing practices. The first part of this strategy should be an understanding of the roles and duties of each member of the testing team. Here, the structure of the test plan and its operating systems should not differ because the test scores need to be standardized.
Development Schedule and Milestones
The overall IT plan should be implemented within two years. Key milestones that should be achieved during this period are outlined below.
- 70% of UPS processes be undertaken virtually
- Integration of mobile technology in the user engagement platform
- Alignment of IT goals with the overall business plan
Transition Overview and Issues
- Resource Availability
- Availability of technical knowledge
- Alignment of data types
Staffing Requirement Training Needs
- Have knowledge of IT systems
- Must undergo mandatory training in information systems management
- Staff must have at least two years of experience in information management
Cyber Security and Compliance Strategy
The overall goal of the cybersecurity strategy is to protect UPS’s systems, programs, and data from security breaches that could jeopardize its operations. To ensure there is adequate compliance with the firm’s cybersecurity program, the standards of operations in the company’s cybersecurity program will be designed to meet global standards. In line with this strategy, the cybersecurity program will have 10 key tenets listed below.
- Business Alignment
- Gap/Risk Assessment
- Assessment of cybersecurity risk
- Identification and mitigation of risks
- Compliance management
- Identity and access management
- Network security and application
- Physicals security management
- A disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity
- Operational security
The ten key tenets of the cybersecurity plan outlined above have been developed with the organizational requirements of UPS in mind. Here, it is imperative to point out that UPS heavily relies on information technology programs to carry out key functions such as parcel tracking. The process of organizing parcels is also dependent on similar techniques from the point of receipt to the point of actual dispatch.
A security breach in any of the company’s processes could result in significant delays or inconveniences that may lead to customer dissatisfaction. The ten key tenets of the cybersecurity plan outlined above are designed to address these key areas of vulnerability in UPS’s operational plan. For example, the physical security management plan complements the virtual security strategy because it restricts access of unauthorized persons to the company’s key installations.
E-Commerce Strategy
For a long time, UPS has used e-commerce to leverage its growth (O’Shea, 2016). This is why the company has made a commitment to invest in e-commerce despite the turmoil and obstacles that stand in the way. To bolster its e-commerce strategy, the company needs to continue making more investments on this platform, as was seen in its plan to buy 14 new freight jets despite increased competition from other players in the market, such as Amazon (O’Shea, 2016). The e-commerce strategy will include the UPS Ready Program and the UPS Capital Merchant Services.
UPS Ready is a program developed by the UPS information technology department as software that offers solutions to customers during package tracking. The solution is both plug-and-play as well as customizable to allow users to find unique solutions to different company issues. In other words, the UPS Ready platform allows for easy matching of customer needs with service providers (UPS Sustainability, 2018).
For example, this strategy has made it easier to match customer needs with warehouse management technologies and customer relationship management (CRM) methods. In line with this development, the provider application software will be merged with UPS application systems to streamline virtual operations across the order, dispatch, and delivery processes. Lastly, the UPS capital merchant services will be used to facilitate the payment of services because it allows for the use of multiple forms of electronic and mobile payments. For example, it allows a customer to pay using all major credit cards, debit cards, and e-checks, and gift cards (O’Shea, 2016).
Data Visualization Strategy
UPS will continue to rely on the On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation (ORION) program to transform contemporary delivery systems (CIO Review, 2014). It has taken more than 10 years to develop the application for use in the management of parcels (CIO Review, 2014). The information used on the platform uses data obtained from gathering information about customer preferences and real-time traffic information.
The ORION system has been partially implemented and the next phase will be executing it in its entirety. The goal of implementing this system is to increase the efficiency and productivity of the parcel delivery process and, by extension, other operating systems that adopt the same model as the delivery system. For example, there should be more focus on rerouting the roads or routes taken by drivers to deliver goods and services to make delivery processes smoother. This strategy is a product of the company’s mantra, which is to drive less and deliver more (CIO Review, 2014).
The partial implementation of ORION shows that the company has saved a lot of money in the delivery of goods to its customers. The savings have mostly been quantified in terms of fuel savings because, since its inception, the ORION has saved the company 15 million gallons of fuel (CIO Review, 2014). There have also been time savings that have been accrued from the implementation of the model because 85 million lesser miles have been driven since the implementation of the program (CIO Review, 2014).
These gains have also resulted in extra benefits because the company has reduced its environmental impact (pollution) because fewer cars are being used and the ones that are on the road are being driven less. While data visualization is an important step in designing delivery routes, it is vital to educate all stakeholders (especially supervisors and planners) on how it works.
Another strategy of data visualization that needs to be pursued is the implementation of an online offering called My Choice. This application will help customers to place their orders conveniently because it has features that allow them to reschedule times of delivery and the routes to be taken to deliver packages. Figure 1 below explains the overall data visualization strategy.

According to figure 1 above, effective data visualization will be achieved when proper strategic insights are obtained from the process. These insights will be received through the effective implementation of 1st level and 2nd level data processes.
References
CIO Review. (2014). UPS shows how to save and earn with ORION big data analytics. Web.
O’Shea, D. (2016). How UPS stays steady in center of e-commerce shipping storm. Web.
UPS Sustainability. (2014). Key performance indicators (KPI). Web.
UPS Sustainability. (2018). Leveraging e-commerce for growth. Web.
Peppard, J., & Ward, J. (2016). The strategic management of information systems: building a digital strategy (4th ed.). London, UK: John Wiley and Sons.